Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Clinical Outlook |
Migraines and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and methodological challenges
The link between migraine and cardiovascular disease is complex and involves overlapping mechanisms, such as endovascular disturbances. Challenges in measuring migraine, in distinguishing between causation and prediction, and in the understanding of clinical implications highlight the need for further research to guide treatment and cardiovascular risk assessment for the millions of individuals living with migraine.
- Tobias Kurth
- & Pamela M. Rist
-
Research Highlight |
 Semaglutide is beneficial in patients with HFpEF and obesity
Semaglutide is beneficial in patients with HFpEF and obesity
In patients with heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction and obesity, treatment with the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide (2.4 mg) leads to large reductions in HF-related symptoms and physical limitations, improves exercise function and decreases body weight compared with placebo, according to the STEP-HFpEF trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Immunomodulation and immunopharmacology in heart failure
Immunomodulation and immunopharmacology in heart failure
In this Review, the authors discuss the clinical and experimental data on immunomodulatory effects of evidence-based treatments for heart failure and their primary mechanisms of action, and highlight potential therapeutic targets and opportunities for the development and application of novel immunomodulatory treatments for heart failure.
- George Markousis-Mavrogenis
- , Lukas Baumhove
- & Peter van der Meer
-
Research Highlight |
Complete revascularization in MI: role in older patients and optimal timing
The FIRE trial showed that complete revascularization improves outcomes in older patients with myocardial infarction (MI) and multivessel disease compared with culprit-lesion-only revascularization, whereas the MULTISTARS AMI trial reported that immediate multivessel revascularization is non-inferior to staged revascularization in patients with ST-segment elevation MI.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Age-induced senescence impairs the neurovascular interface in the heart
Age-induced senescence impairs the neurovascular interface in the heart
An interaction between blood vessels and nerve fibres in the heart contributes to the decline in nerve density in the ageing left ventricle, potentially increasing susceptibility to arrhythmias.
- Jennifer Harman
-
Research Highlight |
Catheter ablation improves outcomes in patients with AF and end-stage HF
In the CASTLE HTx trial, patients with symptomatic atrial fibrillation and end-stage heart failure who underwent catheter ablation and received medical therapy had improved outcomes compared with patients who received medical therapy only.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
VA-ECMO does not increase survival in MI-related cardiogenic shock
New data from the ECLS-SHOCK trial and a meta-analysis indicate that the routine use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation does not increase survival in patients with myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
New insights into OCT-guided PCI
Two clinical trials presented at the ESC Congress 2023 provide conflicting evidence on the use of optical coherence tomography to guide percutaneous coronary intervention.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
No benefit of colchicine to prevent AF or myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery
According to data from the COP-AF trial, anti-inflammatory therapy with colchicine does not reduce the risk of perioperative atrial fibrillation or myocardial injury in patients undergoing major non-cardiac thoracic surgery.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Circadian medicine: a critical strategy for cardiac care
Circadian medicine: a critical strategy for cardiac care
In patients with an acute myocardial infarction, disrupted circadian rhythms during the initial days in the cardiac intensive care unit, caused by factors such as noise, excessive night-time light and frequent patient–staff interactions, can have devastating effects on cardiac repair and long-term prognosis. Providing care that aligns with the patient’s natural circadian rhythms is critical for optimum long-term recovery. Incorporating ‘circadian medicine’ into clinical practice will provide important health-care benefits.
- Michael J. Sole
- & Tami A. Martino
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure
Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure
Novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) have improved pharmacological properties compared with steroidal MRAs. Among the non-steroidal MRAs, finerenone has been approved for patients with chronic kidney disease who have diabetes mellitus and has demonstrated favourable safety and promising early results in patients with heart failure.
- Gerasimos Filippatos
- & Dimitrios Farmakis
-
Clinical Outlook |
Interatrial shunt devices for heart failure
Unloading left atrial hypertension by catheter-based, transvenous creation of atrial shunts is being explored to treat heart failure. So far, trials including sham control have demonstrated safety and efficacy in lowering left-sided cardiac filling pressures. Ongoing trials will determine the effect on clinical outcomes.
- Finn Gustafsson
-
Research Highlight |
Pitavastatin reduces cardiovascular events in patients with HIV infection
In the REPRIEVE trial, pitavastatin treatment in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection without pre-existing cardiovascular disease prevented cardiovascular events compared with placebo.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Heart disease causes sleep disturbances via neuroimmune mechanisms
Heart disease causes sleep disturbances via neuroimmune mechanisms
A new study reveals that the disrupted sleep patterns that are frequently observed in patients with cardiac disease are driven by immune-mediated sympathetic denervation and dysfunction of the pineal gland, which leads to a decrease in the circulating levels of melatonin and subsequent sleep disruption.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Animal models to study cardiac regeneration
Animal models to study cardiac regeneration
Some species have a greater capacity for cardiac regeneration than others. In this Review, Weinberger and Riley summarize the diverse array of vertebrates that have been studied for their cardiac regenerative potential and the core mechanisms that regulate cardiac regeneration across vertebrate species.
- Michael Weinberger
- & Paul R. Riley
-
Review Article |
 Valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathy: reappraisal of their interplay
Valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathy: reappraisal of their interplay
In this Review, Marsan et al. discuss the different clinical scenarios in which valvular heart diseases and cardiomyopathies coexist, either as the cause of one another or because of a common aetiology, to highlight the need for an improved classification of these diseases with potential repercussions in clinical management and personalized treatment.
- Nina Ajmone Marsan
- , Francesca Graziani
- & Filippo Crea
-
Review Article |
 The role of cardiac pericytes in health and disease: therapeutic targets for myocardial infarction
The role of cardiac pericytes in health and disease: therapeutic targets for myocardial infarction
In the infarcted heart, pericytes have crucial roles in inflammatory signalling, angiogenesis, and scar formation and stabilization. In this Review, Avolio and colleagues discuss the numerous roles of cardiac pericytes in homeostasis and disease and describe the potential of pericyte-based therapy for restoring the perivascular niche after myocardial infarction.
- Elisa Avolio
- , Paola Campagnolo
- & Paolo Madeddu
-
Research Highlight |
 Novel macrophage targets for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
Novel macrophage targets for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
A study shows that macrophages undergo substantial expansion in the diseased atria of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), and identifies two potential immunotherapy targets for the treatment of AF.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Cholesterol catabolism and bile acid synthesis in cardiomyocytes promote inflammation and heart failure
Cholesterol catabolism and bile acid synthesis in cardiomyocytes promote inflammation and heart failure
In failing cardiomyocytes, depletion of carnitine acetyltransferase promotes cholesterol catabolism via the bile acid synthesis pathway. The intracellular accumulation of bile acid intermediates induces the release of mitochondrial DNA into the cytosol, triggering type I interferon responses and AIM2 inflammasome activation, thereby contributing to chronic myocardial inflammation and heart failure progression.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Promising novel siRNA for the treatment of hypertension
Patients with hypertension who receive a single subcutaneous dose of zilebesiran, a novel small-interfering RNA that inhibits hepatic angiotensinogen synthesis, have reductions in serum angiotensinogen levels and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure that last for up to 24 weeks, according to a phase I study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Comment |
 Accelerated reduction in global cardiovascular disease is essential to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Accelerated reduction in global cardiovascular disease is essential to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Cardiovascular health is essential to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG3.4. Barriers include inequalities and a lack of political will and prioritization. A comprehensive approach is needed to reduce the global burden of cardiovascular disease and to achieve SDG3.4. The World Heart Federation addresses the determinants of cardiovascular disease and mobilizes the global community through roadmaps, roundtables and advocacy.
- Daniel J. Piñeiro
- , Elisa Codato
- & Jagat Narula
-
Research Highlight |
Unravelling ACS pathophysiology using intracoronary OCT and deep immunophenotyping
According to two papers from the OPTICO-ACS study, patients with acute coronary syndrome and an intact fibrous cap (plaque erosion), tend to have lower levels of inflammation and better prognosis than patients with rupture of the fibrous cap. In addition, Toll-like receptor 2-mediated neutrophil activation has a key role in plaque erosion.
- Jennifer Harman
-
Consensus Statement |
 De-escalation or abbreviation of dual antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes and percutaneous coronary intervention: a Consensus Statement from an international expert panel on coronary thrombosis
De-escalation or abbreviation of dual antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes and percutaneous coronary intervention: a Consensus Statement from an international expert panel on coronary thrombosis
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) reduces the risk of ischaemic events but can increase the risk of bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Gorog and colleagues provide consensus statements on strategies to reduce the risk of bleeding by de-escalating the intensity or abbreviating the duration of DAPT.
- Diana A. Gorog
- , Jose Luis Ferreiro
- & Gregory Y. H. Lip
-
Roadmap |
 Roadmap on the use of artificial intelligence for imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in coronary arteries
Roadmap on the use of artificial intelligence for imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in coronary arteries
In this Roadmap, Föllmer et al. summarize the evidence for the application of artificial intelligence (AI) technology to the imaging of vulnerable plaques in coronary arteries and discuss the current and future approaches to addressing the limitations of AI-guided coronary plaque imaging, such as bias, uncertainty and generalizability.
