Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Designer peptide–DNA cytoskeletons regulate the function of synthetic cells
Designer peptide–DNA cytoskeletons regulate the function of synthetic cells
Advances in the development of cytoskeletal-like materials with modular structures and mechanics are pivotal for the engineering of synthetic cells. Now actin-mimetic supramolecular peptide networks have been designed using programmable peptide–DNA crosslinkers, giving rise to tunable tactoid-shaped bundles and mechanical properties that control spatial localization, the diffusion of payloads and shape changes within artificial cells.
- Margaret L. Daly
- , Kengo Nishi
- & Ronit Freeman
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical scission of a knotted polymer
Mechanical scission of a knotted polymer
Knots reduce the tensile strength of macroscopic threads and fibres. Now it has been shown that the presence of a well-defined overhand knot in a polymer chain can substantially increase the rate of scission of the polymer under tension, as deformation of the polymer backbone induced by the tightening knot activates otherwise unreactive covalent bonds.
- Min Zhang
- , Robert Nixon
- & David A. Leigh
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrameric self-assembling of water-lean solvents enables carbamate anhydride-based CO2 capture chemistry
Tetrameric self-assembling of water-lean solvents enables carbamate anhydride-based CO2 capture chemistry
Carbon capture, utilization and storage is key for climate change mitigation and developing more environmentally friendly technologies. Now it has been shown that CO2 capture in single-component water-lean solvents is accompanied by the self-assembly of reverse-micelle-like tetrameric clusters in solution that enable the formation of various CO2-containing compounds.
- Julien Leclaire
- , David J. Heldebrant
- & Jaelynne King
-
Article |
 Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Although the light-driven generation of hydrogen from water is a promising approach to renewable fuels, the H–H bond formation step represents a persistent mechanistic question. Now light-harvesting molecular catalysts have been shown to self-assemble into nanoscale aggregates that feature improved efficiency for photoelectrochemical H2 evolution.
- Isaac N. Cloward
- , Tianfei Liu
- & Alexander J. M. Miller
-
News & Views |
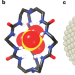 Clever cryptand cage coordinates contaminants
Clever cryptand cage coordinates contaminants
Replicating the ability of enzymes and transport proteins to effectively bind anions is a considerable challenge for supramolecular chemists. A neutral organic cage has now been developed that selectively binds sulfate anions in water.
- Rosemary J. Goodwin
- & Nicholas G. White
-
Article |
 A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
Very few charge-neutral synthetic anion receptors can function in water, and those known typically select weakly hydrated anions such as iodide. Now a neutral molecular cage capable of donating 12 hydrogen bonds has been synthesized and found to bind highly hydrated sulfate in water with a strong selectivity over weakly hydrated anions.
- Liuyang Jing
- , Evelyne Deplazes
- & Xin Wu
-
Article |
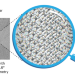 Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Chromophore supramolecular assemblies have long been studied for their exotic photophysical properties arising from their local geometry and long-range sensitive excitonic couplings. Now a high-resolution structure of a model nanotubular system has revealed a uniform brick-layer molecular arrangement and a non-biological supramolecular motif—interlocking sulfonates—enabling clear understanding of supramolecular structure–excitonic property relationships.
- Arundhati P. Deshmukh
- , Weili Zheng
- & Justin R. Caram
-
News & Views |
 Interlocked polyynes towards stable carbynes
Interlocked polyynes towards stable carbynes
Interlocking unstable motifs is a useful way to enhance their stability through shielding protection. Now, stable interlocked polyynes bearing several macrocycles have been prepared, including a [5]rotaxane having 34 contiguous alkynes with properties similar to those of carbyne.
- Adrian Saura-Sanmartin
-
Article |
 Non-statistical assembly of multicomponent [Pd2ABCD] cages
Non-statistical assembly of multicomponent [Pd2ABCD] cages
Metal-mediated self-assembly of organic building blocks is a powerful strategy to generate complex supramolecular objects. The non-statistical combination of multiple different components, however, has been a major challenge. Now integrative self-sorting of low-symmetry multicomponent cages has been achieved by combining shape complementarity and selective backbone interactions under thermodynamic control.
- Kai Wu
- , Elie Benchimol
- & Guido H. Clever
-
Perspective |
 Photoswitchable coordination cages
Photoswitchable coordination cages
The self-assembly of stimuli-responsive building blocks yields functional nano-systems and smart materials. This Perspective discusses how the integration of photoswitches into discrete coordination cages enables control over their assembly, guest binding and systems behaviour. Four scenarios are drawn to highlight the relationship between the photoswitching and dynamic assembly equilibria.
- Elie Benchimol
- , Jacopo Tessarolo
- & Guido H. Clever
-
Article
| Open Access Masked alkynes for synthesis of threaded carbon chains
Masked alkynes for synthesis of threaded carbon chains
Long polyynes have fascinating properties but they are difficult to synthesize as a consequence of their high reactivity. Now, it has been shown that cobalt carbonyl complexes can be used as masked alkyne equivalents, enabling the preparation of stable polyyne polyrotaxanes with up to 34 contiguous triple bonds.
- Connor W. Patrick
- , Yueze Gao
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article |
 Entropy-driven charge-transfer complexation yields thermally activated delayed fluorescence and highly efficient OLEDs
Entropy-driven charge-transfer complexation yields thermally activated delayed fluorescence and highly efficient OLEDs
Although exciplex-forming systems are widely used for fabricating organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), their structural and thermodynamic characterization is limited. Now donor/acceptor inclusion complexes that demonstrate thermally activated delayed fluorescence have been generated. Their cocrystal structures have been resolved and the thermodynamics of exciplex formation determined, which has enabled the fabrication of efficient OLEDs.
- Chun-Yen Lin
- , Chao-Hsien Hsu
- & Pi-Tai Chou
-
Research Briefing |
 Rigid macrocycles with multiple hydrogen-bond donors for effective anion binding and transport
Rigid macrocycles with multiple hydrogen-bond donors for effective anion binding and transport
Aromatic oligoamide macrocycles have been developed in which the constrained backbone enforces hydrogen-bond donors to orient towards the macrocycle centre, forming a highly electropositive cavity. These macrocycles show strong binding for various anions and can partition into biomembranes to facilitate selective transmembrane anion transport.
-
Article |
 Aromatic pentaamide macrocycles bind anions with high affinity for transport across biomembranes
Aromatic pentaamide macrocycles bind anions with high affinity for transport across biomembranes
Effective synthetic anion receptors are challenging to design. Now, star-shaped macrocycles, with a cavity defined by multiple convergent amide NH and phenyl CH groups, have been synthesized in one pot from their monomeric building blocks. These macrocycles strongly bind a variety of anions, selectively transport chloride across cell membranes and restore the function of cystic fibrosis cells.
- Ruikai Cao
- , Robert B. Rossdeutcher
- & Bing Gong
-
News & Views |
 Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
The intentional interweaving of two different metal–organic framework (MOF) lattices could offer a strategy for combining the disparate properties of the two frameworks within a single MOF material. Now, the rational construction of such hetero-interpenetrated MOFs has been demonstrated.
- Tendai Gadzikwa
-
Article |
 Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks offer a highly tunable class of materials for a range of applications, although their dynamic structural transformations are challenging to analyse. Now single-crystal X-ray diffraction is shown to demonstrate single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformations of the imine linkages, showing a well-defined interpenetrating topology and affording structures that have high positive thermal expansion and anhydrous proton-conduction properties.
- Baoqiu Yu
- , Rui-Biao Lin
- & Jianzhuang Jiang
-
Article |
 Light-driven eco-evolutionary dynamics in a synthetic replicator system
Light-driven eco-evolutionary dynamics in a synthetic replicator system
The onset of eco-evolutionary dynamics marks a stepping stone in the transition from chemistry to biology. Now a minimal replicator system showing such dynamics has been developed. The replicators adapt to changes in their environment that they themselves induced through photoredox catalysis.
- Kai Liu
- , Alex Blokhuis
- & Sijbren Otto
-
Article |
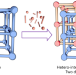 Hetero-interpenetrated metal–organic frameworks
Hetero-interpenetrated metal–organic frameworks
Interpenetration—in which two or more lattices are catenated—is common in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Now a deliberate synthesis of hetero-interpenetrated MOFs, with two distinct lattices, has been developed. It can combine the different properties of the two sublattices in one material, as demonstrated with chirality and catalytic activity, delivering an asymmetric catalyst.
- David Perl
- , Seok J. Lee
- & Shane G. Telfer
-
News & Views |
 Site selectivity steps in
Site selectivity steps in
The concepts of multistep processes and regioselectivity — fundamental in covalent synthesis — have now been applied to the non-covalent synthesis of sequence-controlled multiblock supramolecular polymers.
- Ghislaine Vantomme
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of a glycan hairpin
Synthesis of a glycan hairpin
Inspired by the design of peptide and nucleic acid sequences to adopt particular three-dimensional shapes, natural glycan motifs have now been combined to construct a glycan that adopts a hairpin conformation in water. Thus a designed glycan can now autonomously fold into a stable secondary structure absent in nature.
- Giulio Fittolani
- , Theodore Tyrikos-Ergas
- & Martina Delbianco
-
In Your Element |
 Playing Lego with perylene dyes
Playing Lego with perylene dyes
Rajeev K. Dubey and Frank Würthner discuss the colourful character of perylene bisimides and the impact of aggregation on their functional properties.
- Rajeev K. Dubey
- & Frank Würthner
-
Article |
 Multistep, site-selective noncovalent synthesis of two-dimensional block supramolecular polymers
Multistep, site-selective noncovalent synthesis of two-dimensional block supramolecular polymers
Supramolecular structures are typically formed by the one-step self-assembly of building blocks. Now, a greater level of control has been achieved using stepwise non-covalent reactions under kinetic control. Two-dimensional block supramolecular polymers with tailored compositions and sequences were synthesized, and a site selectivity that is reminiscent of regioselectivity in covalent synthesis was observed.
- Norihiko Sasaki
- , Jun Kikkawa
- & Kazunori Sugiyasu
-
Article |
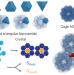 Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Clathrates—open crystals with a hierarchy of polyhedral cages—are mostly found in atomic and molecular systems. Now, it has been shown through Monte Carlo simulations that the formation of colloidal host–guest clathrates can be driven by entropy alone, through entropy compartmentalization.
- Sangmin Lee
- , Thi Vo
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Research Briefing |
 Not all catenanes with oriented rings are topologically chiral
Not all catenanes with oriented rings are topologically chiral
Catenanes that are chiral owing to the relative orientation of their rings have always been referred to as ‘topologically chiral’. It is now shown that although in specific cases the stereochemistry is a topological property of the structure, the underlying stereogenic unit itself is not inherently topological in nature.
-
Article |
 A catenane that is topologically achiral despite being composed of oriented rings
A catenane that is topologically achiral despite being composed of oriented rings
Catenanes are topologically non-trivial and, perhaps for this reason, molecules composed of two oriented rings have always simply been referred to as ‘topologically chiral’. Now it has been shown that the same stereogenic unit can arise in systems whose stereochemistry is Euclidean, suggesting a need to rethink this fundamental form of mechanical chirality.
- Noel Pairault
- , Federica Rizzi
- & Stephen M. Goldup
-
News & Views |
 A liquid quasicrystal of columns
A liquid quasicrystal of columns
Systems that feature long-range order but no translational periodicity are intriguing. Now, a T-shaped molecule consisting of three non-miscible components has been devised that self-assembles into a columnar liquid quasicrystal.
- Marianne Impéror-Clerc
-
Article |
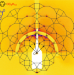 A columnar liquid quasicrystal with a honeycomb structure that consists of triangular, square and trapezoidal cells
A columnar liquid quasicrystal with a honeycomb structure that consists of triangular, square and trapezoidal cells
Quasicrystals are intriguing structures that exhibit long-range positional correlations but no periodicity in real space. Now, T-shaped amphiphilic molecules featuring rigid cores have been found to self-assemble into a columnar liquid quasicrystal with dodecagonal symmetry. The honeycomb structure observed arises from a strictly quasiperiodic tessellation of square, triangular and trapezoidal tiles, rather than from random tiling.
- Xiangbing Zeng
- , Benjamin Glettner
- & Carsten Tschierske
-
Article
| Open Access Control of dynamic sp3-C stereochemistry
Control of dynamic sp3-C stereochemistry
Stereogenic sp3-hybridized carbon centres are the principal building blocks of chiral organic molecules. Usually, these centres are configurationally fixed. Now, low-energy pericyclic rearrangements have been used to create rigid cage molecules with fluxional sp3-stereochemistry, influencing chiral information transfer. The sp3-carbon stereochemistry of the cages is inverted through strain-assisted Cope rearrangements.
- Aisha N. Bismillah
- , Toby G. Johnson
- & Paul R. McGonigal
-
In Your Element |
 Cucurbituril curiosities
Cucurbituril curiosities
Rahul Dev Mukhopadhyay and Kimoon Kim consider how cucurbiturils — pumpkin-shaped macrocycles — went from curiosities to compelling cavitands for a host of applications.
- Rahul Dev Mukhopadhyay
- & Kimoon Kim
-
News & Views |
 Stable organolithium gels
Stable organolithium gels
Organolithium reagents are characterized by their high reactivity towards air and moisture, traditionally requiring strict inert conditions for their handling and utilization. Now, these reagents can be encapsulated within an organogel, enhancing their stability and allowing their use and storage under ambient conditions.
- Andreu Tortajada
- & Eva Hevia
-
Article
| Open Access Organogel delivery vehicles for the stabilization of organolithium reagents
Organogel delivery vehicles for the stabilization of organolithium reagents
Organolithium compounds are important reagents but are often hazardous due to their high reactivity. Now, encapsulating organolithium reagents within a supramolecular organogel has been found to enhance their stability, facilitating their storage and handling under ambient conditions. The homogeneous gels can be easily subdivided and dosed into a wide range of synthetic reactions.
- Petr Slavík
- , Benjamin R. Trowse
- & David K. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible transformations between the non-porous phases of a flexible coordination network enabled by transient porosity
Reversible transformations between the non-porous phases of a flexible coordination network enabled by transient porosity
Sorbent materials that reversibly transform between closed (non-porous) and open (porous) phases on the uptake and release of guests are relevant to gas storage and separation applications. Now, a coordination network has been prepared that exhibits gas-induced transformations between multiple non-porous phases. This phenomenon is attributed to subtle structural rearrangements that enable transient porosity.
- Varvara I. Nikolayenko
- , Dominic C. Castell
- & Michael J. Zaworotko
-
Article |
 Functional advantages of building nanosystems using multiple molecular components
Functional advantages of building nanosystems using multiple molecular components
The advantages and disadvantages of building a nanosystem using one, two or more molecular components are poorly understood. Now, using structural and catalytic DNA-based nanosystems and theoretical simulations, it has been shown that the assembly of trimeric nanosystems displays much higher levels of programmability and functionality than the monomeric or dimeric counterparts.
- D. Lauzon
- & A. Vallée-Bélisle
-
News & Views |
 Interlocked structures on active duty
Interlocked structures on active duty
Interlocking macrocyclic carbon nanomaterials is an exciting way to tune their molecular properties, but all-conjugated catenanes and rotaxanes are extremely challenging to make. Now, fully π-conjugated [2]- and [3]catenanes as well as a [3]rotaxane have been prepared through an ‘active metal template’ approach.
- Satyajit Das
- & Fredrik Schaufelberger
-
Article |
 Enantioselective fullerene functionalization through stereochemical information transfer from a self-assembled cage
Enantioselective fullerene functionalization through stereochemical information transfer from a self-assembled cage
The enantioselective functionalization of C60 is highly challenging, typically requiring complex chiral tethers or demanding chromatography. Fullerenes have now been shown to undergo Diels–Alder reactions in a chemo-, regio- and enantio-selective fashion through confinement within an enantiopure metal–organic cage functionalized with a chiral formylpyridine group.
- Zifei Lu
- , Tanya K. Ronson
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
The nitrogen reduction reaction is an extremely valuable but energy-intensive process. Now, a coordination polymer based on a [Zn–N2–Zn] unit has been shown to promote the formation of ammonia under ambient conditions by a photocatalytic reaction. The N2 moieties within the framework are reduced, creating unsaturated [Zn2+···Zn+] intermediates that are able to capture external N2 and sustain the cycle.
- Yan Xiong
- , Bang Li
- & Zhong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Dimeric and trimeric catenation of giant chiral [8 + 12] imine cubes driven by weak supramolecular interactions
Dimeric and trimeric catenation of giant chiral [8 + 12] imine cubes driven by weak supramolecular interactions
Interlocked shape-persistent organic cages are rare structures and the majority are formed using π-stacking as the driving force. Now it is shown that weak dispersion interactions—which are modulated by changing the 1,4-substituents of the constituent dialdehyde linkers—can be used to form interlocked dimeric and trimeric catenated cages.
- Bahiru Punja Benke
- , Tobias Kirschbaum
- & Michael Mastalerz
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Modulation of surface properties and functions can be achieved through covalent and non-covalent molecular binding, but the lack of responsiveness and requirement for specific binding groups makes spatiotemporal control challenging. Now, it has been shown that adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host is an effective non-covalent binding strategy for programmable surface functionalization.
- Shaohua Zhang
- , Wei Li
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
In Your Element |
 Corrole and squeezed coordination
Corrole and squeezed coordination
Abhik Ghosh explores the structure, chemistry and applications of corroles, a class of sterically constrained macrocyclic tetrapyrroles.
- Abhik Ghosh
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article |
 Using supramolecular machinery to engineer directional charge propagation in photoelectrochemical devices
Using supramolecular machinery to engineer directional charge propagation in photoelectrochemical devices
Photoelectrochemical cells are hampered by electron–hole recombination. Now, supramolecular machinery has enabled the docking of macrocyclic electron-accepting redox mediators to a dye through pseudorotaxane formation. Upon electron transfer from the dye, the anionic redox-mediator rings are launched away from the surface, reducing charge recombination, establishing charge separation and improving the efficiency of the solar cells in which they feature.
- T. Bouwens
- , T. M. A. Bakker
- & J. N. H. Reek
-
Article |
 Efficient room-temperature phosphorescence of covalent organic frameworks through covalent halogen doping
Efficient room-temperature phosphorescence of covalent organic frameworks through covalent halogen doping
Room-temperature phosphorescence in organic solids is attractive for practical applications but remains rare. Now, highly phosphorescent boroxine-linked covalent organic frameworks have been prepared by covalent doping with halogen atoms through the use of halogenated precursors. The resulting porous COFs exhibited oxygen-sensing capabilities with millisecond response time over a wide range of partial oxygen pressures.
- Ehsan Hamzehpoor
- , Cory Ruchlin
- & Dmytro F. Perepichka
-
Article |
 Bending a photonic wire into a ring
Bending a photonic wire into a ring
Meso–meso linked porphyrin arrays have been described as rod-like photonic wires. Now it has been shown that they can be bent into rings using template-directed synthesis. These rings of porphyrins mimic the light-harvesting arrays of chlorophyll molecules responsible for photosynthesis.
- Henrik Gotfredsen
- , Jie-Ren Deng
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
News & Views |
 Pop-up rings to rule reactivity
Pop-up rings to rule reactivity
An alcohol-functionalized cyclophane has been shown to form a bowl-shaped cavity large enough to host tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(ii). The macrocycle captures, and suppresses the activity of, the ruthenium complex in water but, when oxidized to its ketone-bearing counterpart, releases the ruthenium guest.
- David Van Craen
-
News & Views |
 Hopping protons in supramolecular catalysis
Hopping protons in supramolecular catalysis
Supramolecular catalysis can emulate many features of enzymatic transformations. Now, a complex proton wire mechanism — enabling the dual activation of a nucleophile and an electrophile through reciprocal proton transfer — has been shown to operate during the β-glycosylation of sugars within a self-assembled capsule.
- Cally J. E. Haynes
- & Larissa K. S. von Krbek
-
News & Views |
 Porous and permutable peptide frameworks
Porous and permutable peptide frameworks
The rational synthesis of advanced porous materials that mimic the behaviours of biological proteins remains challenging. Now, a distinct type of crystalline porous peptide framework has been prepared through bioinspired noncovalent assembly, enabling chemical tuning of the properties and functions of the pore environments.
- Jinqiao Dong
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article |
 Mimicry of the proton wire mechanism of enzymes inside a supramolecular capsule enables β-selective O-glycosylations
Mimicry of the proton wire mechanism of enzymes inside a supramolecular capsule enables β-selective O-glycosylations
Proton wires in enzyme active sites enable stereoselective reactions under mild conditions by facilitating dual activation of a nucleophile and an electrophile through reciprocal proton transfer. Now it has been shown that such an activation mode can be mimicked inside a supramolecular capsule, enabling a general approach to β-glycosides.
- Tian-Ren Li
- , Fabian Huck
- & Konrad Tiefenbacher
-
Review Article |
 Chemical fuels for molecular machinery
Chemical fuels for molecular machinery
Chemically fuelled synthetic molecular machines are capable of driving and sustaining non-equilibrium motion, analogous to the biomachinery that underpins life. This Review discusses the chemical and physical features of biological and synthetic chemical fuels and highlights potential challenges and opportunities for the development of synthetic chemically fuelled machinery.
- Stefan Borsley
- , David A. Leigh
- & Benjamin M. W. Roberts
-
Article |
 Mechanically axially chiral catenanes and noncanonical mechanically axially chiral rotaxanes
Mechanically axially chiral catenanes and noncanonical mechanically axially chiral rotaxanes
Despite mechanically axially chiral (MAC) catenanes being recognized in 1961, their stereoselective synthesis had not been disclosed until now. Closer inspection of the MAC stereogenic unit has also led to the identification of an analogous, but unremarked upon, form of rotaxane stereochemistry and the conceptualization of a general approach to prepare MAC molecules stereoselectively.
- John R. J. Maynard
- , Peter Gallagher
- & Stephen M. Goldup

 Constructing artificial gap junctions to mediate intercellular signal and mass transport
Constructing artificial gap junctions to mediate intercellular signal and mass transport