Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Dynamic crystal structure of a molecular framework
Dynamic crystal structure of a molecular framework
X-ray diffraction analysis typically affords the static 3D structures of given compounds or materials, but to understand chemical processes, the visualization of fast structural changes is desirable. Time-resolved femtosecond crystallography has now been used to monitor the structural dynamics of a photoactive metal–organic framework.
- Lauren E. Hatcher
- & Paul R. Raithby
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations
Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations
Radical polymerizations yield polymers that cannot easily be degraded. The co-polymerization of cyclobutene-based monomers with conventional vinyl monomers has now been shown to result in co-polymers with cyclobutane mechanophores in their backbone, which facilitate on-demand degradation through a combination of mechanical activation and hydrolysis. This approach offers a promising avenue for the degradation of all-carbon-bond-backbone polymers.
- Peng Liu
- , Sètuhn Jimaja
- & Nico Bruns
-
Article
| Open Access Upcycling of polyethylene to gasoline through a self-supplied hydrogen strategy in a layered self-pillared zeolite
Upcycling of polyethylene to gasoline through a self-supplied hydrogen strategy in a layered self-pillared zeolite
The development of new methodologies to convert plastics into fuels without relying on noble metal-based catalysts is desirable. Now it is shown that a layered self-pillared zeolite enables the conversion of polyethylene to gasoline with a selectivity of 99% and yields of >80% without the need to use external hydrogen.
- Ziyu Cen
- , Xue Han
- & Buxing Han
-
Article |
 Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Accessing longer-wavelength emitting organic fluorophores is critical for diagnostic imaging. Here a series of silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with emission maxima at 1,300 nm, 1,550 nm and 1,700 nm were synthesized. The fluorophores generate high-resolution in vivo fluorescence images in mice and establish design principles for future shortwave-infrared fluorophore designs.
- William E. Meador
- , Eric Y. Lin
- & Jared H. Delcamp
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic three-dimensional structures of a metal–organic framework captured with femtosecond serial crystallography
Dynamic three-dimensional structures of a metal–organic framework captured with femtosecond serial crystallography
Time-resolved femtosecond crystallography (TR-SFX) is a powerful technique to monitor structural transitions in protein crystals at the atomic level, but its use in non-protein synthetic materials remains limited. Now TR-SFX has been used to visualize the structural dynamics of metal–organic frameworks, showing the potential of this tool to study the dynamic motion of crystalline porous materials.
- Jaedong Kang
- , Yunbeom Lee
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfiguring hydrogel assemblies using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive for multiple customized functions
Reconfiguring hydrogel assemblies using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive for multiple customized functions
Although hydrogels with complex, heterogeneous and reconfigurable structures are promising materials for use in intelligent systems, fabricating such hydrogels is challenging. Now it has been shown that they can be fabricated by reversibly gluing different hydrogel units using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive. This method can be used to design hydrogels with customized functions.
- Jiahui Liu
- , Yun-Shuai Huang
- & Si Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons
Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons
The insertion of metal atoms and heteroaromatic units provides a way to tune the optical, electronic and magnetic properties of graphene nanoribbons. Now the synthesis of a porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbon with a narrow bandgap and high charge mobility has been achieved, and this material used to fabricate field-effect and single-electron transistors.
- Qiang Chen
- , Alessandro Lodi
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article |
 Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Valence tautomerism in lanthanide-based materials is rare. Now a one-dimensional samarium–pyrazine polymer has been shown to exhibit a temperature-induced hysteretic Sm(III)-to-Sm(II) reversible switch. The transition temperature is modulated in a 150 K window by alloying with Yb(II), presenting a strategy for developing new materials with chemically tunable magnetic switchability.
- Maja A. Dunstan
- , Anna S. Manvell
- & Kasper S. Pedersen
-
Article |
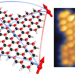 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
The design of open-shell nanographenes is commonly limited to systems featuring a single magnetic origin. Now a strategy that combines topological frustration and electron–electron interactions has been developed to generate a butterfly-shaped nanographene that hosts four highly entangled π-spins and exhibits both ferromagnetic and anti-ferromagnetic coupling.
- Shaotang Song
- , Andrés Pinar Solé
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access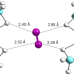 Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Although hydrogen gas could serve as a promising future fuel, its high-capacity storage is a challenge. Now, a nanoporous magnesium borohydride framework is shown to store hydrogen as densely packed penta-dihydrogen clusters having well-defined orientations and directional interactions with the framework.