- Bernhard Föllmer
- , Michelle C. Williams
- & Marc Dewey
-
Review Article |
 Heart transplantation: advances in expanding the donor pool and xenotransplantation
Heart transplantation: advances in expanding the donor pool and xenotransplantation
Heart transplantation for patients with advanced heart failure is limited by a shortage of donor organs. In this Review, Jou and colleagues explore the options to increase the supply of donor hearts, including transplantation from donors with HCV, HIV or SARS-CoV-2 infection, national opt-out organ donation policies, donation after circulatory death, and xenotransplantation.
- Stephanie Jou
- , Sean R. Mendez
- & Claudia Gidea
-
Review Article |
 FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease
FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease
In this Review, the authors present an overview of the role of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and klotho in normal mineral homeostasis, discuss disordered mineral homeostasis in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and explore CKD-associated FGF23 excess and klotho deficiency as novel risk factors and potential therapeutic targets for cardiovascular disease.
- Daniel Edmonston
- , Alexander Grabner
- & Myles Wolf
-
Research Highlight |
Ruxolitinib is a CaMKII inhibitor that can be repurposed to prevent arrhythmias
The FDA-approved drug ruxolitinib has been identified as an inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) that has the potential to be repurposed to treat arrhythmias induced by CaMKII hyperactivity.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 RAPID return to sinus rhythm after SVT using intranasal etripamil
RAPID return to sinus rhythm after SVT using intranasal etripamil
In the multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled RAPID trial, use of symptom-prompted, self-administered, intranasally delivered etripamil was safe and superior to placebo for the conversion of paroxysmal superventricular tachycardia to sinus rhythm.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
Testosterone-replacement therapy does not increase cardiac events in men with hypogonadism
Testosterone-replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism and a high risk of cardiovascular disease does not increase the risk of adverse cardiac events, according to data from the TRAVERSE trial.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
IL-6R antagonism ameliorates atherosclerosis linked to Tet2-related clonal haematopoiesis
Liu and colleagues demonstrate the crucial role of IL-6 signalling in the development of atherosclerosis driven by Tet2-related clonal haematopoiesis.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
Low alcohol intake might lower CVD risk by reducing stress-related brain activity
New research shows that the reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events associated with light or moderate alcohol consumption is partly mediated by attenuation of the activity of a stress-related neural network.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Unravelling the genetic heart–brain connection using MRI
Genetic analysis of multiorgan imaging data provided novel insights into the shared biology between the heart and the brain.
- Karina Huynh
-
Evidence-based Guidelines |
 International Atherosclerosis Society guidance for implementing best practice in the care of familial hypercholesterolaemia
International Atherosclerosis Society guidance for implementing best practice in the care of familial hypercholesterolaemia
Familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) is a preventable cause of premature coronary artery disease and death. This guidance article from the International Atherosclerosis Society provides a comprehensive overview of FH care that includes recommendations on the detection and management of patients with FH, as well as strategies to maximize implementation.
- Gerald F. Watts
- , Samuel S. Gidding
- & Raul D. Santos
-
Review Article |
 Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Riksen and colleagues discuss the molecular and cellular mechanisms of trained immunity, the activation of these mechanisms by cardiovascular risk factors, and how trained immunity might contribute to atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The authors also propose potential strategies for the therapeutic modulation of trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Niels P. Riksen
- , Siroon Bekkering
- & Mihai G. Netea
-
Review Article |
 Interplay of hypoxia-inducible factors and oxygen therapy in cardiovascular medicine
Interplay of hypoxia-inducible factors and oxygen therapy in cardiovascular medicine
The benefits of oxygen therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular disease are unclear, and findings from preclinical studies have suggested potential adverse effects associated with its excessive use. In this Review, Eltzschig and colleagues provide an overview of studies on oxygen therapy for various cardiovascular conditions and describe alternative therapeutic strategies that target oxygen-sensing pathways.
