News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Molecularly defined electrodes host a concert of protons and electrons
Electrocatalytic transformations often involve the concerted transfer of electrons and protons at electrode interfaces; however, these processes are not well understood. Now, experiments on an electrode that features well-defined molecular sites deepen fundamental understanding of such transfers to pave the way for future catalysts.
- Siyuan L. Xie
- & Eva M. Nichols
-
Article |
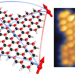 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
The design of open-shell nanographenes is commonly limited to systems featuring a single magnetic origin. Now a strategy that combines topological frustration and electron–electron interactions has been developed to generate a butterfly-shaped nanographene that hosts four highly entangled π-spins and exhibits both ferromagnetic and anti-ferromagnetic coupling.
- Shaotang Song
- , Andrés Pinar Solé
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access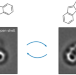 Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Switching the magnetic state of a polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon in a reversible and controlled manner is challenging. Now, by means of single-molecule scanning probe microscopy, an indenofluorene isomer on ultrathin NaCl films has been shown to adopt both open- and closed-shell states. Furthermore, bidirectional switching between the two states is achieved by changing the adsorption site of the molecule.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Manuel Vilas-Varela
- & Leo Gross
-
Article
| Open Access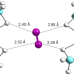 Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Small-pore hydridic frameworks store densely packed hydrogen
Although hydrogen gas could serve as a promising future fuel, its high-capacity storage is a challenge. Now, a nanoporous magnesium borohydride framework is shown to store hydrogen as densely packed penta-dihydrogen clusters having well-defined orientations and directional interactions with the framework.
- Hyunchul Oh
- , Nikolay Tumanov
- & Yaroslav Filinchuk
-
Article |
 A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
A molecular-level mechanistic framework for interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics
Although interfacial proton-coupled electron transfers are critical reaction steps in chemical and biological processes, studies investigating these reactions are complicated by surface heterogeneity. Now, interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer kinetics are studied and modelled at isolated, well-defined active sites to provide a foundation for understanding complex reactions involved in energy conversion and catalysis.
- Noah B. Lewis
- , Ryan P. Bisbey
- & Yogesh Surendranath
-
Article
| Open Access Surface stratification determines the interfacial water structure of simple electrolyte solutions
Surface stratification determines the interfacial water structure of simple electrolyte solutions
The organization of electrolytes at the air/water interface affects the structure of interfacial water and therefore numerous natural processes. It has now been demonstrated that the surface of an electrolyte solution is stratified and consists of an ion-depleted outer surface and an ion-enriched subsurface layer, jointly determining the water interfacial structure.
- Yair Litman
- , Kuo-Yang Chiang
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Surface heterogeneity is generally acknowledged as the major cause of liquid–solid friction, affecting whether droplets slide off the surface or stick to it. Now, a model surface of self-assembled monolayers has been used to investigate how molecular-scale surface heterogeneity affects water contact angle hysteresis and contact line friction. The high-coverage hydrophobic surface is slippery, as—counter-intuitively—is the low-coverage hydrophilic surface.
- Sakari Lepikko
- , Ygor Morais Jaques
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article |
 The role of aromaticity in the cyclization and polymerization of alkyne-substituted porphyrins on Au(111)
The role of aromaticity in the cyclization and polymerization of alkyne-substituted porphyrins on Au(111)
While aromaticity is a useful concept for assessing the reactivity of organic compounds, the connection between aromaticity and on-surface chemistry remains largely unexplored. Now, scanning probe experiments on cyclization reactions of porphyrins on Au(111) show that the peripheral carbon atoms outside of the aromatic 18-π electron pathway exhibit a higher reactivity.
- Nan Cao
- , Jonas Björk
- & Alexander Riss
-
Article |
 On-surface synthesis of ballbot-type N-heterocyclic carbene polymers
On-surface synthesis of ballbot-type N-heterocyclic carbene polymers
Monomeric N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) can act as molecular modifiers of metal surfaces and thus affect heterogeneous catalytic behaviour. Now NHC polymers have been formed on gold surfaces, consisting of ballbot-type repeating units bound to single gold adatoms. Conformational, electronic and charge transport properties explain the high surface mobility of the incommensurate NHC polymers.
- Jindong Ren
- , Maximilian Koy
- & Frank Glorius
-
Article |
 Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Functionalizing two-dimensional transition-metal carbide (MXene) surfaces can alter their properties, but covalent functionalization has been synthetically challenging. Now, it has been shown that various organic groups can be covalently attached to MXene surfaces through amido and imido bonds. The resulting hybrid organic–inorganic structures exhibit Fano resonances and superior stability compared with traditional MXenes with a mixture of –F, –O and –OH surface terminations.
- Chenkun Zhou
- , Di Wang
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-dependent reactivity and spin-flipping dynamics in oxygen atom scattering from graphite
Spin-dependent reactivity and spin-flipping dynamics in oxygen atom scattering from graphite
Electronic spin influences chemistry profoundly, but its role in surface chemistry is poorly established. Now the spin-dependent reaction probabilities of oxygen atoms with a graphite surface have been studied. Molecular dynamics simulations help elucidate the mechanism for spin-flipping, which is observed to occur with low probability in surface scattering experiments.
- Zibo Zhao
- , Yingqi Wang
- & G. Barratt Park
-
Review Article |
 Advances in single-molecule junctions as tools for chemical and biochemical analysis
Advances in single-molecule junctions as tools for chemical and biochemical analysis
The ability to detect and quantify a given analyte at the molecular level is a long-lasting goal for analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. This Review highlights how single-molecule junctions (SMJs) have been used for analytical purposes, from the detection of isomers and reaction intermediates to the detection of proteins and nucleic acids. Different SMJ approaches are discussed, along with their advantages and limitations over bulk analytical techniques.
- Essam M. Dief
- , Paul J. Low
- & Nadim Darwish
-
Article |
 Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Crystals of hexachlorobenzene have now been shown to support the autonomous motion of water and particulate matter over their surface. Parallel microchannels present at the surface of the crystal gradually widen by sublimation, propelling droplets of condensed ambient water that can also transport microscopic amounts of material such as silver microparticles.
- Patrick Commins
- , Marieh B. Al-Handawi
- & Panče Naumov
-
News & Views |
 Mysterious energy losses
Mysterious energy losses
The adiabatic approximation is often applied to describe the scattering of molecules or atoms from solid surfaces. Now, unusual energy loss has been observed during the scattering of hyperthermal hydrogen atoms from a single crystalline Ge(111) surface — suggesting the existence of a non-adiabatic mechanism involving electronic interband transitions in the Ge that are induced by the hydrogen atoms.
- Hermann Nienhaus
-
News & Views |
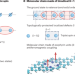 Quantum spin chains go organic
Quantum spin chains go organic
An organic quantum magnet has been prepared in short chains of porphyrin derivatives through a combination of on-surface synthesis and atom manipulation using the tip of a scanning probe microscope.
- P. Jelínek
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen atom collisions with a semiconductor efficiently promote electrons to the conduction band
Hydrogen atom collisions with a semiconductor efficiently promote electrons to the conduction band
Inelastic hydrogen atom scattering from surfaces provides a good benchmark for the validity of the Born–Oppenheimer approximation in surface chemistry. Now it has been shown that hydrogen atoms colliding with a semiconductor surface can efficiently excite electrons above the surface bandgap, representing a clear example of the failure of the approximation.
- Kerstin Krüger
- , Yingqi Wang
- & Oliver Bünermann
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
Incorporating silicon into organic molecules and materials leads to interesting changes in electronic structure and properties; silabenzenes are attractive species for this purpose, but their high reactivity in solution poses challenges. Now, 1D and 2D covalent organic frameworks featuring disilabenzene rings (C4Si2) as linkers have been prepared by reacting silicon atoms and polyaromatic hydrocarbon precursors on a Au(111) surface.
- Kewei Sun
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Shigeki Kawai
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article |
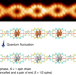 Quantum nanomagnets in on-surface metal-free porphyrin chains
Quantum nanomagnets in on-surface metal-free porphyrin chains
Quantum nanomagnets, which display collective quantum behaviours, serve as important components in modern quantum technologies, but their fabrication has remained challenging. Quantum nanomagnets have now been constructed spin by spin in metal-free porphyrin chains, using on-surface synthesis and hydrogen manipulation using a scanning tunnelling microscope, and their collective quantum behaviours have been clearly resolved.
- Yan Zhao
- , Kaiyue Jiang
- & Shiyong Wang
-
Article |
 Bending a photonic wire into a ring
Bending a photonic wire into a ring
Meso–meso linked porphyrin arrays have been described as rod-like photonic wires. Now it has been shown that they can be bent into rings using template-directed synthesis. These rings of porphyrins mimic the light-harvesting arrays of chlorophyll molecules responsible for photosynthesis.
- Henrik Gotfredsen
- , Jie-Ren Deng
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
On-surface synthesis enables highly reactive structures to be produced under vacuum, but they need to be passivated to be incorporated into practical devices. Here, the facile protection of air-sensitive chiral graphene nanoribbons has been shown, by either hydrogenation or synthesis of an oxidized form. The chemically stable forms can subsequently be deprotected.
- James Lawrence
- , Alejandro Berdonces-Layunta
- & Dimas G. de Oteyza
-
Article
| Open Access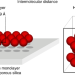 Formation of a super-dense hydrogen monolayer on mesoporous silica
Formation of a super-dense hydrogen monolayer on mesoporous silica
In some cases, hydrogen adsorption close to its boiling temperature shows unusually high monolayer capacities, but the microscopic nature of this adsorbate phase is not well understood. Now, H2 adsorbed on a well-ordered mesoporous silica surface has been shown to form a 2D monolayer with very short H2···H2 intermolecular distances and a density more than twice that of bulk-solid H2.
- Rafael Balderas-Xicohténcatl
- , Hung-Hsuan Lin
- & Michael Hirscher
-
Article |
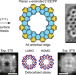 Planar π-extended cycloparaphenylenes featuring an all-armchair edge topology
Planar π-extended cycloparaphenylenes featuring an all-armchair edge topology
The strained topology of [n]paracyclophenylenes ([n]CPPs) typically prevents their π sysytem from being extended, but now the formation of a planar π-extended CPP has been achieved through a bottom-up on-surface synthesis approach. The planar π-extended [12]CPP produced by this method is a nanographene featuring an all-armchair edge, which leads to delocalized electronic states around the entire ring.
- Feifei Xiang
- , Sven Maisel
- & Sabine Maier
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic site seeing
Catalytic site seeing
Understanding how surface structure affects catalyst selectivity is limited by the ability to synthesize atomically precise active-site ensembles. Now, by using intermetallic Pd–Zn, a series of well-defined multinuclear Pd–metal–Pd catalytic sites have been generated and studied, providing insights into their selectivity for the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene.
- Max Mortensen
- & Siris Laursen
-
News & Views |
 The birth of bilayer borophene
The birth of bilayer borophene
Bilayer borophene, predicted to be stabilized by interlayer linkages, has now been grown by molecular beam epitaxy on copper and silver surfaces in two independent studies. The growth substrate and temperature are found to influence the lattice structures formed.
- Maryam Ebrahimi
-
Article |
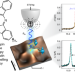 Electron spin resonance of single iron phthalocyanine molecules and role of their non-localized spins in magnetic interactions
Electron spin resonance of single iron phthalocyanine molecules and role of their non-localized spins in magnetic interactions
Electron spin resonance spectroscopy has traditionally been used to study large ensembles of spins, but its combination with scanning tunnelling microscopy recently enabled measurements on single adatoms. Now, individual iron phthalocyanine complexes adsorbed on a surface have been probed. Their spin distribution partially extends on the phthalocyanine, leading to a strong geometry-dependent exchange coupling interaction.
- Xue Zhang
- , Christoph Wolf
- & Taeyoung Choi
-
Article |
 Weakly hydrated anions bind to polymers but not monomers in aqueous solutions
Weakly hydrated anions bind to polymers but not monomers in aqueous solutions
Weakly hydrated anions solubilize macromolecules but cause small molecules that are made from identical chemical constituents to precipitate out of aqueous solutions. Now, this phenomenon has been understood by demonstrating that the binding of anions to polymers is regulated by molecular curvature and interfacial water structure.
- Bradley A. Rogers
- , Halil I. Okur
- & Paul S. Cremer
-
Article |
 Controlled growth of ordered monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on silicon
Controlled growth of ordered monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on silicon
Although monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) readily form on metals, surface reactivity usually hinders their self-assembly on semiconductors. Now, it has been shown that thermally stable, well-ordered monolayers of NHCs can be formed on silicon surfaces. A large reduction in work function is observed and steric effects enable sufficient diffusivity of the NHCs.
- Martin Franz
- , Sandhya Chandola
- & Mario Dähne
-
Article |
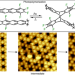 On-surface photopolymerization of two-dimensional polymers ordered on the mesoscale
On-surface photopolymerization of two-dimensional polymers ordered on the mesoscale
On-surface, ultra-high vacuum conditions enable two-dimensional polymerizations to be precisely studied—often with submolecular resolution—but these syntheses are typically thermally activated, which can lead to high defect densities and relatively small domain sizes. Now, a self-assembled monolayer of a three-bladed fantrip monomer on alkane-passivated graphite has been covalently crosslinked into a mesoscale-ordered two-dimensional polymer by [4+4] photocycloaddition.
- Lukas Grossmann
- , Benjamin T. King
- & Markus Lackinger
-
Article |
 Large magnetic exchange coupling in rhombus-shaped nanographenes with zigzag periphery
Large magnetic exchange coupling in rhombus-shaped nanographenes with zigzag periphery
Open-shell nanographenes are promising for quantum technologies, but their magnetic stability has remained limited by weak exchange coupling. Now, two large rhombus-shaped nanographenes with zigzag peripheries, one with 48 carbon atoms and the other with 70, have been synthesized on gold and copper surfaces. The 70-carbon compound exhibits a large magnetic exchange coupling exceeding 100 meV.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Xuelin Yao
- & Roman Fasel
-
News & Views |
 Faster chemistry at surfaces
Faster chemistry at surfaces
The physical properties of a liquid at an interface differ from bulk solution limits, but how this affects chemical reactivity is unclear. Now, ultrafast, surface-sensitive vibrational spectroscopy has revealed that the light-induced reaction of phenol with water is four orders of magnitude faster at the water surface than in bulk.
- Robert A. Walker
-
Article |
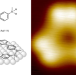 Polymerization of silanes through dehydrogenative Si–Si bond formation on metal surfaces
Polymerization of silanes through dehydrogenative Si–Si bond formation on metal surfaces
On-surface dehydrogenative bond formation between sp3-hybridized carbon atoms usually requires high temperatures. Now, it has been shown that the higher homologue, silicon, can undergo dehydrogenative polymerization at room temperature on metal surfaces. This process creates well-ordered structures on Au(111) and Cu(111), with different stereoselectivity depending on the metal.
- Lacheng Liu
- , Henning Klaasen
- & Armido Studer
-
Article |
 The photochemical reaction of phenol becomes ultrafast at the air–water interface
The photochemical reaction of phenol becomes ultrafast at the air–water interface
Reactions at the interface between water and other phases play important roles in various chemical settings. Now, ultrafast phase-sensitive interface-selective vibrational spectroscopy has revealed that the photoionization of phenol can occur four orders of magnitude faster at the water surface than in the bulk aqueous phase.
- Ryoji Kusaka
- , Satoshi Nihonyanagi
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article |
 Predator–prey interactions between droplets driven by non-reciprocal oil exchange
Predator–prey interactions between droplets driven by non-reciprocal oil exchange
Interactions that generate directed movement in response to a chemical stimulus occur in nature but have been difficult to realize in synthetic systems. Now, it has been shown that asymmetric micelle-mediated exchange of haloalkanes can be used to create tunable chasing interactions between chemically distinct microdroplets. Collective interactions lead to the formation of droplet assemblies with emergent self-organization and collective behaviours.
- Caleb H. Meredith
- , Pepijn G. Moerman
- & Lauren D. Zarzar
-
Article |
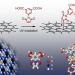 Long-range ordered and atomic-scale control of graphene hybridization by photocycloaddition
Long-range ordered and atomic-scale control of graphene hybridization by photocycloaddition
The controllable functionalization of graphene at the molecular level may prove useful for graphene-based electronics, but is difficult to do in a precise fashion. Now it has been shown that a photocycloaddition reaction between a hydrogen-bonded network of maleimide-derived molecules and single-layer graphene can produce a functionalized array with long-range order.
- Miao Yu
- , Chong Chen
- & Federico Rosei
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry in the making
Symmetry in the making
After years of speculation on the origins of symmetry-making and -breaking during crystallization, time-resolved in situ scanning probe microscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations have shown that the formation of olanzapine crystals largely occurs by the incorporation of centrosymmetric dimers into growth sites.
- Susan M. Reutzel-Edens
-
News & Views |
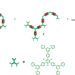 Mesoscale coordination constructs
Mesoscale coordination constructs
A series of mesoscale supramolecular hexagonal grids have been constructed in solution through stepwise intra- then intermolecular coordination-driven self-assembly, and characterized with atomic resolution by scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy.
- Ruoning Li
- & Yongfeng Wang
-
Review Article |
 Covalent on-surface polymerization
Covalent on-surface polymerization
Growing polymers directly on surfaces has emerged as a powerful tool because it can provide a route to otherwise inaccessible structures such as defect-free linear chains, graphene nanoribbons and two-dimensional networks. This Review Article describes general principles and key aspects of this method from the perspectives of surface science and polymer chemistry.
- Leonhard Grill
- & Stefan Hecht
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 On-surface synthesis and characterization of individual polyacetylene chains
On-surface synthesis and characterization of individual polyacetylene chains
Polyacetylene is an ideal system to probe to gain a better understanding of the nature of charge transport in conducting polymers. Now, individual atomically precise polyacetylene chains have been synthesized on a copper surface and characterized using a range of techniques, revealing a doping-induced semiconductor-to-metal transition.
- Shiyong Wang
- , Qiang Sun
- & Wei Xu
-
Article |
 Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy techniques can interrogate entities that fluoresce; however, most chemical or biological processes do not involve fluorescent species. Now, the incorporation of a competitive reaction into a single-molecule fluorescence detection scheme has been shown to enable quantitative super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions.
- Xianwen Mao
- , Chunming Liu
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Vibration-driven reaction of CO2 on Cu surfaces via Eley–Rideal-type mechanism
Vibration-driven reaction of CO2 on Cu surfaces via Eley–Rideal-type mechanism
Vibrational and translational energies have previously been observed to promote reactions at surfaces occurring via dissociative mechanisms. Now, it has been shown that the reaction of CO2 with surface-adsorbed atomic hydrogen—which occurs via an associative (Eley–Rideal-type) mechanism—can be driven by vibrationally exciting CO2.
- Jiamei Quan
- , Fahdzi Muttaqien
- & Junji Nakamura
-
Article |
 Optimization of the facet structure of transition-metal catalysts applied to the oxygen reduction reaction
Optimization of the facet structure of transition-metal catalysts applied to the oxygen reduction reaction
While much effort has been devoted to understanding how nanoparticle morphology can be leveraged to improve catalytic activity, engineering their microstructure from first principles to this end has remained difficult. Now a methodology for designing the optimal structure of a solid catalyst with the aim of achieving the highest possible activity for surface-sensitive reactions has been developed.
- M. Núñez
- , J. L. Lansford
- & D. G. Vlachos
-
Article |
 Non-chemisorbed gold–sulfur binding prevails in self-assembled monolayers
Non-chemisorbed gold–sulfur binding prevails in self-assembled monolayers
Gold–thiol contacts are ubiquitous across the physical and biological sciences, connecting organic molecules to surfaces. Now, conductance measurements of different sulfur-bound single-molecule junctions show that thiols—in contrast to the prevailing view—are not chemisorbed on gold, which strongly suggests that the thiol hydrogen is retained.
- Michael S. Inkpen
- , Zhen–Fei Liu
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
News & Views |
 Surface anchors target golden bullets
Surface anchors target golden bullets
Gold nanomaterials are attractive for a variety of applications, including in medicine, but need to be made stable enough to operate in biological systems. Now, gold nanorods have been stabilized for photothermal therapy by sequential surface anchoring, using a bidendate PEG-based ligand that features a thiolate moiety and an Au–NHC moiety.
- Guillaume Médard
- & Anthoula C. Papageorgiou
-
Article |
 Highly responsive nature of porous coordination polymer surfaces imaged by in situ atomic force microscopy
Highly responsive nature of porous coordination polymer surfaces imaged by in situ atomic force microscopy
Some porous coordination polymers (PCPs) are known to be flexible and guest-responsive. Now, the guest-induced sharp, reversible structural transformation of the surface of a single-crystalline PCP has been visualized by in situ liquid-phase atomic force microscopy. This local response occurred at a guest concentration that was too low to trigger changes to the bulk crystal.
- Nobuhiko Hosono
- , Aya Terashima
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article |
 Robust gold nanorods stabilized by bidentate N-heterocyclic-carbene–thiolate ligands
Robust gold nanorods stabilized by bidentate N-heterocyclic-carbene–thiolate ligands
N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are valuable surface anchors, but their use has remained limited to either spherical or planar nanomaterials. Now, they have been grafted onto gold nanorods through a bidentate ligand featuring a thiolate and a NHC–gold complex. The resulting nanorods are robust towards a wide range of harsh conditions and show promise for photothermal therapy.
- Michelle J. MacLeod
- , Aaron J. Goodman
- & Jeremiah A. Johnson
-
News & Views |
 Catalysis at the limit
Catalysis at the limit
Probing single-atom alloys has shown that, when interactions between the components are weak, the electronic structure of the dilute element resembles that of a free atom, making bonding with reactants more like that in molecular homogeneous catalysts.
- Christian Papp
-
Article |
 Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
MoS2 single layers spontaneously undergo a slow oxygen substitution reaction under ambient conditions giving rise to solid-solution-type 2D molybdenum oxy-sulfide crystals. The oxygen substitution sites of the 2D MoS2−xOx crystals act as efficient single-atom catalytic centres for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- János Pető
- , Tamás Ollár
- & Levente Tapasztó

 Towards zero droplet friction
Towards zero droplet friction