Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Methylation enables high-voltage ether electrolytes for lithium metal batteries
Methylation enables high-voltage ether electrolytes for lithium metal batteries
Ether-based electrolytes are desired for lithium metal batteries owing to their low reduction potentials; however, they suffer from low anodic stability. Strategic methylation of ether solvents is shown to extend their electrochemical stability and facilitate the formation of LiF-rich interphases, enabling high-voltage lithium metal batteries while avoiding the use of fluorinated solvents.
-
Article |
 Methylation enables the use of fluorine-free ether electrolytes in high-voltage lithium metal batteries
Methylation enables the use of fluorine-free ether electrolytes in high-voltage lithium metal batteries
Lithium metal batteries are an attractive energy storage technology, but their development relies on the complex interplay between the components’ chemical, physical and mechanical properties. Now, selective methylation of dimethoxyethane ether electrolytes is shown to improve electrolyte, electrode and solid–electrolyte interphase stabilities to enable high-performance 4.3 V lithium metal batteries.
- Ai-Min Li
- , Oleg Borodin
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Article |
 Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Electrolysers can upgrade CO2 into high-value chemicals, but there are few tools capable of tracking the reactions that occur within these devices during operation. Now an electrolysis optical coherence tomography platform has been developed to visualize the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO, plus the movement of components, within the device.
- Xin Lu
- , Chris Zhou
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
News & Views |
 Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Electrocatalytic transformations often involve the concerted transfer of electrons and protons at electrode interfaces; however, these processes are not well understood. Now, experiments on an electrode that features well-defined molecular sites deepen fundamental understanding of such transfers to pave the way for future catalysts.
- Siyuan L. Xie
- & Eva M. Nichols
-
Article
| Open Access Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Although surface-bound molecular catalysts offer well-defined active sites on heterogeneous supports, it is challenging to identify key radical intermediates in the reaction mechanism. Now, a characterization method has been developed that combines film electrochemistry and EPR spectroscopy to track radical intermediates in real time, exemplified by alcohol oxidation with a surface-immobilized nitroxide.
- Maryam Seif-Eddine
- , Samuel J. Cobb
- & Maxie M. Roessler
-
Article |
 A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
Although interfacial proton-coupled electron transfers are critical reaction steps in chemical and biological processes, studies investigating these reactions are complicated by surface heterogeneity. Now, interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics are studied and modelled at isolated, well-defined active sites to provide a foundation for understanding complex reactions involved in energy conversion and catalysis.
- Noah B. Lewis
- , Ryan P. Bisbey
- & Yogesh Surendranath
-
News & Views |
 Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Gas bubble accumulation at interfaces is a barrier to achieving more efficient electrochemical devices. A clever model system to understand bubble formation during electrochemical hydrogen evolution now reveals similarities between the forces at play during their detachment from the catalyst surface and those involved in wine climbing up a glass.
- Gaurav Ashish Kamat
- & Michaela Burke Stevens
-
News & Views |
 Li–O2 battery redox mediators go positive
Li–O2 battery redox mediators go positive
Although Li–O2 batteries offer high theoretical energy storage capacities, few approach these limits. Now, a class of redox mediators is shown to send the discharge reaction from the electrode surface into the electrolyte solution, boosting device capacities and providing selection criteria for future efforts.
- Zhangquan Peng
-
Article |
 C–H···π interactions disrupt electrostatic interactions between non-aqueous electrolytes to increase solubility
C–H···π interactions disrupt electrostatic interactions between non-aqueous electrolytes to increase solubility
The energy density in redox flow batteries is currently limited by the solubility of dissolved redox species. Now it has been shown that intermolecular C–H···π interactions can disrupt electrostatic forces in these organic electrolytes to improve their solubility in non-aqueous solvents.
- Sharmila Samaroo
- , Charley Hengesbach
- & David P. Hickey
-
Article |
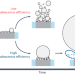 Solutal Marangoni effect determines bubble dynamics during electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Solutal Marangoni effect determines bubble dynamics during electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Although gas bubble dynamics during electrochemical processes dramatically affect performance, the fundamental understanding and manipulation of such dynamics have been limited. Now, electrolyte composition is found to be a key factor in inducing a solutal Marangoni instability that impacts both H2 gas detachment and coalescence between H2 microbubbles.
- Sunghak Park
- , Luhao Liu
- & Marc T. M. Koper
-
Article |
 Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Understanding interfacial and cellular electron transport is essential for guiding efficiency optimization in microbe–semiconductor biohybrids for energy conversion. A multimodal imaging platform that combines optical imaging and photocurrent mapping can now interrogate such electron-transport pathways at the single-cell level, uncovering different roles of hydrogenases and a microbe’s large electron-uptake capacity.
- Bing Fu
- , Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
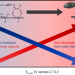 Triarylmethyl cation redox mediators enhance Li–O2 battery discharge capacities
Triarylmethyl cation redox mediators enhance Li–O2 battery discharge capacities
Although Li–O2 batteries offer high theoretical capacities, redox mediators are necessary to control intermediate reaction kinetics and to limit electrode passivation. Now it has been shown that a family of triarylmethyl cations can rival top-performing quinone-based redox mediators. Cations with sluggish catalytic rates were found to suppress surface-mediated O2 reduction and achieve higher capacitances.
- Erik J. Askins
- , Marija R. Zoric
- & Ksenija D. Glusac
-
Article |
 Why charging Li–air batteries with current low-voltage mediators is slow and singlet oxygen does not explain degradation
Why charging Li–air batteries with current low-voltage mediators is slow and singlet oxygen does not explain degradation
Ultra-high-capacity Li–air batteries have low Coulombic efficiency and degrade during re-charging, resulting in a poor cycle life. Redox mediators enable improvements but only at undesirably high potentials. The origin of this high potential and the impact of purported reactive intermediates has now been elucidated by resolving the charging mechanism using Marcus theory.
- Sunyhik Ahn
- , Ceren Zor
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical synthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide on copper nanocrystals
Electrochemical synthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide on copper nanocrystals
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to propylene requires multiple C–C coupling steps and the transfer of 18 electrons, posing kinetic and thermodynamic barriers. Now the electrosynthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide using copper nanocrystals has been demonstrated, with analysis revealing that the key step for its formation is probably the coupling between carbon dioxide or carboxyl with intermediates involved in the ethylene pathway.
- Jing Gao
- , Alimohammad Bahmanpour
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article |
 Inverse kinetic isotope effects in the oxygen reduction reaction at platinum single crystals
Inverse kinetic isotope effects in the oxygen reduction reaction at platinum single crystals
Kinetic isotope effect studies can provide valuable insights into the complex mechanisms of the oxygen reduction reaction; however, inaccessibility to ultra-high-purity D2O has made this difficult. Now, a methodology to prepare ultra-pure D2O has been developed and inverse kinetic isotope effects have subsequently been measured for the oxygen reduction reaction on platinum single-crystal surfaces, providing mechanistic insights.
- Yao Yang
- , Rishi G. Agarwal
- & Héctor D. Abruña
-
News & Views |
 Bringing redox organics back to life
Bringing redox organics back to life
Aqueous organic redox flow batteries are promising for low-cost and large-scale energy storage, but the redox-active molecules they rely on degrade prematurely. Now, a facile electrochemical protocol to regenerate them has been proposed, resulting in extended battery lifetimes.
- Antoni Forner-Cuenca
-
Article |
 In situ electrochemical recomposition of decomposed redox-active species in aqueous organic flow batteries
In situ electrochemical recomposition of decomposed redox-active species in aqueous organic flow batteries
Aqueous organic redox flow batteries offer a safe and inexpensive solution to the problem of storing electricity produced from intermittent renewables. However, decomposition of the redox-active organic molecules that they rely on limits their lifetimes, preventing commercialization. Now it has been shown that these redox molecules can be electro-recomposed in situ, rejuvenating their function.
- Yan Jing
- , Evan Wenbo Zhao
- & Michael J. Aziz
-
Article |
 In situ multiscale probing of the synthesis of a Ni-rich layered oxide cathode reveals reaction heterogeneity driven by competing kinetic pathways
In situ multiscale probing of the synthesis of a Ni-rich layered oxide cathode reveals reaction heterogeneity driven by competing kinetic pathways
Nickel-rich layered oxides, such as NCM622, are promising cathode materials for lithium batteries, but chemo-mechanical failures hinder their practical application. Now the solid-state synthesis of NCM622 has been studied using multiscale in situ techniques, and kinetic competition between precursor decomposition and lithiation has been observed to lead to spatially heterogeneous intermediates and the formation of defects that are detrimental to cycling.
- Hyeokjun Park
- , Hayoung Park
- & Kisuk Kang
-
News & Views |
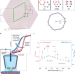 Let’s twist electrochem
Let’s twist electrochem
The electronic structure of an electrode can affect the electron transfer rate of electrochemical processes at its surface. Now, it has been shown that varying the ‘twist’ angle between two stacked layers of graphene modifies the bilayer electronic structure and provides a new dimension to control interfacial redox activity.
- Oluwasegun J. Wahab
- & Patrick R. Unwin
-
Article |
 Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Carbonic anhydrase enzymatically catalyses CO2 hydration, and its effect on enzymatic and heterogeneous CO2 reduction has now been studied. Through the co-immobilization of carbonic anhydrase, it has been shown that faster CO2 hydration kinetics are beneficial for enzymatic catalysis (using formate dehydrogenase) but detrimental for heterogeneous catalysts, such as gold.
- Samuel J. Cobb
- , Vivek M. Badiani
- & Erwin Reisner
-
Article |
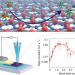 Tunable angle-dependent electrochemistry at twisted bilayer graphene with moiré flat bands
Tunable angle-dependent electrochemistry at twisted bilayer graphene with moiré flat bands
Controlling the crystallographic registry of layered materials through interlayer twist angles has introduced a distinctive degree of freedom for tuning their electronic behaviour. Now, the interfacial electrochemical kinetics of solution-phase redox complexes at twisted bilayer graphene electrodes have been modulated by the angle-dependent tuning of moiré-derived flat bands.
- Yun Yu
- , Kaidi Zhang
- & D. Kwabena Bediako
-
Article |
 Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
The use of ammonia as an alternative fuel relies on its electrochemical conversion to dinitrogen in a fuel cell. Now a stable metal–metal bonded diruthenium complex is shown to spontaneously produce dinitrogen from ammonia under ambient conditions and is also able to electrocatalyse the oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen at low potentials.
- Michael J. Trenerry
- , Christian M. Wallen
- & John F. Berry
-
News & Views |
 Bringing amines back into aziridination
Bringing amines back into aziridination
Aziridines — three-membered nitrogen-containing heterocycles — are important synthetic targets, but N-alkyl aziridines are difficult to synthesize. Now, an electrochemical method, involving a dicationic intermediate, enables the coupling of alkenes and amines.
- Tiffany Piou
- & Louis-Charles Campeau
-
Article |
 Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Self-propelled artificial chemical swimmers have previously been developed for chemical sensing. Now, hybrid bioelectrochemical swimmers, capable of translating chiral molecular information into macroscopic motion, have been developed. Diastereomeric interactions between enantiopure oligomers immobilized on the swimmer and a chiral molecule present in solution control the trajectory of the device.
- Serena Arnaboldi
- , Gerardo Salinas
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article |
 Aqueous interphase formed by CO2 brings electrolytes back to salt-in-water regime
Aqueous interphase formed by CO2 brings electrolytes back to salt-in-water regime
Super-concentrated water-in-salt electrolytes enable high-voltage aqueous batteries, but have considerable drawbacks such as high viscosity, low conductivity and slow kinetics. Now a concentration-dependent association between CO2 and TFSI– has been discovered and leveraged to decouple the interphasial responsibility of an aqueous electrolyte from its bulk properties, making high-voltage aqueous Li-ion batteries practical in dilute salt-in-water electrolytes.
- Jinming Yue
- , Jinkai Zhang
- & Liquan Chen
-
Article |
 Correlating ligand-to-metal charge transfer with voltage hysteresis in a Li-rich rock-salt compound exhibiting anionic redox
Correlating ligand-to-metal charge transfer with voltage hysteresis in a Li-rich rock-salt compound exhibiting anionic redox
The use of anionic redox chemistry in high-capacity Li-rich cathodes is being hampered by voltage hysteresis, the origin of which remains obscure. Now it has been shown that sluggish ligand-to-metal charge transfer kinetically traps an intermediate Fe4+ species and is responsible for voltage hysteresis in the prototypical Li-rich cation-disordered rock-salt Li1.17Ti0.33Fe0.5O2.
- Biao Li
- , Moulay Tahar Sougrati
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
-
Article |
 Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Molecular catalysts can be made more practical by anchoring them onto electrode surfaces, but such systems are less stable than standard heterogeneous electrocatalysts. Now, supramolecular hosts bound to electrode surfaces have enabled the immobilization of molecular electrocatalysts through host–guest interactions. Desorbed or degraded guest molecules can be replaced with fresh guest molecules, extending their lifetimes.
- Laurent Sévery
- , Jacek Szczerbiński
- & S. David Tilley
-
Article |
 Electrochemically driven desaturation of carbonyl compounds
Electrochemically driven desaturation of carbonyl compounds
Excising hydrogen adjacent to a carbonyl group—one of the most basic and widely employed transformations in organic synthesis—is traditionally achieved using metals and/or stoichiometric oxidants. Now, it has been shown that an electrochemically driven approach removes such requirements, resulting in a more sustainable and easily scalable method with wide substrate scope.
- Samer Gnaim
- , Yusuke Takahira
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
 Mechanism of mediated alkali peroxide oxidation and triplet versus singlet oxygen formation
Mechanism of mediated alkali peroxide oxidation and triplet versus singlet oxygen formation
Redox mediators are important for improving the rechargeability of metal–air batteries, however, how they affect singlet oxygen formation and hence parasitic chemistry is unclear, hindering strategies for their improvement. Now, the mechanism of mediated peroxide and superoxide oxidation is elucidated, explaining how redox mediators either enhance or suppress singlet oxygen formation.
- Yann K. Petit
- , Eléonore Mourad
- & Stefan A. Freunberger
-
Thesis |
 The rise and rise of lithium
The rise and rise of lithium
We’re in the middle of an energy revolution, argues Bruce C. Gibb, and chemistry is an integral part of it.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
Article |
 Improving the efficiency of CO2 electrolysis by using a bipolar membrane with a weak-acid cation exchange layer
Improving the efficiency of CO2 electrolysis by using a bipolar membrane with a weak-acid cation exchange layer
Moving towards renewable energy sources requires pathways for efficiently converting electricity to chemicals, and gas-fed CO2 electrolysers show promise. Now, the layer-by-layer assembly of a weak-acid cation exchange layer has been shown to affect the local pH in a bipolar-membrane-based gas-fed CO2 electrolyser, improving the conversion efficiency of CO2 to CO by suppressing the competing hydrogen evolution reaction.
- Zhifei Yan
- , Jeremy L. Hitt
- & Thomas E. Mallouk
-
Matters Arising |
 Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
- Shufeng Zhang
- & Wenhua Leng
-
Matters Arising |
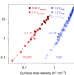 Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Reshma R. Rao
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article |
 Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Efficient and stable water oxidation catalysts are important if photoelectrochemical cells are to be used to provide clean and sustainable solar fuels. A water oxidation catalyst that operates at neutral pH has now been developed that features ruthenium coordination oligomers anchored onto the surfaces of graphitic materials through CH–π interactions.
- Md Asmaul Hoque
- , Marcos Gil-Sepulcre
- & Antoni Llobet
-
Article |
 Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes
Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes
A general method for the enantioselective hydrocyanation of alkenes has been a long-standing synthetic challenge. Now, using a dual electrocatalytic approach that combines two synergistic redox catalytic cycles, a wide variety of chiral nitriles can be synthesized from conjugated alkenes in high enantioselectivity.
- Lu Song
- , Niankai Fu
- & Song Lin
-
Article |
 Coupling N2 and CO2 in H2O to synthesize urea under ambient conditions
Coupling N2 and CO2 in H2O to synthesize urea under ambient conditions
Conventionally, urea is synthesized via two consecutive processes, N2 + H2 → NH3 followed by NH3 + CO2. Now, an electrocatalyst consisting of PdCu alloy nanoparticles on TiO2 nanosheets has been shown to directly couple N2 and CO2 in H2O to produce urea under ambient conditions.
- Chen Chen
- , Xiaorong Zhu
- & Shuangyin Wang
-
Article |
 Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Single-atom catalysts maximize metal atom efficiency and exhibit properties that can be considerably different to their nanoparticle equivalent. Now a general host–guest strategy to make various single-atom catalysts on nitrogen-doped carbon has been developed; the iridium variant electrocatalyses the formic acid oxidation reaction with high mass activity and displays high tolerance to CO poisoning.
- Zhi Li
- , Yuanjun Chen
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
Gene-circuit-based sensors have, to date, largely relied on optical proteins (such as green fluorescent protein) to report the output, which limits the signalling bandwidth. Now, an electrochemical output has been developed and integrated with cell-free gene circuits. This approach enables multiplexing of sensors and introduces the possibility of electronic-based logic, memory and response elements to synthetic biology.
- Peivand Sadat Mousavi
- , Sarah J. Smith
- & Keith Pardee
-
-
Article |
 Rechargeable-battery chemistry based on lithium oxide growth through nitrate anion redox
Rechargeable-battery chemistry based on lithium oxide growth through nitrate anion redox
Phase-forming conversion chemistry, like that observed in Li–S and Li–O2 batteries, shows great promise, but these systems suffer some drawbacks, such as practically low cathode areal capacities and electrolyte decomposition. Now, high-energy conversion battery chemistry—based on nitrate/nitrite redox where one of the products is soluble—has been enabled by using nanoparticulate Ni/NiO electrocatalysts.
- Vincent Giordani
- , Dylan Tozier
- & Dan Addison
-
Article |
 Formation of carbon–nitrogen bonds in carbon monoxide electrolysis
Formation of carbon–nitrogen bonds in carbon monoxide electrolysis
The electroreduction of CO2-derived CO is a promising technology for the sustainable production of value-added chemicals. Now, it is shown how C–N bonds can be formed electrochemically through CO electroreduction on a Cu surface in the presence of amines. The formation of acetamides is observed through nucleophilic addition to a ketene intermediate.
- Matthew Jouny
- , Jing-Jing Lv
- & Feng Jiao
-
News & Views |
 Interphase identity crisis
Interphase identity crisis
Interphases that form on the anode surface of lithium-ion batteries are critical for performance and lifetime, but are poorly understood. Now, a decade-old misconception regarding a main component of the interphase has been revealed, which could potentially lead to improved devices.
- Stefan A. Freunberger
-
Article |
 Identifying the components of the solid–electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries
Identifying the components of the solid–electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries
The solid–electrolyte-interphase layer is extremely important for reversible electrochemical cycling of Li-ion batteries. Now it has been observed that lithium ethylene mono-carbonate, instead of the previously reported lithium ethylene di-carbonate, is the major initial organic species in this layer and it has a high Li-ion conductivity.
- Luning Wang
- , Anjali Menakath
- & Bryan W. Eichhorn
-
Article |
 Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
The production of ammonia from dinitrogen is a well-studied process; however, the catalytic conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen is underdeveloped. Now, ammonia oxidation has been achieved using ruthenium complexes as catalysts. The production of dinitrogen is observed when ammonium salts are treated with a single-electron oxidant, base and ruthenium catalyst.
- Kazunari Nakajima
- , Hiroki Toda
- & Yoshiaki Nishibayashi
-
News & Views |
 Aqueous batteries get energetic
Aqueous batteries get energetic
Aqueous batteries hold promise for large-scale energy storage, but are often maligned because of their low energy densities. Now, a demonstration of halogen conversion–intercalation chemistry inside graphite has blazed a trail for high-energy aqueous batteries.
- Xianyong Wu
- & Xiulei Ji
-
Article |
 Optimization of the facet structure of transition-metal catalysts applied to the oxygen reduction reaction
Optimization of the facet structure of transition-metal catalysts applied to the oxygen reduction reaction
While much effort has been devoted to understanding how nanoparticle morphology can be leveraged to improve catalytic activity, engineering their microstructure from first principles to this end has remained difficult. Now a methodology for designing the optimal structure of a solid catalyst with the aim of achieving the highest possible activity for surface-sensitive reactions has been developed.
- M. Núñez
- , J. L. Lansford
- & D. G. Vlachos
-
Article |
 Fast galvanic lithium corrosion involving a Kirkendall-type mechanism
Fast galvanic lithium corrosion involving a Kirkendall-type mechanism
Developing a stable metallic lithium anode is necessary for next-generation batteries; however, lithium is prone to corrosion, a process that must be better understood if practical devices are to be created. A Kirkendall-type mechanism of lithium corrosion has now been observed. The corrosion is fast and is governed by a galvanic process.
- Dingchang Lin
- , Yayuan Liu
- & Yi Cui

 Deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole serves as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation
Deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole serves as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation Chloride in the battery pool
Chloride in the battery pool Deconvoluting double layers
Deconvoluting double layers The Li-ions share
The Li-ions share