Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
Evolution: Sex and immunity
-
News & Views |
 Each synapse to its own
Each synapse to its own
A neuron can receive thousands of inputs that, together, tell it when to fire. New techniques can image the activity of many inputs, and shed light on how single neurons perform computations in response.
- Nicholas J. Priebe
- & David Ferster
-
Letter |
 Impaired hippocampal–prefrontal synchrony in a genetic mouse model of schizophrenia
Impaired hippocampal–prefrontal synchrony in a genetic mouse model of schizophrenia
A deletion on human chromosome 22 (22q11.2) is one of the largest genetic risk factors for schizophrenia. Mice with a corresponding deletion have problems with working memory, one feature of schizophrenia. It is now found that these mice also show disruptions in synchronous firing between neurons of the prefrontal cortex and of the hippocampus, an electrophysiological phenomenon that has been linked to learning and memory and which is also thought to be disrupted in schizophrenia patients.
- Torfi Sigurdsson
- , Kimberly L. Stark
- & Joshua A. Gordon
-
Article |
 Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
Many sensory neurons in the mammalian cortex are tuned to specific stimulus features — for example, some fire only when horizontal bars move from top to bottom in the visual field. But it has been unclear whether such tuning is encoded in a neuron's inputs, or whether the neuron itself computes its response. Here, a new technique for visualizing and mapping sensory inputs to the dendrites of neurons in the mouse visual cortex has shown that each neuron makes its own 'decision' as to the orientation preference of its output.
- Hongbo Jia
- , Nathalie L. Rochefort
- & Arthur Konnerth
-
Letter |
 Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling
Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling
Although several synaptic adhesion proteins have been identified as genetic risk factors in schizophrenia, it is unclear as to what role they play in disease progression. Here, it is shown that two such proteins — neuregulin 1 and its receptor ErbB4 — function to regulate the connectivity of specific cortical circuits. The study not only implicates these proteins in the wiring of inhibitory synapses, about which little is known, but also provides a new perspective on their involvement in schizophrenia.
- Pietro Fazzari
- , Ana V. Paternain
- & Beatriz Rico
-
Letter
| Open Access The genome of a songbird
The genome of a songbird
The genome of the zebra finch — a songbird and a model for studying the vertebrate brain, behaviour and evolution — has been sequenced. Comparison with the chicken genome, the only other bird genome available, shows that genes that have neural function and are implicated in the cognitive processing of song have been evolving rapidly in the finch lineage. Moreover, vocal communication engages much of the transcriptome of the zebra finch brain.
- Wesley C. Warren
- , David F. Clayton
- & Richard K. Wilson
-
Research Highlights |
Neuropsychology: Morality of murder
-
Research Highlights |
 Addiction: Junk-food junkies
Addiction: Junk-food junkies
-
Research Highlights |
Neurodevelopment: Baby talk
-
Letter |
 Caspase activation precedes and leads to tangles
Caspase activation precedes and leads to tangles
Fibrillar deposits of tau protein (neurofibrillary tangles) are thought to cause neuronal death in patients with Alzheimer's disease, and tau-related frontotemporal dementia. Here, however, the opposite has been found: the activation of executioner caspase enzymes occurs first, preceding tangle formation by hours to days. Tangle-bearing neurons seem to be long-lived, indicating that tangles might be 'off pathway' to acute neuronal death.
- Alix de Calignon
- , Leora M. Fox
- & Bradley T. Hyman
-
Article |
 Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
In the mammalian brain, the subventricular zone (SVZ) produces neural progenitor cells that migrate into the cortex to populate the upper layers. In humans this region is massively expanded, producing an outer SVZ (OSVZ). Here, live-cell imaging of developing human tissue was used to show that the OSVZ has similar characteristics to the SVZ, with progenitor cells proliferating in a way that depends on the Notch protein. The findings have implications for our understanding of how the complex human brain evolved.
- David V. Hansen
- , Jan H. Lui
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Live-action brain cells
-
Opinion |
 How do morals change?
How do morals change?
Emotions such as empathy and disgust might be at the root of morality, but psychologists should also study the roles of deliberation and debate in how our opinions shift over time, argues Paul Bloom.
- Paul Bloom
-
Letter |
 Human memory strength is predicted by theta-frequency phase-locking of single neurons
Human memory strength is predicted by theta-frequency phase-locking of single neurons
Although explored in the rodent, the relationship between single neuron activity, oscillations and behavioural learning is unknown in humans. Here, successful memory formation in humans was predicted by the coordination of spike timing relative to the local theta oscillation. These data provide a direct connection between the behavioural modulation of oscillations and plasticity within specific circuits.
- Ueli Rutishauser
- , Ian B. Ross
- & Erin M. Schuman
-
Review Article |
 Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline
Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline
- Nicholas A. Bishop
- , Tao Lu
- & Bruce A. Yankner
-
Letter |
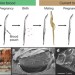 Post-copulatory sexual selection and sexual conflict in the evolution of male pregnancy
Post-copulatory sexual selection and sexual conflict in the evolution of male pregnancy
Male pregnancy is restricted to seahorses, pipefishes and their relatives, in which young are nurtured in the male's brood pouch. It is now clear that the brood pouch has a further function. Studies of Gulf pipefish show that males can selectively abort embryos from females perceived as less attractive, saving resources for more hopeful prospects later. This is the only known example of post-copulatory sexual conflict in a sex-reversed species.
- Kimberly A. Paczolt
- & Adam G. Jones
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Rats on the wagon
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Memory reading
-
Books & Arts |
 Q&A: Hervé This on flavour and perception
Q&A: Hervé This on flavour and perception
French chemist Hervé This is a pioneer of the field of molecular gastronomy, the science of cooking. From perfecting the boiled egg to making custards with meat proteins, he has advised top chefs worldwide. He tells Nature why he is moving on to 'note-by-note' cuisine using compounds to build taste and smells, and why turkey is best cooked in the dishwasher.
- Michael White
-
News Feature |
 Science in court: Head case
Science in court: Head case
Last year, functional magnetic resonance imaging made its debut in court. Virginia Hughes asks whether the technique is ready to weigh in on the fate of murderers.
- Virginia Hughes
-
Letter |
 Analysis of Drosophila TRPA1 reveals an ancient origin for human chemical nociception
Analysis of Drosophila TRPA1 reveals an ancient origin for human chemical nociception
Reactive electrophiles are noxious chemicals, such as acrolein in cigarette smoke, and are detected by the ion channel TRPA1 in humans. Here it is shown that TRPA1 channels sense these chemicals in the gustatory chemosensory neurons of fruitflies and mosquitoes, too. Further findings show that, unlike with other chemical senses such as smell or taste, the detection of reactive electrophiles relies on an ancient sensor that has been conserved in molecular detail through some 500 million years of evolution.
- Kyeongjin Kang
- , Stefan R. Pulver
- & Paul A. Garrity
-
Article |
 Molecular basis of infrared detection by snakes
Molecular basis of infrared detection by snakes
Snakes are notoriously apt at generating 'thermal images' of predators or prey. The underlying physiology has been unclear, although in snakes such as pythons, vipers and boas, infrared signals are initially received by the pit organ. Here it is shown that pit-bearing snakes rely on heat detection by the ion channel TRPA1. This extends the sensory repertoire of the TRPA1 family of proteins, which detect chemical irritants in mammals and thermal variations in insects.
- Elena O. Gracheva
- , Nicholas T. Ingolia
- & David Julius
-
Article |
 Somatic sex identity is cell autonomous in the chicken
Somatic sex identity is cell autonomous in the chicken
In mammals, embryos are considered to be sexually indifferent until the action of a sex-determining gene initiates gonadal differentiation. Here it is demonstrated that this situation is different for birds. Using rare, naturally occurring chimaeric chickens where one side of the animal appears male and the other female, it is shown that avian somatic cells possess an inherent sex identity and that, in birds, sexual differentiation is cell autonomous.
- D. Zhao
- , D. McBride
- & M. Clinton
-
Research Highlights |
 Neuroscience: Nerve cell talk
Neuroscience: Nerve cell talk
-
News |
 Chicken's split sex identity revealed
Chicken's split sex identity revealed
Half-male, half-female fowl explain sex determination.
- Janet Fang
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Use it or lose it
-
News |
 Why the body isn't thirsty at night
Why the body isn't thirsty at night
Body clock is a hormonal dimmer switch that controls water loss.
- Andrew Bennett Hellman
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Baby blues
-
Letter |
 An intrinsic vasopressin system in the olfactory bulb is involved in social recognition
An intrinsic vasopressin system in the olfactory bulb is involved in social recognition
Peptide hormones such as oxytocin and vasopressin influence social behaviour in several mammalian species. Here it is shown that a population of interneurons in the rat olfactory bulb releases vasopressin, and that vasopressin signalling is required in the olfactory system for proper social recognition in rats. Although vasopressin may not work in exactly the same way in humans, social recognition mediated by experience-dependent vasopressin release may be common.
- Vicky A. Tobin
- , Hirofumi Hashimoto
- & Mike Ludwig
-
Letter |
 Rapid spine stabilization and synaptic enhancement at the onset of behavioural learning
Rapid spine stabilization and synaptic enhancement at the onset of behavioural learning
The brain's capacity to respond to instructive capacity underlies behavioural learning, but how instructive experience acts on the juvenile brain, a period in which learning is often enhanced, remains unknown. Here, two-photon in vivo imaging is used to study the brains of zebra finches as they learn to sing. The results indicate that behavioural learning results when instructive experience is able to rapidly stabilize and strengthen synapses on the sensorimotor neurons that control the learned behaviour.
- Todd F. Roberts
- , Katherine A. Tschida
- & Richard Mooney
-
Research Highlights |
Neurobiology: The science of silence
-
Article |
 Neural bases for addictive properties of benzodiazepines
Neural bases for addictive properties of benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines, such as valium, are used both in clinics and for recreational purposes, but lead to addiction in some individuals. Addictive drugs increase the levels of dopamine and trigger synaptic adaptations in the mesolimbic reward system, but the neural basis for the addictive nature of benzodiazepines remains elusive. Here, they are shown to increase firing of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area through GABAA receptor activation in nearby interneurons.
- Kelly R. Tan
- , Matthew Brown
- & Christian Lüscher
-
News & Views |
 Lack of inhibition leads to abuse
Lack of inhibition leads to abuse
Chronic drug use can lead to addiction, which is initiated by specific brain circuits. The mystery of how one class of drugs, the benzodiazepines, affects activity in this circuitry has finally been solved.
- Arthur C. Riegel
- & Peter W. Kalivas
-
Muse |
 Morals don't come from God
Morals don't come from God
The finding that religion scarcely influences moral intuition undermines the idea that a godless society will be immoral, says Philip Ball. Whether it 'explains' religion is another matter.
- Philip Ball
-
Authors |
 Abstractions
Abstractions
-
Books & Arts |
 In Retrospect: Funes the Memorious
In Retrospect: Funes the Memorious
When Rodrigo Quian Quiroga visited Jorge Luis Borges's private library, he found annotated books that bear witness to the writer's fascination for memory and neuroscience.
- Rodrigo Quian Quiroga
-
News |
 Brain scan allows unconscious patient to communicate
Brain scan allows unconscious patient to communicate
Imaging technique pierces vegetative state.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article |
 Odorant reception in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae
Odorant reception in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae
Insect vectors of diseases locate their animal hosts through olfaction via largely unknown molecular processes. Here the 'empty neuron' system of genetically engineered Drosophila is used to assign specific odorants to the entire repertoire of olfactory receptors of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. The results illuminate ecological and neurobiological differences between mosquitoes and fruitflies and provide new potential molecular targets to boost the struggle against insect–borne diseases.
- Allison F. Carey
- , Guirong Wang
- & John R. Carlson
-
Research Highlights |
Neurobiology: Prions at work
-
Research Highlights |
Regenerative biology: New nerve cells connect
-
Letter |
 The cells and peripheral representation of sodium taste in mice
The cells and peripheral representation of sodium taste in mice
Mammals are repelled by large concentrations of salts but attracted to low concentrations of sodium. In mice, the latter behaviour can be blocked by the ion channel inhibitor amiloride. Here, mice have been produced lacking the drug's target sodium channel, ENaC, specifically in taste receptor neurons. It is confirmed that sodium sensing, like the four other taste modalities (sweet, sour, bitter and umami), is mediated by a dedicated 'labelled line'.
- Jayaram Chandrashekar
- , Christina Kuhn
- & Charles S. Zuker
-
Article |
 Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors
Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors
Mouse and human fibroblasts can be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state with a combination of four transcription factors. Here, mature differentiated cells are directed, via a combination of a few transcription factors (distinct from those described for generating iPS cells), to form functional neurons in vitro, without having to revert the fibroblasts to an embryonic state.
- Thomas Vierbuchen
- , Austin Ostermeier
- & Marius Wernig
-
News |
 Men prefer less powerful women
Men prefer less powerful women
The positioning of people's photos affects how attractive and powerful they seem to be.
- Matt Kaplan
-
Letter |
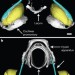 A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
Echolocation is usually associated with bats. Many echolocating bats produce signals in the larynx, but a few species produce tongue clicks. Here, studies show that in all bats that use larynx-generated clicks, the stylohyal bone is connected to the tympanic bone. Study of the stylohyal and tympanic bones of a primitive fossil bat indicates that this species may have been able to echolocate, despite previous evidence to the contrary, raising the question of when and how echolocation evolved in bats.
- Nina Veselka
- , David D. McErlain
- & M. Brock Fenton
-
-
Research Highlights |
Neuropharmacology: Beating depression
-
Opinion |
 Fixing the communications failure
Fixing the communications failure
People's grasp of scientific debates can improve if communicators build on the fact that cultural values influence what and whom we believe, says Dan Kahan.
- Dan Kahan
-
Letter |
 Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network
Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network
Rodents have an orientation map of their surroundings, produced and updated by a network of neurons in the entorhinal cortex known as 'grid cells'. However, it is currently unknown whether humans encode their location in a similar manner. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging in humans, a macroscopic signal representing a subject's position in a virtual reality environment is now detected that meets the criteria for defining grid-cell encoding.
- Christian F. Doeller
- , Caswell Barry
- & Neil Burgess
-
News |
 Robotic roach creates order from chaos
Robotic roach creates order from chaos
Chaos theory eases the path of autonomous robots.
- Zeeya Merali
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Auditory system
- Blood–brain barrier
- Cell death in the nervous system
- Cellular neuroscience
- Circadian rhythms and sleep
- Cognitive ageing
- Cognitive neuroscience
- Computational neuroscience
- Development of the nervous system
- Diseases of the nervous system
- Emotion
- Epigenetics in the nervous system
- Feeding behaviour
- Genetics of the nervous system
- Glial biology
- Gliogenesis
- Gustatory system
- Ion channels in the nervous system
- Learning and memory
- Molecular neuroscience
- Motivation
- Motor control
- Myelin biology and repair
- Neural ageing
- Neural circuits
- Neuro–vascular interactions
- Neurogenesis
- Neuroimmunology
- Neuronal physiology
- Neurotrophic factors
- Oculomotor system
- Olfactory system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Regeneration and repair in the nervous system
- Reward
- Sensorimotor processing
- Sensory processing
- Sexual behaviour
- Social behaviour
- Social neuroscience
- Somatosensory system
- Spine regulation and structure
- Stem cells in the nervous system
- Stress and resilience
- Synaptic plasticity
- Synaptic transmission
- Transporters in the nervous system
- Visual system

 The molecular basis for water taste in Drosophila
The molecular basis for water taste in Drosophila