Featured
-
-
Article |
 Magnetic-field-sensitive charge density waves in the superconductor UTe2
Magnetic-field-sensitive charge density waves in the superconductor UTe2
A study using scanning tunnelling microscopy reveals a charge-density-wave state that is sensitive to magnetic fields and strongly intertwined with superconductivity in the heavy-fermion triplet superconductor UTe2.
- Anuva Aishwarya
- , Julian May-Mann
- & Vidya Madhavan
-
Review Article |
 A second wave of topological phenomena in photonics and acoustics
A second wave of topological phenomena in photonics and acoustics
The current state of the art of topological phenomena in photonics and acoustics is reviewed and future research directions for valuable applications are discussed.
- Xiujuan Zhang
- , Farzad Zangeneh-Nejad
- & Johan Christensen
-
Article |
 Excitonic topological order in imbalanced electron–hole bilayers
Excitonic topological order in imbalanced electron–hole bilayers
This study reports an excitonic topological order emerging in imbalanced electron–hole bilayers.
- Rui Wang
- , Tigran A. Sedrakyan
- & Rui-Rui Du
-
Article |
 Signatures of fractional quantum anomalous Hall states in twisted MoTe2
Signatures of fractional quantum anomalous Hall states in twisted MoTe2
Signatures of fractional quantum anomalous Hall states at zero magnetic field are observed in a fractionally filled moiré superlattice in a molybdenum ditelluride twisted bilayer.
- Jiaqi Cai
- , Eric Anderson
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Article |
 Non-orientable order and non-commutative response in frustrated metamaterials
Non-orientable order and non-commutative response in frustrated metamaterials
We describe globally frustrated matter as deformations of non-orientable surfaces, with the concept of non-orientable order we demonstrate topologically protected mechanical memories, suggesting a design principle for effectively storing information in frustrated metamaterials.
- Xiaofei Guo
- , Marcelo Guzmán
- & Corentin Coulais
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral phonons in quartz probed by X-rays
Chiral phonons in quartz probed by X-rays
Our experimental proof of chiral phonons demonstrates a degree of freedom in condensed matter that is of fundamental importance and opens the door to exploration of emergent phenomena based on chiral bosons.
- Hiroki Ueda
- , Mirian García-Fernández
- & Urs Staub
-
Article |
 Orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in an Ising superconductor
Orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in an Ising superconductor
The discovery of an orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in the multilayer Ising superconductor 2H-NbSe2, in which the translational and rotational symmetries are broken, enables the preparation of such states in other materials with broken inversion symmetries.
- Puhua Wan
- , Oleksandr Zheliuk
- & Jianting Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Density-wave ordering in a unitary Fermi gas with photon-mediated interactions
Density-wave ordering in a unitary Fermi gas with photon-mediated interactions
An experiment with atoms and photons provides a fully tunable and microscopically controllable platform for the experimental study of the interplay of superfluidity and density-wave order.
- Victor Helson
- , Timo Zwettler
- & Jean-Philippe Brantut
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Petahertz-scale optical-field metrology in a pump-probe setting enables the direct observation of how the optical properties of a medium evolve after 1-fs-scale photoinjection.
- Dmitry A. Zimin
- , Nicholas Karpowicz
- & Vladislav S. Yakovlev
-
Article
| Open Access Absence of near-ambient superconductivity in LuH2±xNy
Absence of near-ambient superconductivity in LuH2±xNy
Nitrogen-doped lutetium hydrides LuH2±xNy synthesized using a high-pressure and high-temperature synthesis technique did not show near-ambient superconductivity at pressures below 40.1 GPa.
- Xue Ming
- , Ying-Jie Zhang
- & Hai-Hu Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Abelian braiding of graph vertices in a superconducting processor
Non-Abelian braiding of graph vertices in a superconducting processor
A unitary protocol for braiding projective non-Abelian Ising anyons in a generalized stabilizer code is implemented on a superconducting processor, allowing for verification of their fusion rules and realization of their exchange statistics.
- T. I. Andersen
- , Y. D. Lensky
- & P. Roushan
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced high-temperature ferromagnetism in YTiO3
Photo-induced high-temperature ferromagnetism in YTiO3
All-optical, mode-selective manipulation of the crystal lattice can be used to enhance and stabilize ferromagnetism in YTiO3 well above its equilibrium ordering temperature and for many nanoseconds, enabling dynamic engineering of practically useful non-equilibrium functionalities in fluctuating electronic systems.
