Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Slow on, fast off
Slow on, fast off
The slow turn-on speed in accumulation-mode organic electrochemical transistors is explained by asymmetric ion transport in switching kinetics.
- Hang Yu
- & Jenny Nelson
-
News & Views |
 Driving organic electronics to new heights
Driving organic electronics to new heights
Modified Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization procedures provide a scalable and reproducible route to regioregular conjugated polymers.
- Mario Leclerc
- & Serge Beaupré
-
Article |
 Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures
Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures
Efficient phononic nonlinear processes are demonstrated in an acoustoelectric heterostructure combining a high-mobility semiconductor indium gallium arsenide film heterogeneously integrated onto a lithium niobate thin film.
- Lisa Hackett
- , Matthew Koppa
- & Matt Eichenfield
-
News & Views |
 Injectable and retrievable soft electronics
Injectable and retrievable soft electronics
Liquid bioelectronics based on a permanent fluidic magnet made from three-dimensional assembled magnetic colloidal particles can be injected into the surface of the heart for cardiovascular monitoring and subsequently retrieved after use.
- Jiahong Li
- , Yadong Xu
- & Wei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access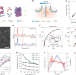 Electrochemically actuated microelectrodes for minimally invasive peripheral nerve interfaces
Electrochemically actuated microelectrodes for minimally invasive peripheral nerve interfaces
Electrode arrays for neurological diagnosis and treatment carry a risk of nerve injury. Nerve cuffs with tiny voltage-controlled shape-reconfigurable electrode arrays have been reported, allowing active wrapping around delicate nerves.
- Chaoqun Dong
- , Alejandro Carnicer-Lombarte
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article |
 Permanent fluidic magnets for liquid bioelectronics
Permanent fluidic magnets for liquid bioelectronics
The magnetism-mediated assembly of non-Brownian magnetic colloidal particles into a three-dimensional oriented and ramified magnetic network yields permanent fluidic magnets that are used in a self-powered, liquid-based wireless cardiovascular sensor.
- Xun Zhao
- , Yihao Zhou
- & Jun Chen
-
Article |
 On-device phase engineering
On-device phase engineering
A strategy of on-device phase engineering of two-dimensional materials is proposed, allowing the in situ realization of various lattice phases with distinct stoichiometries and versatile functions.
- Xiaowei Liu
- , Junjie Shan
- & Feng Miao
-
Article |
 Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
The turn-off time is generally faster than the turn-on time in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs), but the mechanism is less understood. Here the authors find different transient behaviours of turn-on and turn-off in accumulation mode OECTs, and ion transport is the limiting factor of device kinetics.
- Jiajie Guo
- , Shinya E. Chen
- & David S. Ginger
-
Article |
 Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
The authors report a modulation of the magnon spin current by electric polarization reversal.
- Xiaoxi Huang
- , Xianzhe Chen
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Research Briefing |
 Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Soft pressure sensors drift under prolonged high stress because of the creep of soft materials, which causes inaccurate measurements. Now, through molecular-level design, a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer is synthesized, and an iontronic sensor using the polyelectrolyte elastomer shows very low signal drift under a high static pressure.
-
News & Views |
 Efficient blue emitter with a hoop
Efficient blue emitter with a hoop
Highly efficient matrix-free hyperfluorescent organic light-emitting diodes are constructed with remarkably supressed Dexter transfer utilizing narrowband blue emitters encapsulated with hopped alkyl chains.
- Yuewei Zhang
- & Lian Duan
-
Perspective |
 Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Molecular materials for computing progress intensively but the performance and reliability still lag behind. Here the authors assess the current state of computing with molecular-based materials and describe two issues as the basis of a new computing technology: continued exploration of molecular electronic properties and process development for on-chip integration.
- R. Stanley Williams
- , Sreebrata Goswami
- & Sreetosh Goswami
-
Article |
 Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Conventional iontronic pressure sensors suffer from signal drift and inaccuracy owing to creep of soft materials and ion leakage. Here the authors report a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte-elastomer-based iontronic sensor that achieves a drift rate two to three orders of magnitude lower than those of conventional iontronic sensors.
- Yunfeng He
- , Yu Cheng
- & Chuan Fei Guo
-
Research Briefing |
 Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons have been grown through chemical vapour transport, using black phosphorus nanoparticles as seeds. The nanoribbons orient exclusively along the zigzag direction and have good semiconductor properties that render them suitable for use as channel material in field-effect transistors.
