News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Trapping of a phenoxyl radical at a non-haem high-spin iron(II) centre
Trapping of a phenoxyl radical at a non-haem high-spin iron(II) centre
The activation of dioxygen at metal centres, and subsequent functionalization of unactivated C‒H bonds, requires the generation of high-energy radical intermediates that often result in undesirable side reactions. Now an elusive oxygen-derived reactive iron(II)–radical intermediate is spectroscopically characterized as part of a strategy to stabilize phenoxyl radical cofactors during substrate oxidation reactions.
- Dustin Kass
- , Virginia A. Larson
- & Kallol Ray
-
News & Views |
 Anticancer platinum-based photo-oxidants in a new light
Anticancer platinum-based photo-oxidants in a new light
Pharmacologically inactive prodrugs that can be activated by near-infrared light are attractive candidates for clinical applications. Now, platinum-based photo-oxidants have been shown to eradicate tumours in mice with a new mode of action.
- Gloria Vigueras
- & Gilles Gasser
-
Article |
 Near-infrared-activated anticancer platinum(IV) complexes directly photooxidize biomolecules in an oxygen-independent manner
Near-infrared-activated anticancer platinum(IV) complexes directly photooxidize biomolecules in an oxygen-independent manner
Conventional photo-driven cancer treatment agents require oxygen and visible light to induce cell death, limiting their efficacy in deep, oxygen-poor tumours. Now, a class of NIR-activatable Pt(IV) photooxidants that target the endoplasmic reticulum have been shown to effectively overcome these limitations by directly oxidizing intracellular biomolecules in an oxygen-independent fashion, presenting a promising new direction for next-generation metal-based drug development.
- Zhiqin Deng
- , Huangcan Li
- & Guangyu Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo metallophilic self-assembly of a light-activated anticancer drug
In vivo metallophilic self-assembly of a light-activated anticancer drug
The metallophilic interaction between cyclometalated palladium complexes can facilitate supramolecular nanostructure formation in living mice, providing a phototoxic prodrug with a long circulation time and high tumour-targeting efficiency. Upon green light irradiation, this palladium-based drug destroys solid tumours, leaving non-irradiated organs intact.
- Xue-Quan Zhou
- , Peiyuan Wang
- & Sylvestre Bonnet
-
Article |
 Connecting the geometric and electronic structures of the nitrogenase iron–molybdenum cofactor through site-selective 57Fe labelling
Connecting the geometric and electronic structures of the nitrogenase iron–molybdenum cofactor through site-selective 57Fe labelling
The molybdenum nitrogenase catalytic cofactor is composed of seven high-spin Fe sites making it difficult to study spectroscopically. Now it has been shown that 57Fe can be incorporated into a single site and that such site-selectively labelled samples provide insights into the cofactor’s electronic structure and the mechanism of biological nitrogen fixation.
- Edward D. Badding
- , Suppachai Srisantitham
- & Daniel L. M. Suess
-
Article |
 Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β
Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β
Metal-free amyloid-β (Aβ) and metal-bound Aβ (metal–Aβ) are found in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Now, it has been shown that the conformation of a native neuropeptide, somatostatin, is changed in the presence of copper ions, Aβ and metal–Aβ. The conformational change results in a loss of function of somatostatin as a neurotransmitter and a gain of function as a modulator against metal–Aβ.
- Jiyeon Han
- , Jiwon Yoon
- & Mi Hee Lim
-
Review Article |
 Iron–sulfur clusters as inhibitors and catalysts of viral replication
Iron–sulfur clusters as inhibitors and catalysts of viral replication
Viruses use the cellular machinery of their host organism to reproduce. This Review discusses how [FeS] cluster-containing proteins activate, support and modulate the innate immune response to restrict viral infections as well as highlighting how some of these proteins simultaneously support the replication of viruses.
- Kourosh Honarmand Ebrahimi
- , Simone Ciofi-Baffoni
- & Fraser A. Armstrong
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilization of intermediate spin states in mixed-valent diiron dichalcogenide complexes
Stabilization of intermediate spin states in mixed-valent diiron dichalcogenide complexes
Despite extensive investigations of mixed-valence complexes, molecules with intermediate spin states have remained elusive. Now, selenium- and tellurium-bridged mixed-valent iron dimers have been prepared in which a balance of Heisenberg exchange and double-exchange coupling of the unpaired electron, combined with moderate vibronic contributions, stabilizes S = 3/2 ground spin states.
- Justin T. Henthorn
- , George E. Cutsail III
- & Serena DeBeer
-
Article |
 A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
A thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex and its hydrogenation reactivity toward ammonia formation
Multi-iron nitrides are implicated as potential key intermediates in biological nitrogen fixation and the industrial Haber–Bosch process, but well-described functional model systems are rare. Now, a well-defined thiolate-bridged FeIVFeIV μ-nitrido complex has been found to show excellent reactivity toward hydrogenation with H2 through a stepwise pathway to form ammonia in high yield.
- Yixin Zhang
- , Jinfeng Zhao
- & Jingping Qu
-
Article |
 Native mass spectrometry-based metabolomics identifies metal-binding compounds
Native mass spectrometry-based metabolomics identifies metal-binding compounds
The systemic discovery of metal–small-molecule complexes from biological samples is a difficult challenge. Now, a method based on liquid chromatography and native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry has been developed. The approach uses post-column pH adjustment and metal infusion combined with ion identity molecular networking, and a rule-based informatics workflow, to interrogate small-molecule–metal binding.
- Allegra T. Aron
- , Daniel Petras
- & Pieter C. Dorrestein
-
Article |
 Tracing the incorporation of the “ninth sulfur” into the nitrogenase cofactor precursor with selenite and tellurite
Tracing the incorporation of the “ninth sulfur” into the nitrogenase cofactor precursor with selenite and tellurite
Located in the catalytically important belt region, the ‘ninth sulfur’ of the nitrogenase cofactor has now been shown to be inserted through coordination of sulfite by two cluster iron atoms at a vacant belt site. This is followed by in situ reduction of sulfite to sulfide, which enables the subsequent transfer and functionalization of the cofactor.
- Kazuki Tanifuji
- , Andrew J. Jasniewski
- & Markus W. Ribbe
-
Article |
 Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
The molybdenum cofactor (Moco) is found in the active site of numerous enzymes, but the mechanism of molybdate insertion is not clear. Now, the mechanism of the final maturation step, in which adenylated molybdopterin and molybdate are the substrates, has been revealed. X-ray crystallography of an Mo-insertase identified adenylated Moco as an unexpected intermediate in this reaction sequence.
- Corinna Probst
- , Jing Yang
- & Tobias Kruse
-
Article |
 Metal ion fluxes controlling amphibian fertilization
Metal ion fluxes controlling amphibian fertilization
Zinc fluxes have now been shown to be essential in the fertilization of amphibian eggs. Furthermore, manganese(ii), which is initially bound to low-molecular-weight carboxylates, is stored and released with zinc from cortical vesicles following fertilization. This rapid metal ion release blocks the otherwise fatal entry of a second sperm.
- John F. Seeler
- , Ajay Sharma
- & Thomas V. O’Halloran
-
Article |
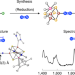 Dinitrogen binding and activation at a molybdenum–iron–sulfur cluster
Dinitrogen binding and activation at a molybdenum–iron–sulfur cluster
Although iron–sulfur cofactors are known to carry out biological nitrogen fixation, how these clusters bind dinitrogen remains poorly understood. Now, a dinitrogen complex of a synthetic iron–sulfur cluster has been characterized, and electronic cooperation in the cluster has been shown to result in strong N–N bond activation.
- Alex McSkimming
- & Daniel L. M. Suess
-
Article |
 Developing the 134Ce and 134La pair as companion positron emission tomography diagnostic isotopes for 225Ac and 227Th radiotherapeutics
Developing the 134Ce and 134La pair as companion positron emission tomography diagnostic isotopes for 225Ac and 227Th radiotherapeutics
134Ce and 134La have great potential as companion diagnostic isotopes for radiotherapeutics labelled with α-emitting 225Ac and 227Th. Now, by controlling the CeIII/CeIV redox couple, the large-scale production, purification and characterization of 134Ce- and 134La-based radiolabels has been achieved and their use for in vivo positron emission tomography is demonstrated.
- Tyler A. Bailey
- , Veronika Mocko
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
Article |
 Heteromeric three-stranded coiled coils designed using a Pb(ii)(Cys)3 template mediated strategy
Heteromeric three-stranded coiled coils designed using a Pb(ii)(Cys)3 template mediated strategy
A method to fabricate heterotrimeric three-stranded coiled-coil peptide structures has now been developed using coordination around a Pb(ii) centre. The heterotrimeric structures require only three cysteines that bind to Pb(ii) to form a trigonal pyramidal structure, and the formation of an adjacent cavity in which water can hydrogen bond to the cysteine sulfur atoms.
- Audrey E. Tolbert
- , Catherine S. Ervin
- & Vincent L. Pecoraro
-
Article |
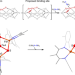 Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
The four-coordinate iron sites of typical iron–sulfur clusters rarely react with small molecules, implicating three-coordinate iron in many catalytic cycles. Now, a [4Fe-3S] cluster featuring three-coordinate iron sulfide that resembles the proposed substrate binding site has been synthesized. This cluster shows biomimetic reactivity with a low-spin electronic configuration.
- Daniel E. DeRosha
- , Vijay G. Chilkuri
- & Patrick L. Holland
-
Article |
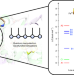 Electronic landscape of the P-cluster of nitrogenase as revealed through many-electron quantum wavefunction simulations
Electronic landscape of the P-cluster of nitrogenase as revealed through many-electron quantum wavefunction simulations
The electronic structures of the metal cofactors of nitrogenase are key to biological nitrogen fixation; however, the [Fe8S7] P-cluster and FeMo cofactor have eluded detailed electronic characterization. Now, the electronic structure of the P-cluster of nitrogenase has been revealed at the many-electron level through exhaustive quantum wavefunction simulations.
- Zhendong Li
- , Sheng Guo
- & Garnet Kin-Lic Chan
-
Article |
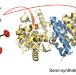 A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
Natural hydrogenases exclusively utilize Ni and/or Fe to activate or produce hydrogen. Now, a catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase has been prepared by incorporating a synthetic Mn complex into the apoenzyme of [Fe]-Hydrogenase. The semi-synthetic [Mn]-hydrogenase shows higher activity than the corresponding Fe analogue.
- Hui-Jie Pan
- , Gangfeng Huang
- & Xile Hu
-
Article |
 An efficient, step-economical strategy for the design of functional metalloproteins
An efficient, step-economical strategy for the design of functional metalloproteins
A concise strategy for engineering functional, supramolecular protein complexes has now been developed based on single-mutation-mediated covalent tethering. Metalloproteins designed with this method can sustain large alterations to the metal coordination environment, bind small molecules, exhibit reversible redox activity and sustain large alterations to the protein structure.
- Jonathan Rittle
- , Mackenzie J. Field
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
News & Views |
 Redox activity goes organic
Redox activity goes organic
Superoxide dismutase mimics can help regulate the levels of O2•− in the body, but typically rely on redox-active metals that are toxic in their free form. Now, a complex featuring a redox-active quinol moiety complexed to a redox-inactive zinc centre has been shown to catalyse O2•− dismutation.
- Diane E. Cabelli
-
Article |
 Superoxide dismutase activity enabled by a redox-active ligand rather than metal
Superoxide dismutase activity enabled by a redox-active ligand rather than metal
Catalytic superoxide dismutase mimics typically involve manganese centres. Now, a complex based on redox-inactive zinc(ii) and a redox-active quinol ligand is found to catalytically degrade superoxide. The reaction, proposed to occur through oxidation of the ligand to a quinoxyl radical, is hastened rather than inhibited by the presence of phosphate.
- Meghan B. Ward
- , Andreas Scheitler
- & Christian R. Goldsmith
-
Article |
 A human MUTYH variant linking colonic polyposis to redox degradation of the [4Fe4S]2+ cluster
A human MUTYH variant linking colonic polyposis to redox degradation of the [4Fe4S]2+ cluster
The [4Fe4S]2+ cluster-containing DNA-repair enzyme MUTYH helps safeguard the integrity of Watson–Crick base pairing and the human genetic code. The MUTYH [4Fe4S]2+ cluster mediates DNA redox signalling and DNA lesion identification. Now, a MUTYH pathologic variant associated with catastrophic [4Fe4S]2+ cluster redox degradation, impairment of DNA signalling and human colonic tumorigenesis has been identified.
- Kevin J. McDonnell
- , Joseph A. Chemler
- & Stephen B. Gruber
-
Article |
 Tracing the ‘ninth sulfur’ of the nitrogenase cofactor via a semi-synthetic approach
Tracing the ‘ninth sulfur’ of the nitrogenase cofactor via a semi-synthetic approach
The M-cluster in the active site of nitrogenase is derived from an 8Fe core assembled via coupling and rearrangement of two [Fe4S4] clusters concomitant with the insertion of an interstitial carbon and a ninth sulfur. Now, by combining synthetic [Fe4S4] clusters and assembly with a protein template, it has been shown that sulfite gives rise to the ninth sulfur that is inserted into the nitrogenase cofactor after the radical SAM-dependent carbide insertion and cofactor core rearrangement.
- Kazuki Tanifuji
- , Chi Chung Lee
- & Markus W. Ribbe
-
Article |
 A [4Fe–4S]-Fe(CO)(CN)-l-cysteine intermediate is the first organometallic precursor in [FeFe] hydrogenase H-cluster bioassembly
A [4Fe–4S]-Fe(CO)(CN)-l-cysteine intermediate is the first organometallic precursor in [FeFe] hydrogenase H-cluster bioassembly
The biosynthesis of the [FeFe] hydrogenase active site H-cluster requires several Fe–S proteins that perform poorly understood reactions. Now, a reaction intermediate trapped in the enzyme HydG is shown to contain a [(Cys)Fe(CO)(CN)] species identified as the first organometallic Fe moiety en route to the catalytic H-cluster.
- Guodong Rao
- , Lizhi Tao
- & R. David Britt
-
Article |
 Evolving artificial metalloenzymes via random mutagenesis
Evolving artificial metalloenzymes via random mutagenesis
Proteins have the potential to serve as powerful scaffolds that control the catalytic activity and selectivity of organometallic centres; however, new methods are needed to optimize artificial metalloenzymes. Now, an efficient approach for evolving the activity and selectivity of artificial metalloenzymes has been demonstrated using dirhodium cyclopropanases. This approach does not require structural or mechanistic data to guide mutagenesis.
- Hao Yang
- , Alan M. Swartz
- & Jared C. Lewis
-
Article |
 Transferring the entatic-state principle to copper photochemistry
Transferring the entatic-state principle to copper photochemistry
According to the entatic-state principle, distortions of the coordination geometry of a reacting compound can optimize the energies of starting and final states to improve reaction rates. Here, the entatic-state principle is observed to apply to photoactive copper complexes that have a constrained ligand geometry, resulting in very short charge-transfer state lifetimes.
- B. Dicke
- , A. Hoffmann
- & S. Herres-Pawlis
-
Article |
 Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation by synthetic catalysts in cancer cells
Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation by synthetic catalysts in cancer cells
Intracellular asymmetric transfer hydrogenation catalysis using Os(II) complexes has now been demonstrated and offers a new approach for selectively killing cancer cells. Enantiomers of Os(II) arene catalysts can penetrate cell membranes enabling the reduction of pyruvate to D- or L-lactate using formate as a hydride source, with high enantioselectivity.
- James P. C. Coverdale
- , Isolda Romero-Canelón
- & Peter J. Sadler
-
Article |
 De novo design of a hyperstable non-natural protein–ligand complex with sub-Å accuracy
De novo design of a hyperstable non-natural protein–ligand complex with sub-Å accuracy
The first demonstration of a protein designed entirely from first principles that binds a small-molecule cofactor in a precisely predetermined orientation has now been described. The design method utilizes a remote protein core that both anchors and predisposes a flexible binding site for the desired cofactor-binding geometry.
- Nicholas F. Polizzi
- , Yibing Wu
- & William F. DeGrado
-
Article |
 UV-light-driven prebiotic synthesis of iron–sulfur clusters
UV-light-driven prebiotic synthesis of iron–sulfur clusters
Current mineral-based theories do not fully address how enzymes emerged from prebiotic catalysts. Now, iron–sulfur clusters can be synthesized by UV-light-mediated photolysis of organic thiols and photooxidation of ferrous ions. Iron–sulfur peptides may have formed easily on early Earth, facilitating the emergence of iron–sulfur-cluster-dependent metabolism.
- Claudia Bonfio
- , Luca Valer
- & Sheref S. Mansy
-
Article |
 Characterization of a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I reveals direct link between electron donation and reactivity
Characterization of a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I reveals direct link between electron donation and reactivity
The oxidative prowess of cytochrome P450s has been suggested to stem from the electron-donating axial ligand. Now, a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I has been trapped and characterized providing an avenue to examine this hypothesis. Measurements reveal that the selenolate-ligated compound I cleaves C–H bonds more rapidly than the wild-type equivalent.
- Elizabeth L. Onderko
- , Alexey Silakov
- & Michael T. Green
-
Article |
 Chelation and stabilization of berkelium in oxidation state +IV
Chelation and stabilization of berkelium in oxidation state +IV
Berkelium is the only transplutonium element predicted to be able to exhibit both +III and +IV oxidation states in solution. Bk(IV) has now been stabilized through chelation with a siderophore derivative. The resulting neutral coordination compound was characterized and compared with the negatively charged species obtained by chelation of neighbouring trivalent actinides.
- Gauthier J.-P. Deblonde
- , Manuel Sturzbecher-Hoehne
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
News & Views |
 Precision in 3D
Precision in 3D
Biomimetic molecules that can be easily tailored offer numerous opportunities. Now, boron-based clusters have been shown to be excellent biomimetics. The ease with which the cluster surfaces can be modified stands to change how chemists might go about preparing materials for imaging, drug delivery and other applications.
- Marek B. Majewski
- , Ashlee J. Howarth
- & Omar K. Farha
-
Article |
 Structural and functional synthetic model of mono-iron hydrogenase featuring an anthracene scaffold
Structural and functional synthetic model of mono-iron hydrogenase featuring an anthracene scaffold
Mono-iron hydrogenase promotes the heterolytic cleavage of H2 and subsequent hydride transfer to its organic substrate, H4MPT+, which serves as a CO2 ‘carrier’ in methanogenic pathways. Now, using an anthracene-scaffold-based approach, a synthetic model featuring enzyme-like Fe-C,N,S facial coordination has been developed. The model complex enables the bidirectional activity of H2 activation and evolution.
- Junhyeok Seo
- , Taylor A. Manes
- & Michael J. Rose
-
-
Article |
 Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
The operational simplicity of modifying the surfaces of thiol-capped gold nanoparticles has been a hallmark of their success in materials chemistry, despite having limited control over the surface composition. Now, SNAr chemistry on activated perfluoroaromatics has been shown to mimic this simplicity and allow for the synthesis of atomically precise nanomolecules.
- Elaine A. Qian
- , Alex I. Wixtrom
- & Alexander M. Spokoyny
-
Article |
 Why copper is preferred over iron for oxygen activation and reduction in haem-copper oxidases
Why copper is preferred over iron for oxygen activation and reduction in haem-copper oxidases
Despite decades of research into heme-copper oxidases, the advantages provided by copper over iron as the non-heme metal has remained unclear. Now, the preference of copper over iron has finally been explained. Copper favours faster electron transfer and higher O–O bond activation, which results in much higher oxidase activity than would be achieved by an iron equivalent.
- Ambika Bhagi-Damodaran
- , Matthew A. Michael
- & Yi Lu
-
Article |
 Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
FeFe hydrogenases are highly efficient H2 producing enzymes; however, they can be inactivated by O2. Now, a mechanism for O2 diffusion within FeFe hydrogenases and its reactions at the active site of the enzyme has been proposed. These findings could help with the design of hydrogenase mutants with increased resistance to oxidative damage.
- Adam Kubas
- , Christophe Orain
- & Christophe Léger
-
Article |
 Nickel-centred proton reduction catalysis in a model of [NiFe] hydrogenase
Nickel-centred proton reduction catalysis in a model of [NiFe] hydrogenase
[NiFe] hydrogenases are enzymes containing nickel and iron centres that catalyse hydrogen evolution with performances that rival those of platinum catalysts. Now, a NiFe model complex has been reported that mimics the structure and the Ni-centred hydrogen evolution activity found at the active site of [NiFe] hydrogenases.
- Deborah Brazzolotto
- , Marcello Gennari
- & Carole Duboc
-
Editorial |
Now we NO
Nitric oxide (NO) is an important signalling molecule in biological systems, but it is unclear exactly how it interacts with some metalloproteins. Now, a collection of articles in this issue reveal how NO binds to proteins containing type-1 copper sites.
-
News & Views |
 A switch for blue copper proteins?
A switch for blue copper proteins?
Nitric oxide (NO) has important functions in all forms of life and serves, for example, as a signalling molecule in mammals. Now, two complementary studies have uncovered how NO binds to blue copper proteins. This research suggests a mechanism by which NO could regulate the activity of blue copper proteins involved in denitrification.
- Subhra Samanta
- & Nicolai Lehnert
-
Article |
 Reversible S-nitrosylation in an engineered azurin
Reversible S-nitrosylation in an engineered azurin
S-Nitrosylation has emerged as an important pathway for dynamic post-translational regulation of many classes of proteins. Now, the reversible insertion of NO into a copper–thiolate bond has been observed under physiologically relevant conditions using an engineered azurin. DFT calculation indicates that the reaction proceeds via a radical combination mechanism.
- Shiliang Tian
- , Jing Liu
- & Yi Lu
-
Article |
 A motif for reversible nitric oxide interactions in metalloenzymes
A motif for reversible nitric oxide interactions in metalloenzymes
NO participates in numerous physiological processes of which many involve the reaction of
NO with metalloenzymes to form a metal–nitrosyl (M–NO). Now, addition ofNO to models of type 1 Cu sites has provided a fully characterized S-nitrosothiol adduct, [CuI](κ1-N(O)SR), that reversibly losesNO upon purging with an inert gas. These findings suggest a new motif for reversible binding of nitric oxide at bioinorganic metal centres.- Shiyu Zhang
- , Marie M. Melzer
- & Timothy H. Warren
-
Article |
 Inhibition of human copper trafficking by a small molecule significantly attenuates cancer cell proliferation
Inhibition of human copper trafficking by a small molecule significantly attenuates cancer cell proliferation
Copper is a transition metal ion essential for the regulation of cellular oxidative stress and ATP production. Now, the inhibition of copper-trafficking proteins by a small molecule has been shown to significantly reduce proliferation of cancer cells. The results indicate that copper-trafficking proteins could represent new anti-tumour therapeutic targets.
- Jing Wang
- , Cheng Luo
- & Chuan He
-
Article |
 Reconstitution of [Fe]-hydrogenase using model complexes
Reconstitution of [Fe]-hydrogenase using model complexes
[Fe]-hydrogenase has an iron-guanylylpyridinol cofactor and catalyses the reversible hydrogenation of a methenyl-tetrahydromethanopterin. Now, [Fe]-hydrogenase has been reconstituted using synthetic cofactor mimics. The enzyme containing a mimic with a 2-hydroxy-pyridine group was active, whereas one containing a 2-methoxy-pyridine group was inactive. This result, together with DFT computations, supports a catalytic mechanism involving the deprotonated pyridinol hydroxy group as a proton acceptor.
- Seigo Shima
- , Dafa Chen
- & Xile Hu
-
News & Views |
 Nanocrystals by design
Nanocrystals by design
Nanocrystals with precisely defined structures offer promise as components of advanced materials yet they are challenging to create. Now, a nanocrystal made up of seven cadmium and twelve chloride ions has been synthesized via a biotemplating approach that uses a de novo designed protein.
- Li Shang
- & Gerd Ulrich Nienhaus
-
News & Views |
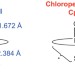 The long and the short of it
The long and the short of it
Preparation and structural characterization of the catalytic intermediates of two similar thiolate-ligated haem proteins (cytochrome P450 Compound-I and chloroperoxidase Compound-I) has explained the structural basis for the difference in their reactivity.
- Ilia G. Denisov
- & Stephen G. Sligar
-
Article |
 Significantly shorter Fe–S bond in cytochrome P450-I is consistent with greater reactivity relative to chloroperoxidase
Significantly shorter Fe–S bond in cytochrome P450-I is consistent with greater reactivity relative to chloroperoxidase
Cytochrome P450 (P450) and chloroperoxidase (CPO) are both thiolate-ligated haem proteins that form a ferryl radical species called compound I. P450-I is, however, significantly more reactive than CPO-I. Variable-temperature Mössbauer and X-ray absorption measurements have now shown that increased electron donation from the axial thiolate ligand in P450-I may explain its greater propensity for C–H bond activation.
- Courtney M. Krest
- , Alexey Silakov
- & Michael T. Green
-

 Lifting iron higher and higher
Lifting iron higher and higher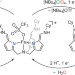 Nitrate NO more
Nitrate NO more Harnessing haemoproteins
Harnessing haemoproteins