Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Contemporary tools to predict cardiovascular risk lack accuracy on an individual-patient level. The use of single-cell RNA sequencing to identify specific leukocyte patterns might overcome some of these limitations, propelling us towards a precision medicine approach.
- Johannes Gollmer
- & Andreas Zirlik
-
Research Highlight |
 Young women with AMI have worse outcomes than men up to 1 year after discharge
Young women with AMI have worse outcomes than men up to 1 year after discharge
Findings from the VIRGO study reveal that young women with acute myocardial infarction are more likely to be rehospitalized within 1 year compared with similarly aged men.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Aggregation of big tau disrupts microtubules and causes diastolic dysfunction
Aggregation of big tau disrupts microtubules and causes diastolic dysfunction
Hyperphosphorylation of tau in the heart reduces the tyrosination of microtubules, leading to myocardial stiffness and heart failure. This novel mechanism of diastolic dysfunction parallels the aggregation of tau in the brain that leads to Alzheimer disease and might be amenable to treatment using monoclonal antibodies against tau.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, assessment and prevention
Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, assessment and prevention
Individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus are at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). In the context of type 2 diabetes mellitus, Wong and Sattar discuss established and novel mechanisms of CVD, risk assessment and patient stratification, and strategies to reduce multiple risk factors to prevent CVD.
- Nathan D. Wong
- & Naveed Sattar
-
Review Article |
 Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
In this Review, Kroemer and colleagues describe eight molecular hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing: disabled macroautophagy, loss of proteostasis, genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, cell senescence, dysregulated neurohormonal signalling and inflammation. Therapeutically targeting these hallmarks might attenuate residual cardiovascular risk in older individuals.
- Mahmoud Abdellatif
- , Peter P. Rainer
- & Guido Kroemer
-
Review Article |
 Interventional therapies for pulmonary embolism
Interventional therapies for pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is the leading cause of in-hospital death and the third most frequent cause of cardiovascular death. In this Review, Mahfoud and colleagues discuss the growing range of interventional, catheter-based approaches for the treatment of pulmonary embolism as well as risk stratification and patient selection for these procedures.
- Felix Götzinger
- , Lucas Lauder
- & Felix Mahfoud
-
Comment |
 Clonal haematopoiesis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Clonal haematopoiesis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is defined as an expansion of mutant blood stem cells in individuals without haematological malignancies. CHIP is linked to an increased risk of non-cancerous disorders such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, possibly because mutant innate immune cells have pro-inflammatory phenotypes. Prospective studies are needed to determine whether individuals with CHIP might benefit from anti-inflammatory therapies.
- Herra Ahmad
- & Siddhartha Jaiswal
-
Comment |
 Mapping the functions of IgM antibodies in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Mapping the functions of IgM antibodies in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
IgM antibodies have gained much attention as risk markers of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but the exact antigenic determinants and the full spectrum of functions remain to be defined. A better understanding of the potentially diverse nature of the antigens that they recognize will help to dissect the function of IgM in atherosclerosis.
- Justine Deroissart
- & Christoph J. Binder
-
Review Article |
 Maternal cardiovascular disorders before and during pregnancy and offspring cardiovascular risk across the life course
Maternal cardiovascular disorders before and during pregnancy and offspring cardiovascular risk across the life course
In this Review, Gaillard and Jaddoe describe how maternal cardiovascular disorders, occurring before and during pregnancy, can influence cardiovascular health in the offspring from embryonic life until adulthood. Furthermore, the authors highlight critical periods for cardiovascular adaptations, including preconception, early pregnancy and infancy, and how the events occurring during these periods can have an effect on future cardiovascular health.
- Romy Gaillard
- & Vincent W. V. Jaddoe
-
Review Article |
 The contribution of the exposome to the burden of cardiovascular disease
The contribution of the exposome to the burden of cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Münzel and colleagues describe the exposome concept with a focus on environmental physical and chemical exposures and their effects on the burden of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, they discuss selected exposome studies and the relevance of the exposome concept for future health research and preventive medicine.
- Thomas Münzel
- , Mette Sørensen
- & Andreas Daiber
-
Comment |
 A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
Lipophagy is a type of selective autophagy that targets lipid droplets for degradation. Since the discovery of lipophagy in 2009, research has uncovered a central role for this process in cellular lipid metabolism, including in atherogenic foam cells. Therefore, increasing lipophagy might be a therapeutic target to reverse lipid build-up in atherosclerosis.
- Thomas Laval
- & Mireille Ouimet
-
Comment |
 A high-salt diet promotes atherosclerosis by altering haematopoiesis
A high-salt diet promotes atherosclerosis by altering haematopoiesis
Excessive salt intake is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease commonly associated with hypertension. However, we propose that a high-salt diet can promote cardiovascular and other diseases independently of high blood pressure through inflammatory pathways that increase the production of myeloid cells.
- Man K. S. Lee
- & Andrew J. Murphy
-
Research Highlight |
AI outperforms sonographers at diagnosing cardiac function on echocardiography
An artificial intelligence-guided workflow for initial evaluation of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiography is non-inferior to initial assessment by a sonographer, according to findings from a blinded, randomized, non-inferiority clinical trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 The bidirectional association between atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction
The bidirectional association between atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction
A bidirectional relationship exists between atrial fibrillation (AF) and myocardial infarction (MI) as a result of shared risk factors and both direct and indirect mechanisms. In this Review, Frederiksen and colleagues discuss the pathogenesis, prevention and management of AF in patients with MI and of MI in patients with AF.
- Tanja Charlotte Frederiksen
- , Christina Catherine Dahm
- & Jelena Kornej
-
Review Article |
 Novel and future lipid-modulating therapies for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
Novel and future lipid-modulating therapies for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
In this Review, the authors discuss current treatment regimens for lowering plasma LDL cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, highlight treatment gaps and challenges, as well as describe opportunities raised by novel available therapies and potential future therapeutic approaches.
- Julia Brandts
- & Kausik K. Ray
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Improving the cardiovascular health care of transgender and non-binary persons
Improving the cardiovascular health care of transgender and non-binary persons
Research consistently shows that gender-affirming practices improve markers of cardiovascular health. Consequently, the focus of the management of the cardiovascular health of transgender and non-binary populations should not be on their hormone therapies and surgical histories, but should instead be rooted in the routine screening of cardiovascular risk factors.
- Arjee Restar
- & Carl G. Streed Jr
-
Research Highlight |
 Increased degradation of desmosomal proteins in ACM
Increased degradation of desmosomal proteins in ACM
Desmosomal protein degradation that occurs via a mechanism involving the ubiquitin–proteasome system might underlie the development of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
- Karina Huynh
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Factor XI inhibitors in patients with cardiovascular disease and a high risk of bleeding: a cautionary tale
Factor XI inhibitors in patients with cardiovascular disease and a high risk of bleeding: a cautionary tale
Factor XIa inhibitors are being tested in clinical trials, with the assumption that these agents are as effective as direct oral anticoagulants but cause fewer bleeding events. Findings from phase II trials of direct inhibitors of factor XIa for the prevention of first-ever and recurrent ischaemic stroke or recurrent major coronary artery events suggest fewer bleeding events but with uncertainty about efficacy.
- Bruna Gigante
- & Hugo ten Cate
-
Review Article |
 Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy
Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy
In this Review, Gawaz and colleagues discuss the pathophysiological role of platelets in acute myocardial ischaemia, vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic progression, summarize the current clinical concepts in antiplatelet therapy and describe novel therapeutic targets for antiplatelet drugs that are currently in development.
- Meinrad Gawaz
- , Tobias Geisler
- & Oliver Borst
-
Comment |
Implementing LGBTQ-inclusive policies for cardiology practice and the workforce
Establishing and enforcing LGBTQ-inclusive policies at the national, state and institutional level are essential for advancing health equity and ensuring the highest quality cardiology workforce.
- Tonia Poteat
- & Mabel Toribio
-
Review Article |
 Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) receptor agonists reduce the rate of major adverse cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this Review, Ussher and Drucker discuss the possible mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit of GLP1 receptor agonists and highlight the novel GLP1-based multi-agonists currently in development.
- John R. Ussher
- & Daniel J. Drucker
-
Research Highlight |
Intravascular imaging improves outcomes
In patients with complex coronary lesions, percutaneous coronary intervention guided by intravascular imaging improved cardiovascular outcomes compared with percutaneous coronary intervention guided by angiography.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Bempedoic acid prevents cardiovascular events in statin-intolerant patients
Bempedoic acid prevents cardiovascular events in statin-intolerant patients
In the CLEAR Outcomes trial, bempedoic acid lowered plasma LDL-cholesterol levels and reduced the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events in individuals who were intolerant to statin therapy.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Transcatheter repair for severe tricuspid regurgitation
Tricuspid transcatheter edge-to-edge repair in patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation improved quality of life and reduced disease severity compared with medical therapy
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
A wearable sensor to measure troponin I levels
A wrist-worn, transdermal sensor can be used to measure plasma levels of cardiac troponin I, potentially facilitating the diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Oral PCSK9 inhibitor is effective and safe
MK-0616, an oral inhibitor of PCSK9, safely and effectively lowers plasma levels of LDL cholesterol in a dose-dependent manner in patients with hypercholesterolaemia.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Immediate non-inferior to staged complete revascularization
Immediate complete revascularization is as safe and effective as staged complete revascularization in patients with acute coronary syndrome and multivessel disease, according to findings from the BIOVASC trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Suitability of TAVI in low-risk patients
In the Evolut Low Risk study, transcatheter aortic valve implantation in low-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis compared favourably with surgical aortic valve replacement in terms of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke at 3 years.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Non-thermal ablation of AF is safe and effective
According to findings from the PULSED AF trial, pulsed field ablation for atrial fibrillation is associated with a very low incidence of serious procedure-related adverse events and has an effectiveness consistent with that of established thermal ablation methods.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
 Sotatercept improves exercise capacity in patients with PAH
Sotatercept improves exercise capacity in patients with PAH
Findings from the STELLAR trial show that the addition of sotatercept to background therapy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension significantly improved exercise capacity compared with placebo.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
 Optically induced tachycardia evokes anxiety in risky settings
Optically induced tachycardia evokes anxiety in risky settings
Deisseroth and colleagues used a novel optogenetic system to pace the heart and determine whether an increase in heart rate can evoke anxiety-like behaviours.
- Karina Huynh
-
Review Article |
 Obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases
Obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases
In this Review, Lucia and colleagues explain why obesity is an evolutionarily novel condition, summarize the epidemiological evidence for its detrimental cardiometabolic consequences, discuss the major mechanisms involved in the association between obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, and examine the evidence for potential ‘healthy’ phenotypes associated with obesity.
- Pedro L. Valenzuela
- , Pedro Carrera-Bastos
- & Alejandro Lucia
-
Research Highlight |
Artificial sweetener linked to higher CVD risk
The non-nutritive sweetener erythritol, a widely used sugar substitute, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including myocardial infarction and stroke, according to a new study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Promising findings for cell therapy in HFrEF
Findings from the DREAM-HF trial, the largest clinical trial of cell therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) to date, suggest that cardiac therapy with mesenchymal precursor cells might benefit patients with HFrEF, particularly those with inflammation.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Obstructive sleep apnoea heterogeneity and cardiovascular disease
Obstructive sleep apnoea heterogeneity and cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Redline and colleagues summarize our understanding of the shared risk factors and causal links between obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and cardiovascular disease and emerging knowledge on the heterogeneity of OSA. They also explore the potential role of new biomarkers for cardiovascular risk stratification in patients with OSA.
- Susan Redline
- , Ali Azarbarzin
- & Yüksel Peker
-
Clinical Outlook |
Detection of subclinical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is defined by ventricular hypertrophy. However, the broader phenotype includes abnormal cardiomyocyte orientation (disarray), myocardial ischaemia and electrical abnormalities, which seem to manifest before overt hypertrophy. With advances in cascade genetic testing and novel therapeutic agents, the detection of subclinical HCM is a rapidly emerging priority. In this context, we outline the role of novel biomarkers, particularly quantitative perfusion and diffusion tensor MRI.
- George Joy
- , James C. Moon
- & Luis R. Lopes
-
News & Views |
Adverse professional life experiences may affect mental health among cardiologists
Understanding how adverse professional life experiences affect the mental well-being of cardiologists is important. An unmet and equally important need is to design and implement strategies to prevent emotional harassment and discrimination at health-care workplaces and to effectively support cardiologists who have been exposed to adverse professional life experiences. These strategies are especially needed for female, younger or divorced cardiologists.
- Maria Panagioti
- & Alexander Hondkinson
-
Research Highlight |
 Genome editing prevents hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mice
Genome editing prevents hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mice
Adenine base editing can be used to correct a genetic variant in preclinical models of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and this approach could be applied to other monogenic cardiac diseases.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
 Preparticipation screening reduces SCD in young athletes
Preparticipation screening reduces SCD in young athletes
A legally mandated preparticipation screening programme for all young people in Italy engaging in competitive sports has resulted in a very low rate of sports-related cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Calcific aortic valve disease: mechanisms, prevention and treatment
Calcific aortic valve disease: mechanisms, prevention and treatment
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a common disorder characterized by thickening, fibrosis and mineralization of the aortic valve leaflets. In this Review, Mathieu and colleagues summarize the risk factors, genetics and molecular mechanisms involved in CAVD and the implications for treatment of the condition.
- Louis-Hippolyte Minvielle Moncla
- , Mewen Briend
- & Patrick Mathieu
-
Comment |
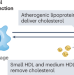 Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol are a risk factor for infection and hospitalization for infectious disease. Recent work suggests that inadequate levels of HDL particles of specific sizes — small and medium — account for this risk. In this Comment, we discuss the mechanistic implications of these observations and the methodologies used to quantify HDL size.
- Jay W. Heinecke
- & W. Sean Davidson
-
Review Article |
 The role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in cardiovascular disease
The role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in cardiovascular disease
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2), a key enzyme for the detoxification of alcohol-derived acetaldehyde, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various types of cardiovascular disease. In this Review, Xu and colleagues present the latest evidence showing a link between the inactivating ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism and an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease such as coronary artery disease.
- Jian Zhang
- , Yunyun Guo
- & Feng Xu
-
Research Highlight |
 A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function
A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function
Researchers have engineered a wearable device that adheres to the skin and uses ultrasound imaging and a deep learning model to produce a dynamic, real-time assessment of cardiac function.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
News & Views |
Implementing an earlier and more intensive follow-up in acute heart failure: the STRONG-HF and COACH trials
The STRONG-HF and COACH trials have shown a reduction in morbidity and mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure, for whom therapeutical options are currently limited, using two different approaches that have in common the aim of more effective treatment optimization through a better transition phase from in-hospital to outpatient care.
- Giuseppe M. C. Rosano
- & Gianluigi Savarese
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Autonomic dysfunction and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in post-acute COVID-19 syndrome
Autonomic dysfunction and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in post-acute COVID-19 syndrome
The post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 present major problems for many patients, their physicians and the health-care system. They are unrelated to the severity of the initial infection, are often highly symptomatic and can occur after vaccination. Many sequelae involve cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction, with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in 30% of individuals. Prognosis is unknown, and treatment is still unsatisfactory.
- Artur Fedorowski
- & Richard Sutton
-
Research Highlight |
 Base editing of CaMKIIδ shows promise as cardiac therapy
Base editing of CaMKIIδ shows promise as cardiac therapy
CRISPR–Cas9 base editing of the oxidative activation sites of CaMKIIδ protects the heart from ischaemia–reperfusion damage in mice.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
News & Views |
Physicians in the era of technology-enabled diagnostics
Health-care delivery is evolving, with an increased availability of consumer and medical technology-enabled diagnostic devices powered by artificial intelligence. Physicians need to evolve by deprioritizing old skills in favour of new skills in statistics and medical decision-making psychology. Technology moves fast; physicians will need to pivot and adapt quickly.
- Rashmee U. Shah
-
Research Highlight |
 Microbial metabolites reduce SBP in patients with resistant hypertension
Microbial metabolites reduce SBP in patients with resistant hypertension
In treatment-naive patients with essential hypertension, supplementation with prebiotic acetylated and butyrylated high amylose maize starch significantly reduces systolic blood pressure levels compared with placebo.
- Karina Huynh
-
Research Highlight |
Cardiac-resident macrophages protect against sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy
A subpopulation of cardiac-resident macrophages protect the heart against sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by scavenging dysfunctional mitochondria ejected from cardiomyocytes; modulation or administration of these macrophages might be a potential therapeutic strategy.
- Gregory B. Lim

 Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes
Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes