Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
Giant energy storage and power density negative capacitance superlattices
- Suraj S. Cheema
- , Nirmaan Shanker
- & Sayeef Salahuddin
-
Article
| Open Access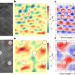 A 2D ferroelectric vortex pattern in twisted BaTiO3 freestanding layers
A 2D ferroelectric vortex pattern in twisted BaTiO3 freestanding layers
The stacking of freestanding ferroelectric perovskite layers with controlled twist angles results in a peculiar pattern of polarization vortices and antivortices that emerges from the flexoelectric coupling of polarization to strain gradients.
- G. Sánchez-Santolino
- , V. Rouco
- & J. Santamaria
-
Article |
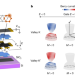 Orbital multiferroicity in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene
Orbital multiferroicity in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene
Orbital multiferroicity reported in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene features ferro-orbital-magnetism and ferro-valleytricity, both of which can be controlled by an electric field.
- Tonghang Han
- , Zhengguang Lu
- & Long Ju
-
Matters Arising |
 Dilemma in optical identification of single-layer multiferroics
Dilemma in optical identification of single-layer multiferroics
- Yucheng Jiang
- , Yangliu Wu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Matters Arising |
 Reply to: Dilemma in optical identification of single-layer multiferroics
Reply to: Dilemma in optical identification of single-layer multiferroics
- Qian Song
- , Connor A. Occhialini
- & Riccardo Comin
-
Article
| Open Access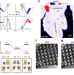 Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
A single-element ferroelectric state is observed in a black phosphorus-like bismuth layer, in which the ordered charge transfer and the regular atom distortion between sublattices happen simultaneously and ferroelectric switching is further visualized experimentally.
- Jian Gou
- , Hua Bai
- & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
-
Article |
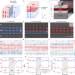 In-plane charged domain walls with memristive behaviour in a ferroelectric film
In-plane charged domain walls with memristive behaviour in a ferroelectric film
The direct observation of in-plane charged domain walls in BiFeO3 ferroelectric films a few nanometres thick, their deterministic creation, manipulation and annihilation by applied voltage, as well the demonstration of their memristive functionality is reported.
- Zhongran Liu
- , Han Wang
- & He Tian
-
Article |
 Coupled ferroelectricity and superconductivity in bilayer Td-MoTe2
Coupled ferroelectricity and superconductivity in bilayer Td-MoTe2
The authors show a hysteretic behaviour of superconductivity as a function of electric field in bilayer Td-MoTe2, representing observations of coupled ferroelectricity and superconductivity.
- Apoorv Jindal
- , Amartyajyoti Saha
- & Daniel A. Rhodes
-
Article |
 Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a non-reciprocal near-infrared femtosecond laser-writing technique for reconfigurable three-dimensional nanoscale ferroelectric domain engineering in LiNbO3 crystals.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Tianxin Wang
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Large harvested energy with non-linear pyroelectric modules
Large harvested energy with non-linear pyroelectric modules
A macroscopic and scalable pyroelectric energy harvester in the form of multilayer capacitors produces 11.2 J of electrical energy, with a pyroelectric material generating up to 4.43 J cm−3 per cycle.
- Pierre Lheritier
- , Alvar Torelló
- & Emmanuel Defay
-
Article |
 Topologically protected magnetoelectric switching in a multiferroic
Topologically protected magnetoelectric switching in a multiferroic
The electric polarization of a multiferroic is reversed by the application and subsequent removal of a magnetic field, resulting in topologically protected unidirectional magnetoelectric switching.
- Louis Ponet
- , S. Artyukhin
- & Andrei Pimenov
-
Article |
 Evidence for a single-layer van der Waals multiferroic
Evidence for a single-layer van der Waals multiferroic
Multiple complementary optical signatures confirm the persistence of ferroelectricity and inversion-symmetry-breaking magnetic order down to monolayer NiI2, introducing the physics of type-II multiferroics into the area of van der Waals materials.
- Qian Song
- , Connor A. Occhialini
- & Riccardo Comin
-
Article |
 Ferroelectric incommensurate spin crystals
Ferroelectric incommensurate spin crystals
Analysing the structure of a PbTiO3 epitaxial layer sandwiched between SrRuO3 electrodes led to observation of a topology with two periodic modulations that form an incommensurate polar crystal, providing an analogue to incommensurate spin crystals.
- Dorin Rusu
- , Jonathan J. P. Peters
- & Marin Alexe
-
Article |
 Subterahertz collective dynamics of polar vortices
Subterahertz collective dynamics of polar vortices
A dynamical study shows that vortices of electrical polarization have higher frequencies and smaller size than their magnetic counterparts, properties that are promising for electric-field-driven data processing.
- Qian Li
- , Vladimir A. Stoica
- & Haidan Wen
-
Article |
 Enhanced ferroelectricity in ultrathin films grown directly on silicon
Enhanced ferroelectricity in ultrathin films grown directly on silicon
Enhanced switchable ferroelectric polarization is achieved in doped hafnium oxide films grown directly onto silicon using low-temperature atomic layer deposition, even at thicknesses of just one nanometre.
- Suraj S. Cheema
- , Daewoong Kwon
- & Sayeef Salahuddin
-
Article |
 Non-volatile electric control of spin–charge conversion in a SrTiO3 Rashba system
Non-volatile electric control of spin–charge conversion in a SrTiO3 Rashba system
The polarization direction of a ferroelectric-like state can be used to control the conversion of spin currents into charge currents at the surface of strontium titanate, a non-magnetic oxide.
- Paul Noël
- , Felix Trier
- & Jean-Philippe Attané
-
Article |
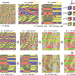 Transparent ferroelectric crystals with ultrahigh piezoelectricity
Transparent ferroelectric crystals with ultrahigh piezoelectricity
The use of alternating-current electric fields to control domain size in ferroelectric crystals affords excellent transparency, piezoelectricity and birefringence.
- Chaorui Qiu
- , Bo Wang
- & Fei Li
-
Article |
 Inverse transition of labyrinthine domain patterns in ferroelectric thin films
Inverse transition of labyrinthine domain patterns in ferroelectric thin films
The labyrinthine domain patterns formed in ultrathin films of ferroelectric oxides by subcritical quenching undergo an inverse phase transition to the less-symmetric parallel-stripe domain structure upon increasing temperature.
- Y. Nahas
- , S. Prokhorenko
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article |
 Real-space charge-density imaging with sub-ångström resolution by four-dimensional electron microscopy
Real-space charge-density imaging with sub-ångström resolution by four-dimensional electron microscopy
A real-space imaging technique that combines scanning transmission electron microscopy with an angle-resolved pixellated fast-electron detector is used to image the charge distribution in SrTiO3, BiFeO3 and the junction between them.
- Wenpei Gao
- , Christopher Addiego
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Large electrocaloric effects in oxide multilayer capacitors over a wide temperature range
Large electrocaloric effects in oxide multilayer capacitors over a wide temperature range
High-quality multilayer capacitors of a perovskite oxide show that large electric-field-driven caloric effects could improve solid-state refrigeration technology and challenge today’s standard (based on magnetocaloric effects in gadolinium).
- B. Nair
- , T. Usui
- & N. D. Mathur
-
Letter |
 Freestanding crystalline oxide perovskites down to the monolayer limit
Freestanding crystalline oxide perovskites down to the monolayer limit
Ultrathin freestanding crystalline films of transition-metal oxide perovskites are fabricated and transferred to various substrates, proving their potential for exploring emergent 2D correlated phases.
- Dianxiang Ji
- , Songhua Cai
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Letter |
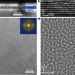 Observation of room-temperature polar skyrmions
Observation of room-temperature polar skyrmions
Chiral polar-skyrmion bubbles are observed in superlattices of titanium-based perovskite oxides at room temperature.
- S. Das
- , Y. L. Tang
- & R. Ramesh
-
Letter |
 Spatially resolved steady-state negative capacitance
Spatially resolved steady-state negative capacitance
Imaging steady-state negative capacitance in SrTiO3/PbTiO3 superlattices with atomic resolution provides solid microscale support for this phenomenon.
- Ajay K. Yadav
- , Kayla X. Nguyen
- & Sayeef Salahuddin
-
Letter |
 Unveiling the double-well energy landscape in a ferroelectric layer
Unveiling the double-well energy landscape in a ferroelectric layer
A ferroelectric thin film that behaves as a single domain is found to exhibit both negative capacitance and the predicted double-well polarization–energy relationship.
- Michael Hoffmann
- , Franz P. G. Fengler
- & Thomas Mikolajick
-
Letter |
 Ferroelectric polymers exhibiting behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary
Ferroelectric polymers exhibiting behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary
An organic copolymer with compositionally tailored tacticity exhibits behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary, with an intramolecular order-to-disorder transition in the crystalline phase and a very large piezoelectric coefficient.
- Yang Liu
- , Haibibu Aziguli
- & Qing Wang
-
Letter |
 Magnetoelectric inversion of domain patterns
Magnetoelectric inversion of domain patterns
The magnetization or polarization of domain states in multiferroics can be reversed while retaining the overall domain pattern, owing to the inherent versatility in coupling the large number of multiferroic order parameters.
- N. Leo
- , V. Carolus
- & M. Fiebig
-
Letter |
 Resonant domain-wall-enhanced tunable microwave ferroelectrics
Resonant domain-wall-enhanced tunable microwave ferroelectrics
The domain-wall structure and dynamics are found to enhance, rather than inhibit, the high-frequency performance of an intrinsically tunable material, obtaining ultralow loss and exceptional frequency selectivity.
- Zongquan Gu
- , Shishir Pandya
- & Jonathan E. Spanier
-
Letter |
 Ferroelectric switching of a two-dimensional metal
Ferroelectric switching of a two-dimensional metal
Two- and three-layer WTe2 exhibits spontaneous out-of-plane electric polarization that can be switched electrically at room temperature and is sufficiently robust for use in applications with other two-dimensional materials.
- Zaiyao Fei
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & David H. Cobden
-
Letter |
 Real-space imaging of non-collinear antiferromagnetic order with a single-spin magnetometer
Real-space imaging of non-collinear antiferromagnetic order with a single-spin magnetometer
A non-invasive scanning magnetometer, based on a single nitrogen–vacancy defect in diamond, visualizes antiferromagnetic order at the nanometre scale in thin films of bismuth ferrite at room temperature.
- I. Gross
- , W. Akhtar
- & V. Jacques
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Tayi et al. reply
Tayi et al. reply
- Alok S. Tayi
- , Alexander K. Shveyd
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Conflicting evidence for ferroelectricity
Conflicting evidence for ferroelectricity
- Gabriele D’Avino
- , Manuel Souto
- & Alberto Girlando
-
Letter |
 Slush-like polar structures in single-crystal relaxors
Slush-like polar structures in single-crystal relaxors
Molecular dynamics simulations of the Pb(Mg1/3,Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 relaxor reveal a multi-domain state analogous to the slush state of water that provides an explanation for the unusual properties of relaxors.
- Hiroyuki Takenaka
- , Ilya Grinberg
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Letter |
 Enhanced flexoelectric-like response in oxide semiconductors
Enhanced flexoelectric-like response in oxide semiconductors
Semiconducting single crystals of doped barium titanate and titanium dioxide exhibit a flexoelectric-like response upon bending that is much larger than in their undoped, insulating counterparts, reaching unprecedentedly large effective flexoelectric coefficients.
- Jackeline Narvaez
- , Fabian Vasquez-Sancho
- & Gustau Catalan
-
Letter |
 Atomically engineered ferroic layers yield a room-temperature magnetoelectric multiferroic
Atomically engineered ferroic layers yield a room-temperature magnetoelectric multiferroic
A single-phase multiferroic material is constructed, in which ferroelectricity and strong magnetic ordering are coupled near room temperature, enabling direct electric-field control of magnetism.
- Julia A. Mundy
- , Charles M. Brooks
- & Darrell G. Schlom
-
Letter |
 Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Molecular dynamics simulations of 90° domain walls in PbTiO3 are used to construct a nucleation-and-growth-based analytical model that quantifies the dynamics of many types of domain walls in various ferroelectrics, suggesting intrinsic domain-wall motion as a universal mechanism for ferroelectric switching.
- Shi Liu
- , Ilya Grinberg
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Letter |
 Negative capacitance in multidomain ferroelectric superlattices
Negative capacitance in multidomain ferroelectric superlattices
Negative capacitance is observed in a model system of multidomain ferroelectric–dielectric superlattices; the multidomain state can increase the temperature range over which negative capacitance can be observed.
- Pavlo Zubko
- , Jacek C. Wojdeł
- & Jorge Íñiguez
-
Letter |
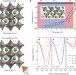 Polar metals by geometric design
Polar metals by geometric design
Ab initio calculations are used to identify the structural conditions under which a polar state in metals might be stabilized; this information is used to guide the experimental realization of new room-temperature polar metals.
- T. H. Kim
- , D. Puggioni
- & C. B. Eom
-
Letter |
 Observation of polar vortices in oxide superlattices
Observation of polar vortices in oxide superlattices
In material systems with several interacting degrees of freedom, the complex interplay between these factors can give rise to exotic phases; now superlattices consisting of alternating layers of PbTiO3 and SrTiO3 are found to exhibit an unusual form of ferroelectric ordering in the PbTiO3 layers, in which the electric dipoles arrange themselves into regular, ordered arrays of vortex–antivortex structures.
- A. K. Yadav
- , C. T. Nelson
- & R. Ramesh
-
Letter |
 Deterministic switching of ferromagnetism at room temperature using an electric field
Deterministic switching of ferromagnetism at room temperature using an electric field
Multiferroic devices that can switch magnetization with electric field at room temperature are desirable, but in BiFeO3 the required direct 180-degree switch is thermodynamically forbidden; here it is shown that such switching is possible because the kinetics of the switching process favours a two-step sequence of partial switching.
- J. T. Heron
- , J. L. Bosse
- & R. Ramesh
-
Letter |
 Artificial chemical and magnetic structure at the domain walls of an epitaxial oxide
Artificial chemical and magnetic structure at the domain walls of an epitaxial oxide
The strain induced on the walls between ferroelastic domains of a thin film of terbium manganite grown on a substrate of strontium titanate can generate an unusual two-dimensional ferromagnetic phase that is yet to be produced by conventional chemical means.
- S. Farokhipoor
- , C. Magén
- & B. Noheda
-
Letter |
 Perovskite oxides for visible-light-absorbing ferroelectric and photovoltaic materials
Perovskite oxides for visible-light-absorbing ferroelectric and photovoltaic materials
Most known ferroelectric photovoltaic materials have very wide electronic bandgaps (that is, they absorb only high-energy photons) but here a family of perovskite oxides is described that have tunable bandgaps, allowing their use across the whole visible-light spectrum.
- Ilya Grinberg
- , D. Vincent West
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Letter |
 Room-temperature ferroelectricity in supramolecular networks of charge-transfer complexes
Room-temperature ferroelectricity in supramolecular networks of charge-transfer complexes
Organic ferroelectrics with switchable electrical polarization would be an attractive prospect for applications if their Curie temperature—below which these materials display ferroelectric behaviour—could be raised to room temperature or above; this goal has now been achieved with a family of organic materials characterized by a supramolecular structural motif.
- Alok S. Tayi
- , Alexander K. Shveyd
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Letter |
 Perpendicular switching of a single ferromagnetic layer induced by in-plane current injection
Perpendicular switching of a single ferromagnetic layer induced by in-plane current injection
- Ioan Mihai Miron
- , Kevin Garello
- & Pietro Gambardella
-
Letter |
 A strong ferroelectric ferromagnet created by means of spin–lattice coupling
A strong ferroelectric ferromagnet created by means of spin–lattice coupling
Ferroelectric ferromagnets — materials that are both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic — are of significant technological interest. But they are rare, and those that do exist have weak ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties. Recently a new way of fabricating such materials was proposed, involving strain from the underlying substrate. This route has now been realized experimentally for EuTiO3. The work shows that a single experimental parameter, strain, can simultaneously control multiple order parameters.
- June Hyuk Lee
- , Lei Fang
- & Darrell G. Schlom
-
Letter |
 Above-room-temperature ferroelectricity in a single-component molecular crystal
Above-room-temperature ferroelectricity in a single-component molecular crystal
Ferroelectrics are electro-active materials that can store and switch their polarity, sense temperature changes, interchange electric and mechanical functions, and manipulate light. Subtle changes in the topology of certain chemical bonds have long been identified as a possible route for achieving ferroelectricity in organic molecular crystals. Ferroelectricity above room temperature is now demonstrated by applying an electric field to coherently align the molecular polarities in crystalline croconic acid.
- Sachio Horiuchi
- , Yusuke Tokunaga
- & Yoshinori Tokura

 Terahertz electric-field-driven dynamical multiferroicity in SrTiO3
Terahertz electric-field-driven dynamical multiferroicity in SrTiO3