News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Clearing the way to cortistatins
Clearing the way to cortistatins
A versatile intermediate has been shown to provide access to a wide variety of compounds in the cortistatin family. This approach offers the most efficient total synthesis of the cortistatins reported so far.
- Richmond Sarpong
-
Article |
 Synthesis of cortistatins A, J, K and L
Synthesis of cortistatins A, J, K and L
The cortistatins have attracted a lot of attention in the synthetic community because of their interesting biological activity. Here, four of the cortistatin family are prepared from a common precursor. This efficient synthesis will assist in an investigation of structure–activity relationships and understanding of the biosynthetic route to these compounds.
- Alec N. Flyer
- , Chong Si
- & Andrew G. Myers
-
Research Highlights |
 Solid oil recovery
Solid oil recovery
A sugar-derived amphiphilic molecule has been prepared that immobilizes oil into a solid from a mixture with water and enables its subsequent recovery.
- Anne Pichon
-
News & Views |
 Linking rings without templates
Linking rings without templates
Interlocking molecules in solution usually requires recognition motifs that direct the assembly of the building blocks. Triply interlocked catenanes have now been constructed just relying on the interpenetration of structures typical of the solid state and slow reversible covalent bond formation.
- Jonathan E. Beves
- & David A. Leigh
-
Article |
 Triply interlocked covalent organic cages
Triply interlocked covalent organic cages
Interlocked molecules commonly include one (or more) monocyclic component — examples comprising bicyclic or tricyclic structures are much more rare and usually involve metal–ligand coordination or additional templates. Now, the dynamic self-assembly of twenty organic molecules in a one-pot synthesis has been shown to produce tetrahedral covalent cages, which interpenetrate during the process to form triply interlocked dimers.
- Tom Hasell
- , Xiaofeng Wu
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Highly enantioselective synthesis and cellular evaluation of spirooxindoles inspired by natural products
Highly enantioselective synthesis and cellular evaluation of spirooxindoles inspired by natural products
A Lewis-acid-catalysed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition provides rapid access to a variety of substituted spirooxindoles. Initial cellular evaluations supports the view that compound collections based on natural-product-inspired scaffolds constructed with complex stereochemistry, and decorated with assorted substituents, will be a rich source of compounds with diverse bioactivity.
- Andrey P. Antonchick
- , Claas Gerding-Reimers
- & Herbert Waldmann
-
News & Views |
 Towards artificial terpene cyclases
Towards artificial terpene cyclases
The plant-derived sesquiterpene englerin A is a potent inhibitor of several renal cancer cell lines. Two recent total syntheses have utilized cationic gold(I)-complexes to coax readily available open-chain precursors into englerin's challenging oxotricyclic core with enzyme-like precision.
- Matthieu Willot
- & Mathias Christmann
-
Article |
 Isolation of a radical dianion of nitrogen oxide (NO)2−
Isolation of a radical dianion of nitrogen oxide (NO)2−
Nitric oxide, NO, has an unpaired electron and is widely used and studied in such diverse fields as biochemistry and atmospheric chemistry. Its radical nature means that singly charged species are common, but now two electrons have been added to give a radical dianion in an yttrium complex.
- William J. Evans
- , Ming Fang
- & Jeffrey I. Zink
-
Research Highlights |
 Resolving rotamers
Resolving rotamers
A peptide-catalysed bromination provides access to an important class of chiral compounds in high enantiomeric purity.
- Stephen Davey
-
Perspective |
 Visible light photocatalysis as a greener approach to photochemical synthesis
Visible light photocatalysis as a greener approach to photochemical synthesis
Sunlight is potentially an ideal green 'reagent' for chemical synthesis, but poor absorption by organic substrates makes direct solar photochemistry generally inefficient. Here, recent progress in the use of the simple organometallic complexes to harness the power of the sun is summarized, and prospects for the future of this exciting field highlighted.
- Tehshik P. Yoon
- , Michael A. Ischay
- & Juana Du
-
Article |
 A layered ionic crystal of polar Li@C60 superatoms
A layered ionic crystal of polar Li@C60 superatoms
Metal-containing fullerene cages are widely known, but hard to characterize because of their reactivity towards empty cages. Now the molecular and crystal structures of lithium-containing C60 molecules have been determined.
- Shinobu Aoyagi
- , Eiji Nishibori
- & Hiromi Tobita
-
Article |
 Lewis acid-catalysed formation of two-dimensional phthalocyanine covalent organic frameworks
Lewis acid-catalysed formation of two-dimensional phthalocyanine covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) organize organic subunits into predictable and precise networks with long-range order. The limited generality of methods for COF synthesis has thus far precluded the incorporation of complex building blocks into these emerging materials. Now, a new Lewis acid-catalysed protocol for boronic ester formation provides a two-dimensional COF containing stacked phthalocyanine chromophores.
- Eric L. Spitler
- & William R. Dichtel
-
Article |
 Reversible dioxygen binding in solvent-free liquid myoglobin
Reversible dioxygen binding in solvent-free liquid myoglobin
Freeze-drying of aqueous myoglobin–polymer surfactant nanoconjugates affords a water-free solid that melts at room temperature to produce a viscous solventless liquid protein that exhibits near-native secondary structure and reversible dioxygen binding. The results challenge the accepted role of solvent molecules in mediating protein structure and function, and offer new opportunities in protein-based nanoscience and bionanotechnology.
- Adam W. Perriman
- , Alex P. S. Brogan
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 Hydroacylation of α,β-unsaturated esters via aerobic C–H activation
Hydroacylation of α,β-unsaturated esters via aerobic C–H activation
The development of benign methods for carbon–carbon bond formation is a continuing challenge. Here, a simple procedure for the hydroacylation of α,β-unsaturated esters is described, in which auto-oxidation of aldehydes and subsequent acyl radical addition to α,β-unsaturated esters occurs without the need for additional reagents.
- Vijay Chudasama
- , Richard J. Fitzmaurice
- & Stephen Caddick
-
News & Views |
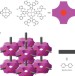 Towards artificial enzymes
Towards artificial enzymes
Despite knowing that the active centres of many metalloprotein enzymes are iron porphyrin 'haem' complexes, chemists find them difficult to imitate. Now, the assembly of haem-like centres into a crystalline, stable, nanoporous array shows promise for biomimetic catalysis.
- Joseph T. Hupp
-
Article |
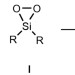 From silicon(II)-based dioxygen activation to adducts of elusive dioxasiliranes and sila-ureas stable at room temperature
From silicon(II)-based dioxygen activation to adducts of elusive dioxasiliranes and sila-ureas stable at room temperature
Converting dioxygen into more reactive species is extremely useful for direct oxygenation of organic compounds, but doing this with cheap and non-polluting elements is difficult. Now, a carbene-activated silylene has been shown to activate dioxygen, resulting in the isolation of elusive silicon–oxygen species at room temperature.
- Yun Xiong
- , Shenglai Yao
- & Matthias Driess
-
Article |
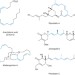 Convergent and stereospecific synthesis of complex skipped polyenes and polyunsaturated fatty acids
Convergent and stereospecific synthesis of complex skipped polyenes and polyunsaturated fatty acids
A convergent route to stereodefined skipped polyenes, which proceeds through the direct union of vinylcyclopropanes with alkynes, is described. Overall, C?C bond formation occurs in concert with the establishment of up to three stereodefined alkenes, through a tandem stereoselective metallacycle-mediated coupling/stereospecific fragmentation sequence.
- Todd K. Macklin
- & Glenn C. Micalizio
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Optically driven phase transitions are widely used in optical memory devices, and the materials showing this effect are normally chalcogenides or organic compounds. Now a room-temperature light-induced phase transition between metal and semiconducting phases has been observed in a titanium oxide material.
- Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
- , Yoshihide Tsunobuchi
- & Hiroko Tokoro
-
Article |
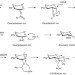 Chiral-auxiliary-mediated 1,2-cis-glycosylations for the solid-supported synthesis of a biologically important branched α-glucan
Chiral-auxiliary-mediated 1,2-cis-glycosylations for the solid-supported synthesis of a biologically important branched α-glucan
The difficulty in the stereoselective introduction of 1,2-cis-glycosides is a major stumbling block in the solid-supported synthesis of oligosaccharides. Now, this has been achieved for a biologically important glucoside containing multiple 1,2-cis-glycosidic linkages with complete anomeric control by using glycosyl donors having a participating (S)-(phenylthiomethyl)benzyl chiral auxiliary at C-2.
- Thomas J. Boltje
- , Jin-Hwan Kim
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article |
 Triggering N2 uptake via redox-induced expulsion of coordinated NH3 and N2 silylation at trigonal bipyramidal iron
Triggering N2 uptake via redox-induced expulsion of coordinated NH3 and N2 silylation at trigonal bipyramidal iron
In nature, iron takes a direct role in converting nitrogen to ammonia through a variety of NxHy intermediates. A series of synthetic iron complexes that mimic these intermediates could lead to an increased understanding of the process and eventually to effective catalysts.
- Yunho Lee
- , Neal P. Mankad
- & Jonas C. Peters
-
Article |
 Nucleophilic catalysis of acylhydrazone equilibration for protein-directed dynamic covalent chemistry
Nucleophilic catalysis of acylhydrazone equilibration for protein-directed dynamic covalent chemistry
The composition of a dynamic combinatorial library can be altered by adding a target molecule that either stabilizes (or destabilizes) one or more of its members. The range of reversible chemical reactions compatible with biological targets such as proteins is somewhat limited, but now it has been shown that aniline-catalysed acylhydrazone formation is effective in this context.
- Venugopal T. Bhat
- , Anne M. Caniard
- & Michael F. Greaney
-
Article |
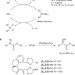 Enantioselective iron-catalysed O–H bond insertions
Enantioselective iron-catalysed O–H bond insertions
Iron is an abundant, low cost and environmentally benign metal. Here, iron complexes are shown to be the most effective catalysts for asymmetric O–H insertion reactions. These results should encourage the use of iron, rather than more traditional precious metals, in the development of greener organometallic catalysts for asymmetric transformations.
- Shou-Fei Zhu
- , Yan Cai
- & Qi-Lin Zhou
-
Article |
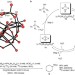 Efficient stereo- and regioselective hydroxylation of alkanes catalysed by a bulky polyoxometalate
Efficient stereo- and regioselective hydroxylation of alkanes catalysed by a bulky polyoxometalate
The ability to selectively transform the C–H bonds of simple alkanes to useful functional groups such as alcohols is a key step in the move away from petrochemical feedstocks. Now, it has been shown that the oxidation of alkanes can be catalysed by a bulky polyoxometalate species using hydrogen peroxide as a stoichiometric oxidant.
- Keigo Kamata
- , Kazuhiro Yonehara
- & Noritaka Mizuno
-
Research Highlights |
 Pseudosymmetry solved
Pseudosymmetry solved
Two different but successful approaches to the synthesis of (+)-complanadine A will help in investigations of its interesting biological activity.
- Stephen Davey
-
Review Article |
 Induction of chiral porous solids containing only achiral building blocks
Induction of chiral porous solids containing only achiral building blocks
The synthesis or separation of chiral compounds is crucial for many areas of chemistry, with chiral solids having important roles as catalysts or separating agents. This Review covers recent progress and future avenues for developing methods of preparing chiral solids from achiral starting materials.
- Russell E. Morris
- & Xianhui Bu
-
Article |
 Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Porous coordination polymers — PCPs, also known as metal–organic framework materials — have been widely investigated for their useful properties, but controlling their size and shape in a nanocrystalline form is difficult. Now, a rapid method of preparing porous crystalline nanosized PCPs that uses a microemulsion system under ultrasonic irradiation has been reported.
- Daisuke Tanaka
- , Artur Henke
- & Juergen Groll
-
Article |
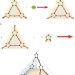 Assembly of a metal–organic framework by sextuple intercatenation of discrete adamantane-like cages
Assembly of a metal–organic framework by sextuple intercatenation of discrete adamantane-like cages
There has been much interest in the assembly and properties of metal–organic frameworks. Here, a new type is described in which an infinite three-dimensional polycatenane is assembled from a discrete octahedral nanocage through the interlocking of all its six vertices.
- Xiaofei Kuang
- , Xiaoyuan Wu
- & Can-Zhong Lu
-
Research Highlights |
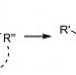 Twice as nice
Twice as nice
A double-reductive alkylation of amides with two different organometallic compounds allows the direct formation of a tertiary alkylamines in one pot.
- Stephen Davey
-
News & Views |
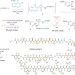 Totally tubular peptide synthesis
Totally tubular peptide synthesis
The convergent total synthesis of the pore-forming polytheonamide B — a linear peptide natural product — pokes holes through perceived limitations in de novo peptide synthesis, and provides access to novel synthetic membrane channels.
- Craig J. Forsyth
-
News & Views |
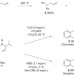 Without a trace
Without a trace
A strong acid catalyst and a small change to one reactant have transformed a 37-year-old 'curiosity' into a useful chemical reaction that has great potential in organic synthesis.
- Sarah E. Steinhardt
- & Christopher D. Vanderwal
-
Article |
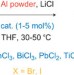 Preparation of functionalized organoaluminiums by direct insertion of aluminium to unsaturated halides
Preparation of functionalized organoaluminiums by direct insertion of aluminium to unsaturated halides
The reactivity of organoaluminium reagents makes them particularly attractive nucleophiles for a wide range of organic reactions. Here, the use of metal halide catalysts provides access to functionalized organoaluminium reagents directly from the metal. The utility of these organoaluminium reagents is then demonstrated by their reaction with a wide variety of electrophilic coupling partners.
- Tobias Blümke
- , Yi-Hung Chen
- & Paul Knochel
-
Article |
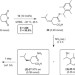 Synergistic organocatalysis in the kinetic resolution of secondary thiols with concomitant desymmetrization of an anhydride
Synergistic organocatalysis in the kinetic resolution of secondary thiols with concomitant desymmetrization of an anhydride
Chiral thiols and organosulfur compounds are important in many areas of chemistry but there are relatively few methods available for their efficient enantioselective synthesis. Here, a kinetic resolution of chiral thiols is reported along with a demonstration that a concomitant desymmetrization of the acylating agent is beneficial for the selectivity of both processes.
- Aldo Peschiulli
- , Barbara Procuranti
- & Stephen J. Connon
-
News & Views |
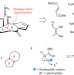 Stitching together palau'amine
Stitching together palau'amine
The long-awaited first total synthesis of the structurally intriguing natural product palau'amine has now been achieved. The synthesis features cascade reactions and an 'across ring' stitching of a 'macropalau'amine', and sets the bar for future efforts towards an enantioselective variant.
- Daniel Romo
-
Article |
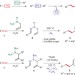 Triflimide-catalysed sigmatropic rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones as an example of a traceless bond construction
Triflimide-catalysed sigmatropic rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones as an example of a traceless bond construction
A triflimide-catalysed rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones has been developed that allows for the generation of a sigma bond between two unfunctionalized sp3 carbons such that no clear marker remains for how the bond was formed. This traceless bond construction offers new avenues for convergent fragment coupling in synthetic strategies.
- Devon A. Mundal
- , Christopher T. Avetta Jr
- & Regan J. Thomson
-
Review Article |
 Organocatalytic cascade reactions as a new tool in total synthesis
Organocatalytic cascade reactions as a new tool in total synthesis
The field of organocatalysis has grown rapidly in the past decade to become, along with metal catalysis and biocatalysis, a third pillar of asymmetric catalysis. Here, progress in the use of organocatalytic cascade reactions for total synthesis is reviewed. The elegance and efficiency of such cascades mean that they have emerged as a powerful tool in synthetic organic chemistry.
- Christoph Grondal
- , Matthieu Jeanty
- & Dieter Enders
-
Article |
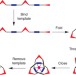 Synthesis of a molecular trefoil knot by folding and closing on an octahedral coordination template
Synthesis of a molecular trefoil knot by folding and closing on an octahedral coordination template
The synthesis of interlocked compounds such as catenanes and rotaxanes has undergone much development in recent years, but molecular knots are still relatively hard to make. It has now been shown that a linear bipyridine oligomer can fold around a single zinc-ion template to form a complex that can be cyclized to give a molecular trefoil knot.
- Jun Guo
- , Paul C. Mayers
- & Christopher A. Hunter
-
Research Highlights |
Advancing vaccines
Replacing readily hydrolysable ester linkages with amides in a natural adjuvant has resulted in not only more stable, but significantly more active and less toxic analogues.
- Georgia Tsoukala
-
News & Views |
 Stereochemistry by remote control
Stereochemistry by remote control
The stereochemical lability of cycloalkylzinc reagents combined with a large difference in reactivity between epimers has been exploited to form a wide variety of interesting organic compounds with both high yields and diastereoselectivities.
- Frank Glorius
-
News & Views |
 Sweet flexibility
Sweet flexibility
An enzyme that is unusually tolerant of a truly broad range of substrates can catalyse aldol-type chemistry on sugars in which the various hydroxyl groups are protected. The new methodology combines some of the most important advantages of enzyme and small-molecule catalysis.
- Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article |
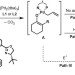 A palladium-catalysed enolate alkylation cascade for the formation of adjacent quaternary and tertiary stereocentres
A palladium-catalysed enolate alkylation cascade for the formation of adjacent quaternary and tertiary stereocentres
The selective construction of multiple adjacent stereocentres is an important challenge for synthetic organic methodology, and only a handful of catalytic methods exist that can forge adjacent quaternary and tertiary stereocentres. Here, a palladium-catalysed multiple-bond-forming cascade leads to the construction of such systems in high yield, diastereomeric ratio and enantiomeric excess.
- Jan Streuff
- , David E. White
- & Brian M. Stoltz
-
Article |
 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of differentially protected 3-deoxysugars
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of differentially protected 3-deoxysugars
Ready access to sugars in which the various hydroxyl groups are differentially protected will be of benefit in the production of vaccines, antibiotics and drugs. Here, a chemoenzymatic method that provides a direct route to such protected sugars is described.
- Dennis G. Gillingham
- , Pierre Stallforth
- & Donald Hilvert
-
Thesis |
 Life is the variety of spice
Life is the variety of spice
Bruce C. Gibb wonders why curry is not part of the chemistry curriculum.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
News & Views |
 The best of both worlds
The best of both worlds
Embedding platinum nanoparticles in a polymer matrix produces a system that reacts like a homogeneous catalyst, but provides the stability and separation advantages of a heterogeneous one.
- Gadi Rothenberg
-
News & Views |
 Producing 'perfect' particles
Producing 'perfect' particles
Synthetic procedures for making nanoparticles often result in samples that contain a range of different particle sizes. By using hollow self-assembled metal–organic spheres as templates, however, it is possible to make silica nanoparticles with uniform shapes and sizes in a precisely controlled fashion.
- Boris Breiner
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Asymmetric synthesis
- Automation
- Biomimetic synthesis
- Catalyst synthesis
- Chemical libraries
- Diversity-oriented synthesis
- Flow chemistry
- Fluorescent labelling
- Synthetic chemistry methodology
- Microwave chemistry
- Nanoparticle synthesis
- Natural product synthesis
- Polymer synthesis
- Reactive precursors
- Solid-phase synthesis

 Moving backwards in new ways
Moving backwards in new ways