Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular disease and cancer: shared risk factors and mechanisms
Cardiovascular disease and cancer: shared risk factors and mechanisms
Patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have an increased risk of cancer, and patients with cancer have an increased risk of CVD. In this Review, the authors discuss the shared modifiable risk factors and the shared pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the bidirectional relationship between these two prevalent diseases.
- Nicholas S. Wilcox
- , Uri Amit
- & Bonnie Ky
-
Obituary |
 Alain Cribier (1945–2024)
Alain Cribier (1945–2024)
Gilard and Wijns reflect on the life of Alain Cribier, who revolutionized the management of patients with valvular disease.
- Martine Gilard
- & William Wijns
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Interventional thrombus modification in STEMI
Interventional thrombus modification in STEMI
In ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the role of interventional modification of thrombi in the coronary arteries before stenting is controversial. However, innovations in stroke intervention have sparked renewed interest in thrombus modification approaches. We discuss current and emerging techniques to extract or disperse thrombi, aiming to reduce downstream embolization, microvascular obstruction and myocardial injury.
- Jason L. Walsh
- , Rafail A. Kotronias
- & Giovanni Luigi De Maria
-
Review Article |
 Optimizing antithrombotic therapy in patients with coexisting cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disease
Optimizing antithrombotic therapy in patients with coexisting cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disease
In this Review, the authors address considerations for enteral antithrombotic therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease and gastrointestinal comorbidities, who often have an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Approaches include tailoring of antithrombotic regimens and gastrointestinal-protection strategies.
- Azita H. Talasaz
- , Parham Sadeghipour
- & Behnood Bikdeli
-
Review Article |
 Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in ischaemic heart disease
Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in ischaemic heart disease
Non-coding RNAs are implicated in the pathophysiology of ischaemic heart disease and heart failure. In this Review, Caporali and colleagues examine the biology of these molecules and discuss the potential of non-coding RNAs for translation to the clinic as biomarkers and therapeutics in adverse cardiac remodelling leading to ischaemic heart failure.
- Andrea Caporali
- , Maryam Anwar
- & Costanza Emanueli
-
Review Article |
 Sex-related similarities and differences in responses to heart failure therapies
Sex-related similarities and differences in responses to heart failure therapies
In this Review, Lam and colleagues evaluate the current literature on sex-related differences in treatment responses in patients with heart failure and highlight potential approaches for tailored therapies and the need for sex-specific evaluation of treatment efficacy and safety in future research.
- Janice Y. Chyou
- , Hailun Qin
- & Carolyn S. P. Lam
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Novel drug therapies for atrial fibrillation
Novel drug therapies for atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is the most common sustained arrhythmia and imposes a substantial burden on patients and health-care providers. Clinical evidence suggests that antiarrhythmic therapy to restore and maintain sinus rhythm (rhythm control) can reduce adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with new-onset atrial fibrillation. As a result, a paradigm shift towards rhythm control over rate control therapy is emerging, increasing the clinical need for effective and safe antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Felix Wiedmann
- & Constanze Schmidt
-
Research Highlight |
 Weight loss from surgery or drug therapy reduces blood pressure
Weight loss from surgery or drug therapy reduces blood pressure
Two studies indicate that a reduction in body mass index as a result of either bariatric surgery or pharmacological therapy is associated with a blood pressure-lowering effect.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Iron deficiency and supplementation in heart failure
Iron deficiency and supplementation in heart failure
In this Review, Lakhal-Littleton and Cleland use the latest understanding of iron homeostasis to evaluate existing and emerging markers of iron status, describe the reciprocal relationship between iron status and heart failure, and mechanistically examine the benefits of oral and intravenous iron replacement therapies.
- Samira Lakhal-Littleton
- & John G. F. Cleland
-
Comment |
 Ultra-processed foods and cardiovascular disease
Ultra-processed foods and cardiovascular disease
In this Comment, we critically examine the association between the increasing consumption of ultra-processed foods and their negative effect on cardiovascular health. We explore the historical evolution of food processing, the Nova food classification and the epidemiological evidence, and highlight the need for urgent public health interventions.
- Fernanda Rauber
- & Renata Bertazzi Levy
-
Correspondence |
Graded exercise therapy should not be recommended for patients with post-exertional malaise
- Femke Christina Ching-Chuan van Rhijn-Brouwer
- , Merel Hellemons
- & David Putrino
-
Clinical Outlook |
 The role of the molecular autopsy in sudden cardiac death in young individuals
The role of the molecular autopsy in sudden cardiac death in young individuals
A molecular autopsy is undertaken in cases of sudden cardiac death with no definitive cause found after conventional autopsy, with the aim of identifying a pathological genetic variant that could account for the death. Greater awareness of malignant arrhythmias in the absence of structural changes in inherited cardiomyopathies has increased the applicability of molecular autopsies, and resulted in improved care of families but new challenges for clinicians.
- Julia C. Isbister
- & Christopher Semsarian
-
Research Highlight |
 Fibroblast-like cells promote plaque stability in response to anti-IL-1β therapy
Fibroblast-like cells promote plaque stability in response to anti-IL-1β therapy
Anti-inflammatory therapy involving IL-1β inhibition might reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with clonal haematopoiesis by increasing the number of fibroblast-like cells in the fibrous cap region of atherosclerotic plaques, thereby stabilizing the plaque and reducing the likelihood of rupture.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Fredman and Serhan discuss the role of specialized pro-resolving mediators, a superfamily of endogenous signalling lipids that mediate resolution of inflammation processes in atherosclerosis, and appraise the therapeutic potential of specialized pro-resolving mediators for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, and the resolution of uncontrolled vascular inflammation.
- Gabrielle Fredman
- & Charles N. Serhan
-
Review Article |
 Atherosclerotic plaque stabilization and regression: a review of clinical evidence
Atherosclerotic plaque stabilization and regression: a review of clinical evidence
In this Review, Sarraju and Nissen summarize the clinical trial evidence for coronary atherosclerotic plaque stabilization and regression with plasma LDL-cholesterol-lowering therapy and other treatments. Invasive and non-invasive imaging modalities used to assess plaque burden and composition are discussed.
- Ashish Sarraju
- & Steven E. Nissen
-
Review Article |
 Improving medication adherence in cardiovascular disease
Improving medication adherence in cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Bosworth and colleagues describe the causes of medication non-adherence, discuss interventions that have been clinically shown to improve adherence and identify areas for future research.
- Adam J. Nelson
- , Neha J. Pagidipati
- & Hayden B. Bosworth
-
Review Article |
 Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension
Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension
In this Review, Guzik and colleagues discuss immune and inflammatory mechanisms of hypertension, including upstream regulators and downstream effectors as well as the complex interplay between the immune system, blood pressure regulation and end-organ damage, which can help to identify new targets for therapeutic interventions.
- Tomasz J. Guzik
- , Ryszard Nosalski
- & Grant R. Drummond
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in post-COVID-19 syndrome: a major health-care burden
Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in post-COVID-19 syndrome: a major health-care burden
Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction (CVAD) is a malfunction of the autonomic control of circulatory homeostasis and is an important component of post-COVID-19 syndrome. In this Review, Fedorowski and colleagues define the major forms of CVAD (including postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome), and discuss the aetiology, diagnosis and management of post-COVID-19 syndrome-associated CVAD.
- Artur Fedorowski
- , Alessandra Fanciulli
- & Richard Sutton
-
Review Article |
 RNA-binding proteins in cardiovascular biology and disease: the beat goes on
RNA-binding proteins in cardiovascular biology and disease: the beat goes on
In this Review, the authors discuss the latest insights on RNA-binding proteins and RNA biology and appraise them in the context of cardiovascular research, summarizing the progress in our understanding of the involvement of RNA-binding proteins in cardiac biology and disease.
- Mirko Völkers
- , Thomas Preiss
- & Matthias W. Hentze
-
Research Highlight |
 Bone marrow adipocytes support fatty acid metabolism during MI-mediated emergency haematopoiesis
Bone marrow adipocytes support fatty acid metabolism during MI-mediated emergency haematopoiesis
During myocardial infarction, haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells increase fatty acid oxidation, and bone marrow adipocytes can act as a local energy resource for these cells.
- Karina Huynh
-
Clinical Outlook |
Left atrial appendage occlusion
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) has been rapidly adopted for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and a contraindication to oral anticoagulation. Ongoing and planned clinical trials on LAAO and the development of new devices might expand clinical indications and address the remaining challenges of device-related thrombus and peridevice leak.
- Jacqueline Saw
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Anticoagulation in patients with atrial high-rate episodes
Anticoagulation in patients with atrial high-rate episodes
The risk of stroke in patients with atrial high-rate episodes (AHREs) depends on age, comorbidities and AHRE burden. Two randomized clinical trials on the use of oral anticoagulant therapy for stroke prevention in older patients with short and rare AHREs have reported conflicting findings on the efficacy of oral anticoagulation in this patient population, although both trials report a significantly increased risk of major bleeding with oral anticoagulation.
- Tatjana Potpara
- & Carina Blomstrom-Lundqvist
-
Research Highlight |
MINT trial signals potential benefit of liberal transfusion strategy in MI with anaemia
A liberal strategy of blood transfusion might improve outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction and anaemia, according to results from the MINT trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
 SELECT shows cardiovascular risk reduction with weight-loss drug semaglutide in people without diabetes
SELECT shows cardiovascular risk reduction with weight-loss drug semaglutide in people without diabetes
Treatment with the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide, administered subcutaneously at a dose of 2.4 mg once per week, reduces the risk of major cardiovascular events by 20% compared with placebo in patients who are overweight or obese and with pre-existing cardiovascular disease but without diabetes mellitus, according to findings from the SELECT trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Coronary microvascular obstruction and dysfunction in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Coronary microvascular obstruction and dysfunction in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Coronary microvascular obstruction and dysfunction (CMVO) is common in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) despite prompt reperfusion. In this Review, the authors discuss the mechanisms of CMVO as well as strategies to reduce its incidence and improve prognosis.
- Mattia Galli
- , Giampaolo Niccoli
- & Filippo Crea
-
Comment |
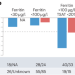 Defining iron deficiency in patients with heart failure
Defining iron deficiency in patients with heart failure
For patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, intravenous iron is likely to deliver clinical and prognostic benefits for those with anaemia and transferrin saturation <20%, especially if serum ferritin exceeds 100 μg/l. A serum ferritin of <100 μg/l does not appear to be useful as a marker of iron deficiency.
- John G. F. Cleland
-
Review Article |
 Oxidized phospholipids in cardiovascular disease
Oxidized phospholipids in cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Tsimikas and Witztum discuss the role of oxidized phospholipids (OxPLs) in atherosclerosis, describe the methods for measuring OxPLs on apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins (OxPL–apoB) and their relationship with lipoprotein(a), and discuss the clinical applications of the OxPL–apoB measurement for improving diagnosis, prognosis, risk reclassification and therapeutic interventions in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Sotirios Tsimikas
- & Joseph L. Witztum
-
Review Article |
 Socioeconomic inequalities in cardiovascular disease: a causal perspective
Socioeconomic inequalities in cardiovascular disease: a causal perspective
Low socioeconomic position (SEP) is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), but whether this association is causal is uncertain. In this Review, Bann and colleagues discuss how evidence from divergent study designs can help in understanding the causal relationship between SEP and CVD and how this relationship might have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- David Bann
- , Liam Wright
- & Nish Chaturvedi
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology at high altitude
Cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology at high altitude
Hypoxic conditions encountered at high altitude affect all physiological functions. In this Review, Richalet et al. describe the cardiovascular responses to acute and chronic exposure to hypoxia and provide recommendations that clinicians can give to patients with cardiovascular disease who wish to travel to high-altitude destinations.
- Jean-Paul Richalet
- , Eric Hermand
- & François J. Lhuissier
-
Review Article |
 Sex-specific and ethnicity-specific differences in MINOCA
Sex-specific and ethnicity-specific differences in MINOCA
Myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries (MINOCA) has been the focus of an increasing number of studies in the past decade. In this Review, Tavella and colleagues detail the prevalence and clinical presentation of MINOCA, describe the mechanisms underlying the syndrome, and summarize the sex-specific and ethnicity-specific differences in the clinical features, pathophysiological mechanisms, treatment and prognosis of MINOCA.
- Sarena La
- , John Beltrame
- & Rosanna Tavella
-
Review Article |
 Effects of lifestyle factors on leukocytes in cardiovascular health and disease
Effects of lifestyle factors on leukocytes in cardiovascular health and disease
In this Review, Swirski and co-workers discuss how lifestyle factors modulate haematopoiesis and leukocyte migration in the context of cardiovascular homeostasis and disease, with particular focus on the role of the nervous system as the key executor connecting environmental influences to leukocyte behaviour.
- Henrike Janssen
- , Laura L. Koekkoek
- & Filip K. Swirski
-
Research Highlight |
 CHIP in HF: prognostic role and cell-intrinsic effects
CHIP in HF: prognostic role and cell-intrinsic effects
Two studies now report that TET2-driven clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with heart failure (HF) and preserved ejection fraction and that DNMT3A CHIP driver mutations promote dysregulated gene expression profiles that are associated with inflammation in monocytes in the setting of HF.
- Karina Huynh
-
Clinical Outlook |
Migraines and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and methodological challenges
The link between migraine and cardiovascular disease is complex and involves overlapping mechanisms, such as endovascular disturbances. Challenges in measuring migraine, in distinguishing between causation and prediction, and in the understanding of clinical implications highlight the need for further research to guide treatment and cardiovascular risk assessment for the millions of individuals living with migraine.
- Tobias Kurth
- & Pamela M. Rist
-
Research Highlight |
 Semaglutide is beneficial in patients with HFpEF and obesity
Semaglutide is beneficial in patients with HFpEF and obesity
In patients with heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction and obesity, treatment with the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide (2.4 mg) leads to large reductions in HF-related symptoms and physical limitations, improves exercise function and decreases body weight compared with placebo, according to the STEP-HFpEF trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Circadian medicine: a critical strategy for cardiac care
Circadian medicine: a critical strategy for cardiac care
In patients with an acute myocardial infarction, disrupted circadian rhythms during the initial days in the cardiac intensive care unit, caused by factors such as noise, excessive night-time light and frequent patient–staff interactions, can have devastating effects on cardiac repair and long-term prognosis. Providing care that aligns with the patient’s natural circadian rhythms is critical for optimum long-term recovery. Incorporating ‘circadian medicine’ into clinical practice will provide important health-care benefits.
- Michael J. Sole
- & Tami A. Martino
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure
Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure
Novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) have improved pharmacological properties compared with steroidal MRAs. Among the non-steroidal MRAs, finerenone has been approved for patients with chronic kidney disease who have diabetes mellitus and has demonstrated favourable safety and promising early results in patients with heart failure.
- Gerasimos Filippatos
- & Dimitrios Farmakis
-
Clinical Outlook |
Interatrial shunt devices for heart failure
Unloading left atrial hypertension by catheter-based, transvenous creation of atrial shunts is being explored to treat heart failure. So far, trials including sham control have demonstrated safety and efficacy in lowering left-sided cardiac filling pressures. Ongoing trials will determine the effect on clinical outcomes.
- Finn Gustafsson
-
Research Highlight |
Pitavastatin reduces cardiovascular events in patients with HIV infection
In the REPRIEVE trial, pitavastatin treatment in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection without pre-existing cardiovascular disease prevented cardiovascular events compared with placebo.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Heart disease causes sleep disturbances via neuroimmune mechanisms
Heart disease causes sleep disturbances via neuroimmune mechanisms
A new study reveals that the disrupted sleep patterns that are frequently observed in patients with cardiac disease are driven by immune-mediated sympathetic denervation and dysfunction of the pineal gland, which leads to a decrease in the circulating levels of melatonin and subsequent sleep disruption.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathy: reappraisal of their interplay
Valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathy: reappraisal of their interplay
In this Review, Marsan et al. discuss the different clinical scenarios in which valvular heart diseases and cardiomyopathies coexist, either as the cause of one another or because of a common aetiology, to highlight the need for an improved classification of these diseases with potential repercussions in clinical management and personalized treatment.
- Nina Ajmone Marsan
- , Francesca Graziani
- & Filippo Crea
-
Research Highlight |
 Novel macrophage targets for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
Novel macrophage targets for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
A study shows that macrophages undergo substantial expansion in the diseased atria of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), and identifies two potential immunotherapy targets for the treatment of AF.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Cholesterol catabolism and bile acid synthesis in cardiomyocytes promote inflammation and heart failure
Cholesterol catabolism and bile acid synthesis in cardiomyocytes promote inflammation and heart failure
In failing cardiomyocytes, depletion of carnitine acetyltransferase promotes cholesterol catabolism via the bile acid synthesis pathway. The intracellular accumulation of bile acid intermediates induces the release of mitochondrial DNA into the cytosol, triggering type I interferon responses and AIM2 inflammasome activation, thereby contributing to chronic myocardial inflammation and heart failure progression.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Comment |
 Accelerated reduction in global cardiovascular disease is essential to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Accelerated reduction in global cardiovascular disease is essential to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Cardiovascular health is essential to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG3.4. Barriers include inequalities and a lack of political will and prioritization. A comprehensive approach is needed to reduce the global burden of cardiovascular disease and to achieve SDG3.4. The World Heart Federation addresses the determinants of cardiovascular disease and mobilizes the global community through roadmaps, roundtables and advocacy.
- Daniel J. Piñeiro
- , Elisa Codato
- & Jagat Narula
-
Consensus Statement |
 De-escalation or abbreviation of dual antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes and percutaneous coronary intervention: a Consensus Statement from an international expert panel on coronary thrombosis
De-escalation or abbreviation of dual antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes and percutaneous coronary intervention: a Consensus Statement from an international expert panel on coronary thrombosis
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) reduces the risk of ischaemic events but can increase the risk of bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Gorog and colleagues provide consensus statements on strategies to reduce the risk of bleeding by de-escalating the intensity or abbreviating the duration of DAPT.
- Diana A. Gorog
- , Jose Luis Ferreiro
- & Gregory Y. H. Lip
-
Roadmap |
 Roadmap on the use of artificial intelligence for imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in coronary arteries
Roadmap on the use of artificial intelligence for imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque in coronary arteries
In this Roadmap, Föllmer et al. summarize the evidence for the application of artificial intelligence (AI) technology to the imaging of vulnerable plaques in coronary arteries and discuss the current and future approaches to addressing the limitations of AI-guided coronary plaque imaging, such as bias, uncertainty and generalizability.
- Bernhard Föllmer
- , Michelle C. Williams
- & Marc Dewey
-
Review Article |
 Heart transplantation: advances in expanding the donor pool and xenotransplantation
Heart transplantation: advances in expanding the donor pool and xenotransplantation
Heart transplantation for patients with advanced heart failure is limited by a shortage of donor organs. In this Review, Jou and colleagues explore the options to increase the supply of donor hearts, including transplantation from donors with HCV, HIV or SARS-CoV-2 infection, national opt-out organ donation policies, donation after circulatory death, and xenotransplantation.
- Stephanie Jou
- , Sean R. Mendez
- & Claudia Gidea
-
Review Article |
 FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease
FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease
In this Review, the authors present an overview of the role of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and klotho in normal mineral homeostasis, discuss disordered mineral homeostasis in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and explore CKD-associated FGF23 excess and klotho deficiency as novel risk factors and potential therapeutic targets for cardiovascular disease.
- Daniel Edmonston
- , Alexander Grabner
- & Myles Wolf
-
Review Article |
 Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Riksen and colleagues discuss the molecular and cellular mechanisms of trained immunity, the activation of these mechanisms by cardiovascular risk factors, and how trained immunity might contribute to atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The authors also propose potential strategies for the therapeutic modulation of trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Niels P. Riksen
- , Siroon Bekkering
- & Mihai G. Netea
-
Evidence-based Guidelines |
 International Atherosclerosis Society guidance for implementing best practice in the care of familial hypercholesterolaemia
International Atherosclerosis Society guidance for implementing best practice in the care of familial hypercholesterolaemia
Familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) is a preventable cause of premature coronary artery disease and death. This guidance article from the International Atherosclerosis Society provides a comprehensive overview of FH care that includes recommendations on the detection and management of patients with FH, as well as strategies to maximize implementation.
- Gerald F. Watts
- , Samuel S. Gidding
- & Raul D. Santos
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Dental diseases
- Endocrine system and metabolic diseases
- Eye diseases
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Haematological diseases
- Immunological disorders
- Infectious diseases
- Kidney diseases
- Metabolic disorders
- Neurological disorders
- Nutrition disorders
- Oral diseases
- Psychiatric disorders
- Reproductive disorders
- Respiratory tract diseases
- Rheumatic diseases
- Skin diseases
- Trauma
- Urogenital diseases

 Canonical and non-canonical roles of complement in atherosclerosis
Canonical and non-canonical roles of complement in atherosclerosis