In Your Element |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Binding methane to a metal centre
Binding methane to a metal centre
Catalytic transformations of methane frequently involve the formation of a metal–methane complex, but these compounds are challenging to observe. Now, a relatively long-lived osmium–methane complex has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy and forms from the direct binding of methane to a photolytically generated, coordinatively unsaturated cationic osmium–carbonyl complex dissolved in an inert hydrofluorocarbon solvent at –90 °C.
- James. D. Watson
- , Leslie. D. Field
- & Graham. E. Ball
-
Article |
 Stabilization of hexazine rings in potassium polynitride at high pressure
Stabilization of hexazine rings in potassium polynitride at high pressure
The planar hexazine dianion ring (N62–), which had previously been predicted to exist, has now been synthesized from potassium azide (KN3) under laser heating in a diamond anvil cell above 45 GPa; it remains metastable down to 20 GPa. By contrast, at 30 GPa an unusual N2-containing compound with the formula K3(N2)4 was produced.
- Yu Wang
- , Maxim Bykov
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article |
 Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion pairing is ubiquitous in low-dielectric-constant solvents, but whether it influences the reactivity of common cationic photoredox catalysts has been unclear. However, it has now been shown that ion pairing is responsible for a 4-fold modulation in reactivity in a prototypical Ir(III) complex and is explained by excited-state ion-pair reorganization.
- J. D. Earley
- , A. Zieleniewska
- & G. Rumbles
-
Article |
 Direct conversion of white phosphorus to versatile phosphorus transfer reagents via oxidative onioation
Direct conversion of white phosphorus to versatile phosphorus transfer reagents via oxidative onioation
White phosphorus (P4) is selectively transformed by oxidative onioation into salts of P1-transfer reagents that feature reactive P–N bonds. These P1 compounds can be used in P–N, P–O and P–C bond-forming reactions to form value-added phosphorus chemicals, representing a viable alternative to the most relevant, yet problematic, P(III) precursor, namely PCl3.
- Maximilian Donath
- , Kai Schwedtmann
- & Jan J. Weigand
-
Article |
 Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Although cobalt–carbene radicals have proved to be highly versatile intermediates for homogeneous catalysis, their spectroscopic detection and characterization have been limited. Now, by using hypervalent iodonium ylides, the formation and spectroscopic detection of a biscarbenoid N-enolate–carbene radical—which undergoes a complex catalytic pathway involving reversible N-enolate formation—has been demonstrated.
- Roel F. J. Epping
- , Mees M. Hoeksma
- & Bas de Bruin
-
Article |
 A terminal neptunium(V)–mono(oxo) complex
A terminal neptunium(V)–mono(oxo) complex
Neptunium was the first actinide to be artificially synthesized, yet its chemistry has remained relatively unexplored. Most neptunium chemistry involves the neptunyl di(oxo) motif, and transuranic compounds with only one metal–ligand multiple bond are generally rare. Now, a stable complex of neptunium in the +5 oxidation state has been isolated that features a single terminal Np–O multiple bond.
- Michał S. Dutkiewicz
- , Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article |
 A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
Decoupling the processes of light harvesting and catalytic hydrogen evolution could be a potentially important step in storing solar energy. This has now been achieved with a single molecular unit: a light-harvesting ruthenium complex–polyoxometalate dyad that absorbs light, separates and stores charge and then generates hydrogen on demand following the addition of a proton donor.
- Sebastian Amthor
- , Sebastian Knoll
- & Carsten Streb
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilization of intermediate spin states in mixed-valent diiron dichalcogenide complexes
Stabilization of intermediate spin states in mixed-valent diiron dichalcogenide complexes
Despite extensive investigations of mixed-valence complexes, molecules with intermediate spin states have remained elusive. Now, selenium- and tellurium-bridged mixed-valent iron dimers have been prepared in which a balance of Heisenberg exchange and double-exchange coupling of the unpaired electron, combined with moderate vibronic contributions, stabilizes S = 3/2 ground spin states.
- Justin T. Henthorn
- , George E. Cutsail III
- & Serena DeBeer
-
News & Views |
 Ammonia formation revisited
Ammonia formation revisited
Dinitrogen conversion to ammonia is of great biological and industrial relevance, but modelling this process on a molecular level is challenging. Now, a biomimetic model offers new insights into the functionalization of a nitrido ligand to form NH3 using either H2 or H+/e–.
- Marc D. Walter
-
News & Views |
 The birth of bilayer borophene
The birth of bilayer borophene
Bilayer borophene, predicted to be stabilized by interlayer linkages, has now been grown by molecular beam epitaxy on copper and silver surfaces in two independent studies. The growth substrate and temperature are found to influence the lattice structures formed.
- Maryam Ebrahimi
-
Article |
 A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
Multi-iron nitrides are implicated as potential key intermediates in biological nitrogen fixation and the industrial Haber–Bosch process, but well-described functional model systems are rare. Now, a well-defined thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex has been found to show excellent reactivity toward hydrogenation with H2 through a stepwise pathway to form ammonia in high yield.
- Yixin Zhang
- , Jinfeng Zhao
- & Jingping Qu
-
Article |
 Synthesis of bilayer borophene
Synthesis of bilayer borophene
Several polymorphs of borophene have been synthesized on metal substrates, but typically as monolayers. Now large-size, single-crystalline bilayer borophene has been grown on Cu(111)—a sufficient electron provider to enable the bonding of the second boron layer. The resulting bilayer possesses a metallic character and is less susceptible to oxidation than its monolayer counterpart.
- Caiyun Chen
- , Haifeng Lv
- & Lan Chen
-
-
Article |
 Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Diazoolefins tend to be highly reactive compounds, and thus experimental evidence of these species is currently limited. Now, the reactivity and coordination chemistry of N-heterocyclic diazoolefins has been described. Diazoolefins are observed to form in reactions of N-heterocyclic olefins with nitrous oxide. The products benefit from resonance stabilization, enabling isolation on a preparative scale and comprehensive characterization.
- Paul Varava
- , Zhaowen Dong
- & Kay Severin
-
Article |
 SuFExable polymers with helical structures derived from thionyl tetrafluoride
SuFExable polymers with helical structures derived from thionyl tetrafluoride
Sulfur(vi) fluoride exchange (SuFEx)—a type of click chemistry that generates SVI-centred covalent linkages—has previously been used for polymer synthesis. Now, modular SuFEx polymerization using SOF4 has been used to generate helical polymers. Unlike previous examples of SuFEx polymerization, the backbone retains SVI–F motifs and therefore is able to undergo further SuFEx click reactions, enabling facile and efficient post-polymerization modification.
- Suhua Li
- , Gencheng Li
- & K. Barry Sharpless
-
News & Views |
 Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Carbon–carbon single bonds are generally among the least reactive chemical bonds. While olefin metathesis reactions are well established, direct metathesis of C–C single bonds is rare. Now, a C–C single bond metathesis reaction has been developed, forming cross-biaryl products from unstrained homo-biaryl compounds.
- Michael M. Gilbert
- & Daniel J. Weix
-
Article |
 Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Metathesis reactions involving carbon–carbon double bonds have been well established, but direct metathesis of carbon–carbon single bonds is extremely rare. Now, a ruthenium-catalysed carbon–carbon single-bond metathesis reaction has been developed with unstrained homo-biaryl substrates. The reaction shows wide functional group tolerance and operates via an ‘olefin-metathesis-like’ mechanism.
- Jun Zhu
- , Rui Zhang
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 Isolation of a triplet benzene dianion
Isolation of a triplet benzene dianion
Molecules with 4n π electrons should display Baird aromaticity in the triplet state, but isolation of ring systems with this electronic ground state is stymied by structural distortion. Now, a benzene diradical dianion has been stabilized by being held rigid in a binucleating ligand as well as through magnetic exchange; single-crystal X-ray diffraction data and NICS calculations support its ground-state Baird aromaticity.
- Colin A. Gould
- , Jonathan Marbey
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
The molybdenum cofactor (Moco) is found in the active site of numerous enzymes, but the mechanism of molybdate insertion is not clear. Now, the mechanism of the final maturation step, in which adenylated molybdopterin and molybdate are the substrates, has been revealed. X-ray crystallography of an Mo-insertase identified adenylated Moco as an unexpected intermediate in this reaction sequence.
- Corinna Probst
- , Jing Yang
- & Tobias Kruse
-
Article |
 Cyclic polyacetylene
Cyclic polyacetylene
Lustrous flexible thin films of semiconducting cyclic polyacetylene (c-PA) have been synthesized and characterized. Rapid and efficient tungsten-catalysed acetylene polymerization conditions produce temporarily soluble c-PA, enabling the in situ derivatization of this typically insoluble polymer. Compelling evidence for the cyclic topology—and its influence on the physical properties of the polymer—are presented.
- Zhihui Miao
- , Stella A. Gonsales
- & Adam S. Veige
-
Article |
 Dinitrogen binding and activation at a molybdenum–iron–sulfur cluster
Dinitrogen binding and activation at a molybdenum–iron–sulfur cluster
Although iron–sulfur cofactors are known to carry out biological nitrogen fixation, how these clusters bind dinitrogen remains poorly understood. Now, a dinitrogen complex of a synthetic iron–sulfur cluster has been characterized, and electronic cooperation in the cluster has been shown to result in strong N–N bond activation.
- Alex McSkimming
- & Daniel L. M. Suess
-
Article |
 Adaptive response of a metal–organic framework through reversible disorder–disorder transitions
Adaptive response of a metal–organic framework through reversible disorder–disorder transitions
Some flexible metal–organic frameworks are known to exhibit an adaptive behaviour as they convert between two stable forms in response to their environment. Now, a metal–organic framework based on nonlinear linkers has been shown to adopt a much more complex family of degenerate disordered configurations, which can be reversibly interconverted through guest exchange.
- S. Ehrling
- , E. M. Reynolds
- & S. Kaskel
-
Article |
 Switching the magnetic hysteresis of an [Feii–NC–Wv]-based coordination polymer by photoinduced reversible spin crossover
Switching the magnetic hysteresis of an [Feii–NC–Wv]-based coordination polymer by photoinduced reversible spin crossover
Photoinduced spin crossover offers a convenient handle on the spin states and magnetic interactions within a material, which is promising for the development of photoresponsive nanomagnets. Now, a Wv–CN–Feii-based coordination polymer has been prepared that behaves either as a single-chain magnet or as single-molecule magnets under different light irradiations. Its magnetic hysteresis can also be switched on and off.
- Liang Zhao
- , Yin-Shan Meng
- & Tao Liu
-
Article |
 Melting of hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites
Melting of hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites
A series of dicyanamide-based hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite structures has been shown to melt at temperatures below 300 °C. On melt-quenching, they form glasses that possess coordination bonding and show very low thermal conductivities and moderate electrical conductivities as well as polymer-like thermomechanical properties.
- Bikash Kumar Shaw
- , Ashlea R. Hughes
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
News & Views |
 The blue hue of einsteinium
The blue hue of einsteinium
A complex containing the unstable isotope 254Es has been synthesized on a nanogram scale. Analysis of the fundamental bonding and spectroscopic characteristics of this einsteinium compound shows a blue shift of Es(iii) luminescence upon complexation, and the ligand serves as an antenna to sensitize the excited state.
- Louise S. Natrajan
- & Stephen Faulkner
-
Article |
 Isolation and reactivity of an elusive diazoalkene
Isolation and reactivity of an elusive diazoalkene
Although diazoalkenes have been reported as reactive intermediates in organic chemistry, their detection and isolation remains challenging. Such species have previously only been detected at low temperatures in matrix-isolation studies. Now, a room-temperature stable diazoalkene has been reported, which shows dual-site nucleophilicity and can undergo N2 exchange or lose dinitrogen under irradiation.
- P. W. Antoni
- , C. Golz
- & M. M. Hansmann
-
Article |
 Magnetic ordering through itinerant ferromagnetism in a metal–organic framework
Magnetic ordering through itinerant ferromagnetism in a metal–organic framework
The development of metal–organic magnets that combine tunable magnetic properties with other desirable physical properties remains challenging despite numerous potential applications. Now, a mixed-valent chromium–triazolate material has been prepared that exhibits itinerant ferromagnetism with a magnetic ordering temperature of 225 K, a high conductivity and large negative magnetoresistance (23%).
- Jesse G. Park
- , Brianna A. Collins
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Synthesis of monophosphines directly from white phosphorus
Synthesis of monophosphines directly from white phosphorus
State-of-the-art industrial methods for transforming P4 into useful phosphorus compounds currently rely on indirect, multi-step strategies. It has now been shown that straightforward one-pot reactions can convert P4 directly into industrially relevant products while requiring only mild conditions and simple, inexpensive reagents—and can also functionalize P4 catalytically.
- Daniel J. Scott
- , Jose Cammarata
- & Robert Wolf
-
Article |
 Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Molecular catalysts can be made more practical by anchoring them onto electrode surfaces, but such systems are less stable than standard heterogeneous electrocatalysts. Now, supramolecular hosts bound to electrode surfaces have enabled the immobilization of molecular electrocatalysts through host–guest interactions. Desorbed or degraded guest molecules can be replaced with fresh guest molecules, extending their lifetimes.
- Laurent Sévery
- , Jacek Szczerbiński
- & S. David Tilley
-
Article |
 Metathesis of Ge=Ge double bonds
Metathesis of Ge=Ge double bonds
The metathesis of carbon–carbon double bonds is an important tool in organic synthesis and now a similar reshuffling has been carried out with heavier alkene analogues featuring unsymmetrically substituted Ge=Ge double bonds. This reaction enables the synthesis of symmetric molecular digermenes as well as a polymer based on Ge=Ge repeat units.
- Lukas Klemmer
- , Anna-Lena Thömmes
- & David Scheschkewitz
-
News & Views |
 Probing precipitation properties
Probing precipitation properties
Superheavy elements are short-lived and only available on a single-atom level, making their chemical properties very challenging to study. Now, through their co-precipitation with samarium, single atoms of rutherfordium have been shown to form hydroxide complexes but not ammine ones.
- Alexander Yakushev
-
Article |
 Co-precipitation behaviour of single atoms of rutherfordium in basic solutions
Co-precipitation behaviour of single atoms of rutherfordium in basic solutions
It is difficult to investigate the chemical properties of superheavy elements, which are only available an atom at a time and rapidly decay. A co-precipitation method with samarium has now been developed that suggests rutherfordium would form hydroxide precipitates—but not ammine ones—if it were possible to perform these experiments on macroscopic quantities.
- Yoshitaka Kasamatsu
- , Keigo Toyomura
- & Atsushi Shinohara
-
Article |
 Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Unlike ferrocene and its cationic counterpart ferrocenium, the ferrocene monoanion is an unusual species that has been observed through low-temperature electrochemical studies. Now, a family of isostructural 3d metallocenates has been isolated that consists of a manganocene, a cobaltocene and a high-spin ferrocene anion stabilized by cyclopentadienyl ligands bearing bulky aliphatic groups.
- Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- , Marcus J. Giansiracusa
- & David P. Mills
-
Article |
 Developing the 134Ce and 134La pair as companion positron emission tomography diagnostic isotopes for 225Ac and 227Th radiotherapeutics
Developing the 134Ce and 134La pair as companion positron emission tomography diagnostic isotopes for 225Ac and 227Th radiotherapeutics
134Ce and 134La have great potential as companion diagnostic isotopes for radiotherapeutics labelled with α-emitting 225Ac and 227Th. Now, by controlling the CeIII/CeIV redox couple, the large-scale production, purification and characterization of 134Ce- and 134La-based radiolabels has been achieved and their use for in vivo positron emission tomography is demonstrated.
- Tyler A. Bailey
- , Veronika Mocko
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
Article |
 Substantial π-aromaticity in the anionic heavy-metal cluster [Th@Bi12]4−
Substantial π-aromaticity in the anionic heavy-metal cluster [Th@Bi12]4−
A wide variety of organic and inorganic compounds show π-aromaticity, yet for all-metal systems it has remained restricted to compounds with three to five atoms. Now, the anionic cluster [Th@Bi12]4− has been shown to exhibit π-aromaticity, with a significant ring current despite relying on the delocalization of only two π-electrons.
- Armin R. Eulenstein
- , Yannick J. Franzke
- & Stefanie Dehnen
-
Article |
 Isolable dicarbon stabilized by a single phosphine ligand
Isolable dicarbon stabilized by a single phosphine ligand
Diatomic C2 is an elusive species that has only been indirectly observed in the gas phase. It had previously been stabilized in the condensed phase using two ligands, but now a monoligated L→C2 complex has been prepared with a bulky phosphine ligand (L) bearing two imidazolidin-2-iminato groups. Reactivity studies and theoretical quantum chemical analysis point to the C2 moiety having a dicarbene character.
- Tsz-Fai Leung
- , Dandan Jiang
- & Gernot Frenking
-
News & Views |
 Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
As a consequence of their high instability, main-group carbonyl complexes are rare — only a few have been detected, typically in low-temperature matrices. Now, two silicon–carbonyl complexes have been isolated using innovative substituent patterns at the Si centre; their reactivity resembles that of their transition-metal counterparts.
- Debdeep Mandal
- & Diego M. Andrada
-
Article |
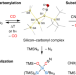 Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silyl-substituted silicon–carbonyl complexes that are stable at room temperature have been prepared by exposure of highly reactive bis(silyl)silylenes to carbon monoxide. The compounds show structural features and reactivity that are reminiscent of their ubiquitous transition-metal–carbonyl counterparts, including π-backbonding and ligand liberation as well as substitution and functionalization reactions.
- Dominik Reiter
- , Richard Holzner
- & Shigeyoshi Inoue
-
Article |
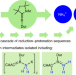 One-pot, room-temperature conversion of dinitrogen to ammonium chloride at a main-group element
One-pot, room-temperature conversion of dinitrogen to ammonium chloride at a main-group element
The vast majority of species capable of converting dinitrogen to ammonia rely on transition metals. Now, a boron compound has been shown to mediate the one-pot binding, cleavage and reduction of N2 to ammonium salts under mild conditions through a complex cascade mechanism involving multiple reduction–protonation sequences.
- Marc-André Légaré
- , Guillaume Bélanger-Chabot
- & Holger Braunschweig
-
News & Views |
 A convenient P– source
A convenient P– source
White phosphorus is a prominent source of P atoms but has remained difficult to activate without using transition metals. Now, a bidentate ligand based on silicon(ii) donors has successfully stabilized a P2 moiety, and the resulting complex acts as a transfer reagent for P– anions.
- David Scheschkewitz
-
Article |
 A bis(silylene)-stabilized diphosphorus compound and its reactivity as a monophosphorus anion transfer reagent
A bis(silylene)-stabilized diphosphorus compound and its reactivity as a monophosphorus anion transfer reagent
White phosphorus (P4) is very reactive but is relatively difficult to activate without relying on transition metals. Now, it has been shown that the degradation of P4 can be mediated by two divalent silicon atoms in a bis(silylene) scaffold to give a diphosphorus complex that can be further functionalized and also act as a P− transfer agent.
- Yuwen Wang
- , Tibor Szilvási
- & Matthias Driess
-
Article |
 Complexes featuring a linear [N≡U≡N] core isoelectronic to the uranyl cation
Complexes featuring a linear [N≡U≡N] core isoelectronic to the uranyl cation
Three crystalline complexes comprising a linear [UN2] moiety that is isoelectronic to the ubiquitous uranyl cation [UO2]2+ have been prepared by reaction of UCl5 or UBr5 with liquid ammonia. Quantum chemical calculations showed that the bonding in the [UN2] moieties is best described with two U≡N triple bonds.
- Stefan S. Rudel
- , H. Lars Deubner
- & Florian Kraus
-
News & Views |
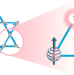 Taking titanium for a spin
Taking titanium for a spin
Spin-1/2 kagome lattice antiferromagnets are geometrically frustrated materials poised to host yet-unobserved behaviours. Now, such a lattice has been prepared that shows no structural distortions and hosts its spin in the dxy orbital of d1 Ti3+ centres, rather than the more-widely investigated d9 Cu2+ ions.
- Kelsey A. Collins
- & Danna E. Freedman
-
Article |
 NH3 formation from N2 and H2 mediated by molecular tri-iron complexes
NH3 formation from N2 and H2 mediated by molecular tri-iron complexes
The reduction of N2 to NH3 is mediated in living systems by the enzyme nitrogenase and in the chemical industry by the Haber–Bosch process; both systems rely on iron-based catalysis. Now, a molecular tri(iron)bis(nitrido) complex, prepared by reduction of a bis(iron)bis(iodo) precursor under an N2 atmosphere, has been isolated and shown to promote the formation of NH3 from H2.
- Matthias Reiners
- , Dirk Baabe
- & Marc D. Walter
-
Article |
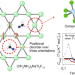 Synthesis of a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet
Synthesis of a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet
The highly frustrated spin-1/2 kagome lattice antiferromagnet, predicted to exhibit unconventional magnetic behaviours, has remained difficult to synthesize without structural imperfections. Now, a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet has been prepared in which there is only one crystallographically distinct Ti3+ site and one type of bridging fluoride, and it is shown to be a frustrated magnet with unusual magnetic properties.
- Ningxin Jiang
- , Arun Ramanathan
- & Henry S. La Pierre
-
Article |
 Synthesis and characterization of crystalline niobium and tantalum carbonyl complexes at room temperature
Synthesis and characterization of crystalline niobium and tantalum carbonyl complexes at room temperature
In contrast to the variety of stable carbonyl complexes of group 7–12 metals, few are known for group 3–5 metals; among those, cations have only been identified in the gas phase or by matrix isolation. Now, several unusual niobium and tantalum carbonyl compounds have been prepared as bulk crystalline compounds, including heptacarbonyl salts and the neutral ditantalum dodecacarbonyl.
- W. Unkrig
- , M. Schmitt
- & I. Krossing
-
Article |
 Metallacyclic actinide catalysts for dinitrogen conversion to ammonia and secondary amines
Metallacyclic actinide catalysts for dinitrogen conversion to ammonia and secondary amines
Metallacycles formed from two large, under-coordinated actinide MIV cations and two rigid arene-bridged aryloxide ligands are capable of binding dinitrogen inside their cavity. These f-block complexes can catalyse the reduction and functionalization of dinitrogen as well as the catalytic conversion of molecular dinitrogen to a secondary silylamine.
- Polly L. Arnold
- , Tatsumi Ochiai
- & Laurent Maron
-
Article |
 A silicon–carbonyl complex stable at room temperature
A silicon–carbonyl complex stable at room temperature
Compounds of main-group elements rarely undergo direct carbonylation reactions. Now, an electron-rich silylene intermediate has been shown to readily react with CO to form a silylene carbonyl complex that is stable at room temperature. This complex engages in CO substitution as well as oxidative addition reactions.
- Chelladurai Ganesamoorthy
- , Juliane Schoening
- & Stephan Schulz
-
Article |
 A photoswitchable polar crystal that exhibits superionic conduction
A photoswitchable polar crystal that exhibits superionic conduction
A material based on a three-dimensional –Fe–N≡C–Mo– anionic framework that hosts a Cs+ cation in every other pore has been shown to exhibit superionic conductivity, despite its polar crystal structure. It also exhibits second harmonic generation (SHG)—usually observed in insulators—and its ionic conductivity was reversibly altered under light irradiation.
- Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
- , Kosuke Nakagawa
- & Asuka Namai

 The fruit fly of photophysics
The fruit fly of photophysics Antimony cation acquired
Antimony cation acquired