News Explainer |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Mitotic tethering enables inheritance of shattered micronuclear chromosomes
Mitotic tethering enables inheritance of shattered micronuclear chromosomes
Chromothriptically produced pieces of a micronucleated chromosome are shown to be tethered together in mitosis by a protein complex consisting of MDC1, TOPBP1 and CIP2A, thus enabling their inheritance by a single daughter cell.
- Prasad Trivedi
- , Christopher D. Steele
- & Don W. Cleveland
-
Article
| Open Access A tripartite rheostat controls self-regulated host plant resistance to insects
A tripartite rheostat controls self-regulated host plant resistance to insects
Insect salivary protein (BISP) targets OsRLCK185 to suppress defence in susceptible plants, whereas in resistant plants BISP binds BPH14 to activate host plant resistance. To restore cellular homeostasis, the resistance mechanism is fine-tuned by selective autophagy.
- Jianping Guo
- , Huiying Wang
- & Guangcun He
-
Article |
 Break-induced replication orchestrates resection-dependent template switching
Break-induced replication orchestrates resection-dependent template switching
Break-induced telomere synthesis initiates recruitment of the SNM1A nuclease, which promotes DNA end resection that in turn allows template switching to enable bypass of lesions.
- Tianpeng Zhang
- , Yashpal Rawal
- & Roger A. Greenberg
-
Technology Feature |
 Powerful microscope captures motor proteins in unprecedented detail
Powerful microscope captures motor proteins in unprecedented detail
Called MINFLUX, the super-resolution method allows researchers to track molecules under cellular conditions.
- Amanda Heidt
-
Article
| Open Access Heritable transcriptional defects from aberrations of nuclear architecture
Heritable transcriptional defects from aberrations of nuclear architecture
Micronuclei, which are common features of nuclei in cancer cells, can generate heritable sources of transcriptional suppression, a finding that establishes an inherent relationship between chromosomal instability and variation in chromatin state and gene expression.
- Stamatis Papathanasiou
- , Nikos A. Mynhier
- & David Pellman
-
Article
| Open Access A cytosolic surveillance mechanism activates the mitochondrial UPR
A cytosolic surveillance mechanism activates the mitochondrial UPR
We identify a highly controlled cytosolic surveillance mechanism that integrates independent mitochondrial stress signals to initiate the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPR), revealing a link between mitochondrial and cytosolic proteostasis.
- F. X. Reymond Sutandy
- , Ines Gößner
- & Christian Münch
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic dysregulation from chromosomal transit in micronuclei
Epigenetic dysregulation from chromosomal transit in micronuclei
Missegregated chromosomes that are sequestrated in micronuclei are subject to changes in histone modifications leading to abnormalities in chromatin accessibility that remain long after the chromosomes have been reincorporated into the primary nucleus.
- Albert S. Agustinus
- , Duaa Al-Rawi
- & Samuel F. Bakhoum
-
Research Briefing |
 A structural model of the core of cilia
A structural model of the core of cilia
Axonemes are molecular machines that enable the movement of cilia, the hair-like structures found on the surface of some cells. Atomic models of axonemes from the flagella of green algae and from the cilia of human respiratory-tract cells reveal how the axoneme enables the cilia to move, and explain the effects of genetic mutations that cause human ciliary disease.
-
Article
| Open Access Axonemal structures reveal mechanoregulatory and disease mechanisms
Axonemal structures reveal mechanoregulatory and disease mechanisms
Detailed atomic models of axonemes from algal flagella and human respiratory cilia, which are hair-like protrusions from cells that enable motility and clear mucus from human airways, could provide insights into how they function.
- Travis Walton
- , Miao Gui
- & Alan Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-KRAS inhibitor disables oncogenic signalling and tumour growth
Pan-KRAS inhibitor disables oncogenic signalling and tumour growth
A non-covalent inhibitor that binds preferentially to the inactive state of KRAS while sparing NRAS and HRAS is reported, indicating that most KRAS oncoproteins cycle between an active state and an inactive state in cancer cells.
- Dongsung Kim
- , Lorenz Herdeis
- & Piro Lito
-
Article |
 Nuclear export of pre-60S particles through the nuclear pore complex
Nuclear export of pre-60S particles through the nuclear pore complex
We report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of native pre-60S particles trapped in the channel of the yeast nuclear pore complex, suggesting a translocation model for the export of pre-60S particles through the complex.
- Zongqiang Li
- , Shuaijiabin Chen
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitination regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of endoplasmic reticulum
Ubiquitination regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of endoplasmic reticulum
Ubiquitination of the receptor FAM134B regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of the endoplasmic reticulum in response to cellular demands.
- Alexis González
- , Adriana Covarrubias-Pinto
- & Ivan Dikić
-
Outlook |
 A fat-blocking drug could help to fight metastatic cancer
A fat-blocking drug could help to fight metastatic cancer
The antibody drug is moving closer to being tested in people with advanced stages of cancer.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Outlook |
 RNA splicing targets age-related diseases
RNA splicing targets age-related diseases
Manipulating genetic molecules could return cells to a younger state.
- Christine Evans-Pughe
-
Article
| Open Access Heteromeric clusters of ubiquitinated ER-shaping proteins drive ER-phagy
Heteromeric clusters of ubiquitinated ER-shaping proteins drive ER-phagy
The membrane-shaping protein ARL6IP1 is involved in the selective degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum, and this process depends on its ubiquitination and interaction with other membrane-shaping proteins such as FAM134B.
- Hector Foronda
- , Yangxue Fu
- & Christian A. Hübner
-
Article |
 A small-molecule PI3Kα activator for cardioprotection and neuroregeneration
A small-molecule PI3Kα activator for cardioprotection and neuroregeneration
A new specific, small-molecule activator of the PI3Kα isoform (UCL-TRO-1938) identified through high-throughput screening can transiently activate PI3K signalling and biological responses in cells and tissues, with potential therapeutic applications in tissue protection and regeneration.
- Grace Q. Gong
- , Benoit Bilanges
- & Bart Vanhaesebroeck
-
News & Views |
 The role of NINJ1 protein in programmed cellular destruction
The role of NINJ1 protein in programmed cellular destruction
The protein NINJ1 drives membrane rupture associated with certain types of cell death. Investigation of NINJ1 reveals mechanistic details of how it functions, raising the possibility of developing new therapeutics.
- James C. Whisstock
- & Ruby H. P. Law
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of NINJ1-mediated plasma membrane rupture in cell death
Structural basis of NINJ1-mediated plasma membrane rupture in cell death
Structural, biochemical and mutagenesis studies indicate that, in dying cells, the membrane protein NINJ1 assembles into filaments, disrupting the cell membrane.
- Morris Degen
- , José Carlos Santos
- & Sebastian Hiller
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibiting membrane rupture with NINJ1 antibodies limits tissue injury
Inhibiting membrane rupture with NINJ1 antibodies limits tissue injury
A monoclonal antibody that binds NINJ1 and inhibits NINJ1 oligomerization prevents plasma membrane rupture in dying cells, resulting in decreased inflammation of surrounding tissue in mice.
- Nobuhiko Kayagaki
- , Irma B. Stowe
- & Vishva M. Dixit
-
Article |
 Peroxisome biogenesis initiated by protein phase separation
Peroxisome biogenesis initiated by protein phase separation
A study presents evidence to support a model in which liquid–liquid phase separation of components of the transport machinery mediates formation of transient protein transport channels on peroxisomes.
- Rini Ravindran
- , Isabel O. L. Bacellar
- & Stephen W. Michnick
-
Article |
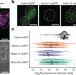 In situ architecture of the ER–mitochondria encounter structure
In situ architecture of the ER–mitochondria encounter structure
Integrative structural biology combining quantitative live imaging, cryo-correlative microscopy, subtomogram averaging and molecular modelling enables in situ determination of the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria encounter complex in yeast.
- Michael R. Wozny
- , Andrea Di Luca
- & Wanda Kukulski
-
Article |
 EDA2R–NIK signalling promotes muscle atrophy linked to cancer cachexia
EDA2R–NIK signalling promotes muscle atrophy linked to cancer cachexia
Gene expression analysis in muscle tissues showed upregulation of ectodysplasin A2 receptor in tumour-bearing mice and patients with cachectic cancer, and thus therapeutic targeting of relevant pathways may be beneficial in prevention of muscle loss.
- Sevval Nur Bilgic
- , Aylin Domaniku
- & Serkan Kir
-
Article
| Open Access Mitotic clustering of pulverized chromosomes from micronuclei
Mitotic clustering of pulverized chromosomes from micronuclei
The CIP2A–TOPBP1 complex tethers fragmented chromosomes from micronuclei for asymmetric mitotic inheritance, explaining distinct patterns of chromosome rearrangements in cancers and genomic disorders.
- Yu-Fen Lin
- , Qing Hu
- & Peter Ly
-
News |
 New cellular ‘organelle’ discovered inside fruit-fly intestines
New cellular ‘organelle’ discovered inside fruit-fly intestines
Fruit-fly cells use previously unknown complex cellular structures to store phosphate, a molecule essential to life
- Gemma Conroy
-
News & Views |
 Phosphate-storing organelle discovered in fruit flies
Phosphate-storing organelle discovered in fruit flies
Inorganic phosphate is an essential mineral for cellular metabolism and signalling. It emerges that a fruit-fly organelle can store this chemical in the form of phospholipids, releasing it in times of need.
- Emily Strachan
- & Irene Miguel-Aliaga
-
Article |
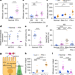 A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis
A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis
PXo bodies, non-canonical multilamellar organelles, serve as a reservoir for intracellular inorganic phosphate and are a critical regulator of both cytosolic phosphate levels and tissue homeostasis.
- Chiwei Xu
- , Jun Xu
- & Norbert Perrimon
-
Research Briefing |
 Copper catalyses changes in cell state
Copper catalyses changes in cell state
It emerges that copper ions found in cell organelles called mitochondria regulate the cellular changes that underlie transitions in cell state. A small molecule that inhibits copper-mediated catalysis can suppress the activation of immune cells called macrophages, conferring therapeutic benefits in models of acute inflammation.
-
News & Views |
 An unexpected timer for cell division
An unexpected timer for cell division
A serendipitous observation has revealed that cells make several versions of a key protein needed for cell division. The ratio of these protein isoforms influences how long division can be delayed when errors arise.
- Silke Hauf
-
Article |
 Alternative CDC20 translational isoforms tune mitotic arrest duration
Alternative CDC20 translational isoforms tune mitotic arrest duration
Human cells modulate the duration of their mitotic arrest through the presence of conserved alternative CDC20 translational isoforms.
- Mary-Jane Tsang
- & Iain M. Cheeseman
-
Article |
 Cryptochrome–Timeless structure reveals circadian clock timing mechanisms
Cryptochrome–Timeless structure reveals circadian clock timing mechanisms
Structural analysis of a protein complex in the circadian clock of Drosophila reveals how a light-sensing cryptochrome recognizes and engages its target.
- Changfan Lin
- , Shi Feng
- & Brian R. Crane
-
Article
| Open Access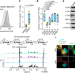 A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation
A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation
Cellular uptake of copper(ii) by CD44 has a key role in regulating cellular plasticity via copper(ii)-dependent downstream signalling events.
- Stéphanie Solier
- , Sebastian Müller
- & Raphaël Rodriguez
-
News & Views |
 Learning the metabolic language of cancer
Learning the metabolic language of cancer
The conversion of dietary sugar to the molecule lactate is a hallmark of many cancers. The discovery of a new binding partner of lactate provides insight into how cells link nutrient metabolism to the decision to divide.
- Minervo Perez
- & Jordan L. Meier
-
Research Highlight |
 Lab-grown fat with texture like the real thing could enrich cultured meat
Lab-grown fat with texture like the real thing could enrich cultured meat
Approach could make it easier to scale up production of cultivated meat.
-
Nature Video |
 ‘Touch-taste’: how the octopus repurposed its nervous system to hunt
‘Touch-taste’: how the octopus repurposed its nervous system to hunt
Researchers identify the structural basis for octopuses chemo-tactile sense.
- Dan Fox
-
Article |
 Chromosomal fragile site breakage by EBV-encoded EBNA1 at clustered repeats
Chromosomal fragile site breakage by EBV-encoded EBNA1 at clustered repeats
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 is shown to induce breakage of a fragile site on chromosome 11 by binding to a cluster of EBV-like imperfect palindromic repeats.
- Julia Su Zhou Li
- , Ammal Abbasi
- & Don W. Cleveland
-
News |
 Stem-cell-derived ‘embryos’ implanted in monkeys
Stem-cell-derived ‘embryos’ implanted in monkeys
An embryo-like ball of cells offers a way to study pregnancy and its complications without the typical ethical dilemmas.
- Gemma Conroy
-
Research Briefing |
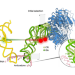 Mechanism of messenger-RNA decoding in humans illuminated
Mechanism of messenger-RNA decoding in humans illuminated
Intracellular machines called ribosomes use messenger-RNA sequences to synthesize proteins. Investigations using single-molecule imaging and cryo-electron microscopy techniques reveal structural and kinetic differences in how human ribosomes function compared with those of bacteria. These differences explain why ribosomes in cell-nucleus-bearing species are slower and more accurate than their bacterial counterparts.
-
Article |
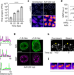 A viral biomolecular condensate coordinates assembly of progeny particles
A viral biomolecular condensate coordinates assembly of progeny particles
Phase separation of the human adenovirus 52-kDa protein has an essential role in the formation of biomolecular condensates, regulating the coordinated assembly of viral progeny particles.
- Matthew Charman
- , Nicholas Grams
- & Matthew D. Weitzman
-
News & Views |
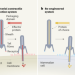 Mix-and-match tools for protein injection into cells
Mix-and-match tools for protein injection into cells
An injection system from bacteria has been re-engineered in an effort to develop a programmable system for protein delivery into cells. Its customizability opens the door to a multitude of biomedical applications.
- Charles F. Ericson
- & Martin Pilhofer
-
Article |
 Norovirus MLKL-like protein initiates cell death to induce viral egress
Norovirus MLKL-like protein initiates cell death to induce viral egress
The murine norovirus NTPase NS3 induces mitochondrial disruption, resulting in cell death, which is required for viral egress.
- Guoxun Wang
- , Di Zhang
- & Tiffany A. Reese
-
Article |
 Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Functional mutations identified in patients with androgen insensitivity syndrome, in the formin and actin nucleator DAAM2, uncover signal-regulated nuclear actin assembly at a steroid hormone receptor necessary for transcription.
- Julian Knerr
- , Ralf Werner
- & Nadine C. Hornig
-
News & Views |
 From the archive: the cell cycle and Antarctic exploration
From the archive: the cell cycle and Antarctic exploration
Snippets from Nature’s past.
-
Research Briefing |
 Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Cells in which the whole genome has been doubled do not upscale protein synthesis to cope with the increase in DNA. Instead, a shortage of proteins that regulate the packing of DNA in the nucleus leads to poor segregation of DNA structures, which eventually contributes to the development of cancer.
-
Research Briefing |
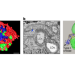 Diversity of mitochondrial networks in lung cancer imaged
Diversity of mitochondrial networks in lung cancer imaged
The structure and function of mitochondrial networks were analysed using a combination of approaches to generate detailed maps of these cellular organelles. This analysis revealed that the mitochondria in different subtypes of lung cancer show distinct functional and structural signatures.
-
Article |
 Lactate regulates cell cycle by remodelling the anaphase promoting complex
Lactate regulates cell cycle by remodelling the anaphase promoting complex
Discovery of a biochemical mechanism through which lactate binds and inhibits the SUMO protease SENP1, stimulating timed degradation of cell cycle proteins, and resulting in mitotic exit.
- Weihai Liu
- , Yun Wang
- & Edward T. Chouchani
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer
Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer
A study describing an approach that combines imaging and profiling techniques to structurally and functionally analyse lung cancer in vivo, revealing heterogeneous mitochondrial networks and an association between bioenergetic phenotypes and mitochondrial organization and function.
- Mingqi Han
- , Eric A. Bushong
- & David B. Shackelford
-
News |
 Gigantic map of fly brain is a first for a complex animal
Gigantic map of fly brain is a first for a complex animal
Fruit fly ‘connectome’ will help researchers to study how the brain works, and could further understanding of neurological diseases.
- Miryam Naddaf
-
News |
 The mice with two dads: scientists create eggs from male cells
The mice with two dads: scientists create eggs from male cells
Proof-of-concept mouse experiment will have a long road before use in humans is possible.
- Heidi Ledford
- & Max Kozlov
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial molecule controls inflammation
Mitochondrial molecule controls inflammation
Cellular organelles called mitochondria contain their own DNA and RNA. The molecule fumarate has now been found to trigger the release of these nucleic acids into the cytosol, aberrantly activating inflammation.
- Taylor A. Poor
- & Navdeep S. Chandel
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Autophagy
- Cell adhesion
- Cell death
- Cell division
- Cell growth
- Cell migration
- Cell polarity
- Cell signalling
- Cellular imaging
- Chromosomes
- Circadian rhythms
- Cytoskeleton
- Glycobiology
- Mechanisms of disease
- Membrane trafficking
- Nuclear organization
- Nuclear transport
- Organelles
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Protein transport
- Proteolysis
- Senescence

 Most advanced synthetic human embryo models yet spark controversy
Most advanced synthetic human embryo models yet spark controversy