Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
A previous investigation of the anti-aromatic dianion of [18]annulene concluded that it consists of a mixture of two isomers. Now it has been shown that this dianion exists as a single isomer, with a different geometry from neutral [18]annulene, and that it can be reduced further to an aromatic tetraanion.
- Wojciech Stawski
- , Yikun Zhu
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article |
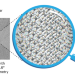 Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Near-atomic-resolution structure of J-aggregated helical light-harvesting nanotubes
Chromophore supramolecular assemblies have long been studied for their exotic photophysical properties arising from their local geometry and long-range sensitive excitonic couplings. Now a high-resolution structure of a model nanotubular system has revealed a uniform brick-layer molecular arrangement and a non-biological supramolecular motif—interlocking sulfonates—enabling clear understanding of supramolecular structure–excitonic property relationships.
- Arundhati P. Deshmukh
- , Weili Zheng
- & Justin R. Caram
-
Article
| Open Access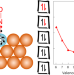 Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Single-atom alloys have emerged as highly active and selective catalysts that do not follow the traditional models of heterogeneous catalysis. Now it has been shown that the binding of adsorbates at their surface abides by a simple 10-electron count rule, which can identify promising catalysts for various applications.
- Julia Schumann
- , Michail Stamatakis
- & Romain Réocreux
-
Article |
 Structural characterization and reactivity of a room-temperature-stable, antiaromatic cyclopentadienyl cation salt
Structural characterization and reactivity of a room-temperature-stable, antiaromatic cyclopentadienyl cation salt
The synthesis, structure and reactivity of room-temperature-stable [Cp(C6F5)5]+[Sb3F16]− is presented. Coordination of the cyclopentadienyl cation by [Sb3F16]− or C6F6 stabilizes the antiaromatic singlet state in the solid state. Calculated hydride and fluoride ion affinities of the [Cp(C6F5)5]+ cation are higher than those of the tritylium cation [C(C6F5)3]+.
- Yannick Schulte
- , Christoph Wölper
- & Stephan Schulz
-
Article
| Open Access Surface stratification determines the interfacial water structure of simple electrolyte solutions
Surface stratification determines the interfacial water structure of simple electrolyte solutions
The organization of electrolytes at the air/water interface affects the structure of interfacial water and therefore numerous natural processes. It has now been demonstrated that the surface of an electrolyte solution is stratified and consists of an ion-depleted outer surface and an ion-enriched subsurface layer, jointly determining the water interfacial structure.
- Yair Litman
- , Kuo-Yang Chiang
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article |
 Analogies between photochemical reactions and ground-state post-transition-state bifurcations shed light on dynamical origins of selectivity
Analogies between photochemical reactions and ground-state post-transition-state bifurcations shed light on dynamical origins of selectivity
Selectivity of photochemical reactions is notoriously difficult to model. Now it has been shown that by employing an analogy to ground-state reactions with post-transition-state bifurcations, selectivity for a complex photochemical denitrogenation reaction can be captured and rationalized, and its dynamical origins understood.
- Zhitao Feng
- , Wentao Guo
- & Dean J. Tantillo
-
Article |
 Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Activation of H2 by a metal–olefin complex is characterized experimentally and computationally using a nickel pincer complex, showing that the reaction proceeds via a direct ligand-to-ligand hydrogen transfer mechanism. An application of this cooperative H2-activation mechanism is demonstrated in the nickel-catalysed semihydrogenation of diphenylacetylene.
- María L. G. Sansores-Paredes
- , Martin Lutz
- & Marc-Etienne Moret
-
News & Views |
 An open-shell molecule that exhibits conformational dynamics
An open-shell molecule that exhibits conformational dynamics
Open-shell organic molecules with properties that can be modulated by external stimuli are of interest for spintronics applications. Now, an overcrowded alkene with open-shell tetraradical character has been synthesized in which the interaction between the π-conjugated subunits depends on the charge and spin state.
- Yoshito Tobe
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrafluorenofulvalene as a sterically frustrated open-shell alkene
Tetrafluorenofulvalene as a sterically frustrated open-shell alkene
Tetrafluorenofulvalene (TFF) defies conventional rules of bond strength in organic chemistry. In particular, the central alkene bond of TFF becomes stronger in the quintet state and in the tetraanion. These changes arise from the unusual interplay between the twist, aromaticity and spin pairing in the π-electron system of TFF.
- Bibek Prajapati
- , Madan D. Ambhore
- & Marcin Stępień
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
Research Briefing |
 Hot spots of radiation damage from extensive water ionization around metal ions
Hot spots of radiation damage from extensive water ionization around metal ions
Radiation damage in biological systems by radicals and low-energy electrons formed from water ionization is a consequence of ultrafast processes that follow core-level ionization of hydrated metal ions. More details of the complex pathway are now revealed from the study of aluminium-ion relaxation through sequential electron-transfer-mediated decay.
-
Article |
 Direct observation of geometric-phase interference in dynamics around a conical intersection
Direct observation of geometric-phase interference in dynamics around a conical intersection
Wavepacket dynamics around conical intersections are influenced by geometric phase, which can affect chemical reaction outcomes but has only been observed through indirect signatures. Now, by engineering a controllable conical intersection in a trapped-ion quantum simulator, the destructive wavepacket interference caused by a geometric phase has been observed.
- C. H. Valahu
- , V. C. Olaya-Agudelo
- & I. Kassal
-
Article
| Open Access Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Pump–probe measurements conventionally achieve femtosecond time resolution for X-ray crystallography of reactive processes, but the measured structural dynamics are complex. Using coherent control techniques, we show that the ultrafast crystallographic differences of a fluorescent protein are dominated by ground-state vibrational processes that are unconnected to the photoisomerization reaction of the chromophore.
- Christopher D. M. Hutchison
- , James M. Baxter
- & Jasper J. van Thor
-
Article |
 Imaging of the charge-transfer reaction of spin–orbit state-selected Ar+(2P3/2) with N2 reveals vibrational-state-specific mechanisms
Imaging of the charge-transfer reaction of spin–orbit state-selected Ar+(2P3/2) with N2 reveals vibrational-state-specific mechanisms
Quantum state-to-state understanding of collisional charge transfer is a long-time goal of chemical dynamics. Now, using high-resolution molecular-beam experiments with spin–orbit state-selected ions and surface-hopping calculations, a vibrational-state-specific mechanism has been observed for the reaction Ar+(2P3/2) + N2 → Ar + N2+(v′, J′). Besides the well-known long-range harpooning mechanism, a hard-collision glory scattering mechanism was also identified.
- Guodong Zhang
- , Dandan Lu
- & Hong Gao
-
Article |
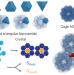 Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Clathrates—open crystals with a hierarchy of polyhedral cages—are mostly found in atomic and molecular systems. Now, it has been shown through Monte Carlo simulations that the formation of colloidal host–guest clathrates can be driven by entropy alone, through entropy compartmentalization.
- Sangmin Lee
- , Thi Vo
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-dependent reactivity and spin-flipping dynamics in oxygen atom scattering from graphite
Spin-dependent reactivity and spin-flipping dynamics in oxygen atom scattering from graphite
Electronic spin influences chemistry profoundly, but its role in surface chemistry is poorly established. Now the spin-dependent reaction probabilities of oxygen atoms with a graphite surface have been studied. Molecular dynamics simulations help elucidate the mechanism for spin-flipping, which is observed to occur with low probability in surface scattering experiments.
- Zibo Zhao
- , Yingqi Wang
- & G. Barratt Park
-
Article |
 Indole-5,6-quinones display hallmark properties of eumelanin
Indole-5,6-quinones display hallmark properties of eumelanin
Indole-5,6-quinone (IQ) is a long-sought intermediate and structural subunit of eumelanin pigments whose instability has precluded isolation and characterization. It has now been shown that a sterically shielded derivative of IQ exhibits hallmark eumelanin properties, including near-infrared absorption, ultrafast nonradiative decay and a persistent semiquinone radical formed by comproportionation.
- Xueqing Wang
- , Lilia Kinziabulatova
- & Jean-Philip Lumb
-
Research Briefing |
 Serial rotation electron diffraction for rapid phase analysis to accelerate materials development
Serial rotation electron diffraction for rapid phase analysis to accelerate materials development
Serial rotation electron diffraction (SerialRED) enables rapid and reliable phase analysis and structure determination of complex polycrystalline materials that cannot be routinely characterized using X-ray diffraction. Five zeolite phases were identified in a single synthesis product by automated screening of hundreds of crystals, demonstrating the power of SerialRED for materials development.
-
Article
| Open Access Janus-type emission from a cyclometalated iron(iii) complex
Janus-type emission from a cyclometalated iron(iii) complex
Noble metals dominate the field of photosensitizers and luminophores. Now, an approach incorporating cyclometalating and carbene functions into FeIII complexes has been shown to enable dual emission from the opposing ligand-to-metal and metal-to-ligand charge-transfer states. The latter shows an exceptionally long lifetime of 4.6 ns and is quenched by oxygen and other quenchers.
- Jakob Steube
- , Ayla Kruse
- & Matthias Bauer
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials using serial rotation electron diffraction
High-throughput phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials using serial rotation electron diffraction
X-ray diffraction is crucial for the phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials but remains challenging for complex multiphase systems. Now serial rotation electron diffraction has been shown to enable rapid, reliable and semiquantitative phase analysis of such systems, facilitating high-throughput screening of complex synthesis systems and providing new opportunities for materials development.
- Yi Luo
- , Bin Wang
- & Xiaodong Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Photoswitching neutral homoaromatic hydrocarbons
Photoswitching neutral homoaromatic hydrocarbons
Neutral homoaromatic hydrocarbons—which possess an interrupted π-system yet display aromatic properties owing to through-space or through-bond interactions—have remained rare as they are typically unstable. Now a class of stable neutral homoaromatic homoannulenes has been synthesized, including one that acts as a photoswitch through a reversible [1, 11] sigmatropic rearrangement.
- Trung Tran Ngoc
- , Niklas Grabicki
- & Johannes F. Teichert
-
Article
| Open Access φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
Aromaticity is a ubiquitous concept in organic chemistry yet it is less widespread for inorganic species. Now the cluster [(CpRu)3Bi6]–, obtained as part of a soluble salt, has been shown to exhibit aromatic behaviour referred to as φ-type, owing to a highly regular {Bi6} substructure causing a non-localizable molecular orbital of \(f_{z^3}\)-like symmetry.
- Benjamin Peerless
- , Andreas Schmidt
- & Stefanie Dehnen
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
The nitrogen reduction reaction is an extremely valuable but energy-intensive process. Now, a coordination polymer based on a [Zn–N2–Zn] unit has been shown to promote the formation of ammonia under ambient conditions by a photocatalytic reaction. The N2 moieties within the framework are reduced, creating unsaturated [Zn2+···Zn+] intermediates that are able to capture external N2 and sustain the cycle.
- Yan Xiong
- , Bang Li
- & Zhong Jin
-
Article |
 How synonymous mutations alter enzyme structure and function over long timescales
How synonymous mutations alter enzyme structure and function over long timescales
Enzymes with identical sequences of amino acids can display varying activities when encoded with mRNA with different properties, but why this is the case has been a mystery. Now, it has been shown that synonymous mutations in mRNA alter the partitioning of proteins into long-lived soluble misfolded states with varying activities.
- Yang Jiang
- , Syam Sundar Neti
- & Edward P. O’Brien
-
Article |
 Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Gold nanoparticles typically exhibit hard-sphere-like assembly behaviour, but now the size, morphology and symmetry of crystals of Au25 nanoparticles have been tuned. The presence of excess tetraethylammonium cations has been shown to promote the one-dimensional assembly of the nanoparticles, which in turn form rod-like crystals, by stabilizing dynamically detached ligands from adjacent particles into interparticle linkers through CH⋯π and ion-pairing interactions.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Lingmei Liu
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article |
 Intersystem crossing in the entrance channel of the reaction of O(3P) with pyridine
Intersystem crossing in the entrance channel of the reaction of O(3P) with pyridine
Intersystem crossing in reaction entrance channels usually arises from ‘heavy-atom’ effects. Now molecular-beam experiments show that even without heavy atoms, the O(3P) + pyridine reaction leads to spin-forbidden pyrrole + CO products. Theoretical calculations reveal efficient intersystem crossing before the entrance barrier for O-atom addition to the N-atom lone pair, which dominates reactivity at low to moderate temperatures.
- Pedro Recio
- , Silvia Alessandrini
- & Vincenzo Barone
-
News & Views |
 Isolating intermediates
Isolating intermediates
Noyori-type catalysts and inorganic bases are frequently used together for homogeneous hydrogenation, but key intermediates have not yet been isolated. Now, the structure and reactivity of a long-postulated intermediate — the alkali metal amidate complex — have been reported through experimental and computational studies.
- Pavel A. Dub
-
News & Views |
 The chemistry of errors
The chemistry of errors
The application of machine learning to big data, to make quantitative predictions about reaction outcomes, has been fraught with failure. This is because so many chemical-reaction data are not fit for purpose, but predictions would be less error-prone if synthetic chemists changed their reaction design and reporting practices.
- Jacqueline M. Cole
-
Article |
 Different timescales during ultrafast stilbene isomerization in the gas and liquid phases revealed using time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
Different timescales during ultrafast stilbene isomerization in the gas and liquid phases revealed using time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
The influence that liquid environments have on the ultrafast excited-state dynamics of molecules is poorly understood. Using time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy, the dynamics of the photoisomerization of stilbene in the gas and liquid phases have now been shown to be qualitatively similar—including the observation of vibrational coherences—but the timescales are significantly longer in the liquid phase.
- Chuncheng Wang
- , Max D. J. Waters
- & Hans Jakob Wörner
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Although neutral and anionic low-valent aluminium complexes are widespread, their cationic counterparts have remained rare. Now, a salt of [Al(AlCp*)3]+ featuring a formal low-valent Al+ cation has been isolated that dimerizes in concentrated solutions and the solid state, and also forms Al4 clusters on coordinating with Lewis bases.
- Philipp Dabringhaus
- , Julie Willrett
- & Ingo Krossing
-
Article |
 Functionalizing aromatic compounds with optical cycling centres
Functionalizing aromatic compounds with optical cycling centres
Laser cooling of molecules with more than six atoms is challenging, mainly due to vibrational loss to dark states. Now, taking a step towards the development of a ‘quantum functional group’, it has been shown that such vibrational loss in molecules like phenol can be greatly restricted by functionalizing with a Ca(I)–O unit, which may serve as a generic qubit moiety.
- Guo-Zhu Zhu
- , Debayan Mitra
- & Eric R. Hudson
-
Article |
 Taming phosphorus mononitride
Taming phosphorus mononitride
Precursors for the release of phosphorus mononitride in solution under mild conditions have remained elusive. Now, an explosive anthracene-stabilized azidophosphine has shown PN transfer reactivity in the synthesis of an Fe–NP complex. The PN ligand is N-bonded, as the Fe–N interaction shows significant covalent character and a less unfavourable Pauli repulsion than its Fe–P counterpart.
- André K. Eckhardt
- , Martin-Louis Y. Riu
- & Christopher C. Cummins
-
Article |
 Deep learning study of tyrosine reveals that roaming can lead to photodamage
Deep learning study of tyrosine reveals that roaming can lead to photodamage
Amino acids are one of the major building blocks of life, but the ways in which they respond to light excitation are not fully understood. Now, the photochemistry of tyrosine has been studied using physically inspired deep neural networks, leading to the observation of unconventional dynamically controlled reactivity that involves ‘roaming’ radicals that can cause photodamage.
- Julia Westermayr
- , Michael Gastegger
- & Philipp Marquetand
-
Article |
 Condensates in RNA repeat sequences are heterogeneously organized and exhibit reptation dynamics
Condensates in RNA repeat sequences are heterogeneously organized and exhibit reptation dynamics
The molecular driving forces underlying the liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) of RNA are not well understood. Now simulations show that low-complexity RNA sequences undergo LLPS at high RNA concentrations, driven by the formation of Watson–Crick base pairs between distinct RNA polymers. LLPS occurs by merger of small droplets into larger ones and RNA chains in the large droplets exhibit reptation dynamics.
- Hung T. Nguyen
- , Naoto Hori
- & D. Thirumalai
-
Article |
 Binding methane to a metal centre
Binding methane to a metal centre
Catalytic transformations of methane frequently involve the formation of a metal–methane complex, but these compounds are challenging to observe. Now, a relatively long-lived osmium–methane complex has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy and forms from the direct binding of methane to a photolytically generated, coordinatively unsaturated cationic osmium–carbonyl complex dissolved in an inert hydrofluorocarbon solvent at –90 °C.
- James. D. Watson
- , Leslie. D. Field
- & Graham. E. Ball
-
Article |
 Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Most chemical glycosylation methods operate by acid-promoted, ionic activation of donors. Now, by exploiting the formation of a halogen-bond complex, the activation of glycosyl donors was achieved via a visible light-promoted radical cascade process, resulting in a general, simple and mild way to build challenging 1,2-cis-glycosidic bonds.
- Chen Zhang
- , Hao Zuo
- & Dawen Niu
-
Article |
 Glory scattering in deeply inelastic molecular collisions
Glory scattering in deeply inelastic molecular collisions
Molecular energy transfer is thought to follow a simple rule of thumb: high energy transfer requires hard collisions that result in backscattering. However, now it has been observed that an unexpected forward scattering occurs in NO–CO and NO–HD collisions even for high energy transfer. This is attributed to ‘hard-collision glory scattering’, a mechanism that appears to be ubiquitous in molecule–molecule collisions.
- Matthieu Besemer
- , Guoqiang Tang
- & Tijs Karman
-
Article |
 Insights from an information thermodynamics analysis of a synthetic molecular motor
Insights from an information thermodynamics analysis of a synthetic molecular motor
Information is physical, but the flow between information, energy and mechanics in chemical systems remains largely unexplored. Now, an autonomous molecular motor has been analysed with information thermodynamics, which relates information to other thermodynamic parameters. This treatment provides a general thermodynamic understanding of molecular motors, with practical implications for machine design.
- Shuntaro Amano
- , Massimiliano Esposito
- & Benjamin M. W. Roberts
-
Article |
 A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
The s-orbital mixing into the spin-bearing d orbital associated with a molecular Lu(II) complex is shown to both reduce spin–orbit coupling and increase electron–nuclear hyperfine interactions, which substantially improves electron spin coherence. Combined with the potential to tune interactions through coordination chemistry, it makes this system attractive for quantum information applications.
- Krishnendu Kundu
- , Jessica R. K. White
- & Stephen Hill
-
Article |
 Quantum–classical simulations of rhodopsin reveal excited-state population splitting and its effects on quantum efficiency
Quantum–classical simulations of rhodopsin reveal excited-state population splitting and its effects on quantum efficiency
Rhodopsin activation is driven by an ultrafast double-bond isomerization, but questions remain about the origin of its sensitivity. Now, quantum–classical simulations show that, 15 fs after light absorption, a degeneracy between the reactive excited state and a neighbouring state causes the splitting of the rhodopsin population into subpopulations, which propagate with different velocities, leading to distinct contributions to the quantum efficiency.
- Xuchun Yang
- , Madushanka Manathunga
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article |
 Tunable angle-dependent electrochemistry at twisted bilayer graphene with moiré flat bands
Tunable angle-dependent electrochemistry at twisted bilayer graphene with moiré flat bands
Controlling the crystallographic registry of layered materials through interlayer twist angles has introduced a distinctive degree of freedom for tuning their electronic behaviour. Now, the interfacial electrochemical kinetics of solution-phase redox complexes at twisted bilayer graphene electrodes have been modulated by the angle-dependent tuning of moiré-derived flat bands.
- Yun Yu
- , Kaidi Zhang
- & D. Kwabena Bediako
-
News & Views |
 Fast track to structural biology
Fast track to structural biology
Machine learning algorithms are fast surpassing human abilities in multiple tasks, from image recognition to medical diagnostics. Now, machine learning algorithms have been shown to be capable of accurately predicting the folded structures of proteins.
- Cecilia Clementi
-
Article |
 Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
A haem protein that serves as a dual-function catalyst capable of inserting a carbene into a N–H bond to form α-amino lactones has been reported. The enzyme catalyses both carbene transfer and the subsequent proton transfer in a single active site. This transformation can proceed at the gram scale with high efficiency and enantioselective control.
- Zhen Liu
- , Carla Calvó-Tusell
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Article |
 Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Computationally designed enzymes can be substantially improved by directed evolution. Now, it has been shown that evolution can introduce a dynamic network that selectively tightens the transition-state ensemble, giving rise to a negative activation heat capacity. Targeting such transition state conformational dynamics may expedite de novo enzyme creation.
- H. Adrian Bunzel
- , J. L. Ross Anderson
- & Adrian J. Mulholland
-
Q&A |
 Artificial, augmented and automated chemistry
Artificial, augmented and automated chemistry
Jeremy Frey, professor of physical chemistry at the University of Southampton and principal investigator for the AI3SD Network+, talks with Nature Chemistry about the perils of uncertainty in the quality of machine learning data and the synergies between AI and other technologies.
- Russell Johnson
-
Article |
 Atomistic dynamics of elimination and nucleophilic substitution disentangled for the F− + CH3CH2Cl reaction
Atomistic dynamics of elimination and nucleophilic substitution disentangled for the F− + CH3CH2Cl reaction
As the number of atoms involved in a reaction increases, so do the experimental and theoretical challenges faced when studying their dynamics. Now, using ion-imaging experiments and quasi-classical trajectory simulations, the dynamics of the polyatomic reaction F– + CH3CH2Cl have been studied and the competition between bimolecular nucleophilic substitution and base-induced elimination has been disentangled.
- Jennifer Meyer
- , Viktor Tajti
- & Roland Wester
-
Article |
 Using collective knowledge to assign oxidation states of metal cations in metal–organic frameworks
Using collective knowledge to assign oxidation states of metal cations in metal–organic frameworks
Oxidation states help chemists to understand the bonding, properties and reactivity of compounds, but they can be difficult to determine for metal ions in extended crystalline materials. Now, oxidation states manually assigned to metal–organic frameworks have been harvested from the Cambridge Structural Database and used to build a machine-learning model that predicts oxidation states in metal–organic frameworks with good accuracy.
- Kevin Maik Jablonka
- , Daniele Ongari
- & Berend Smit
-
Article |
 Controlled growth of ordered monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on silicon
Controlled growth of ordered monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on silicon
Although monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) readily form on metals, surface reactivity usually hinders their self-assembly on semiconductors. Now, it has been shown that thermally stable, well-ordered monolayers of NHCs can be formed on silicon surfaces. A large reduction in work function is observed and steric effects enable sufficient diffusivity of the NHCs.
- Martin Franz
- , Sandhya Chandola
- & Mario Dähne
-
Comment |
 Best practices in machine learning for chemistry
Best practices in machine learning for chemistry
Statistical tools based on machine learning are becoming integrated into chemistry research workflows. We discuss the elements necessary to train reliable, repeatable and reproducible models, and recommend a set of guidelines for machine learning reports.
- Nongnuch Artrith
- , Keith T. Butler
- & Aron Walsh

 Exploring the frontiers of condensed-phase chemistry with a general reactive machine learning potential
Exploring the frontiers of condensed-phase chemistry with a general reactive machine learning potential