- Yafen Liang
- , Wei Ruan
- & Holger K. Eltzschig
-
Research Highlight |
 Antibody treatment to deplete transthyretin amyloid deposits in the heart
Antibody treatment to deplete transthyretin amyloid deposits in the heart
An antibody-based therapy for transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy is safe, and initial findings from a phase I trial suggest that it might deplete amyloid deposits in the heart.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Sacubitril–valsartan shows benefit in heart failure with ejection fraction of >40%
In a diverse population of patients with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction stabilized after a recent worsening heart failure event, treatment with sacubitril–valsartan induces greater reductions in plasma NT-proBNP levels and is associated with clinical benefit compared with valsartan alone, despite a higher rate of symptomatic hypotension.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
 Implantable haemodynamic sensor to remotely MONITOR HF
Implantable haemodynamic sensor to remotely MONITOR HF
Results from the MONITOR-HF trial show that remote monitoring of pulmonary artery pressure using the implantable CardioMEMS sensor in patients with chronic heart failure improves quality of life and reduces hospitalizations.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
A fatty acid from mother’s milk drives cardiomyocyte maturation in newborn mice
The essential omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid γ-linolenic acid present in maternal milk coordinates cardiac adaptation and survival in newborn mice, according to a new study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Consensus Statement |
 Clinical quantitative coronary artery stenosis and coronary atherosclerosis imaging: a Consensus Statement from the Quantitative Cardiovascular Imaging Study Group
Clinical quantitative coronary artery stenosis and coronary atherosclerosis imaging: a Consensus Statement from the Quantitative Cardiovascular Imaging Study Group
In this Consensus Statement, Dewey and the other members of the Quantitative Cardiovascular Imaging Study Group provide clinical consensus recommendations on the optimal use of different imaging techniques in various patient populations to detect and assess coronary artery stenosis and atherosclerosis.
- Aldo J. Vázquez Mézquita
- , Federico Biavati
- & Marc Dewey
-
Research Highlight |
 Targeting ALK1 to block LDL transcytosis and halt atherosclerosis
Targeting ALK1 to block LDL transcytosis and halt atherosclerosis
In a mouse model of atherosclerosis, a selective monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of LDL to activin receptor-like kinase 1 reduced plaque formation in the aorta.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Simvastatin protects against endothelial dysfunction via epigenetic mechanisms
Simvastatin protects against endothelial dysfunction via epigenetic mechanisms
Simvastatin improves endothelial cell function by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition through an epigenetic regulatory mechanism, according to a new study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Metabolic mechanisms in physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: new paradigms and challenges
Metabolic mechanisms in physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: new paradigms and challenges
In this Review, Ritterhoff and Tian describe the metabolic reprogramming that occurs in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure; discuss the contribution of metabolism to energy-generating and non-energy-generating functions, including signalling, protein function and gene expression regulation; and highlight the role of metabolism in non-cardiomyocytes and the potential to develop metabolic therapies for heart failure.
- Julia Ritterhoff
- & Rong Tian
-
Review Article |
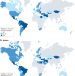 Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes
Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) are a major contributor to death from cardiovascular disease. In this Review, Timmis and colleagues present data on mortality from ACS for 122 countries and examine the regional and temporal changes in the epidemiology of ACS over the past 20 years.
- Adam Timmis
- , Denis Kazakiewicz
- & Panos Vardas
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Contemporary tools to predict cardiovascular risk lack accuracy on an individual-patient level. The use of single-cell RNA sequencing to identify specific leukocyte patterns might overcome some of these limitations, propelling us towards a precision medicine approach.
- Johannes Gollmer
- & Andreas Zirlik
-
Research Highlight |
 Young women with AMI have worse outcomes than men up to 1 year after discharge
Young women with AMI have worse outcomes than men up to 1 year after discharge
Findings from the VIRGO study reveal that young women with acute myocardial infarction are more likely to be rehospitalized within 1 year compared with similarly aged men.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Aggregation of big tau disrupts microtubules and causes diastolic dysfunction
Aggregation of big tau disrupts microtubules and causes diastolic dysfunction
Hyperphosphorylation of tau in the heart reduces the tyrosination of microtubules, leading to myocardial stiffness and heart failure. This novel mechanism of diastolic dysfunction parallels the aggregation of tau in the brain that leads to Alzheimer disease and might be amenable to treatment using monoclonal antibodies against tau.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, assessment and prevention
Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, assessment and prevention
Individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus are at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). In the context of type 2 diabetes mellitus, Wong and Sattar discuss established and novel mechanisms of CVD, risk assessment and patient stratification, and strategies to reduce multiple risk factors to prevent CVD.
- Nathan D. Wong
- & Naveed Sattar
-
Review Article |
 Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
In this Review, Kroemer and colleagues describe eight molecular hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing: disabled macroautophagy, loss of proteostasis, genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, cell senescence, dysregulated neurohormonal signalling and inflammation. Therapeutically targeting these hallmarks might attenuate residual cardiovascular risk in older individuals.
- Mahmoud Abdellatif
- , Peter P. Rainer
- & Guido Kroemer

 CHIP in HF: prognostic role and cell-intrinsic effects
CHIP in HF: prognostic role and cell-intrinsic effects