-
Article |
 High-temperature Josephson diode
High-temperature Josephson diode
A large Josephson diode effect has been reported at liquid-nitrogen temperatures in twisted flakes of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ.
- Sanat Ghosh
- , Vilas Patil
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
News & Views |
 Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Early detection of electrical degradation can be identified by colour change due to the chromogenic response of blended molecules in dielectric polymers.
- Gregory A. Sotzing
- & Pritish S. Aklujkar
-
Research Briefing |
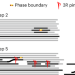 Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Metal monochalcogenides — a class of van der Waals layered semiconductors — can exhibit ultrahigh plasticity. Investigation of the deformation mechanism reveals that on mechanical loading, these materials undergo local phase transitions that, coupled with the concurrent generation of a microcrack network, give rise to the ultrahigh plasticity.
-
Article |
 General room-temperature Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization for organic electronics
General room-temperature Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization for organic electronics
A general process for a room-temperature, homogeneous Suzuki–Miyaura-type polymerization is reported, demonstrating a route for the scalable production of device-quality conjugated polymers.
- Haigen Xiong
- , Qijie Lin
- & Hui Huang
-
Article |
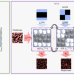 All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
Employing light-transformable polymers, multiple physical unclonable functions are demonstrated within a single device with all-optical reversible reconfigurability. Such devices may enable quantum secure authentication and nonlinear cryptographic key generation applications.
- Sara Nocentini
- , Ulrich Rührmair
- & Francesco Riboli
-
Feature |
Lifting the fog in ferroelectric thin-film synthesis
Frustrated by reproducibility in electrical measurements on ferroelectric films, Lane Martin, Jon-Paul Maria and Darrell Schlom discuss tactics to reliably synthesize ‘good’ ferroelectric samples, especially in the search for superior materials and device heterostructures.
- Lane W. Martin
- , Jon-Paul Maria
- & Darrell G. Schlom
-
Feature |
 2D materials for logic device scaling
2D materials for logic device scaling
Peng Wu, Tianyi Zhang, Jiadi Zhu, Tomás Palacios and Jing Kong discuss the reproducibility issues in the synthesis and device fabrication of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides that need to be addressed to enable the lab-to-fab transition.
- Peng Wu
- , Tianyi Zhang
- & Jing Kong
-
Article |
 Solution-processable mixed-anion cluster chalcohalide Rb6Re6S8I8 in a light-emitting diode
Solution-processable mixed-anion cluster chalcohalide Rb6Re6S8I8 in a light-emitting diode
Rhenium chalcohalide cluster compounds are promising photoluminescent materials. Here the authors report a new material in this family, Rb6Re6S8I8, which shows broad photoluminescence (PL) range, high PL quantum yield and long PL lifetime.
- Craig C. Laing
- , Daehan Kim
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Research Briefing |
 Sublattice matching enables texturing of dissimilar materials
Sublattice matching enables texturing of dissimilar materials
Inspired by the observed coherent interface between hexagonal α-Fe2O3 and tetragonal fluorine-doped SnO2, an oxygen sublattice-matching paradigm is proposed to grow textured films on lattice-mismatched substrates. Through assessing the similarity of Voronoi cells for sublattices, this approach offers opportunities to synthesize (semi)coherent heterostructures and textured films.
-
News & Views |
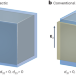 Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
By forming a heterostructure interface, and by judicious choice of crystallographic orientation, piezoelectrics are developed that show expansion or contraction along all axes on application of an electric field.
- Eugene A. Eliseev
- & Anna N. Morozovska
-
Article |
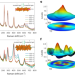 Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Depositing textured functional materials on transparent conducting oxides remains a challenge. We demonstrate the formation of a coherent interface between a set of functional oxides and fluorine-doped-tin-oxide-based transparent conducting oxide substrate despite the lattice mismatch, owing to dimensional and chemical matching of oxygen sublattices at the interface.
- Huiting Huang
- , Jun Wang
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Article |
 Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of electronics based on fully 2D materials is demonstrated in the performance of artificial intelligence tasks.
- Ji-Hoon Kang
- , Heechang Shin
- & Sang-Hoon Bae
-
Article |
 Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Early detection of electrical degradation in dielectric polymers is crucial but remains challenging. A general strategy of blending the polymer with chromogenic molecules is reported, which generates a visually discernible colour change as chemically activated by oxygen radicals generated in situ, indicating the early stage of electrical degradation in polymers.
- Xiaoyan Huang
- , Shuai Zhang
- & Jinliang He
-
Research Briefing |
 Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
A traditional physical-reservoir device has limited flexibility and cannot perform well across a range of computing tasks, owing to the fixed reservoir properties of the physical system. However, by exploiting the rich magnetic phase spaces of a single chiral magnet, reservoir properties can be reconfigured. This control enables on-demand optimization of computational performance across diverse machine-learning tasks.
-
Article
| Open Access Task-adaptive physical reservoir computing
Task-adaptive physical reservoir computing
Current physical neuromorphic computing faces critical challenges of how to reconfigure key physical dynamics of a system to adapt computational performance to match a diverse range of tasks. Here the authors present a task-adaptive approach to physical neuromorphic computing based on on-demand control of computing performance using various magnetic phases of chiral magnets.
- Oscar Lee
- , Tianyi Wei
- & Hidekazu Kurebayashi
-
Editorial |
 Electronics can be more sustainable
Electronics can be more sustainable
Integrated design assisted by materials and technology innovations can help a transition from traditional to sustainable electronics.
-
News & Views |
 Faster holes by delocalization
Faster holes by delocalization
Terahertz photoconductivity measurements coupled with theoretical modelling reveals that thermal transient excitations to more delocalized states enhances hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors.
- Zhigang Shuai
-
Comment |
 The organic electrochemical transistor conundrum when reporting a mixed ionic–electronic transport figure of merit
The organic electrochemical transistor conundrum when reporting a mixed ionic–electronic transport figure of merit
An essential part of developing organic mixed ionic–electronic conducting materials and organic electrochemical transistors is consistent and standardized reporting of the product of charge carrier mobility and volumetric capacitance, the μC* product. This Comment argues that unexpected changes in transistor channel resistance can overestimate this figure of merit, leading to a confusion of comparisons in the literature.
- Maryam Shahi
- , Vianna N. Le
- & Alexandra F. Paterson
-
Article |
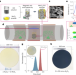 12-inch growth of uniform MoS2 monolayer for integrated circuit manufacture
12-inch growth of uniform MoS2 monolayer for integrated circuit manufacture
A route to the rapid and batch production of 12 inch MoS2 monolayers is reported, which shows a synergistic optimization of scale–cost–performance metrics for a transition from lab to fab.
- Yin Xia
- , Xinyu Chen
- & Peng Zhou
-
News & Views |
 Bioelectronics goes vertical
Bioelectronics goes vertical
Remotely powered vertical electrochemical transistors are demonstrated to track subtle nerve-cell activity even when the transistor core is fully shielded from the biological environment.
- C. Eckel
- & R. T. Weitz
-
Article |
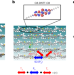 Transiently delocalized states enhance hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors
Transiently delocalized states enhance hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors
Dynamic disorder reduces the carrier mobility in organic semiconductors (OSs) to an extent that depends on their specific electronic band structure. Here the authors study the temperature-dependent hole mobility of two structurally similar OSs and find that thermal access to transiently delocalized states enhances hole mobility in C8-DNTT-C8 compared to DNTT.
- Samuele Giannini
- , Lucia Di Virgilio
- & David Beljonne
-
News & Views |
 Hybrid dielectrics for two-dimensional electronics
Hybrid dielectrics for two-dimensional electronics
Using the van der Waals crystal Sb2O3 as a buffer layer enables the growth of high-κ dielectrics on two-dimensional materials via atomic layer deposition.
- Yang Liu
- & James C. Hone
-
Research Briefing |
 Large-bandgap organic semiconductors with trap-free charge transport
Large-bandgap organic semiconductors with trap-free charge transport
By optimizing the molecular organization of blue-emitting organic semiconductors, the vulnerability of the materials to extrinsic impurities that cause charge trapping, such as oxygen and water, is strongly reduced. Steric shielding of the electron-transporting core is shown to increase the electron transport by several orders of magnitude.
-
News & Views |
 The hole truth
The hole truth
By tracking the electrochromic doping front, a hole-limited electrochemical doping mechanism is discovered in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Jonathan Rivnay
-
Perspective |
 Colloidal robotics
Colloidal robotics
This Perspective provides an overview on the emergent field of colloidal robotics, discussing recent developments on colloidal and micrometre-sized particles that can perform functions such as sensing, communication, computation and motion.
- Albert Tianxiang Liu
- , Marek Hempel
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Research Briefing |
 Designing air-entrapment interfaces for near-ideal pressure sensors
Designing air-entrapment interfaces for near-ideal pressure sensors
Pressure sensing is challenging in liquid environments, where typical solid-state sensors do not perform well. A sensor with solid–liquid–liquid–gas multiphasic interfaces — its design inspired by the lotus leaf, and in which a trapped air layer modulates capacitance changes with pressure — is shown to achieve near-ideal pressure sensing and is well suited to liquid environments.
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel muscles powering reconfigurable micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum programmability
Hydrogel muscles powering reconfigurable micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum programmability
It is difficult to program a single stimuli-responsive geometry to transform into diverse final configurations in a systematic manner. Here, linearly responsive transparent hydrogels are developed to create micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum thermal reconfigurability.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Aniket Pal
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article |
 Frictionless multiphasic interface for near-ideal aero-elastic pressure sensing
Frictionless multiphasic interface for near-ideal aero-elastic pressure sensing
Solid-state pressure sensors have performance limitations in liquid environments. Here, the authors design a pressure sensor using solid–liquid–liquid–gas multiphasic interfaces where a trapped air layer modulates capacitance changes with pressure to achieve near-friction-free contact line motions for near-ideal pressure sensing.
- Wen Cheng
- , Xinyu Wang
- & Benjamin C. K. Tee
-
News & Views |
 A double-helix dislocation in graphene
A double-helix dislocation in graphene
By means of a precise folding–tearing process, screw dislocations with helical cores — appearing in pairs and taking on a DNA-like double-helix structure — are engineered to control the growth of twisted bilayer graphene.
- Pascal Pochet
- & Harley T. Johnson
-
Article |
 Ferroelectricity in hafnia controlled via surface electrochemical state
Ferroelectricity in hafnia controlled via surface electrochemical state
Ferroelectricity in hafnia-based systems seems to be correlated with oxygen vacancy dynamics, but the coupling of this and ferroelectric response is rarely studied. Here it is shown that Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 can be antiferroionic, with antiferroelectric behaviour coupled to surface electrochemistry.
- Kyle P. Kelley
- , Anna N. Morozovska
- & Sergei V. Kalinin
-
News & Views |
 Microcrystal actuator arrays see the light
Microcrystal actuator arrays see the light
Photochromic molecular crystal arrays aligned in the micropores of a polymer membrane show high-performance actuation when stimulated by light. These soft composites might find applications in soft robotic devices.
- Albert P. H. J. Schenning
-
Article |
 Scalable integration of hybrid high-κ dielectric materials on two-dimensional semiconductors
Scalable integration of hybrid high-κ dielectric materials on two-dimensional semiconductors
A van der Waals buffer layer of Sb2O3 enables the integration of high-κ dielectric layer with sub-1 nm equivalent oxide thickness on two-dimensional semiconductors, resulting in high performance of two-dimensional field-effect transistors.
- Yongshan Xu
- , Teng Liu
- & Tianyou Zhai
-
Perspective |
 Sustainable electronic textiles towards scalable commercialization
Sustainable electronic textiles towards scalable commercialization
The commercialization of electronic textile (e-textile) products requires balanced sustainability considerations. Here the authors propose an e-textile design framework involving repair, recycle, replacement and reduction that can unify environmental friendliness, market viability, supply-chain resilience and user experience quality.
- HaoTian Harvey Shi
- , Yifei Pan
- & Yan Yan Shery Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
The two-dimensional layered crystal structure of niobium oxide polymorph T-Nb2O5 exhibits fast Li-ion diffusion that is promising for energy storage applications. Epitaxial growth of single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with ionic transport channels oriented perpendicular to the surface are now demonstrated.
- Hyeon Han
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article |
 Photo-actuators via epitaxial growth of microcrystal arrays in polymer membranes
Photo-actuators via epitaxial growth of microcrystal arrays in polymer membranes
Photomechanical crystals are promising materials for converting photon energy into macroscopic work via reversible structural changes when exposed to light. Here the authors demonstrate highly ordered and compliant microcrystalline composites with a photomechanical performance exceeding that of single crystals.
- Wenwen Xu
- , David M. Sanchez
- & Ryan C. Hayward

 Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace
Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace