Featured
-
-
Article |
 Polyglutamine-mediated ribotoxicity disrupts proteostasis and stress responses in Huntington’s disease
Polyglutamine-mediated ribotoxicity disrupts proteostasis and stress responses in Huntington’s disease
Aviner et al. show that translation and aggregation of Huntingtin (HTT) are regulated by a stress-responsive upstream open reading frame. Mutant HTT depletes translation elongation factor eIF5A, leading to ribosome pausing and collisions.
- Ranen Aviner
- , Ting-Ting Lee
- & Judith Frydman
-
Article |
 Mammalian IRE1α dynamically and functionally coalesces with stress granules
Mammalian IRE1α dynamically and functionally coalesces with stress granules
Liu, Zhang, Yao et al. report that IRE1 α clustering, known to be part of the unfolded protein response, is membrane-bound phase separation and that IRE1 can coalesce with the phase-separated stress granules.
- Songzi Liu
- , Xiaoge Zhang
- & Yong Liu
-
News & Views |
 Adding a transcription-coupled repair pathway
Adding a transcription-coupled repair pathway
When transcription by RNA polymerase II is stalled by ultraviolet-induced DNA damage, it recruits repair factors, leading to excision of the damaged site and DNA synthesis to fill the gap. Three new studies show that, for aldehyde-induced DNA crosslinks, repair is activated by the same factors, but without base excision and gap filling.
- Marco Saponaro
-
News & Views |
 Tissue pressure and YAP during organogenesis
Tissue pressure and YAP during organogenesis
Organ morphogenesis begins with proliferation, which results in tissue pressures and site-specific YAP expression, nuclear translocation and signalling. A study now reports the involvement of anisotropy, localized pressure and YAP signalling in organizer-forming cascades, introducing a new chapter of molecular mechanobiology of organogenesis.
- Qian Xu
- & Thomas G. H. Diekwisch
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription-coupled DNA–protein crosslink repair by CSB and CRL4CSA-mediated degradation
Transcription-coupled DNA–protein crosslink repair by CSB and CRL4CSA-mediated degradation
Three studies identify a transcription-coupled DNA–protein crosslink repair pathway that depends on the Cockayne syndrome proteins and the proteasome.
- Marjolein van Sluis
- , Qing Yu
- & Jurgen A. Marteijn
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenous aldehyde-induced DNA–protein crosslinks are resolved by transcription-coupled repair
Endogenous aldehyde-induced DNA–protein crosslinks are resolved by transcription-coupled repair
Three studies identify a transcription-coupled DNA–protein crosslink repair pathway that depends on the Cockayne syndrome proteins and the proteasome.
- Yasuyoshi Oka
- , Yuka Nakazawa
- & Tomoo Ogi
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription-coupled repair of DNA–protein cross-links depends on CSA and CSB
Transcription-coupled repair of DNA–protein cross-links depends on CSA and CSB
Three studies identify a transcription-coupled DNA–protein cross-link repair pathway that depends on the Cockayne syndrome proteins and the proteasome.
- Christopher J. Carnie
- , Aleida C. Acampora
- & Julian Stingele
-
News & Views |
 Transcriptional bodies manage tight resources
Transcriptional bodies manage tight resources
Eukaryotic transcriptional machinery often shows local enrichment in dynamic clusters at sites of high expression. A study of zebrafish embryos shows that such clusters can fine-tune the timing of zygotic genome activation by sequestering a component required for productive transcription, thus limiting its availability to other genes.
- Natalia Stec
- & Adam Klosin
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription bodies regulate gene expression by sequestering CDK9
Transcription bodies regulate gene expression by sequestering CDK9
Ugolini et al. show that transcription bodies regulate gene expression during zygotic genome activation in zebrafish development by sequestering CDK9 to limit the transcription of genes away from transcription bodies.
- Martino Ugolini
- , Maciej A. Kerlin
- & Nadine L. Vastenhouw
-
Article |
 Disordered C-terminal domain drives spatiotemporal confinement of RNAPII to enhance search for chromatin targets
Disordered C-terminal domain drives spatiotemporal confinement of RNAPII to enhance search for chromatin targets
Using single-molecule tracking and spatiotemporal mapping, Ling et al. show that the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II facilitates its dynamic confinement in subnuclear regions enriched in active genes, where it promotes targeted transcription.
- Yick Hin Ling
- , Ziyang Ye
- & Carl Wu
-
Article |
 Redox regulation of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in β-cells controls the innate immune response in type 1 diabetes
Redox regulation of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in β-cells controls the innate immune response in type 1 diabetes
De Jesus et al. describe the redox-mediated regulation of m6A writer methyltransferase 3, which blunts innate immune responses by modification of RNA sensor and editor component mRNAs during the onset of type 1 diabetes in β-cells.
- Dario F. De Jesus
- , Zijie Zhang
- & Rohit N. Kulkarni
-
News & Views |
 tRNA flux and consistency in differentiation
tRNA flux and consistency in differentiation
tRNA transcriptome composition and regulation are poorly understood. A study reports tRNA transcriptome reprogramming during human cell differentiation, where the abundance of individual tRNA gene transcripts is drastically changed, but each pool of tRNAs containing the same anticodon remains stable.
- Yichen Hou
- & Tao Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Selective gene expression maintains human tRNA anticodon pools during differentiation
Selective gene expression maintains human tRNA anticodon pools during differentiation
Using modification-induced misincorporation tRNA sequencing, Gao and Behrens find that on differentiation, reduced mTORC1 signalling activates MAF1, which restricts RNA polymerase III to human tRNA housekeeping genes, to ensure that tRNA anticodon pools remain stable.
- Lexi Gao
- , Andrew Behrens
- & Danny D. Nedialkova
-
Article |
 A chaperone-like function of FUS ensures TAZ condensate dynamics and transcriptional activation
A chaperone-like function of FUS ensures TAZ condensate dynamics and transcriptional activation
Shao et al. report that FUS interacts with the transcriptional coactivator TAZ, maintaining liquid-like properties of TAZ biomolecular condensates and enhancing TAZ transcriptional activity.
- Yangqing Shao
- , Xin Shu
- & Huasong Lu
-
Technical Report
| Open Access Joint epigenome profiling reveals cell-type-specific gene regulatory programmes in human cortical organoids
Joint epigenome profiling reveals cell-type-specific gene regulatory programmes in human cortical organoids
Noack and Vangelisti et al. present 3DRAM-seq, which simultaneously profiles genome organization, chromatin accessibility and DNA methylation at high resolution and allows mapping cell-type-specific epigenetic regulation in human neurogenesis.
- Florian Noack
- , Silvia Vangelisti
- & Boyan Bonev
-
Article
| Open Access NAD+ regulates nucleotide metabolism and genomic DNA replication
NAD+ regulates nucleotide metabolism and genomic DNA replication
Munk et al. show that exogenous NAD+, but not its precursors, induces metabolic changes in mitochondria affecting nucleotide metabolism with impacts on genomic DNA synthesis and genome integrity.
- Sebastian Howen Nesgaard Munk
- , Joanna Maria Merchut-Maya
- & Apolinar Maya-Mendoza
-
News & Views |
 O-GlcNAc regulates YTHDF1 and YTHDF3 activity
O-GlcNAc regulates YTHDF1 and YTHDF3 activity
YTHDF family members are ‘readers’ of a common mRNA modification, but their effects on mRNA translation and stability have been disputed. A new study shows that YTHDF1 and YTHDF3 are post-translationally regulated through O-GlcNAcylation, unifying disparate results and pointing to environmental cues that could modulate YTHDF function.
- Mary W. N. Burns
- & Jennifer J. Kohler
-
Article |
 O-GlcNAcylation determines the translational regulation and phase separation of YTHDF proteins
O-GlcNAcylation determines the translational regulation and phase separation of YTHDF proteins
Chen et al. report that the YTHDF family of m6A-RNA-binding proteins can be differentially regulated by the post-translational modification O-GlcNAcylation, leading to differential regulation of the YTHDF proteins on translation and phase separation.
- Yulin Chen
- , Ruixi Wan
- & Shixian Lin
-
News & Views |
 Keeping membraneless organelles apart
Keeping membraneless organelles apart
How spatial organization in the cell is achieved on the organelle scale is unclear. A new study finds that tethering specific proteins near the surface of micelle-like paraspeckles modifies their properties and determines whether these subnuclear organelles are separate from, adhere to, or are engulfed by nuclear speckles.
- Jeremy D. Schmit
- & Miroslav Dundr
-
Article |
 Shell protein composition specified by the lncRNA NEAT1 domains dictates the formation of paraspeckles as distinct membraneless organelles
Shell protein composition specified by the lncRNA NEAT1 domains dictates the formation of paraspeckles as distinct membraneless organelles
Takakuwa, Yamazaki et al. show that the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 domains specify a set of proteins that localize to the outer shell and distinguish nuclear speckles from paraspeckles to preserve their structural identity.
- Hiro Takakuwa
- , Tomohiro Yamazaki
- & Tetsuro Hirose
-
News & Views |
 Hijacking host ribosomes via tRNA mimicry
Hijacking host ribosomes via tRNA mimicry
The bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila uses effectors — toxins — to facilitate pathogenesis within host cells. A recent study identifies dual mechanisms of the effector SidI as an inhibitor of translation elongation. The N-terminal domain mimics tRNA, whereas the C-terminal domain glycosylates the ribosome.
- Saori Uematsu
- & Shu-Bing Qian
-
Article |
 A Legionella toxin exhibits tRNA mimicry and glycosyl transferase activity to target the translation machinery and trigger a ribotoxic stress response
A Legionella toxin exhibits tRNA mimicry and glycosyl transferase activity to target the translation machinery and trigger a ribotoxic stress response
Subramanian et al. show that the secreted Legionella protein SidI is a tRNA mimic and glycosyltransferase. SidI inhibits host cell translation by mannosylating ribosomes to induce ribosome collisions and trigger the ribotoxic stress response.
- Advait Subramanian
- , Lan Wang
- & Shaeri Mukherjee
-
Article |
 Regulators of mitonuclear balance link mitochondrial metabolism to mtDNA expression
Regulators of mitonuclear balance link mitochondrial metabolism to mtDNA expression
Kramer, Prakash et al. share genome-wide CRISPR screens for factors that alter the levels of two dual-genome-encoded Complex IV subunits, COX1 and COX4. They identify PREPL and NME6 as genes that connect mitochondrial metabolism to mtDNA expression.
- Nicholas J. Kramer
- , Gyan Prakash
- & L. Stirling Churchman
-
Article
| Open Access DMRT1 regulates human germline commitment
DMRT1 regulates human germline commitment
Irie, Lee et al. report a role for DMRT1 in human germline development and show that induction of DMRT1 in primordial germ cell-like cells triggers germline commitment, but suppresses pluripotency genes, thus promoting the onset of gametogenesis.
- Naoko Irie
- , Sun-Min Lee
- & M. Azim Surani
-
News & Views |
 o8G modifications rewire tumoral microRNAs
o8G modifications rewire tumoral microRNAs
RNA modifications have emerged as key gene regulators. A new study shows that increased levels of reactive oxygen species in cancer induce widespread, sequence-specific modifications of guanines in the seed regions of microRNAs, altering the targets of those miRNAs and influencing tumorigenesis.
- Marta Montes
- & Maite Huarte
-
Article |
 m6A RNA methylation orchestrates transcriptional dormancy during paused pluripotency
m6A RNA methylation orchestrates transcriptional dormancy during paused pluripotency
Collignon et al. report that Mettl3-mediated m6A RNA methylation promotes developmental pausing in embryonic stem cells and blastocysts by establishing transcriptional dormancy.
- Evelyne Collignon
- , Brandon Cho
- & Miguel Ramalho-Santos
-
Resource |
 Widespread 8-oxoguanine modifications of miRNA seeds differentially regulate redox-dependent cancer development
Widespread 8-oxoguanine modifications of miRNA seeds differentially regulate redox-dependent cancer development
Eom, Peak, Park, Ahn and colleagues reveal and provide a comprehensive resource of 8-oxoguanine modifications in tumour microRNAs and show how they differentially influence malignancy progression in gliomas and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Sangkyeong Eom
- , Jongjin Peak
- & Sung Wook Chi
-
News & Views |
 A non-coding m6A reader promotes leukaemia
A non-coding m6A reader promotes leukaemia
Pathways linked to the modification of RNA with N6-methyladenosine (m6A) are known to be involved in initiating and maintaining cancer. But many of the key components of these pathways remain undiscovered. The RBFOX2 protein has now been identified as an m6A reader involved in locus-specific chromatin regulation, with therapeutic implications for myeloid leukaemia.
- James Russell
- & Konstantinos Tzelepis
-
Article
| Open Access RBFOX2 recognizes N6-methyladenosine to suppress transcription and block myeloid leukaemia differentiation
RBFOX2 recognizes N6-methyladenosine to suppress transcription and block myeloid leukaemia differentiation
Dou, Xiao, Shen, Wang et al. show that RBFOX2 recognizes m6A on chromatin-associated RNAs and recruits RBM15, YTHDC1 and PRC2 to facilitate transcription suppression. Inhibition of the axis exerts anti-leukaemic effects.
- Xiaoyang Dou
- , Yu Xiao
- & Chuan He
-
News & Views |
 Epigenetic control of cancer inflammation
Epigenetic control of cancer inflammation
The interaction of non-immune and immune cells in the tumour microenvironment (TME) determines the quality of the immune attack on nascent tumour cells. A new study in melanoma cells shows that specific histone variants dampen the expression of cytokine genes in cancer-associated fibroblasts, leading to an immunosuppressive TME.
- David Corujo
- & Marcus Buschbeck
-
Article |
 Young LINE-1 transposon 5′ UTRs marked by elongation factor ELL3 function as enhancers to regulate naïve pluripotency in embryonic stem cells
Young LINE-1 transposon 5′ UTRs marked by elongation factor ELL3 function as enhancers to regulate naïve pluripotency in embryonic stem cells
Meng et al. show that the RNA polymerase II elongation factor ELL3 suppresses the 5′ untranslated region activities of a subset of young LINE-1 elements, which activate genes such as Akt3, and regulate ERK signalling and naïve pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells.
- Siyan Meng
- , Xiaoxu Liu
- & Chengqi Lin
-
Article
| Open Access The pioneer factor SOX9 competes for epigenetic factors to switch stem cell fates
The pioneer factor SOX9 competes for epigenetic factors to switch stem cell fates
Yang, Gomez et al. show that the pioneer factor SOX9 regulates the switch from epidermal stem cell to hair follicle stem cell fate by binding and opening hair follicle enhancers, while recruiting epigenetic factors away from epidermal enhancers.
- Yihao Yang
- , Nicholas Gomez
- & Elaine Fuchs
-
Article |
 H3K36 methylation maintains cell identity by regulating opposing lineage programmes
H3K36 methylation maintains cell identity by regulating opposing lineage programmes
Hoetker et al. show that H3K36 methylation exerts a dual role in cell identity maintenance: it integrates TGFβ signals at mesenchymal targets to keep them active and prevents the activation of alternative lineage programmes via enhancer methylation.
- Michael S. Hoetker
- , Masaki Yagi
- & Konrad Hochedlinger
-
News & Views |
 Transient chromatin compaction in fork restart
Transient chromatin compaction in fork restart
The compact state of chromatin induced by the methylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 has long been implicated in a heritable state of transcriptional repression. A study now shows that transient deposition of H3K9me3 helps to stabilize stalled DNA replication forks, while its reversal enables accurate fork restart.
- Susan M. Gasser
-
Article |
 Transmembrane nuclease NUMEN/ENDOD1 regulates DNA repair pathway choice at the nuclear periphery
Transmembrane nuclease NUMEN/ENDOD1 regulates DNA repair pathway choice at the nuclear periphery
Through a genome-wide CRISPR synthetic viability screen for PARP-inhibitor resistance, Chen and Ge et al. show that transmembrane nuclease NUMEN directs double-stranded DNA break repair pathway choice at the nuclear periphery.
- Bohong Chen
- , Tianyu Ge
- & Zhou Songyang
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid droplet-associated lncRNA LIPTER preserves cardiac lipid metabolism
Lipid droplet-associated lncRNA LIPTER preserves cardiac lipid metabolism
Han et al. identify the long non-coding RNA LIPTER as a key mediator of lipid droplet transport and metabolism in human cardiomyocytes. LIPTER overexpression mitigates cardiomyopathy and preserves cardiac function in obese and diabetic mouse models.
- Lei Han
- , Dayang Huang
- & Lei Yang
-
News & Views |
 Tailoring 3′ UTRs alters metastatic potential
Tailoring 3′ UTRs alters metastatic potential
In cancer, alternative polyadenylation has been shown to lead to altered 3′ UTRs with different regulatory potentials. A study now suggests a mechanism that leads to 3′ UTR lengthening and translational repression of a subset of metastasis-suppressing genes, revealing a new prospective therapeutic vulnerability.
- Kathleen Watt
- & Lynne-Marie Postovit
-
Article
| Open Access An mRNA processing pathway suppresses metastasis by governing translational control from the nucleus
An mRNA processing pathway suppresses metastasis by governing translational control from the nucleus
Using ribosome profiling, Navickas et al. show that heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C functions with PABPC4 to regulate alternative polyadenylation of a set of mRNAs, which inhibits lung metastasis in xenograft models of breast cancer.
- Albertas Navickas
- , Hosseinali Asgharian
- & Hani Goodarzi
-
News & Views |
 A shared fate for nuclear and cytosolic inclusions
A shared fate for nuclear and cytosolic inclusions
Coordination of protein quality control processes across organelles is poorly understood. A study now shows that the cytosolic juxtanuclear quality control (JUNQ) and intranuclear quality control (INQ) compartments face each other on opposite sides of the nuclear envelope before their vacuolar degradation, promoting proteostasis.
- Simon Alberti
- & Serena Carra
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue memory relies on stem cell priming in distal undamaged areas
Tissue memory relies on stem cell priming in distal undamaged areas
Levra Levron et al. report that epidermal injury elicits the priming of distant memory progenitors that have not contributed in the original healing, but acquire enhanced repair abilities, although favouring field cancerization.
- Chiara Levra Levron
- , Mika Watanabe
- & Giacomo Donati
-
News & Views |
 Arginyl-tRNA synthetase in inflammation
Arginyl-tRNA synthetase in inflammation
The house-keeping aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are increasingly recognized for their regulatory roles beyond protein synthesis. Research now uncovers a function of nuclear arginyl-tRNA synthetase in the regulation of alternative mRNA splicing through SRRM2 in response to inflammation and decreased arginine levels.
- Jie Chen
-
Article |
 Arg-tRNA synthetase links inflammatory metabolism to RNA splicing and nuclear trafficking via SRRM2
Arg-tRNA synthetase links inflammatory metabolism to RNA splicing and nuclear trafficking via SRRM2
Cui et al. find that arginine depletion and inflammation reduces nuclear localization of arginyl-tRNA synthetase, which influences alternative splicing via condensate-like serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 2, and regulates cellular metabolism and response to inflammation.
- Haissi Cui
- , Jolene K. Diedrich
- & Paul Schimmel
-
Article |
 Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify ILF3 as a mediator of mTORC1-dependent amino acid sensing
Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify ILF3 as a mediator of mTORC1-dependent amino acid sensing
Yan et al. harness genome-wide CRISPR screens and identify ILF3 as a signalling intermediate negatively regulating mTORC1 activation upon amino acid sensing. ILF3 recruits GATOR2 to tether the GATOR complexes to lysosomes and regulate mTORC1 activity.
- Guokai Yan
- , Jinxin Yang
- & Ying Liu
-
Technical Report
| Open Access Metaboverse enables automated discovery and visualization of diverse metabolic regulatory patterns
Metaboverse enables automated discovery and visualization of diverse metabolic regulatory patterns
Berg et al. describe Metaboverse, a tool for automated discovery and visualization of metabolic data. Metaboverse enhances the user’s ability to extract meaningful patterns from multi-omics datasets to describe metabolic responses and signatures.
- Jordan A. Berg
- , Youjia Zhou
- & Jared Rutter
-
Article
| Open Access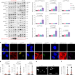 SARS-CoV-2 infection induces DNA damage, through CHK1 degradation and impaired 53BP1 recruitment, and cellular senescence
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces DNA damage, through CHK1 degradation and impaired 53BP1 recruitment, and cellular senescence
Gioia, Tavella et al. show that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 causes DNA damage through CHK1 degradation and impairs 53BP1 recruitment to DNA lesions. The induced DNA damage is associated with expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and senescence markers.
- Ubaldo Gioia
- , Sara Tavella
- & Fabrizio d’Adda di Fagagna
-
Article |
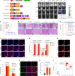 Nuclear condensates of YAP fusion proteins alter transcription to drive ependymoma tumourigenesis
Nuclear condensates of YAP fusion proteins alter transcription to drive ependymoma tumourigenesis
Hu et al. report that patient-derived YAP fusion proteins undergo liquid–liquid phase separation in the nucleus to drive ependymoma tumourigenesis, altering transcription through transcription factor recruitment and alteration of genomic methylation.
- Xiaohua Hu
- , Xiaoping Wu
- & Q. Richard Lu
-
Article |
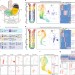 Dissection of gastric homeostasis in vivo facilitates permanent capture of isthmus-like stem cells in vitro
Dissection of gastric homeostasis in vivo facilitates permanent capture of isthmus-like stem cells in vitro
Huebner et al. develop a 2D culture system to study gastric isthmus stem cells and identify a role for Sox2 in specifying enterochromaffin cells in the stomach.
- Aaron J. Huebner
- , Rebecca A. Gorelov
- & Konrad Hochedlinger
-
Comment |
 A guide to naming eukaryotic circular RNAs
A guide to naming eukaryotic circular RNAs
Alternative splicing of eukaryotic messenger RNA transcripts often leads to the production of several mature RNAs — including linear RNAs and circular RNAs (circRNAs) — from a single gene locus. The names given to circRNAs are often ambiguous and lack consistency across studies. This Comment calls on the community to embrace a common nomenclature for naming circRNAs to ensure clarity and reproducibility.
- Ling-Ling Chen
- , Albrecht Bindereif
- & Fangqing Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Oncogenic role for an EWS–FLI1 suppressor
Oncogenic role for an EWS–FLI1 suppressor
Tight regulation of the activity of EWS–ETS fusion proteins is essential for the growth of Ewing sarcomas. Two new studies show that the transcriptional repressor ETV6 is essential for tumour growth, acting to restrain fusion-protein-mediated gene activation, and revealing the importance of tissue-specific transcription factors to oncogenesis.
- April A. Apfelbaum
- & Elizabeth R. Lawlor
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cell division
- Chromatin
- Chromosomes
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- DNA damage and repair
- DNA metabolism
- DNA recombination
- DNA replication
- Epigenetics
- Non-coding RNAs
- Nuclear organization
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- Riboswitches
- Ribozymes
- RNA metabolism
- RNAi
- Single-molecule biophysics
- Transcription
- Transcriptomics
- Translation
- Transposition

 Phase separation-competent FBL promotes early pre-rRNA processing and translation in acute myeloid leukaemia
Phase separation-competent FBL promotes early pre-rRNA processing and translation in acute myeloid leukaemia