Featured
-
-
Article |
 Discovery and synthesis of atropisomerically chiral acyl-substituted stable vinyl sulfoxonium ylides
Discovery and synthesis of atropisomerically chiral acyl-substituted stable vinyl sulfoxonium ylides
The synthesis of optically enriched atropisomers has so far been limited to molecules containing aryl groups. Now a variant of non-aryl atropisomerism has been identified in vinyl sulfoxonium ylides, and an organocatalytic method has been developed to produce these molecules. This type of axial chirality is characterized by restricted rotation of the central C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond.
- Fengjin Wu
- , Yichi Zhang
- & Yong Huang
-
Article |
 Structure and bonding of a radium coordination compound in the solid state
Structure and bonding of a radium coordination compound in the solid state
Radium complexes are of interest for use as cancer therapeutic agents, but the structure and bonding are poorly understood. Here, the synthesis of a Ra2+ complex is reported, and the structure and bonding characteristics are elucidated using single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
- Frankie D. White
- , Nikki A. Thiele
- & Samantha K. Cary
-
Article |
 RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
The physicochemical driving forces of protein-free, RNA-driven phase transitions were previously unclear, but it is now shown that RNAs undergo entropically driven liquid–liquid phase separation upon heating in the presence of magnesium ions. In the condensed phase, RNAs can undergo an enthalpically favourable percolation transition that leads to arrested condensates.
- Gable M. Wadsworth
- , Walter J. Zahurancik
- & Priya R. Banerjee
-
Article |
 Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Bottom-up assembly of protocells into networking superstructures represents a further key step towards rudimentary formation of life. Now it has been shown that a pool of biomolecules can self-organize into an interactive binary population of protocell coacervates with a self-sorting chain-like configuration, allowing for biomolecular extraction, translocation and macroscale separation.
- Wenjing Mu
- , Liyan Jia
- & Yan Qiao
-
-
News & Views |
 An open-shell molecule that exhibits conformational dynamics
An open-shell molecule that exhibits conformational dynamics
Open-shell organic molecules with properties that can be modulated by external stimuli are of interest for spintronics applications. Now, an overcrowded alkene with open-shell tetraradical character has been synthesized in which the interaction between the π-conjugated subunits depends on the charge and spin state.
- Yoshito Tobe
-
-
News & Views |
 Enyne difluorination
Enyne difluorination
Fluorination strategies are important in assisting the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Iodine(I/III) catalysis has become particularly useful for installing gem-difluoro groups but is limited to styrenes. Now, the hypervalent iodane-catalysed difluorination of enynes has enabled access to diverse homopropargylic difluorides.
- Rachel C. Epplin
- & Tanja Gulder
-
Meeting Report |
 Altogether changed, and yet the same
Altogether changed, and yet the same
Organic chemists meet biennially to present exciting developments in the realm of synthesis. Thomas Barber discusses the standout themes of this year’s international synthesis in organic chemistry symposium.
- Thomas Barber
-
In Your Element |
 The numerous paths of ferrocene
The numerous paths of ferrocene
Didier Astruc surveys the numerous applications of ferrocene, from catalysis to materials and redox-related devices including biosensors and nanomedicine.
- Didier Astruc
-
Article |
 Entropy-driven charge-transfer complexation yields thermally activated delayed fluorescence and highly efficient OLEDs
Entropy-driven charge-transfer complexation yields thermally activated delayed fluorescence and highly efficient OLEDs
Although exciplex-forming systems are widely used for fabricating organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), their structural and thermodynamic characterization is limited. Now donor/acceptor inclusion complexes that demonstrate thermally activated delayed fluorescence have been generated. Their cocrystal structures have been resolved and the thermodynamics of exciplex formation determined, which has enabled the fabrication of efficient OLEDs.
- Chun-Yen Lin
- , Chao-Hsien Hsu
- & Pi-Tai Chou
-
Article |
 Programmable late-stage functionalization of bridge-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane bis-boronates
Programmable late-stage functionalization of bridge-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane bis-boronates
The bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane (BCP) motif has drawn increasing attention recently in drug discovery. Now, a programmable bis-functionalization strategy has been developed to modularly access bridge-substituted BCP scaffolds, based on the inherent chemoselectivity of BCP bis-boronates (3° > 2°). This strategy should enable further structure–activity relationship studies of BCP-containing drug candidates and open the door to unexplored chemical space.
- Yangyang Yang
- , Jet Tsien
- & Tian Qin
-
Article |
 Heteromultivalency enables enhanced detection of nucleic acid mutations
Heteromultivalency enables enhanced detection of nucleic acid mutations
Detecting genetic mutations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), is essential for disease diagnostics but can be difficult using homomultivalent DNA hybridization-based approaches. Now, heteromultivalent hybridization is used to fine-tune binding specificity for the detection of one or two SNPs in a single target, enabling straightforward discrimination between adjacent and distant mutations and different viral strains.
- Brendan R. Deal
- , Rong Ma
- & Khalid Salaita
-
News & Views |
 Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Gas bubble accumulation at interfaces is a barrier to achieving more efficient electrochemical devices. A clever model system to understand bubble formation during electrochemical hydrogen evolution now reveals similarities between the forces at play during their detachment from the catalyst surface and those involved in wine climbing up a glass.
- Gaurav Ashish Kamat
- & Michaela Burke Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Surface heterogeneity is generally acknowledged as the major cause of liquid–solid friction, affecting whether droplets slide off the surface or stick to it. Now, a model surface of self-assembled monolayers has been used to investigate how molecular-scale surface heterogeneity affects water contact angle hysteresis and contact line friction. The high-coverage hydrophobic surface is slippery, as—counter-intuitively—is the low-coverage hydrophilic surface.
- Sakari Lepikko
- , Ygor Morais Jaques
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article |
 Stereocontrolled access to thioisosteres of nucleoside di- and triphosphates
Stereocontrolled access to thioisosteres of nucleoside di- and triphosphates
Nucleoside diphosphates and triphosphates impact nearly every aspect of biochemistry. Now, a modular, reagent-based platform has been developed to enable the stereocontrolled and scalable synthesis of a library of such molecules. This operationally simple approach provides access to pure stereoisomers of nucleoside α-thiodiphosphates and α-thiotriphosphates.
- Hai-Jun Zhang
- , Michał Ociepa
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article
| Open Access Regioselective, catalytic 1,1-difluorination of enynes
Regioselective, catalytic 1,1-difluorination of enynes
Hypervalent iodine catalysis remains a powerful method to enable geminal difluoromethylenation of alkenes. However, the scope is mainly limited to styrene derivatives. Now, enynes have been validated as competent substrates where a formal 1,2-shift of the alkyne occurs, thereby enabling highly versatile homopropargylic difluorides to be generated.
- Zi-Xuan Wang
- , Keith Livingstone
- & Ryan Gilmour
-
Research Briefing |
 Rigid macrocycles with multiple hydrogen-bond donors for effective anion binding and transport
Rigid macrocycles with multiple hydrogen-bond donors for effective anion binding and transport
Aromatic oligoamide macrocycles have been developed in which the constrained backbone enforces hydrogen-bond donors to orient towards the macrocycle centre, forming a highly electropositive cavity. These macrocycles show strong binding for various anions and can partition into biomembranes to facilitate selective transmembrane anion transport.
-
Article |
 Aromatic pentaamide macrocycles bind anions with high affinity for transport across biomembranes
Aromatic pentaamide macrocycles bind anions with high affinity for transport across biomembranes
Effective synthetic anion receptors are challenging to design. Now, star-shaped macrocycles, with a cavity defined by multiple convergent amide NH and phenyl CH groups, have been synthesized in one pot from their monomeric building blocks. These macrocycles strongly bind a variety of anions, selectively transport chloride across cell membranes and restore the function of cystic fibrosis cells.
- Ruikai Cao
- , Robert B. Rossdeutcher
- & Bing Gong
-
Article |
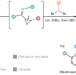 Modular synthesis of 1,2-azaborines via ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation
Modular synthesis of 1,2-azaborines via ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation
Preparation of monocyclic 1,2-azaborines, a unique class of benzene isosteres, has been challenging. Now, an efficient and modular method has been developed to access diverse multi-substituted 1,2-azaborines from readily available cyclopropyl imines/ketones and dibromoboranes. The reaction goes through an unusual ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation mechanism.
- Hairong Lyu
- , Thomas H. Tugwell
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrafluorenofulvalene as a sterically frustrated open-shell alkene
Tetrafluorenofulvalene as a sterically frustrated open-shell alkene
Tetrafluorenofulvalene (TFF) defies conventional rules of bond strength in organic chemistry. In particular, the central alkene bond of TFF becomes stronger in the quintet state and in the tetraanion. These changes arise from the unusual interplay between the twist, aromaticity and spin pairing in the π-electron system of TFF.
- Bibek Prajapati
- , Madan D. Ambhore
- & Marcin Stępień
-
News & Views |
 A foggy day in London dispersion town
A foggy day in London dispersion town
The factors that control the solubility of a salt are many and varied. Now a set of salts with closely related cations suggests that weak London dispersion-controlled CH···π interactions can dominate solubility, despite the presence of much stronger forces.
- Steve Scheiner
-
News & Views |
 Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
The intentional interweaving of two different metal–organic framework (MOF) lattices could offer a strategy for combining the disparate properties of the two frameworks within a single MOF material. Now, the rational construction of such hetero-interpenetrated MOFs has been demonstrated.
- Tendai Gadzikwa
-
News & Views |
 Photophysical oxidation of atmospheric carbonyls
Photophysical oxidation of atmospheric carbonyls
Light is a major driver of the chemistry of the atmosphere and usually involves the photolytic fragmentation of molecules into radicals before their reaction. New results show that formaldehyde, excited by low-energy light, can react with oxygen, opening up alternative atmospheric oxidation pathways.
- Paul W. Seakins
-
In Your Element |
 Casting TNT as an explosive
Casting TNT as an explosive
Few explosives are better-known to non-chemists than trinitrotoluene (TNT). Thomas M. Klapötke reflects on the enduring appeal of TNT and whether its starring role as an explosive is nearing its end.
- Thomas M. Klapötke
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrically frustrated interactions drive structural complexity in amorphous calcium carbonate
Geometrically frustrated interactions drive structural complexity in amorphous calcium carbonate
Although amorphous calcium carbonate represents an important biomineralization precursor, its structure has been difficult to understand. Now, amorphous calcium carbonate’s structure is shown to arise from the different bridging modes available to the calcium ions. This effective multi-well potential that drives calcium arrangements creates a geometric incompatibility between preferred Ca–Ca distances and frustrates crystallization.
- Thomas C. Nicholas
- , Adam Edward Stones
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article
| Open Access The interface of condensates of the hnRNPA1 low-complexity domain promotes formation of amyloid fibrils
The interface of condensates of the hnRNPA1 low-complexity domain promotes formation of amyloid fibrils
Understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the maturation of protein condensates into amyloid fibrils associated with neurodegenerative diseases has so far remained elusive. Now it has been shown that in condensates formed by the low-complexity domain of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated protein hnRNPA1, fibril formation is promoted at the interface, which provides a potential therapeutic target for counteracting aberrant protein aggregation.
- Miriam Linsenmeier
- , Lenka Faltova
- & Paolo Arosio
-
Article |
 The role of aromaticity in the cyclization and polymerization of alkyne-substituted porphyrins on Au(111)
The role of aromaticity in the cyclization and polymerization of alkyne-substituted porphyrins on Au(111)
While aromaticity is a useful concept for assessing the reactivity of organic compounds, the connection between aromaticity and on-surface chemistry remains largely unexplored. Now, scanning probe experiments on cyclization reactions of porphyrins on Au(111) show that the peripheral carbon atoms outside of the aromatic 18-π electron pathway exhibit a higher reactivity.
- Nan Cao
- , Jonas Björk
- & Alexander Riss
-
Article |
 Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks offer a highly tunable class of materials for a range of applications, although their dynamic structural transformations are challenging to analyse. Now single-crystal X-ray diffraction is shown to demonstrate single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformations of the imine linkages, showing a well-defined interpenetrating topology and affording structures that have high positive thermal expansion and anhydrous proton-conduction properties.
- Baoqiu Yu
- , Rui-Biao Lin
- & Jianzhuang Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Deuterated compounds are used in many applications such as mass-spectrometry standards, drugs or in organic light-emitting diodes. Now, hydrogen-activated homogeneous pincer complex catalysts can be used to perform selective alkene deuteration with the cheapest available deuterium source, D2O.
- Anika Tarasewicz
- & Volker Derdau
-
Research Briefing |
 Iron(iii) porphyrin complexes as metalloradical catalysts
Iron(iii) porphyrin complexes as metalloradical catalysts
Experimental and computational studies establish the operation of Fe(iii)-based metalloradical catalysis for the asymmetric cyclopropanation of alkenes with different classes of diazo compounds. The reaction proceeds through a stepwise radical mechanism involving α-Fe(iv)-alkyl and γ-Fe(iv)-alkyl radical intermediates. This work provides a future direction for the development of metalloradical catalysis.
-
Article |
 DNAzyme-based faithful probing and pulldown to identify candidate biomarkers of low abundance
DNAzyme-based faithful probing and pulldown to identify candidate biomarkers of low abundance
The discovery of biomarkers remains challenging owing to a lack of methods sensitive enough to identify such rare molecules. Now, by simultaneously exploiting the catalysis and affinity of a DNAzyme, candidate biomarkers with low abundance in cancers can be pulled down for identification and validation.
- Qinqin Hu
- , Zongxuan Tong
- & Hongzhou Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Assembling membraneless organelles from de novo designed proteins
Assembling membraneless organelles from de novo designed proteins
Phase separation is being revealed as important in many biological processes. Most attempts to mimic and deconstruct this use engineered natural proteins. Now it is shown that de novo proteins can be designed from first principles to undergo liquid–liquid phase separation in cells, with the potential to organize multi-enzyme pathways.
- Alexander T. Hilditch
- , Andrey Romanyuk
- & Derek N. Woolfson
-
News & Views |
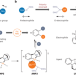 Aryl ortho methoxylation
Aryl ortho methoxylation
Aryl ethers are useful intermediates in organic synthesis and are found in countless biologically active compounds. Now, through palladium/norbornene cooperative catalysis and incorporation of a polarity-reversed N–O reagent as the O-electrophile, an efficient arene methoxylation approach has been successfully developed.
- Kun Zhao
- & Zhenhua Gu
-
Article |
 Carbonyl cross-metathesis via deoxygenative gem-di-metal catalysis
Carbonyl cross-metathesis via deoxygenative gem-di-metal catalysis
Merging carbonyls to form an alkene by removing their oxygens is rare, yet synthetically useful, and the selective combination of two different carbonyls is especially challenging. Now, two strategies for cross-metathesis of unbiased carbonyls have been developed. An Fe-catalysed carbene/ylide strategy affords Z-alkenes, while Cr-catalysed gem-di-metals yield E-alkenes.
- Lumin Zhang
- & David A. Nagib
-
Article |
 Iron(III)-based metalloradical catalysis for asymmetric cyclopropanation via a stepwise radical mechanism
Iron(III)-based metalloradical catalysis for asymmetric cyclopropanation via a stepwise radical mechanism
Cobalt(II) complexes of porphyrins have dominated the development of metalloradical catalysts. Now it has been shown that five-coordinate iron(III) complexes of porphyrins with an axial ligand are also potent metalloradical catalysts for olefin cyclopropanation. They are shown to react with different classes of diazo compounds via a stepwise radical mechanism.
- Wan-Chen Cindy Lee
- , Duo-Sheng Wang
- & X. Peter Zhang
-
Article |
 Hydrogenative alkene perdeuteration aided by a transient cooperative ligand
Hydrogenative alkene perdeuteration aided by a transient cooperative ligand
Deuterogenation methods typically introduce only two deuterium atoms per unsaturation. Now the single-step hydrogenative perdeuteration of alkenes has been achieved using H2 and D2O, with incorporation of up to 4.9 D atoms per C=C double bond. The reaction is catalysed by a ruthenium pincer complex with a catalytic amount of thiol, which serves as a transient cooperative ligand.
- Jie Luo
- , Lijun Lu
- & David Milstein
-
In Your Element |
 Out of the African soil
Out of the African soil
Clinton Veale and Fanie van Heerden discuss the story of natamycin. From its humble telluric origins in Pietermaritzburg, this unique antimicrobial agent has risen to become a mainstay of the food and beverages industry.
- Clinton G. L. Veale
- & Fanie R. van Heerden
-
Article |
 Ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides enabled by a polarity-reversed N–O reagent
Ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides enabled by a polarity-reversed N–O reagent
Pd/norbornene cooperative catalysis provides a strategy for arene functionalization, but the electrophile scope is typically limited to ‘soft’ elements such as carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. Now the ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides has been realized using a polarity-reversed N−O reagent and facilitated by a C7-bromo-substituted norbornene mediator.
- Xin Liu
- , Yue Fu
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 Light-driven eco-evolutionary dynamics in a synthetic replicator system
Light-driven eco-evolutionary dynamics in a synthetic replicator system
The onset of eco-evolutionary dynamics marks a stepping stone in the transition from chemistry to biology. Now a minimal replicator system showing such dynamics has been developed. The replicators adapt to changes in their environment that they themselves induced through photoredox catalysis.
- Kai Liu
- , Alex Blokhuis
- & Sijbren Otto
-
Article |
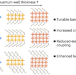 Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Two-dimensional hybrid perovskites have gained substantial interest recently due to their controllable optoelectronic properties; however precise control over layer thickness has been synthetically challenging. Now a crystal growth method is shown to achieve high-quality single crystals of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites with control over their thickness and length through judicious solvent choice, affording precisely tuned optoelectronic properties.
- Jee Yung Park
- , Ruyi Song
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
 Discovering covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions from trillions of sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange-modified oligonucleotides
Discovering covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions from trillions of sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange-modified oligonucleotides
Covalent inhibitors offer high potency but their potential is hindered by off-target reactivity. Now, an in vitro selection method has been developed to enable the discovery of covalent inhibitors from trillions of oligonucleotides endowed with the sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange chemistry. This strategy generates covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions with optimally balanced selectivity and reactivity.
- Zichen Qin
- , Kaining Zhang
- & Yu Xiang
-
Article |
 Pervasive transcriptome interactions of protein-targeted drugs
Pervasive transcriptome interactions of protein-targeted drugs
Now a reactivity-based RNA profiling strategy can measure the global off-target transcriptome interactions of small-molecule drugs at single-nucleotide resolution. Using this approach, three FDA-approved drugs were evaluated, uncovering pervasive drug–RNA interactions and interactions that perturb RNA functions in cells.
- Linglan Fang
- , Willem A. Velema
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Research Briefing |
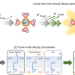 Hot spots of radiation damage from extensive water ionization around metal ions
Hot spots of radiation damage from extensive water ionization around metal ions
Radiation damage in biological systems by radicals and low-energy electrons formed from water ionization is a consequence of ultrafast processes that follow core-level ionization of hydrated metal ions. More details of the complex pathway are now revealed from the study of aluminium-ion relaxation through sequential electron-transfer-mediated decay.
-
News & Views |
 Insights into ultrafast H3+ formation provide a glimpse into primordial chemistry
Insights into ultrafast H3+ formation provide a glimpse into primordial chemistry
When atoms first appeared in the Universe, molecules were needed to help coalesce them into stars. The trihydrogen cation H3+ is among the prime candidates for that process, and now two independent studies provide detailed insight into the ultrafast dynamics of the formation of this important ion from two hydrogen molecules.
- Marcos Dantus
-
News & Views |
 Li–O2 battery redox mediators go positive
Li–O2 battery redox mediators go positive
Although Li–O2 batteries offer high theoretical energy storage capacities, few approach these limits. Now, a class of redox mediators is shown to send the discharge reaction from the electrode surface into the electrolyte solution, boosting device capacities and providing selection criteria for future efforts.
- Zhangquan Peng
-
Article |
 Direct observation of geometric-phase interference in dynamics around a conical intersection
Direct observation of geometric-phase interference in dynamics around a conical intersection
Wavepacket dynamics around conical intersections are influenced by geometric phase, which can affect chemical reaction outcomes but has only been observed through indirect signatures. Now, by engineering a controllable conical intersection in a trapped-ion quantum simulator, the destructive wavepacket interference caused by a geometric phase has been observed.
- C. H. Valahu
- , V. C. Olaya-Agudelo
- & I. Kassal
-
Article |
 Quantum simulation of conical intersections using trapped ions
Quantum simulation of conical intersections using trapped ions
Geometric phase interference has been predicted to appear around conical intersections but has been experimentally illusive owing to competing effects in molecular systems. Now, this effect has been demonstrated in chains of trapped ions using state-of-the-art quantum simulation and read-out techniques.
- Jacob Whitlow
- , Zhubing Jia
- & Kenneth R. Brown
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers
Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers A 21-electron cobalt sandwich
A 21-electron cobalt sandwich Taking copper’s pulse with Raman
Taking copper’s pulse with Raman