In Your Element |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
A previous investigation of the anti-aromatic dianion of [18]annulene concluded that it consists of a mixture of two isomers. Now it has been shown that this dianion exists as a single isomer, with a different geometry from neutral [18]annulene, and that it can be reduced further to an aromatic tetraanion.
- Wojciech Stawski
- , Yikun Zhu
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Review Article |
 Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics
Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics
Nanopore label-free sequencing of DNA and RNA at the single-molecule level offers rapid readout, high accuracy, low cost and portability. This Review surveys technologies underpinning commercial and academic nanopore sequencing, and examines how underlying biochemical advances can fuel future developments in nanopore-based protein sequencing.
- Adam Dorey
- & Stefan Howorka
-
Article |
 Tunable molecular editing of indoles with fluoroalkyl carbenes
Tunable molecular editing of indoles with fluoroalkyl carbenes
The rapid generation of molecular complexity from a given molecular scaffold is crucial to drug discovery and development. Now the chemodivergent molecular editing of indoles using fluoroalkyl carbenes has been developed to modularly access four different types of fluorine-containing N-heterocyclic compound with high molecular complexity.
- Shaopeng Liu
- , Yong Yang
- & Xihe Bi
-
Perspective |
 The impact of UV light on synthetic photochemistry and photocatalysis
The impact of UV light on synthetic photochemistry and photocatalysis
Although generally perceived as an old-fashioned and unselective tool to build molecules, the photochemistry community is now re-discovering the power of UV light and is using key mechanistic information to develop new catalytic processes driven by visible light. This Perspective discusses the progress and impact of UV light in organic synthesis.
- Giulio Goti
- , Kavyasree Manal
- & Luca Dell’Amico
-
Article |
 Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Electrolysers can upgrade CO2 into high-value chemicals, but there are few tools capable of tracking the reactions that occur within these devices during operation. Now an electrolysis optical coherence tomography platform has been developed to visualize the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO, plus the movement of components, within the device.
- Xin Lu
- , Chris Zhou
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
News & Views |
 Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Electrocatalytic transformations often involve the concerted transfer of electrons and protons at electrode interfaces; however, these processes are not well understood. Now, experiments on an electrode that features well-defined molecular sites deepen fundamental understanding of such transfers to pave the way for future catalysts.
- Siyuan L. Xie
- & Eva M. Nichols
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded bioorthogonal tryptophan decaging in living cells
Genetically encoded bioorthogonal tryptophan decaging in living cells
Developing a generalizable method for blocking and rescuing tryptophan (Trp) interactions would enable the gain-of-function manipulation of various Trp-containing proteins but has so far been challenging. Now a genetically encoded N1-vinyl-caged Trp capable of rapid and bioorthogonal decaging enables site-specific activation of Trp on a protein of interest within living cells.
- Yuchao Zhu
- , Wenlong Ding
- & Peng R. Chen
-
Article |
 Photoinduced dual bond rotation of a nitrogen-containing system realized by chalcogen substitution
Photoinduced dual bond rotation of a nitrogen-containing system realized by chalcogen substitution
Although photoinduced concerted multiple-bond-rotation processes are known in photoactive biological systems, the synthesis of compounds exhibiting similar behaviour has proven challenging. Now a thioamide-based system featuring chalcogen substituents has been shown to exhibit photoinduced C–N/C–C rotation; the rotation mode can be switched depending on external stimuli such as temperature and light irradiation.
- Shotaro Nagami
- , Rintaro Kaguchi
- & Akira Katsuyama
-
Article
| Open Access Tandem catalysis enables chlorine-containing waste as chlorination reagents
Tandem catalysis enables chlorine-containing waste as chlorination reagents
While chlorinated compounds are ubiquitous in chemical synthesis, they have a negative impact on human health and the environment. Now, a sustainable tandem catalytic process has been developed that uses chlorine-containing waste as chlorination reagents. This approach represents a promising way for the viable management of chlorinated compounds.
- Mingyang Liu
- , Xinbang Wu
- & Paul J. Dyson
-
Research Briefing |
 Carbon isotope exchange for pharmaceutical radiolabelling through metal-catalysed functional group metathesis
Carbon isotope exchange for pharmaceutical radiolabelling through metal-catalysed functional group metathesis
A method for carbon isotope exchange involving a metal-catalysed metathesis reaction of in situ formed acyl chlorides is demonstrated. The platform provides access to 13C- or 14C-enriched carboxylic acids, including natural products and pharmaceuticals, without the need for radioactive gases, using a single carboxylic acid carbon donor.
-
Article |
 Thorium(iv)–antimony complexes exhibiting single, double, and triple polar covalent metal–metal bonds
Thorium(iv)–antimony complexes exhibiting single, double, and triple polar covalent metal–metal bonds
Actinide–metal multiple bonds are relatively rare, with isolable examples under normal experimental conditions typically restricted to complexes containing a polar covalent σ bond supplemented by up to two dative π bonds. Now complexes featuring polar covalent double and triple bonds between thorium and antimony have been synthesized.
- Jingzhen Du
- , Kevin Dollberg
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article |
 Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Valence tautomerism in lanthanide-based materials is rare. Now a one-dimensional samarium–pyrazine polymer has been shown to exhibit a temperature-induced hysteretic Sm(III)-to-Sm(II) reversible switch. The transition temperature is modulated in a 150 K window by alloying with Yb(II), presenting a strategy for developing new materials with chemically tunable magnetic switchability.
- Maja A. Dunstan
- , Anna S. Manvell
- & Kasper S. Pedersen
-
Article |
 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
The design of open-shell nanographenes is commonly limited to systems featuring a single magnetic origin. Now a strategy that combines topological frustration and electron–electron interactions has been developed to generate a butterfly-shaped nanographene that hosts four highly entangled π-spins and exhibits both ferromagnetic and anti-ferromagnetic coupling.
- Shaotang Song
- , Andrés Pinar Solé
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article |
 A metal-catalysed functional group metathesis approach to the carbon isotope labelling of carboxylic acids
A metal-catalysed functional group metathesis approach to the carbon isotope labelling of carboxylic acids
The preparation of 14C-labelled compounds is a crucial step in pharmaceutical development but typically requires using toxic, radioactive gases. Now a broadly applicable functional group metathesis reaction has been developed that forms 14C-labelled carboxylic acids in one pot, without added gases, via dynamic exchange with an easily handled carboxylic acid 14C source.
- R. Garrison Kinney
- , José Zgheib
- & Bruce A. Arndtsen
-
Article |
 A catalytic process enables efficient and programmable access to precisely altered indole alkaloid scaffolds
A catalytic process enables efficient and programmable access to precisely altered indole alkaloid scaffolds
New drug leads can be developed through modification of a natural product’s framework, but this is possible only if the compound is abundant and contains modifiable moieties. Now a strategy is introduced for accessing a scarce indole alkaloid and several expanded, contracted and distorted analogues, one of which shows anti-cancer activity.
- Youming Huang
- , Xinghan Li
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
News & Views |
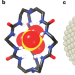 Clever cryptand cage coordinates contaminants
Clever cryptand cage coordinates contaminants
Replicating the ability of enzymes and transport proteins to effectively bind anions is a considerable challenge for supramolecular chemists. A neutral organic cage has now been developed that selectively binds sulfate anions in water.
- Rosemary J. Goodwin
- & Nicholas G. White
-
Article |
 Diazobutanone-assisted isobaric labelling of phospholipids and sulfated glycolipids enables multiplexed quantitative lipidomics using tandem mass spectrometry
Diazobutanone-assisted isobaric labelling of phospholipids and sulfated glycolipids enables multiplexed quantitative lipidomics using tandem mass spectrometry
Lipidomics aims to uncover lipid functions in biological systems and disease. Quantifying lipids is challenging due to highly diverse chemical structures. Here a diazobutanone-assisted isobaric labelling method is developed that relies on diazobutanone and isobaric mass tags to target phosphate- and sulfate-containing lipids, enabling multiplexed lipidomic quantification in complex mixtures.
- Ting-Jia Gu
- , Peng-Kai Liu
- & Lingjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access A divergent intermediate strategy yields biologically diverse pseudo-natural products
A divergent intermediate strategy yields biologically diverse pseudo-natural products
Design strategies that possess both biological relevance and structural diversity may lead to compound collections that are enriched in diverse bioactivities. Now a diverse pseudo-natural product design principle has been established to efficiently explore biologically relevant chemical space. Through dearomatization reactions, a compound collection enriched in both structural and biological diversity was rapidly generated.
- Sukdev Bag
- , Jie Liu
- & Herbert Waldmann
-
News & Views |
 Asymmetric construction of sulfur(VI)–fluorine cores
Asymmetric construction of sulfur(VI)–fluorine cores
Molecules containing a chiral S(VI) moiety have found extensive applications in drug design and organic synthesis, despite a lack of diverse asymmetric methods for their creation. Now, a ligand-mediated process has enabled the production of enantioenriched S(VI)–F motifs, providing a foundation for further stereospecific elaborations.
- Patrick R. Melvin
-
Research Briefing |
 Site-selective episulfonium formation on protein surfaces
Site-selective episulfonium formation on protein surfaces
Covalent protein conjugation facilitates the study of biological processes and the synthesis of therapeutic biomacromolecules. A method that uses vinyl thianthrenium reagents for the site-selective formation of highly reactive episulfonium species on proteins is demonstrated. These in situ-formed intermediates react with diverse nucleophiles, providing access to protein conjugates in one step without purification.
-
Article
| Open Access Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Although surface-bound molecular catalysts offer well-defined active sites on heterogeneous supports, it is challenging to identify key radical intermediates in the reaction mechanism. Now, a characterization method has been developed that combines film electrochemistry and EPR spectroscopy to track radical intermediates in real time, exemplified by alcohol oxidation with a surface-immobilized nitroxide.
- Maryam Seif-Eddine
- , Samuel J. Cobb
- & Maxie M. Roessler
-
Article |
 Mapping the mechanisms of oxidative addition in cross-coupling reactions catalysed by phosphine-ligated Ni(0)
Mapping the mechanisms of oxidative addition in cross-coupling reactions catalysed by phosphine-ligated Ni(0)
The mechanism for the oxidative addition of aryl halides to nickel(0)–phosphine complexes was proposed over four decades ago. Now, this elementary reaction, which occurs during common cross-coupling reactions, has been re-examined. Both one- and two-electron pathways occur, and their relative contribution depends on the electronic properties of the reaction partners.
- Christina N. Pierson
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 Enantioselective sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange reaction of iminosulfur oxydifluorides
Enantioselective sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange reaction of iminosulfur oxydifluorides
Chirality is an intrinsic property in unsymmetric three-dimensional molecular assembly, contributing to the utility of the corresponding process and the resulting scaffolds. Now, on the sulfur(VI) hub, a three-step sequential ligand-exchange method has been established with precise stereocontrol, enabling the enantioselective synthesis of optically active S(VI) functional molecules.
- Zhiyuan Peng
- , Shoujun Sun
- & Bing Gao
-
Article |
 Biocatalytic strategy for the construction of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds from directed evolution and computational modelling
Biocatalytic strategy for the construction of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds from directed evolution and computational modelling
The use of biocatalysis to support early-stage drug discovery campaigns remains largely untapped. Here, engineered biocatalysts enable the synthesis of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds through an intramolecular cyclopropanation of benzothiophenes, affording a class of complex scaffolds potentially useful for fragment-based drug discovery campaigns.
- David A. Vargas
- , Xinkun Ren
- & Rudi Fasan
-
Article |
 A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
Very few charge-neutral synthetic anion receptors can function in water, and those known typically select weakly hydrated anions such as iodide. Now a neutral molecular cage capable of donating 12 hydrogen bonds has been synthesized and found to bind highly hydrated sulfate in water with a strong selectivity over weakly hydrated anions.
- Liuyang Jing
- , Evelyne Deplazes
- & Xin Wu
-
Research Briefing |
 A protein-templated selection approach for the identification of full ligands from DNA-encoded libraries
A protein-templated selection approach for the identification of full ligands from DNA-encoded libraries
A protein-templated selection approach has been developed for the discovery of full ligands from dual-pharmacophore DNA-encoded libraries by incorporating fragment linking into the selection process. The performance of this method was demonstrated with selections against protein–protein interaction and protein–DNA interaction targets, through which potent and selective inhibitors were identified.
-
Article
| Open Access Chelation enables selectivity control in enantioconvergent Suzuki–Miyaura cross-couplings on acyclic allylic systems
Chelation enables selectivity control in enantioconvergent Suzuki–Miyaura cross-couplings on acyclic allylic systems
Achieving selectivity control in allylic arylations is a long-standing challenge in catalysis. Now a rhodium-catalysed system demonstrates chemo-, regio- and enantioselectivity, enabling Suzuki–Miyaura-type arylation with racemic, non-symmetrical, acyclic allylic systems; chelation is speculated to facilitate oxidative addition and enable both enantiomers of the starting material to converge onto a single product.
- Violeta Stojalnikova
- , Stephen J. Webster
- & Stephen P. Fletcher
-
Article
| Open Access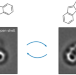 Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Switching the magnetic state of a polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon in a reversible and controlled manner is challenging. Now, by means of single-molecule scanning probe microscopy, an indenofluorene isomer on ultrathin NaCl films has been shown to adopt both open- and closed-shell states. Furthermore, bidirectional switching between the two states is achieved by changing the adsorption site of the molecule.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Manuel Vilas-Varela
- & Leo Gross
-
Article |
 Oxidative two-state photoreactivity of a manganese(IV) complex using near-infrared light
Oxidative two-state photoreactivity of a manganese(IV) complex using near-infrared light
The design of highly oxidizing Earth-abundant transition metal complexes for photochemical applications is desirable, but progress in this area remains limited. Now a manganese(IV) diguanidylpyridine complex has been shown to photooxidize naphthalene, benzene and acetonitrile to their radical cations after excitation with near-infrared light. Experimental and theoretical studies indicate the presence of two distinct ligand-to-metal charge transfer excited states.
- Nathan R. East
- , Robert Naumann
- & Katja Heinze
-
Article |
 Protein-templated ligand discovery via the selection of DNA-encoded dynamic libraries
Protein-templated ligand discovery via the selection of DNA-encoded dynamic libraries
Dual-pharmacophore DNA-encoded chemical libraries enable the identification of two synergistic binders for a biological target, but subsequent linking of this pair is required to obtain a full ligand, which can be challenging. Here we report a protein-templated selection of DNA-encoded dynamic library that can identify full ligands from fragment libraries without the need for subsequent fragment linking.
- Yu Zhou
- , Wenyin Shen
- & Xiaoyu Li
-
In Your Element |
 Redefining peptide therapeutics with semaglutide
Redefining peptide therapeutics with semaglutide
Thomas Kruse and Søren Østergaard reflect on the development of the GLP-1 analogue, semaglutide, which is reshaping peptide therapeutics in type 2 diabetes, weight management, and beyond.
- Thomas Kruse
- & Søren Østergaard
-
Article
| Open Access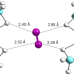 Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Although hydrogen gas could serve as a promising future fuel, its high-capacity storage is a challenge. Now, a nanoporous magnesium borohydride framework is shown to store hydrogen as densely packed penta-dihydrogen clusters having well-defined orientations and directional interactions with the framework.
- Hyunchul Oh
- , Nikolay Tumanov
- & Yaroslav Filinchuk
-
Article |
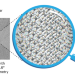 Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Chromophore supramolecular assemblies have long been studied for their exotic photophysical properties arising from their local geometry and long-range sensitive excitonic couplings. Now a high-resolution structure of a model nanotubular system has revealed a uniform brick-layer molecular arrangement and a non-biological supramolecular motif—interlocking sulfonates—enabling clear understanding of supramolecular structure–excitonic property relationships.
- Arundhati P. Deshmukh
- , Weili Zheng
- & Justin R. Caram
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast electronic relaxation pathways of the molecular photoswitch quadricyclane
Ultrafast electronic relaxation pathways of the molecular photoswitch quadricyclane
Light-induced ultrafast switching between the molecular isomers norbornadiene and quadricyclane can reversibly store and release a substantial amount of chemical energy. Two competing pathways have now been identified by which electronically excited quadricyclane molecules relax to the electronic ground state, facilitating interconversion between the two isomers on different timescales.
- Kurtis D. Borne
- , Joseph C. Cooper
- & Daniel Rolles
-
Research Briefing |
 Photodriven nitrogen fixation by lithium hydride
Photodriven nitrogen fixation by lithium hydride
Dinitrogen (N2) fixation to ammonia (NH3) is typically challenging under mild conditions. Now, lithium hydride (LiH) is shown to mediate photodriven N2 fixation under ambient conditions. Under ultraviolet illumination, LiH is photolysed to release H2, leaving electrons residing in surface hydrogen vacancies, which facilitate N2 activation and photocatalytic NH3 synthesis.
-
Article
| Open Access The synthesis and characterization of an iron(VII) nitrido complex
The synthesis and characterization of an iron(VII) nitrido complex
Complexes of iron in high oxidation states play a pivotal role as active intermediates in numerous catalytic processes. Now, using a multimethod approach on a single molecular system, it has been shown that a stable high-valent Fe(VI) nitride can be converted to a reactive, superoxidized, heptavalent Fe(VII) nitride.
- Martin Keilwerth
- , Weiqing Mao
- & Karsten Meyer
-
Article |
 Synthesis of polysubstituted azepanes by dearomative ring expansion of nitroarenes
Synthesis of polysubstituted azepanes by dearomative ring expansion of nitroarenes
While saturated N-heterocycles are widespread motifs in drug discovery, the seven-membered ring azepane is highly underrepresented. Now nitroarenes have been validated as competent substrates for azepane synthesis through conversion into singlet nitrenes for ring enlargement via N insertion and hydrogenolysis. This enables a highly versatile access towards polysubstituted azepanes in just two steps.
- Rory Mykura
- , Raquel Sánchez-Bento
- & Daniele Leonori
-
News & Views |
 Discovering cryptic natural products by substrate manipulation
Discovering cryptic natural products by substrate manipulation
Cryptic halogenation reactions result in natural products with diverse structural motifs and bioactivities. However, these halogenated species are difficult to detect with current analytical methods because the final products are often not halogenated. An approach to identify products of cryptic halogenation using halide depletion has now been discovered, opening up space for more effective natural product discovery.
- Ludek Sehnal
- , Libera Lo Presti
- & Nadine Ziemert
-
News & Views |
 Interlocked polyynes towards stable carbynes
Interlocked polyynes towards stable carbynes
Interlocking unstable motifs is a useful way to enhance their stability through shielding protection. Now, stable interlocked polyynes bearing several macrocycles have been prepared, including a [5]rotaxane having 34 contiguous alkynes with properties similar to those of carbyne.
- Adrian Saura-Sanmartin
-
Article
| Open Access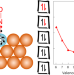 Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Single-atom alloys have emerged as highly active and selective catalysts that do not follow the traditional models of heterogeneous catalysis. Now it has been shown that the binding of adsorbates at their surface abides by a simple 10-electron count rule, which can identify promising catalysts for various applications.
- Julia Schumann
- , Michail Stamatakis
- & Romain Réocreux
-
News & Views |
 Doing away with radium’s proxies
Doing away with radium’s proxies
Despite the growing clinical use of radium in cancer treatments, the fundamental chemistry of nature’s largest +2 cation remains largely unexplored. Now, structural analysis of a radium complex reveals that its behaviour cannot always be predicted from the chemistry of its closest nonradioactive congener, barium.
- Joshua J. Woods
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
Article |
 Non-statistical assembly of multicomponent [Pd2ABCD] cages
Non-statistical assembly of multicomponent [Pd2ABCD] cages
Metal-mediated self-assembly of organic building blocks is a powerful strategy to generate complex supramolecular objects. The non-statistical combination of multiple different components, however, has been a major challenge. Now integrative self-sorting of low-symmetry multicomponent cages has been achieved by combining shape complementarity and selective backbone interactions under thermodynamic control.
- Kai Wu
- , Elie Benchimol
- & Guido H. Clever
-
News & Views |
 Sulfur stereochemistry takes centre stage
Sulfur stereochemistry takes centre stage
Directional interactions and three-dimensional functional groups are crucial to medicinal compounds. Consequently, new functional groups require stereocontrolled synthetic methods. Now, an enantiopure building block provides controlled and divergent access to valuable sulfonimidoyl functional groups.
- James A. Bull
-
Article |
 Asymmetric synthesis of sulfoximines, sulfonimidoyl fluorides and sulfonimidamides enabled by an enantiopure bifunctional S(VI) reagent
Asymmetric synthesis of sulfoximines, sulfonimidoyl fluorides and sulfonimidamides enabled by an enantiopure bifunctional S(VI) reagent
The stereochemical control and bifunctional manipulation of chiral sulfur functional groups is a long-standing challenge. Now, an enantiopure bench-stable S(VI) fluoride exchange reagent enables the asymmetric synthesis of sulfoximines, sulfonimidamides and sulfonimidoyl fluorides. The bifunctional nature of this reagent provides a practical method for the introduction of S(VI) functionality.
- Shun Teng
- , Zachary P. Shultz
- & Justin M. Lopchuk
-
Article
| Open Access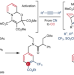 Skeletal editing of pyridines through atom-pair swap from CN to CC
Skeletal editing of pyridines through atom-pair swap from CN to CC
Skeletal editing enables diversification of compounds not possible by applying peripheral editing strategies. Now, a catalyst-free atom-pair swap strategy for pyridine editing has been developed via one-pot sequential dearomatization, cycloaddition and rearomative retrocyclization. Benzenes and naphthalenes with precisely installed functional groups are produced, and the mild conditions enable late-stage skeletal diversification of pyridine cores.
- Qiang Cheng
- , Debkanta Bhattacharya
- & Armido Studer
-
Article |
 Mirror-image trypsin digestion and sequencing of D-proteins
Mirror-image trypsin digestion and sequencing of D-proteins
The lack of effective methods for mirror-image (d-) protein sequencing hampers the development of mirror-image biology systems and related applications. Now, total chemical synthesis of mirror-image trypsin enables the sequencing of long d-peptides and d-proteins, which may facilitate applications of d-peptides and d-proteins as potential therapeutic and informational tools.
- Guanwei Zhang
- & Ting F. Zhu
-
Article |
 A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
Although interfacial proton-coupled electron transfers are critical reaction steps in chemical and biological processes, studies investigating these reactions are complicated by surface heterogeneity. Now, interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics are studied and modelled at isolated, well-defined active sites to provide a foundation for understanding complex reactions involved in energy conversion and catalysis.
- Noah B. Lewis
- , Ryan P. Bisbey
- & Yogesh Surendranath
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral arylsulfinylamides as reagents for visible light-mediated asymmetric alkene aminoarylations
Chiral arylsulfinylamides as reagents for visible light-mediated asymmetric alkene aminoarylations
Single-electron-mediated difunctionalizations of internal olefins allow the simultaneous formation of two contiguous Csp3-stereocentres. Here, we describe enantioenriched arylsulfinylamides as all-in-one reagents for the efficient asymmetric, intermolecular aminoarylation of alkenes. Mechanistic studies revealed an interesting dichotomy in the initiation of the reaction depending on the olefin redox potential.
- Cédric Hervieu
- , Mariia S. Kirillova
- & Cristina Nevado
-
Article |
 A general alkene aminoarylation enabled by N-centred radical reactivity of sulfinamides
A general alkene aminoarylation enabled by N-centred radical reactivity of sulfinamides
Single-step addition of an aryl ring and a protected amine across an alkene is a succinct route to valuable phenethylamine products, but existing methods suffer from limited scope. Now a family of compounds containing a sulfinamide functional group have been developed to react via electrophilic radicals to yield phenethylamines through an aryl migration with precise stereochemical control.
- Efrey A. Noten
- , Cody H. Ng
- & Corey R. J. Stephenson
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 A blueprint for catalysis
A blueprint for catalysis