- Hyunchul Oh
- , Nikolay Tumanov
- & Yaroslav Filinchuk
-
News & Views |
 Isotropic models for anisotropic inorganics
Isotropic models for anisotropic inorganics
The study of disordered materials poses numerous challenges, and computational approaches have proved useful to supplement and support structural experiments. Now, an abstract computational model has been used to study the structure of amorphous calcium carbonate, providing mechanistic insights into the emergence of the disordered phase as well as its atomic-level configurations.
- Julia Dshemuchadse
-
Article |
 Azobenzene as a photoswitchable mechanophore
Azobenzene as a photoswitchable mechanophore
Light-induced azobenzene cis/trans isomerization has been extensively investigated, but the mechanical strength of its cis/trans structure is not well understood. Now it has been shown that cis azobenzene is mechanically less stable than the trans isomer due to its regiochemical structure, as revealed by single-molecule force spectroscopy.
- Yiran Li
- , Bin Xue
- & Yi Cao
-
Article |
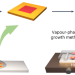 Lateral epitaxial growth of two-dimensional organic heterostructures
Lateral epitaxial growth of two-dimensional organic heterostructures
The synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) organic lateral heterostructures with desirable properties from organic single crystals remains challenging. Now, 2D organic lateral heterostructures have been produced by using a liquid-phase growth approach and vapour-phase growth method, enabling the structural inversion of organic lateral heterostructures via a two-step strategy.
- Qiang Lv
- , Xue-Dong Wang
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article |
 Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Bottom-up assembly of protocells into networking superstructures represents a further key step towards rudimentary formation of life. Now it has been shown that a pool of biomolecules can self-organize into an interactive binary population of protocell coacervates with a self-sorting chain-like configuration, allowing for biomolecular extraction, translocation and macroscale separation.
- Wenjing Mu
- , Liyan Jia
- & Yan Qiao
-
Article |
 RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
The physicochemical driving forces of protein-free, RNA-driven phase transitions were previously unclear, but it is now shown that RNAs undergo entropically driven liquid–liquid phase separation upon heating in the presence of magnesium ions. In the condensed phase, RNAs can undergo an enthalpically favourable percolation transition that leads to arrested condensates.
- Gable M. Wadsworth
- , Walter J. Zahurancik
- & Priya R. Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Surface heterogeneity is generally acknowledged as the major cause of liquid–solid friction, affecting whether droplets slide off the surface or stick to it. Now, a model surface of self-assembled monolayers has been used to investigate how molecular-scale surface heterogeneity affects water contact angle hysteresis and contact line friction. The high-coverage hydrophobic surface is slippery, as—counter-intuitively—is the low-coverage hydrophilic surface.
- Sakari Lepikko
- , Ygor Morais Jaques
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
News & Views |
 Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
Interweaving different metal–organic frameworks
The intentional interweaving of two different metal–organic framework (MOF) lattices could offer a strategy for combining the disparate properties of the two frameworks within a single MOF material. Now, the rational construction of such hetero-interpenetrated MOFs has been demonstrated.
- Tendai Gadzikwa
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrically frustrated interactions drive structural complexity in amorphous calcium carbonate
Geometrically frustrated interactions drive structural complexity in amorphous calcium carbonate
Although amorphous calcium carbonate represents an important biomineralization precursor, its structure has been difficult to understand. Now, amorphous calcium carbonate’s structure is shown to arise from the different bridging modes available to the calcium ions. This effective multi-well potential that drives calcium arrangements creates a geometric incompatibility between preferred Ca–Ca distances and frustrates crystallization.
- Thomas C. Nicholas
- , Adam Edward Stones
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article |
 Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Linkage conversions in single-crystalline covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks offer a highly tunable class of materials for a range of applications, although their dynamic structural transformations are challenging to analyse. Now single-crystal X-ray diffraction is shown to demonstrate single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformations of the imine linkages, showing a well-defined interpenetrating topology and affording structures that have high positive thermal expansion and anhydrous proton-conduction properties.
- Baoqiu Yu
- , Rui-Biao Lin
- & Jianzhuang Jiang
-
Article |
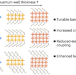 Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Two-dimensional hybrid perovskites have gained substantial interest recently due to their controllable optoelectronic properties; however precise control over layer thickness has been synthetically challenging. Now a crystal growth method is shown to achieve high-quality single crystals of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites with control over their thickness and length through judicious solvent choice, affording precisely tuned optoelectronic properties.
- Jee Yung Park
- , Ruyi Song
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
 Chemical upcycling of commodity thermoset polyurethane foams towards high-performance 3D photo-printing resins
Chemical upcycling of commodity thermoset polyurethane foams towards high-performance 3D photo-printing resins
Current strategies for recycling cross-linked polyurethane foam waste are economically unattractive and/or lead to recycled products with inferior properties. Now it has been shown that a cost-effective chemical strategy can be used to turn the foam into high-performance value-added three-dimensional photo-printing resins.
- Zenghe Liu
- , Zizheng Fang
- & Tao Xie
-
Article |
 Nucleation-mediated growth of chiral 3D organic–inorganic perovskite single crystals
Nucleation-mediated growth of chiral 3D organic–inorganic perovskite single crystals
While chiral hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites are promising materials for optoelectronic applications, the synthesis of three-dimensional single crystals has proven challenging. Now, a general strategy has been shown to synthesize chiral, three-dimensional perovskites by heterogeneous nucleation. The single-crystalline materials contain no chiral component; their chiroptical activity arises from supercells formed by chiral patterns of the A-site cations.
- Gaoyu Chen
- , Xiaoyu Liu
- & Xun Wang
-
Article |
 Hetero-interpenetrated metal–organic frameworks
Hetero-interpenetrated metal–organic frameworks
Interpenetration—in which two or more lattices are catenated—is common in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Now a deliberate synthesis of hetero-interpenetrated MOFs, with two distinct lattices, has been developed. It can combine the different properties of the two sublattices in one material, as demonstrated with chirality and catalytic activity, delivering an asymmetric catalyst.
- David Perl
- , Seok J. Lee
- & Shane G. Telfer
-
In Your Element |
 The many lives of calcium carbonate
The many lives of calcium carbonate
Fiona C. Meldrum and Helmut Cölfen chalk up some of the myriad forms and uses of calcium carbonate to burnish a ‘dull’ reputation.
- Fiona C. Meldrum
- & Helmut Cölfen
-
Article |
 Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
The kinetics of liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) in cell-like confinements remains poorly understood. Now it has been shown that it involves complex interplay between the incipient phases and the membrane boundary, which arrests phase coarsening, deforms the membrane and couples LLPS with lipid phase separation.
- Wan-Chih Su
- , James C. S. Ho
- & Atul N. Parikh
-
Article |
 Selective scandium ion capture through coordination templating in a covalent organic framework
Selective scandium ion capture through coordination templating in a covalent organic framework
Scandium is challenging and expensive to isolate in pure form using conventional solvent extraction. Now a covalent organic framework (COF) has been synthesized that can incorporate scandium coordination complexes; subsequent removal of the scandium ions generates open coordination sites, and the resulting ‘metal-imprinted’ COF can be used for highly selective, cyclable scandium capture.
- Ye Yuan
- , Yajie Yang
- & Guangshan Zhu
-
Article |
 A trivalent 4f complex with two bis-silylamide ligands displaying slow magnetic relaxation
A trivalent 4f complex with two bis-silylamide ligands displaying slow magnetic relaxation
A trivalent 4f cationic complex bearing two bis-silylamide ligands has been prepared that displays slow magnetic relaxation. The bulky ligands and weakly coordinating anion stabilize the pseudotrigonal geometry necessary to elicit strong ground-state magnetic anisotropy in this axially coordinated Yb(III) complex with well-localized charges.
- Dylan Errulat
- , Katie L. M. Harriman
- & Muralee Murugesu
-
News & Views |
 Benzene-like N6 hexazine rings
Benzene-like N6 hexazine rings
The chemistry of polynitrogens has been enriched by a new isomer of N6 through the synthesis, in a laser-heated diamond anvil cell, of a charged aromatic [N6]4– ring that is recoverable at ambient temperature under high pressure.
- Sandra Ninet
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction is a powerful technique to determine structures from nanocrystals. A data treatment method that takes into account dynamical diffraction effects has now been shown to lead to more accurate structure models, better sensitivity to weak signals and a reliable determination of absolute configuration—even for materials containing only light atoms.
- Paul B. Klar
- , Yaşar Krysiak
- & Lukas Palatinus
-
Article
| Open Access Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
The synthesis of two-dimensional nanostructures with controlled dimensions from polymeric precursors remains challenging. Now, two-dimensional nanoparticles with chemically different spatially defined cores have been fabricated through seeded growth and are shown to undergo a programmable degradation process.
- Zaizai Tong
- , Yujie Xie
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
Article |
 Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have remained difficult to grow as single crystals. Now, amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives that assemble in micelles in aqueous solutions have been shown to promote the growth of a variety of imine-bridged COFs into single crystals, in a step-by-step fashion, within their hydrophobic compartment.
- Zhipeng Zhou
- , Lei Zhang
- & Zhikun Zheng
-
Article |
 Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Crystals of hexachlorobenzene have now been shown to support the autonomous motion of water and particulate matter over their surface. Parallel microchannels present at the surface of the crystal gradually widen by sublimation, propelling droplets of condensed ambient water that can also transport microscopic amounts of material such as silver microparticles.
- Patrick Commins
- , Marieh B. Al-Handawi
- & Panče Naumov
-
Research Briefing |
 Serial rotation electron diffraction for rapid phase analysis to accelerate materials development
Serial rotation electron diffraction for rapid phase analysis to accelerate materials development
Serial rotation electron diffraction (SerialRED) enables rapid and reliable phase analysis and structure determination of complex polycrystalline materials that cannot be routinely characterized using X-ray diffraction. Five zeolite phases were identified in a single synthesis product by automated screening of hundreds of crystals, demonstrating the power of SerialRED for materials development.
-
Article |
 Aromatic hexazine [N6]4− anion featured in the complex structure of the high-pressure potassium nitrogen compound K9N56
Aromatic hexazine [N6]4− anion featured in the complex structure of the high-pressure potassium nitrogen compound K9N56
Aromatic polynitrogen units can display both high stability and high energy content. A hexazine anion has now been identified in a complex compound, K9N56, which is formed at high pressures and temperatures under laser-heating in a diamond anvil cell. The [N6]4− ring is planar and proposed to be aromatic.
- Dominique Laniel
- , Florian Trybel
- & Natalia Dubrovinskaia
-
Article |
 End-of-life upcycling of polyurethanes using a room temperature, mechanism-based degradation
End-of-life upcycling of polyurethanes using a room temperature, mechanism-based degradation
Extensive crosslinking in thermosetting polymers provides their desirable durability but makes them difficult to recycle. Now acetal-based monomers containing nucleophilic pendant groups have been incorporated into polyurethanes, which are stable in aqueous acid yet degradable at room temperature under organic acidic conditions. The degradation products were upcycled into higher-value, long-lasting materials.
- Ephraim G. Morado
- , Mara L. Paterson
- & Steven C. Zimmerman
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible transformations between the non-porous phases of a flexible coordination network enabled by transient porosity
Reversible transformations between the non-porous phases of a flexible coordination network enabled by transient porosity
Sorbent materials that reversibly transform between closed (non-porous) and open (porous) phases on the uptake and release of guests are relevant to gas storage and separation applications. Now, a coordination network has been prepared that exhibits gas-induced transformations between multiple non-porous phases. This phenomenon is attributed to subtle structural rearrangements that enable transient porosity.
- Varvara I. Nikolayenko
- , Dominic C. Castell
- & Michael J. Zaworotko
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials using serial rotation electron diffraction
High-throughput phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials using serial rotation electron diffraction
X-ray diffraction is crucial for the phase elucidation of polycrystalline materials but remains challenging for complex multiphase systems. Now serial rotation electron diffraction has been shown to enable rapid, reliable and semiquantitative phase analysis of such systems, facilitating high-throughput screening of complex synthesis systems and providing new opportunities for materials development.
- Yi Luo
- , Bin Wang
- & Xiaodong Zou
-
Article |
 Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Current strategies for photoinduced olefin metathesis lack wavelength tunability. Now, plasmonic nanoparticles have been used to activate latent ruthenium catalysts, enabling light-induced olefin metathesis in the infrared range with several advantages when compared with conventional heating. Implementing this approach in ring-opening metathesis polymerization resulted in photoresponsive polymer–nanoparticle composites with enhanced mechanical properties.
- Nir Lemcoff
- , Noy B. Nechmad
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
The nitrogen reduction reaction is an extremely valuable but energy-intensive process. Now, a coordination polymer based on a [Zn–N2–Zn] unit has been shown to promote the formation of ammonia under ambient conditions by a photocatalytic reaction. The N2 moieties within the framework are reduced, creating unsaturated [Zn2+···Zn+] intermediates that are able to capture external N2 and sustain the cycle.
- Yan Xiong
- , Bang Li
- & Zhong Jin
-
Review Article |
 Merging molecular catalysts and metal–organic frameworks for photocatalytic fuel production
Merging molecular catalysts and metal–organic frameworks for photocatalytic fuel production
The light-driven conversion of abundant resources such as CO2 and H2O into chemical fuels for energy storage is crucial to end our dependence on fossil fuels. This Review highlights how molecular catalysts and photosensitizers can be grafted onto metal–organic frameworks to combine the advantages of both classes of compounds. Different synthetic strategies are discussed, along with their advantages and limitations.
- P. M. Stanley
- , J. Haimerl
- & J. Warnan
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
Incorporating silicon into organic molecules and materials leads to interesting changes in electronic structure and properties; silabenzenes are attractive species for this purpose, but their high reactivity in solution poses challenges. Now, 1D and 2D covalent organic frameworks featuring disilabenzene rings (C4Si2) as linkers have been prepared by reacting silicon atoms and polyaromatic hydrocarbon precursors on a Au(111) surface.
- Kewei Sun
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Shigeki Kawai
-
Article |
 Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Identifying and quantifying the biodistribution of synthetic polymeric nanoparticles in biological milieu is crucial for biomedical applications. Now, it has been shown that encoded polymeric amphiphiles with discrete molar masses undergo sequence- and length-dependent self-assembly into precise digital micelles that can be used in direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification assays.
- Qiangqiang Shi
- , Hao Yin
- & Shiyong Liu
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Perspective |
 Challenges to developing materials for the transport and storage of hydrogen
Challenges to developing materials for the transport and storage of hydrogen
Hydrogen, which possesses the highest gravimetric energy density of any energy carrier, is attractive for both mobile and stationary power, but its low volumetric energy density poses major storage and transport challenges. This Perspective delineates potential use cases and defines the challenges facing the development of materials for efficient hydrogen storage.
- Mark D. Allendorf
- , Vitalie Stavila
- & Tom Autrey
-
Article |
 Photoinduced inverse vulcanization
Photoinduced inverse vulcanization
Inverse vulcanization (IV) generates sulfur-rich functional polymers from elemental sulfur and organic crosslinkers, but the harsh reaction conditions required limit the scope of suitable crosslinkers. Now, a photoinduced IV has been shown to proceed at ambient temperatures, enabling the use of volatile and gaseous alkenes and alkynes as crosslinkers and broadening the range of products.
- Jinhong Jia
- , Jingjiang Liu
- & Zheng-Jun Quan
-
Article |
 Efficient room-temperature phosphorescence of covalent organic frameworks through covalent halogen doping
Efficient room-temperature phosphorescence of covalent organic frameworks through covalent halogen doping
Room-temperature phosphorescence in organic solids is attractive for practical applications but remains rare. Now, highly phosphorescent boroxine-linked covalent organic frameworks have been prepared by covalent doping with halogen atoms through the use of halogenated precursors. The resulting porous COFs exhibited oxygen-sensing capabilities with millisecond response time over a wide range of partial oxygen pressures.
- Ehsan Hamzehpoor
- , Cory Ruchlin
- & Dmytro F. Perepichka
-
Article |
 A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
Creating hierarchical synthetic materials that can modulate microbial communities remains a great challenge due to the complex interactions between microbiota and their colonized environments. Now, a soil-inspired chemical system that responds to chemical, optical and mechanical stimuli has been developed. The soil-inspired chemical system can enhance microbial cultures and biofuel production, enrich gut bacterial diversity and alleviate ulcerative colitis symptoms.
- Yiliang Lin
- , Xiang Gao
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article |
 Recyclable and malleable thermosets enabled by activating dormant dynamic linkages
Recyclable and malleable thermosets enabled by activating dormant dynamic linkages
Alkyl and aryl polycyanurate networks have now been prepared through polymerization of diols and substituted triazines via a dynamic SNAr reaction. When treated with excess mono alcohol or phenol, the polycyanurate networks can be depolymerized into the starting monomers, which can be separated and reused, thus achieving closed-loop recycling.
- Zepeng Lei
- , Hongxuan Chen
- & Wei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
On-surface synthesis enables highly reactive structures to be produced under vacuum, but they need to be passivated to be incorporated into practical devices. Here, the facile protection of air-sensitive chiral graphene nanoribbons has been shown, by either hydrogenation or synthesis of an oxidized form. The chemically stable forms can subsequently be deprotected.
- James Lawrence
- , Alejandro Berdonces-Layunta
- & Dimas G. de Oteyza

 Dynamic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks
Dynamic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks