Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A nucleophilic beryllyl complex via metathesis at [Be–Be]2+
A nucleophilic beryllyl complex via metathesis at [Be–Be]2+
The chemistry of beryllium, one of the periodic table’s lightest elements, remains poorly understood. Now, a nucleophilic beryllium complex with a highly polarized Be–Be bond has been prepared—this compound could be seen as a mixed-oxidation state Be(0)/Be(II) complex. The Be–Be bond is cleaved upon reaction with an organic substrate.
- Josef T. Boronski
- , Agamemnon E. Crumpton
- & Simon Aldridge
-
Article
| Open Access A lithium–aluminium heterobimetallic dimetallocene
A lithium–aluminium heterobimetallic dimetallocene
Dimetallocenes are a narrow class of compounds represented by the homobimetallic examples dizincocene and diberyllocene. Now a heterobimetallic dimetallocene featuring lithium and aluminium centres has been synthesized. The Al–Li bond is shown to cleave upon reaction with N-heterocyclic carbenes and heteroallenes.
- Inga-Alexandra Bischoff
- , Sergi Danés
- & André Schäfer
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling nucleophilic reactivity in molecular calcium fluoride complexes
Enabling nucleophilic reactivity in molecular calcium fluoride complexes
Calcium difluoride is a source of fluorochemicals, but the reactivity of Ca–F moieties is not well understood. Now a library of molecular Ca–F complexes featuring unique structural motifs has been synthesized, including via fluorochemical defluorination. Studies of mono- and dinuclear systems provided structure–activity relationships for E–F bond formation.
- Job J. C. Struijs
- , Mathias A. Ellwanger
- & Simon Aldridge
-
News & Views |
 Lifting iron higher and higher
Lifting iron higher and higher
Biological and synthetic catalysts often utilize iron in high oxidation states (+IV and greater) to perform challenging molecular transformations. A coordination complex featuring an Fe(VII) ion has now been synthesized through sequential oxidations of nonheme iron–nitrido precursors.
- Adam T. Fiedler
- & Laxmi Devkota
-
Article |
 Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Although the light-driven generation of hydrogen from water is a promising approach to renewable fuels, the H–H bond formation step represents a persistent mechanistic question. Now light-harvesting molecular catalysts have been shown to self-assemble into nanoscale aggregates that feature improved efficiency for photoelectrochemical H2 evolution.
- Isaac N. Cloward
- , Tianfei Liu
- & Alexander J. M. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
A previous investigation of the anti-aromatic dianion of [18]annulene concluded that it consists of a mixture of two isomers. Now it has been shown that this dianion exists as a single isomer, with a different geometry from neutral [18]annulene, and that it can be reduced further to an aromatic tetraanion.
- Wojciech Stawski
- , Yikun Zhu
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access The synthesis and characterization of an iron(VII) nitrido complex
The synthesis and characterization of an iron(VII) nitrido complex
Complexes of iron in high oxidation states play a pivotal role as active intermediates in numerous catalytic processes. Now, using a multimethod approach on a single molecular system, it has been shown that a stable high-valent Fe(VI) nitride can be converted to a reactive, superoxidized, heptavalent Fe(VII) nitride.
- Martin Keilwerth
- , Weiqing Mao
- & Karsten Meyer
-
Article |
 Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Activation of H2 by a metal–olefin complex is characterized experimentally and computationally using a nickel pincer complex, showing that the reaction proceeds via a direct ligand-to-ligand hydrogen transfer mechanism. An application of this cooperative H2-activation mechanism is demonstrated in the nickel-catalysed semihydrogenation of diphenylacetylene.
- María L. G. Sansores-Paredes
- , Martin Lutz
- & Marc-Etienne Moret
-
-
In Your Element |
 The numerous paths of ferrocene
The numerous paths of ferrocene
Didier Astruc surveys the numerous applications of ferrocene, from catalysis to materials and redox-related devices including biosensors and nanomedicine.
- Didier Astruc
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
In Your Element |
 The curious chemistry of carbones
The curious chemistry of carbones
Martin Johansen and Abhik Ghosh reflect on the unusual chemistry of carbones — whose central carbon atom bears two lone pairs — and their role as double-dative ligands.
- Martin A. L. Johansen
- & Abhik Ghosh
-
Article |
 Anions featuring an aluminium–silicon core with alumanyl silanide and aluminata-silene characteristics
Anions featuring an aluminium–silicon core with alumanyl silanide and aluminata-silene characteristics
Aluminium and silicon, two Earth-abundant, well-understood elements, typically form weak Al–Si bonds. Now, complexes featuring an anionic Al–Si core stabilized by bulky substituents and a Si–Na interaction have been isolated. This Al–Si interaction possesses partial double bond character, which can be increased by sequestration of the sodium counterion.
- Moritz Ludwig
- , Daniel Franz
- & Shigeyoshi Inoue
-
Research Briefing |
 A near-linear lanthanide complex that displays magnet-like behaviour
A near-linear lanthanide complex that displays magnet-like behaviour
Low-coordinate lanthanide complexes with strong magnetic anisotropy could afford high-performance single-molecule magnets (SMMs) but are challenging to synthesize. Now, through ligand design, a near-linear pseudo-two-coordinate Yb(iii) complex that exhibits slow magnetic relaxation is reported. The complex has a large total splitting of the ground-state manifold, arising from the crystal field imposed by the ligands.
-
Article |
 A trivalent 4f complex with two bis-silylamide ligands displaying slow magnetic relaxation
A trivalent 4f complex with two bis-silylamide ligands displaying slow magnetic relaxation
A trivalent 4f cationic complex bearing two bis-silylamide ligands has been prepared that displays slow magnetic relaxation. The bulky ligands and weakly coordinating anion stabilize the pseudotrigonal geometry necessary to elicit strong ground-state magnetic anisotropy in this axially coordinated Yb(III) complex with well-localized charges.
- Dylan Errulat
- , Katie L. M. Harriman
- & Muralee Murugesu
-
News & Views |
 A discrete antimony(v) oxide
A discrete antimony(v) oxide
Monomeric stibine oxide has remained elusive due to the large antimony orbitals coupled with a high electronegativity difference with oxygen. Now, a free tris(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)stibine oxide has been isolated that can act as oxo-transfer reagent.
- Moumita Majumdar
-
Article
| Open Access Isolation, bonding and reactivity of a monomeric stibine oxide
Isolation, bonding and reactivity of a monomeric stibine oxide
In contrast to phosphine and arsine oxides, stibine oxides have been challenging to isolate in monomeric forms as they tend to polymerize. Now, such a SbO moiety has been kinetically stabilized using sterically bulky protecting groups, and its reactivity found to be substantially different to that of its lighter pnictogen counterparts.
- John S. Wenger
- , Monica Weng
- & Timothy C. Johnstone
-
Article
| Open Access φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
Aromaticity is a ubiquitous concept in organic chemistry yet it is less widespread for inorganic species. Now the cluster [(CpRu)3Bi6]–, obtained as part of a soluble salt, has been shown to exhibit aromatic behaviour referred to as φ-type, owing to a highly regular {Bi6} substructure causing a non-localizable molecular orbital of \(f_{z^3}\)-like symmetry.
- Benjamin Peerless
- , Andreas Schmidt
- & Stefanie Dehnen
-
News & Views |
 Rare radioisotopes at the ready
Rare radioisotopes at the ready
The study of rare isotopes, including many in the f-block, is a key step to advancing our fundamental understanding of these elements, but their scarcity poses challenges. Now, minute amounts of such materials have been isolated and characterized through complexation with polyoxometalate clusters.
- Kristina O. Kvashnina
-
Article |
 An isolable germylyne radical with a one-coordinate germanium atom
An isolable germylyne radical with a one-coordinate germanium atom
Heavy analogues of carbynes of the type R–\({{{\dot{\mathrm E:}}}}\), where E is a group 14 element, are difficult to isolate in the condensed phase due to their high reactivity. Now, a germylyne radical supported by a sterically hindered hydrindacene ligand has been prepared and structurally characterized. Theoretical calculations show that the spin density mainly resides at the germanium centre.
- Dongmin Wang
- , Cai Zhai
- & Gengwen Tan
-
In Your Element |
 Shapeshifting xantphos
Shapeshifting xantphos
Lukas Veth and Paweł Dydio discuss the importance of ligands in transition metal catalysis, looking at the success story of xantphos and why it should earn the title of ‘privileged ligand’.
- Lukas Veth
- & Paweł Dydio
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Although neutral and anionic low-valent aluminium complexes are widespread, their cationic counterparts have remained rare. Now, a salt of [Al(AlCp*)3]+ featuring a formal low-valent Al+ cation has been isolated that dimerizes in concentrated solutions and the solid state, and also forms Al4 clusters on coordinating with Lewis bases.
- Philipp Dabringhaus
- , Julie Willrett
- & Ingo Krossing
-
Article |
 Taming phosphorus mononitride
Taming phosphorus mononitride
Precursors for the release of phosphorus mononitride in solution under mild conditions have remained elusive. Now, an explosive anthracene-stabilized azidophosphine has shown PN transfer reactivity in the synthesis of an Fe–NP complex. The PN ligand is N-bonded, as the Fe–N interaction shows significant covalent character and a less unfavourable Pauli repulsion than its Fe–P counterpart.
- André K. Eckhardt
- , Martin-Louis Y. Riu
- & Christopher C. Cummins
-
Article |
 Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Despite much research, the high-spin-state relaxation mechanism of Fe(II) spin-crossover complexes is unresolved. Using ultrafast circular dichroism spectroscopy it has now been revealed that the spin relaxation is driven by a torsional twisting mode, which breaks the chiral symmetry of a prototypical Fe(II) compound. Stereocontrolling the configuration of the complex can thus be used to slow down the spin relaxation.
- Malte Oppermann
- , Francesco Zinna
- & Majed Chergui
-
Article |
 Binding methane to a metal centre
Binding methane to a metal centre
Catalytic transformations of methane frequently involve the formation of a metal–methane complex, but these compounds are challenging to observe. Now, a relatively long-lived osmium–methane complex has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy and forms from the direct binding of methane to a photolytically generated, coordinatively unsaturated cationic osmium–carbonyl complex dissolved in an inert hydrofluorocarbon solvent at –90 °C.
- James. D. Watson
- , Leslie. D. Field
- & Graham. E. Ball
-
Article |
 Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion pairing is ubiquitous in low-dielectric-constant solvents, but whether it influences the reactivity of common cationic photoredox catalysts has been unclear. However, it has now been shown that ion pairing is responsible for a 4-fold modulation in reactivity in a prototypical Ir(III) complex and is explained by excited-state ion-pair reorganization.
- J. D. Earley
- , A. Zieleniewska
- & G. Rumbles
-
News & Views |
 Molecular spins clock in
Molecular spins clock in
Electron spin relaxation, important in quantum information science, can be slowed down at clock transitions — which are insensitive to magnetic noise. It has now been shown that such transitions can be tuned, to high frequency, in rare-earth coordination complexes through control of s- and d-orbital mixing.
- Eric J. L. McInnes
-
Article |
 Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Although cobalt–carbene radicals have proved to be highly versatile intermediates for homogeneous catalysis, their spectroscopic detection and characterization have been limited. Now, by using hypervalent iodonium ylides, the formation and spectroscopic detection of a biscarbenoid N-enolate–carbene radical—which undergoes a complex catalytic pathway involving reversible N-enolate formation—has been demonstrated.
- Roel F. J. Epping
- , Mees M. Hoeksma
- & Bas de Bruin
-
Article |
 A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
The s-orbital mixing into the spin-bearing d orbital associated with a molecular Lu(II) complex is shown to both reduce spin–orbit coupling and increase electron–nuclear hyperfine interactions, which substantially improves electron spin coherence. Combined with the potential to tune interactions through coordination chemistry, it makes this system attractive for quantum information applications.
- Krishnendu Kundu
- , Jessica R. K. White
- & Stephen Hill
-
News & Views |
 Ammonia formation revisited
Ammonia formation revisited
Dinitrogen conversion to ammonia is of great biological and industrial relevance, but modelling this process on a molecular level is challenging. Now, a biomimetic model offers new insights into the functionalization of a nitrido ligand to form NH3 using either H2 or H+/e–.
- Marc D. Walter
-
Article |
 A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
Multi-iron nitrides are implicated as potential key intermediates in biological nitrogen fixation and the industrial Haber–Bosch process, but well-described functional model systems are rare. Now, a well-defined thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex has been found to show excellent reactivity toward hydrogenation with H2 through a stepwise pathway to form ammonia in high yield.
- Yixin Zhang
- , Jinfeng Zhao
- & Jingping Qu
-
-
Article |
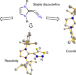 Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Isolation and characterization of diazoolefins
Diazoolefins tend to be highly reactive compounds, and thus experimental evidence of these species is currently limited. Now, the reactivity and coordination chemistry of N-heterocyclic diazoolefins has been described. Diazoolefins are observed to form in reactions of N-heterocyclic olefins with nitrous oxide. The products benefit from resonance stabilization, enabling isolation on a preparative scale and comprehensive characterization.
- Paul Varava
- , Zhaowen Dong
- & Kay Severin
-
News & Views |
 Made with manganese
Made with manganese
Transition metal complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) luminescence and photoactivity typically rely on precious metals such as ruthenium or iridium. Now, two complexes of the Earth-abundant 3d manganese have displayed room-temperature MLCT luminescence in solution and a unique excited-state reactivity.
- Katja Heinze
-
News & Views |
 Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Carbon–carbon single bonds are generally among the least reactive chemical bonds. While olefin metathesis reactions are well established, direct metathesis of C–C single bonds is rare. Now, a C–C single bond metathesis reaction has been developed, forming cross-biaryl products from unstrained homo-biaryl compounds.
- Michael M. Gilbert
- & Daniel J. Weix
-
Article |
 Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Metathesis reactions involving carbon–carbon double bonds have been well established, but direct metathesis of carbon–carbon single bonds is extremely rare. Now, a ruthenium-catalysed carbon–carbon single-bond metathesis reaction has been developed with unstrained homo-biaryl substrates. The reaction shows wide functional group tolerance and operates via an ‘olefin-metathesis-like’ mechanism.
- Jun Zhu
- , Rui Zhang
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
The formation of weak chemical bonds at or near thermodynamic potential is a challenge in chemical synthesis and catalysis. A bifunctional iridium hydride catalyst has now been discovered that absorbs visible light and promotes proton-coupled electron transfer to a range of substrates—creating element–hydrogen bonds—using dihydrogen as the terminal reductant.
- Yoonsu Park
- , Sangmin Kim
- & Paul J. Chirik
-
Article |
 Metathesis of Ge=Ge double bonds
Metathesis of Ge=Ge double bonds
The metathesis of carbon–carbon double bonds is an important tool in organic synthesis and now a similar reshuffling has been carried out with heavier alkene analogues featuring unsymmetrically substituted Ge=Ge double bonds. This reaction enables the synthesis of symmetric molecular digermenes as well as a polymer based on Ge=Ge repeat units.
- Lukas Klemmer
- , Anna-Lena Thömmes
- & David Scheschkewitz
-
Article |
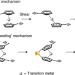 Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Metallocenes are attractive mechanophores because they are stable in the absence of force, yet reactive under tension. Now, covalently bridging the two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) ligands of ferrocenes embedded in a polymer has been shown to alter their mechanochemical reactivity, leading to a faster dissociation of the Fe–Cp bond, which occurs through a peeling mechanism rather than a shearing one.
- Yudi Zhang
- , Zi Wang
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article |
 Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Unlike ferrocene and its cationic counterpart ferrocenium, the ferrocene monoanion is an unusual species that has been observed through low-temperature electrochemical studies. Now, a family of isostructural 3d metallocenates has been isolated that consists of a manganocene, a cobaltocene and a high-spin ferrocene anion stabilized by cyclopentadienyl ligands bearing bulky aliphatic groups.
- Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- , Marcus J. Giansiracusa
- & David P. Mills
-
Article |
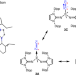 Isolable dicarbon stabilized by a single phosphine ligand
Isolable dicarbon stabilized by a single phosphine ligand
Diatomic C2 is an elusive species that has only been indirectly observed in the gas phase. It had previously been stabilized in the condensed phase using two ligands, but now a monoligated L→C2 complex has been prepared with a bulky phosphine ligand (L) bearing two imidazolidin-2-iminato groups. Reactivity studies and theoretical quantum chemical analysis point to the C2 moiety having a dicarbene character.
- Tsz-Fai Leung
- , Dandan Jiang
- & Gernot Frenking
-
News & Views |
 Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
Surprisingly stable Si–CO species
As a consequence of their high instability, main-group carbonyl complexes are rare — only a few have been detected, typically in low-temperature matrices. Now, two silicon–carbonyl complexes have been isolated using innovative substituent patterns at the Si centre; their reactivity resembles that of their transition-metal counterparts.
- Debdeep Mandal
- & Diego M. Andrada
-
Article |
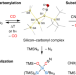 Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silylated silicon–carbonyl complexes as mimics of ubiquitous transition-metal carbonyls
Silyl-substituted silicon–carbonyl complexes that are stable at room temperature have been prepared by exposure of highly reactive bis(silyl)silylenes to carbon monoxide. The compounds show structural features and reactivity that are reminiscent of their ubiquitous transition-metal–carbonyl counterparts, including π-backbonding and ligand liberation as well as substitution and functionalization reactions.
- Dominik Reiter
- , Richard Holzner
- & Shigeyoshi Inoue
-
Article |
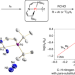 A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
Transient metallonitrenes (M–N) have been proposed as key intermediates in nitrogen atom transfer reactions, but well-defined examples have remained elusive. Now, a platinum complex with an atomic nitrogen ligand, best described as a subvalent nitrogen diradical singly bonded to a platinum(ii) ion (Pt–N), has been isolated and shows ambiphilic reactivity.
- Jian Sun
- , Josh Abbenseth
- & Sven Schneider
-
News & Views |
 A convenient P– source
A convenient P– source
White phosphorus is a prominent source of P atoms but has remained difficult to activate without using transition metals. Now, a bidentate ligand based on silicon(ii) donors has successfully stabilized a P2 moiety, and the resulting complex acts as a transfer reagent for P– anions.
- David Scheschkewitz
-
Thesis |
 The centenary (maybe) of the hydrogen bond
The centenary (maybe) of the hydrogen bond
Despite the romantic mythology that often accompanies stories of scientific discovery, pinpointing the exact moment in history when a new concept emerged is often a matter of debate — and the hydrogen bond is no exception explains Bruce C. Gibb.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
Article |
 NH3 formation from N2 and H2 mediated by molecular tri-iron complexes
NH3 formation from N2 and H2 mediated by molecular tri-iron complexes
The reduction of N2 to NH3 is mediated in living systems by the enzyme nitrogenase and in the chemical industry by the Haber–Bosch process; both systems rely on iron-based catalysis. Now, a molecular tri(iron)bis(nitrido) complex, prepared by reduction of a bis(iron)bis(iodo) precursor under an N2 atmosphere, has been isolated and shown to promote the formation of NH3 from H2.
- Matthias Reiners
- , Dirk Baabe
- & Marc D. Walter
-
Article |
 Synthesis and characterization of crystalline niobium and tantalum carbonyl complexes at room temperature
Synthesis and characterization of crystalline niobium and tantalum carbonyl complexes at room temperature
In contrast to the variety of stable carbonyl complexes of group 7–12 metals, few are known for group 3–5 metals; among those, cations have only been identified in the gas phase or by matrix isolation. Now, several unusual niobium and tantalum carbonyl compounds have been prepared as bulk crystalline compounds, including heptacarbonyl salts and the neutral ditantalum dodecacarbonyl.
- W. Unkrig
- , M. Schmitt
- & I. Krossing
-
Article |
 Metallacyclic actinide catalysts for dinitrogen conversion to ammonia and secondary amines
Metallacyclic actinide catalysts for dinitrogen conversion to ammonia and secondary amines
Metallacycles formed from two large, under-coordinated actinide MIV cations and two rigid arene-bridged aryloxide ligands are capable of binding dinitrogen inside their cavity. These f-block complexes can catalyse the reduction and functionalization of dinitrogen as well as the catalytic conversion of molecular dinitrogen to a secondary silylamine.
- Polly L. Arnold
- , Tatsumi Ochiai
- & Laurent Maron

 Supramolecular trapping of a cationic all-metal σ-aromatic {Bi4} ring
Supramolecular trapping of a cationic all-metal σ-aromatic {Bi4} ring A 21-electron cobalt sandwich
A 21-electron cobalt sandwich Antimony cation acquired
Antimony cation acquired