- A. S. Disa
- , J. Curtis
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article |
 Particle–hole symmetry protects spin-valley blockade in graphene quantum dots
Particle–hole symmetry protects spin-valley blockade in graphene quantum dots
Bilayer graphene allows the realization of electron–hole double-quantum dots that exhibit near-perfect particle–hole symmetry, in which transport occurs via the creation and annihilation of single electron–hole pairs with opposite quantum numbers.
- L. Banszerus
- , S. Möller
- & C. Stampfer
-
Article |
 Partitioning of diluted anyons reveals their braiding statistics
Partitioning of diluted anyons reveals their braiding statistics
A simple experimental method identifies the statistical phase of highly diluted abelian anyons weakly partitioned in fractional quantum Hall states and reveals their braiding statistics.
- June-Young M. Lee
- , Changki Hong
- & H.-S. Sim
-
Article |
 Nodeless electron pairing in CsV3Sb5-derived kagome superconductors
Nodeless electron pairing in CsV3Sb5-derived kagome superconductors
The authors report that with the use of angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, nodeless electron pairing in CsV3Sb5-derived kagome superconductors can be observed directly.
- Yigui Zhong
- , Jinjin Liu
- & Kozo Okazaki
-
Article |
 Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Experimental observation and calculations show that broken reflection symmetry in graphene heterostructures allows tunable electron–flexural phonon coupling, providing a way to control quantum matter at the atomic scale.
- Mir Mohammad Sadeghi
- , Yajie Huang
- & Li Shi
-
Article |
 Quantum critical dynamics in a 5,000-qubit programmable spin glass
Quantum critical dynamics in a 5,000-qubit programmable spin glass
Using a quantum annealing processor to study three-dimensional spin glasses demonstrates an accurate large-scale quantum simulation of critical dynamics and a scaling advantage over analogous classical methods for energy optimization.
- Andrew D. King
- , Jack Raymond
- & Mohammad H. Amin
-
Research Briefing |
 Quantization observed for ‘heavy’ electrons
Quantization observed for ‘heavy’ electrons
Quantum materials can host exotic phases of matter in which electrons form unusual collective states. Scientists have struggled to observe the quantization that these electronic states are expected to show, but this phenomenon has now been detected in heavy states at the surface of a superconducting quantum material.
-
Article |
 Build-up and dephasing of Floquet–Bloch bands on subcycle timescales
Build-up and dephasing of Floquet–Bloch bands on subcycle timescales
The build-up and dephasing of Floquet-–Bloch bands is visualized in both subcycle band-structure videography and quantum theory, revealing the interplay of strong-field intraband and interband excitations in a non-equilibrium Floquet picture.
- S. Ito
- , M. Schüler
- & R. Huber
-
News & Views |
 Elusive excited states identified from cutting-edge molecular movies
Elusive excited states identified from cutting-edge molecular movies
A molecular process called singlet fission might boost solar-cell efficiency, but the mechanism must first be determined. A technique that probes molecules undergoing this process finally reveals the excited states involved.
- Andrew J. Musser
- & Hannah Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Giant magnetoresistance of Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene
Giant magnetoresistance of Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene
A Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene shows anomalous magnetotransport and giant magnetoresistance that reaches more than 100 per cent in a low magnetic field at room temperature.
- Na Xin
- , James Lourembam
- & Alexey I. Berdyugin
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital-resolved observation of singlet fission
Orbital-resolved observation of singlet fission
Time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy is used to observe the primary step of singlet fission with orbital resolution indicating a charge-transfer mediated mechanism with a hybridization of states in the lowest bright singlet exciton.
- Alexander Neef
- , Samuel Beaulieu
- & Ralph Ernstorfer
-
Article
| Open Access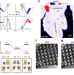 Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
A single-element ferroelectric state is observed in a black phosphorus-like bismuth layer, in which the ordered charge transfer and the regular atom distortion between sublattices happen simultaneously and ferroelectric switching is further visualized experimentally.
- Jian Gou
- , Hua Bai
- & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
-
Article |
 Mechanistic formulation of inorganic membranes at the air–liquid interface
Mechanistic formulation of inorganic membranes at the air–liquid interface
By switching the nucleation preferences in aqueous systems of inorganic precursors to bias formation and growth at the air–liquid interface, the mechanistic formation of inorganic membranes from the floating-particle system is demonstrated.
- Chen Zhang
- , Wanheng Lu
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum-well states at the surface of a heavy-fermion superconductor
Quantum-well states at the surface of a heavy-fermion superconductor
By using millikelvin scanning tunnelling microscopy to study atomically flat terraces on U-terminated surfaces of the heavy-fermion superconductor URu2Si2, the two-dimensional heavy fermions are shown to form quantum-well states on the surface.
- Edwin Herrera
- , Isabel Guillamón
- & Hermann Suderow
-
Article |
 Gate-tunable heavy fermions in a moiré Kondo lattice
Gate-tunable heavy fermions in a moiré Kondo lattice
A Kondo lattice was realized in AB-stacked MoTe2/WSe2 moiré bilayers and widely and continuously gate-tunable Kondo temperatures were demonstrated.
- Wenjin Zhao
- , Bowen Shen
- & Jie Shan
-
News & Views |
 Hopes raised for room-temperature superconductivity, but doubts remain
Hopes raised for room-temperature superconductivity, but doubts remain
A hydrogen-rich compound has taken the lead in the race for a material that can conduct electricity with zero resistance at room temperature and ambient pressure — the conditions required for many technological applications.
- ChangQing Jin
- & David Ceperley
-
Article |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: Evidence of near-ambient superconductivity in a N-doped lutetium hydride
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Evidence of near-ambient superconductivity in a N-doped lutetium hydride
A nitrogen-doped lutetium hydride was synthesized under high-pressure high-temperature conditions and, following full recoverability, examination along compression pathways showed evidence of superconductivity at room temperature and near-ambient pressures.
- Nathan Dasenbrock-Gammon
- , Elliot Snider
- & Ranga P. Dias
-
Article |
 Anomalous intense coherent secondary photoemission from a perovskite oxide
Anomalous intense coherent secondary photoemission from a perovskite oxide
The reconstructed surface of single crystals of SrTiO3(100), prepared by simple vacuum annealing, produces discrete secondary photoemission spectra at room temperature and has increased peak intensities at low temperatures.
- Caiyun Hong
- , Wenjun Zou
- & Rui-Hua He
-
Article
| Open Access Diode effect in Josephson junctions with a single magnetic atom
Diode effect in Josephson junctions with a single magnetic atom
By analysing atomic-scale Pb–Pb Josephson junctions including magnetic atoms in a scanning tunnelling microscope, a new mechanism for diode behaviour is demonstrated, opening up new paths to tune their properties by means of single-atom manipulation.
- Martina Trahms
- , Larissa Melischek
- & Katharina J. Franke
-
Article |
 Critical role of hydrogen for superconductivity in nickelates
Critical role of hydrogen for superconductivity in nickelates
In optimally doped Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2H epitaxial film, combined state-of-the-art experimental and theoretical approaches show abundant hydrogen with zero resistivity, and its critical role in superconductivity in epitaxial infinite-layer nickelates.
- Xiang Ding
- , Charles C. Tam
- & Liang Qiao
-
Article |
 Disorder-tuned conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon
Disorder-tuned conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon
Varying growth temperatures enables the tuning of the degree of disorder, which is fully described by the absence/presence of medium-range order and temperature-dependent densities of nanocrystallites, and electrical conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon films.
- Huifeng Tian
- , Yinhang Ma
- & Lei Liu
-
Article |
 Continuous symmetry breaking in a two-dimensional Rydberg array
Continuous symmetry breaking in a two-dimensional Rydberg array
A two-dimensional dipolar XY model with a continuous spin-rotational symmetry is realized using a programmable Rydberg quantum simulator, complementing recent studies using the Rydberg-blockade mechanism to realize Ising-type interactions showing discrete spin rotation symmetry.
- Cheng Chen
- , Guillaume Bornet
- & Antoine Browaeys
-
Article |
 Geometric frustration of Jahn–Teller order in the infinite-layer lattice
Geometric frustration of Jahn–Teller order in the infinite-layer lattice
A distorted infinite-layer lattice of single-crystal CaCoO2 originates from competition between an ordered Jahn–Teller effect and geometric frustration.
- Woo Jin Kim
- , Michelle A. Smeaton
- & Harold Y. Hwang
-
News & Views |
 A twist in the bid to probe electrons in solids
A twist in the bid to probe electrons in solids
Two microscopy techniques have been merged into a tool for twisting ultrathin sheets of atoms relative to each other. The approach offers a new angle for studying the electronic properties of exotic layered materials.
- Rebeca Ribeiro-Palau
-
Research Briefing |
 Twisted-bilayer materials simulated using ultracold atoms
Twisted-bilayer materials simulated using ultracold atoms
A system of ultracold rubidium atoms confined by two misaligned laser-beam arrays has been used to simulate remarkable structures called twisted-bilayer materials. The atomic technology exhibits phenomena such as superfluidity — the frictionless flow of atoms — typically observed in these materials.
-
Article |
 Topological spin texture in the pseudogap phase of a high-Tc superconductor
Topological spin texture in the pseudogap phase of a high-Tc superconductor
Using Lorentz transmission electron microscopy, one of the first direct observations of topological spin texture is described, in the pseudogap phase of a high-temperature cuprate superconductor based on YBa2Cu3O6+x.
- Zechao Wang
- , Ke Pei
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article |
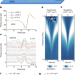 Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
By using new on-chip terahertz spectroscopy techniques to measure the absorption spectra of a graphene microribbon as well as the energy waves close to charge neutrality, hydrodynamic collective excitations are observed.
- Wenyu Zhao
- , Shaoxin Wang
- & Feng Wang
-
Article |
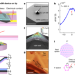 The quantum twisting microscope
The quantum twisting microscope
A quantum twisting microscope based on a unique van der Waals tip and capable of performing local interference experiments opens the way for new classes of experiments on quantum materials.
- A. Inbar
- , J. Birkbeck
- & S. Ilani
-
Article |
 Realization of a minimal Kitaev chain in coupled quantum dots
Realization of a minimal Kitaev chain in coupled quantum dots
A minimal artificial Kitaev chain can be realized by using two spin-polarized quantum dots in an InSb nanowire strongly coupled by both elastic co-tunnelling and crossed Andreev reflection.
- Tom Dvir
- , Guanzhong Wang
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article |
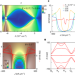 Evidence for Dirac flat band superconductivity enabled by quantum geometry
Evidence for Dirac flat band superconductivity enabled by quantum geometry
The authors investigate the effect of small velocity in a superconducting Dirac flat band system, finding evidence for small pairs and that superfluid stiffness is not dominated by kinetic energy.
- Haidong Tian
- , Xueshi Gao
- & Marc W. Bockrath
-
Article |
 Spin-polarized spatially indirect excitons in a topological insulator
Spin-polarized spatially indirect excitons in a topological insulator
A topological insulator, Bi2Te3, has been found to have spatially indirect spin-polarized excitonic states, opening the prospect of combining exciton and topological physics.
- Ryo Mori
- , Samuel Ciocys
- & Alessandra Lanzara
-
News & Views |
 Light tailors the electronic properties of a model semiconductor
Light tailors the electronic properties of a model semiconductor
When a semiconductor material called black phosphorus is hit with intense laser light, the behaviour of its electrons is found to change. The discovery opens a route to time-dependent engineering of exotic electronic phases in solids.
- Alberto Crepaldi
-
Article |
 Pseudospin-selective Floquet band engineering in black phosphorus
Pseudospin-selective Floquet band engineering in black phosphorus
In black phosphorus, a model semiconductor, analysis of time and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy measurements demonstrates a strong light-induced band renormalization with light polarization dependence, suggesting pseudospin-selective Floquet band engineering.
- Shaohua Zhou
- , Changhua Bao
- & Shuyun Zhou
-
Article |
 Down-conversion of a single photon as a probe of many-body localization
Down-conversion of a single photon as a probe of many-body localization
An experiment is described in which the conversion of a single photon in a multimode cavity into a shower of low-energy photons was attempted, but failed owing to many-body localization and violation of Fermi’s golden rule.
- Nitish Mehta
- , Roman Kuzmin
- & Vladimir E. Manucharyan
-
Obituary |
 Alexander Müller (1927–2023)
Alexander Müller (1927–2023)
Physicist and co-discoverer of high-temperature superconductivity.
- Joseph D. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Octupole-driven magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnetic tunnel junction
Octupole-driven magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnetic tunnel junction
The authors report observation of tunnelling magnetoresistance in an all-antiferromagnetic tunnel junction consisting of Mn3Sn/MgO/Mn3Sn, laying the foundation for the development of ultrafast and efficient spintronic devices using antiferromagnets.
- Xianzhe Chen
- , Tomoya Higo
- & Satoru Nakatsuji
-
Article |
 Giant spin polarization and a pair of antiparallel spins in a chiral superconductor
Giant spin polarization and a pair of antiparallel spins in a chiral superconductor
The simultaneous observation of spin–orbit interaction enhancement and chirality represented by a pair of oppositely polarized spins is reported for an organic chiral superconductor in the vicinity of the superconducting transition temperature.
- R. Nakajima
- , D. Hirobe
- & H. M. Yamamoto
-
News & Views |
 Broken mirror symmetry boosts current conversion in a superconductor
Broken mirror symmetry boosts current conversion in a superconductor
The intrinsic structure of a material called a chiral superconductor enhances the separation of charge carriers, transforming an electric current in a way that could change the future of memory storage at low temperatures.
- Angelo Di Bernardo
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

 Smectic pair-density-wave order in EuRbFe4As4
Smectic pair-density-wave order in EuRbFe4As4