Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access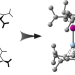 A lithium–aluminium heterobimetallic dimetallocene
A lithium–aluminium heterobimetallic dimetallocene
Dimetallocenes are a narrow class of compounds represented by the homobimetallic examples dizincocene and diberyllocene. Now a heterobimetallic dimetallocene featuring lithium and aluminium centres has been synthesized. The Al–Li bond is shown to cleave upon reaction with N-heterocyclic carbenes and heteroallenes.
- Inga-Alexandra Bischoff
- , Sergi Danés
- & André Schäfer
-
Article |
 A tetrahedral neptunium(V) complex
A tetrahedral neptunium(V) complex
The number of known high-oxidation-state transuranic compounds remains limited, and these typically feature high coordination numbers and/or multiply-bonded donor atoms. Now, a tetrahedral, pentavalent neptunium complex supported by four monoanionic ligands has been isolated and characterized. This complex is stable in the solid state and undergoes a proton-coupled electron transfer reaction in solution.
- Julie E. Niklas
- , Kaitlyn S. Otte
- & Henry S. La Pierre
-
News & Views |
 Lifting iron higher and higher
Lifting iron higher and higher
Biological and synthetic catalysts often utilize iron in high oxidation states (+IV and greater) to perform challenging molecular transformations. A coordination complex featuring an Fe(VII) ion has now been synthesized through sequential oxidations of nonheme iron–nitrido precursors.
- Adam T. Fiedler
- & Laxmi Devkota
-
Article
| Open Access Cage escape governs photoredox reaction rates and quantum yields
Cage escape governs photoredox reaction rates and quantum yields
The spontaneous recombination of photogenerated radicals surrounded by solvent molecules is an important energy-wasting elementary step in photoredox reactions. Now the decisive role that cage escape plays in these reactions is shown in three benchmark photocatalytic reactions, with quantitative correlations observed between photoredox product formation rates and cage escape quantum yields.
- Cui Wang
- , Han Li
- & Oliver S. Wenger
-
Article |
 Thorium(iv)–antimony complexes exhibiting single, double, and triple polar covalent metal–metal bonds
Thorium(iv)–antimony complexes exhibiting single, double, and triple polar covalent metal–metal bonds
Actinide–metal multiple bonds are relatively rare, with isolable examples under normal experimental conditions typically restricted to complexes containing a polar covalent σ bond supplemented by up to two dative π bonds. Now complexes featuring polar covalent double and triple bonds between thorium and antimony have been synthesized.
- Jingzhen Du
- , Kevin Dollberg
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article |
 Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Valence tautomerism in lanthanide-based materials is rare. Now a one-dimensional samarium–pyrazine polymer has been shown to exhibit a temperature-induced hysteretic Sm(III)-to-Sm(II) reversible switch. The transition temperature is modulated in a 150 K window by alloying with Yb(II), presenting a strategy for developing new materials with chemically tunable magnetic switchability.
- Maja A. Dunstan
- , Anna S. Manvell
- & Kasper S. Pedersen
-
Article |
 A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
A charge-neutral organic cage selectively binds strongly hydrated sulfate anions in water
Very few charge-neutral synthetic anion receptors can function in water, and those known typically select weakly hydrated anions such as iodide. Now a neutral molecular cage capable of donating 12 hydrogen bonds has been synthesized and found to bind highly hydrated sulfate in water with a strong selectivity over weakly hydrated anions.
- Liuyang Jing
- , Evelyne Deplazes
- & Xin Wu
-
Article |
 Oxidative two-state photoreactivity of a manganese(IV) complex using near-infrared light
Oxidative two-state photoreactivity of a manganese(IV) complex using near-infrared light
The design of highly oxidizing Earth-abundant transition metal complexes for photochemical applications is desirable, but progress in this area remains limited. Now a manganese(IV) diguanidylpyridine complex has been shown to photooxidize naphthalene, benzene and acetonitrile to their radical cations after excitation with near-infrared light. Experimental and theoretical studies indicate the presence of two distinct ligand-to-metal charge transfer excited states.
- Nathan R. East
- , Robert Naumann
- & Katja Heinze
-
Article |
 Trapping of a phenoxyl radical at a non-haem high-spin iron(II) centre
Trapping of a phenoxyl radical at a non-haem high-spin iron(II) centre
The activation of dioxygen at metal centres, and subsequent functionalization of unactivated C‒H bonds, requires the generation of high-energy radical intermediates that often result in undesirable side reactions. Now an elusive oxygen-derived reactive iron(II)–radical intermediate is spectroscopically characterized as part of a strategy to stabilize phenoxyl radical cofactors during substrate oxidation reactions.
- Dustin Kass
- , Virginia A. Larson
- & Kallol Ray
-
Article |
 Air- and photo-stable luminescent carbodicarbene-azaboraacenium ions
Air- and photo-stable luminescent carbodicarbene-azaboraacenium ions
Borenium ions have traditionally served as main group (pre-)catalysts, and their use in materials-related applications have been limited by their instability. Now, a series of fully π-conjugated azaboraacenium ions derived from carbodicarbene have been developed that exhibit high air and moisture stability with full colour-tunable luminescence. Furthermore, these azaboraacene cations mimic the electronic structures of higher-order carbonaceous acenes while featuring enhanced resistance to photo-oxidation.
- Chun-Lin Deng
- , Akachukwu D. Obi
- & Robert J. Gilliard Jr.
-
Article |
 Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Activation of H2 by a metal–olefin complex is characterized experimentally and computationally using a nickel pincer complex, showing that the reaction proceeds via a direct ligand-to-ligand hydrogen transfer mechanism. An application of this cooperative H2-activation mechanism is demonstrated in the nickel-catalysed semihydrogenation of diphenylacetylene.
- María L. G. Sansores-Paredes
- , Martin Lutz
- & Marc-Etienne Moret
-
Article |
 Structure and bonding of a radium coordination compound in the solid state
Structure and bonding of a radium coordination compound in the solid state
Radium complexes are of interest for use as cancer therapeutic agents, but the structure and bonding are poorly understood. Here, the synthesis of a Ra2+ complex is reported, and the structure and bonding characteristics are elucidated using single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
- Frankie D. White
- , Nikki A. Thiele
- & Samantha K. Cary
-
-
Article |
 Stabilizing Au2+ in a mixed-valence 3D halide perovskite
Stabilizing Au2+ in a mixed-valence 3D halide perovskite
The Au2+ oxidation state is rarely stable in molecules or extended solids, where extreme synthetic conditions or exotic ligands are often necessary. Now, Au2+ has been stabilized with simple Cl− ligands in Cs4AuIIAuIII2Cl12, an extended solid with a perovskite-derived structure that is readily synthesized under mild conditions and is stable to ambient conditions.
- Kurt P. Lindquist
- , Armin Eghdami
- & Hemamala I. Karunadasa
-
Article
| Open Access Photoredox-active Cr(0) luminophores featuring photophysical properties competitive with Ru(II) and Os(II) complexes
Photoredox-active Cr(0) luminophores featuring photophysical properties competitive with Ru(II) and Os(II) complexes
Although noble metal coordination complexes typically show promising photophysical properties that enable applications in lighting, photocatalysis and solar energy conversion, first-row transition metal complexes rarely display properties as attractive. Now, two Cr(0) complexes are shown to afford excited-state lifetimes of ~50 ns and photophysical properties analogous to noble metal complexes, enabling efficient photoredox catalysis.
- Narayan Sinha
- , Christina Wegeberg
- & Oliver S. Wenger
-
Article |
 Selective scandium ion capture through coordination templating in a covalent organic framework
Selective scandium ion capture through coordination templating in a covalent organic framework
Scandium is challenging and expensive to isolate in pure form using conventional solvent extraction. Now a covalent organic framework (COF) has been synthesized that can incorporate scandium coordination complexes; subsequent removal of the scandium ions generates open coordination sites, and the resulting ‘metal-imprinted’ COF can be used for highly selective, cyclable scandium capture.
- Ye Yuan
- , Yajie Yang
- & Guangshan Zhu
-
Article |
 Anions featuring an aluminium–silicon core with alumanyl silanide and aluminata-silene characteristics
Anions featuring an aluminium–silicon core with alumanyl silanide and aluminata-silene characteristics
Aluminium and silicon, two Earth-abundant, well-understood elements, typically form weak Al–Si bonds. Now, complexes featuring an anionic Al–Si core stabilized by bulky substituents and a Si–Na interaction have been isolated. This Al–Si interaction possesses partial double bond character, which can be increased by sequestration of the sodium counterion.
- Moritz Ludwig
- , Daniel Franz
- & Shigeyoshi Inoue
-
Article |
 Surface-exposed silver nanoclusters inside molecular metal oxide cavities
Surface-exposed silver nanoclusters inside molecular metal oxide cavities
Atomically precise metal nanoclusters can serve a variety of purposes, yet their high reactivity also makes them difficult to synthesize. Now, well-defined {Ag30} nanoclusters have been prepared within ring-shaped polyoxometalates. These nanoclusters show good stability in solution and the solid state, can undergo redox-induced structural transformation, and possess exposed surfaces that can serve as catalytically active sites.
- Kentaro Yonesato
- , Daiki Yanai
- & Kosuke Suzuki
-
News & Views |
 Something new under the sun
Something new under the sun
Charge-transfer emission of any type is extremely rare for coordination complexes of iron. Now, an Fe(iii) complex has been devised that shows two-colour luminescence arising from dual metal-to-ligand and ligand-to-metal charge-transfer emission.
- Robert J. Ortiz
- & David E. Herbert
-
Article
| Open Access Control of dynamic sp3-C stereochemistry
Control of dynamic sp3-C stereochemistry
Stereogenic sp3-hybridized carbon centres are the principal building blocks of chiral organic molecules. Usually, these centres are configurationally fixed. Now, low-energy pericyclic rearrangements have been used to create rigid cage molecules with fluxional sp3-stereochemistry, influencing chiral information transfer. The sp3-carbon stereochemistry of the cages is inverted through strain-assisted Cope rearrangements.
- Aisha N. Bismillah
- , Toby G. Johnson
- & Paul R. McGonigal
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
The nitrogen reduction reaction is an extremely valuable but energy-intensive process. Now, a coordination polymer based on a [Zn–N2–Zn] unit has been shown to promote the formation of ammonia under ambient conditions by a photocatalytic reaction. The N2 moieties within the framework are reduced, creating unsaturated [Zn2+···Zn+] intermediates that are able to capture external N2 and sustain the cycle.
- Yan Xiong
- , Bang Li
- & Zhong Jin
-
News & Views |
 Rare radioisotopes at the ready
Rare radioisotopes at the ready
The study of rare isotopes, including many in the f-block, is a key step to advancing our fundamental understanding of these elements, but their scarcity poses challenges. Now, minute amounts of such materials have been isolated and characterized through complexation with polyoxometalate clusters.
- Kristina O. Kvashnina
-
Article |
 Polyoxometalates as ligands to synthesize, isolate and characterize compounds of rare isotopes on the microgram scale
Polyoxometalates as ligands to synthesize, isolate and characterize compounds of rare isotopes on the microgram scale
The study of rare isotopes is hampered by their scarcity, cost and sometimes toxicity. Now polyoxometalate ligands have been shown to facilitate the capture of f-block elements and their characterization. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction structures have been obtained for several molecular complexes, including three of the rare curium-248, from minute amounts (micrograms) of material.
- Ian Colliard
- , Jonathan R. I. Lee
- & Gauthier J.-P. Deblonde
-
In Your Element |
 Shapeshifting xantphos
Shapeshifting xantphos
Lukas Veth and Paweł Dydio discuss the importance of ligands in transition metal catalysis, looking at the success story of xantphos and why it should earn the title of ‘privileged ligand’.
- Lukas Veth
- & Paweł Dydio
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Although neutral and anionic low-valent aluminium complexes are widespread, their cationic counterparts have remained rare. Now, a salt of [Al(AlCp*)3]+ featuring a formal low-valent Al+ cation has been isolated that dimerizes in concentrated solutions and the solid state, and also forms Al4 clusters on coordinating with Lewis bases.
- Philipp Dabringhaus
- , Julie Willrett
- & Ingo Krossing
-
Article |
 Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Despite much research, the high-spin-state relaxation mechanism of Fe(II) spin-crossover complexes is unresolved. Using ultrafast circular dichroism spectroscopy it has now been revealed that the spin relaxation is driven by a torsional twisting mode, which breaks the chiral symmetry of a prototypical Fe(II) compound. Stereocontrolling the configuration of the complex can thus be used to slow down the spin relaxation.
- Malte Oppermann
- , Francesco Zinna
- & Majed Chergui
-
Article |
 Tunable acetylene sorption by flexible catenated metal–organic frameworks
Tunable acetylene sorption by flexible catenated metal–organic frameworks
Flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) in which guest uptake and release occur above certain threshold pressures are attractive adsorbents. Now, the gated sorption behaviour of such a zinc-based mixed-ligand MOF has been tuned to match the narrow temperature and pressure range required for safe, efficient acetylene storage by adjusting the ratio of two different functional groups on its benzenedicarboxylate ligands.
- Mickaele Bonneau
- , Christophe Lavenn
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
News & Views |
 Molecular spins clock in
Molecular spins clock in
Electron spin relaxation, important in quantum information science, can be slowed down at clock transitions — which are insensitive to magnetic noise. It has now been shown that such transitions can be tuned, to high frequency, in rare-earth coordination complexes through control of s- and d-orbital mixing.
- Eric J. L. McInnes
-
Article |
 Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Although cobalt–carbene radicals have proved to be highly versatile intermediates for homogeneous catalysis, their spectroscopic detection and characterization have been limited. Now, by using hypervalent iodonium ylides, the formation and spectroscopic detection of a biscarbenoid N-enolate–carbene radical—which undergoes a complex catalytic pathway involving reversible N-enolate formation—has been demonstrated.
- Roel F. J. Epping
- , Mees M. Hoeksma
- & Bas de Bruin
-
Article |
 A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
The s-orbital mixing into the spin-bearing d orbital associated with a molecular Lu(II) complex is shown to both reduce spin–orbit coupling and increase electron–nuclear hyperfine interactions, which substantially improves electron spin coherence. Combined with the potential to tune interactions through coordination chemistry, it makes this system attractive for quantum information applications.
- Krishnendu Kundu
- , Jessica R. K. White
- & Stephen Hill
-
Article |
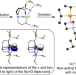 A terminal neptunium(V)–mono(oxo) complex
A terminal neptunium(V)–mono(oxo) complex
Neptunium was the first actinide to be artificially synthesized, yet its chemistry has remained relatively unexplored. Most neptunium chemistry involves the neptunyl di(oxo) motif, and transuranic compounds with only one metal–ligand multiple bond are generally rare. Now, a stable complex of neptunium in the +5 oxidation state has been isolated that features a single terminal Np–O multiple bond.
- Michał S. Dutkiewicz
- , Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
News & Views |
 Ammonia formation revisited
Ammonia formation revisited
Dinitrogen conversion to ammonia is of great biological and industrial relevance, but modelling this process on a molecular level is challenging. Now, a biomimetic model offers new insights into the functionalization of a nitrido ligand to form NH3 using either H2 or H+/e–.
- Marc D. Walter
-
Article |
 A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
Multi-iron nitrides are implicated as potential key intermediates in biological nitrogen fixation and the industrial Haber–Bosch process, but well-described functional model systems are rare. Now, a well-defined thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex has been found to show excellent reactivity toward hydrogenation with H2 through a stepwise pathway to form ammonia in high yield.
- Yixin Zhang
- , Jinfeng Zhao
- & Jingping Qu
-
Article |
 Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
The use of ammonia as an alternative fuel relies on its electrochemical conversion to dinitrogen in a fuel cell. Now a stable metal–metal bonded diruthenium complex is shown to spontaneously produce dinitrogen from ammonia under ambient conditions and is also able to electrocatalyse the oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen at low potentials.
- Michael J. Trenerry
- , Christian M. Wallen
- & John F. Berry
-
Article |
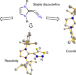 Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Diazoolefins tend to be highly reactive compounds, and thus experimental evidence of these species is currently limited. Now, the reactivity and coordination chemistry of N-heterocyclic diazoolefins has been described. Diazoolefins are observed to form in reactions of N-heterocyclic olefins with nitrous oxide. The products benefit from resonance stabilization, enabling isolation on a preparative scale and comprehensive characterization.
- Paul Varava
- , Zhaowen Dong
- & Kay Severin
-
News & Views |
 Made with manganese
Made with manganese
Transition metal complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) luminescence and photoactivity typically rely on precious metals such as ruthenium or iridium. Now, two complexes of the Earth-abundant 3d manganese have displayed room-temperature MLCT luminescence in solution and a unique excited-state reactivity.
- Katja Heinze
-
News & Views |
 A ravel alliance
A ravel alliance
A new class of interwoven metal–organic containers, including one with a cubic architecture, twelve crossing points and a large internal volume, has now been reported. Interconversion between different self-assembled structures can be triggered by simply exchanging the associated anions.
- Andrew W. Heard
- , Natasha M. A. Speakman
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article |
 Manganese(i) complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer luminescence and photoreactivity
Manganese(i) complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer luminescence and photoreactivity
Manganese(i) is isoelectronic to iron(ii) but has typically been overlooked as a cheap Earth-abundant metal for the development of 3d6 metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) emitters and photosensitizers. Now, using chelating isocyanide ligands, air-stable manganese(i) complexes have been obtained that exhibit MLCT luminescence, as well as energy- and electron-transfer photoreactivity.
- Patrick Herr
- , Christoph Kerzig
- & Oliver S. Wenger
-
Article |
 Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
The formation of weak chemical bonds at or near thermodynamic potential is a challenge in chemical synthesis and catalysis. A bifunctional iridium hydride catalyst has now been discovered that absorbs visible light and promotes proton-coupled electron transfer to a range of substrates—creating element–hydrogen bonds—using dihydrogen as the terminal reductant.
- Yoonsu Park
- , Sangmin Kim
- & Paul J. Chirik
-
Article |
 Isolation of a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo intermediate in the water oxidation reaction
Isolation of a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo intermediate in the water oxidation reaction
Obtaining mechanistic data after the rate-determining step of a chemical reaction is difficult but essential for its understanding. Now, a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo complex has been isolated following the rate-determining step of the water oxidation reaction (O–O bond formation) carried out using a Ru-based molecular catalyst.
- Carla Casadevall
- , Vlad Martin-Diaconescu
- & Julio Lloret-Fillol
-
Article |
 Magnetic ordering through itinerant ferromagnetism in a metal–organic framework
Magnetic ordering through itinerant ferromagnetism in a metal–organic framework
The development of metal–organic magnets that combine tunable magnetic properties with other desirable physical properties remains challenging despite numerous potential applications. Now, a mixed-valent chromium–triazolate material has been prepared that exhibits itinerant ferromagnetism with a magnetic ordering temperature of 225 K, a high conductivity and large negative magnetoresistance (23%).
- Jesse G. Park
- , Brianna A. Collins
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
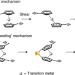 Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Metallocenes are attractive mechanophores because they are stable in the absence of force, yet reactive under tension. Now, covalently bridging the two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) ligands of ferrocenes embedded in a polymer has been shown to alter their mechanochemical reactivity, leading to a faster dissociation of the Fe–Cp bond, which occurs through a peeling mechanism rather than a shearing one.
- Yudi Zhang
- , Zi Wang
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article |
 Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Unlike ferrocene and its cationic counterpart ferrocenium, the ferrocene monoanion is an unusual species that has been observed through low-temperature electrochemical studies. Now, a family of isostructural 3d metallocenates has been isolated that consists of a manganocene, a cobaltocene and a high-spin ferrocene anion stabilized by cyclopentadienyl ligands bearing bulky aliphatic groups.
- Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- , Marcus J. Giansiracusa
- & David P. Mills
-
Article |
 Charge transfer driven by ultrafast spin transition in a CoFe Prussian blue analogue
Charge transfer driven by ultrafast spin transition in a CoFe Prussian blue analogue
Cyanide-bridged CoFe coordination networks exhibit photomagnetism because of coupled charge-transfer and spin transition. Now, femtosecond X-ray and optical absorption spectroscopies have enabled the electronic and structural dynamics of this light-induced process to be disentangled and show that it is the spin transition on the cobalt atom, occurring within ~50 fs, that induces the Fe-to-Co charge-transfer within ~200 fs.
- Marco Cammarata
- , Serhane Zerdane
- & Eric Collet
-
News & Views |
 Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
As a consequence of their high instability, main-group carbonyl complexes are rare — only a few have been detected, typically in low-temperature matrices. Now, two silicon–carbonyl complexes have been isolated using innovative substituent patterns at the Si centre; their reactivity resembles that of their transition-metal counterparts.
- Debdeep Mandal
- & Diego M. Andrada
-
Article |
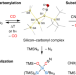 Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silyl-substituted silicon–carbonyl complexes that are stable at room temperature have been prepared by exposure of highly reactive bis(silyl)silylenes to carbon monoxide. The compounds show structural features and reactivity that are reminiscent of their ubiquitous transition-metal–carbonyl counterparts, including π-backbonding and ligand liberation as well as substitution and functionalization reactions.
- Dominik Reiter
- , Richard Holzner
- & Shigeyoshi Inoue
-
Article |
 Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Efficient and stable water oxidation catalysts are important if photoelectrochemical cells are to be used to provide clean and sustainable solar fuels. A water oxidation catalyst that operates at neutral pH has now been developed that features ruthenium coordination oligomers anchored onto the surfaces of graphitic materials through CH–π interactions.
- Md Asmaul Hoque
- , Marcos Gil-Sepulcre
- & Antoni Llobet
-
Article |
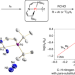 A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
Transient metallonitrenes (M–N) have been proposed as key intermediates in nitrogen atom transfer reactions, but well-defined examples have remained elusive. Now, a platinum complex with an atomic nitrogen ligand, best described as a subvalent nitrogen diradical singly bonded to a platinum(ii) ion (Pt–N), has been isolated and shows ambiphilic reactivity.
- Jian Sun
- , Josh Abbenseth
- & Sven Schneider
-
Article |
 Complexes featuring a linear [N≡U≡N] core isoelectronic to the uranyl cation
Complexes featuring a linear [N≡U≡N] core isoelectronic to the uranyl cation
Three crystalline complexes comprising a linear [UN2] moiety that is isoelectronic to the ubiquitous uranyl cation [UO2]2+ have been prepared by reaction of UCl5 or UBr5 with liquid ammonia. Quantum chemical calculations showed that the bonding in the [UN2] moieties is best described with two U≡N triple bonds.
- Stefan S. Rudel
- , H. Lars Deubner
- & Florian Kraus

 Enabling nucleophilic reactivity in molecular calcium fluoride complexes
Enabling nucleophilic reactivity in molecular calcium fluoride complexes A 21-electron cobalt sandwich
A 21-electron cobalt sandwich