Featured
-
-
Article |
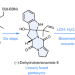 Total synthesis of brevianamide A
Total synthesis of brevianamide A
Despite five decades of research, the alkaloid (+)-brevianamide A has remained an elusive target for chemical synthesis. Now, it has been shown that the total synthesis of (+)-brevianamide A can be achieved in seven steps and 7.2% overall yield to give 750 mg of the target compound.
- Robert C. Godfrey
- , Nicholas J. Green
- & Andrew L. Lawrence
-
Article |
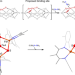 Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
The four-coordinate iron sites of typical iron–sulfur clusters rarely react with small molecules, implicating three-coordinate iron in many catalytic cycles. Now, a [4Fe-3S] cluster featuring three-coordinate iron sulfide that resembles the proposed substrate binding site has been synthesized. This cluster shows biomimetic reactivity with a low-spin electronic configuration.
- Daniel E. DeRosha
- , Vijay G. Chilkuri
- & Patrick L. Holland
-
Article |
 Fungal indole alkaloid biogenesis through evolution of a bifunctional reductase/Diels–Alderase
Fungal indole alkaloid biogenesis through evolution of a bifunctional reductase/Diels–Alderase
The complete biosynthesis of the fungal indole alkaloid malbrancheamide, which culminates in an intramolecular [4+2] hetero-Diels–Alder cyclization to produce the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane scaffold, has now been discovered. Chemical synthesis and protein structural analysis were used to provide mechanistic insight into this enzyme-dependent diastereo- and enantioselective cycloaddition.
- Qingyun Dan
- , Sean A. Newmister
- & Robert M. Williams
-
Article |
 A unifying paradigm for naphthoquinone-based meroterpenoid (bio)synthesis
A unifying paradigm for naphthoquinone-based meroterpenoid (bio)synthesis
Bacterial naphthoquinone meroterpenoid natural products defy biosynthetic logic via classical biochemical paradigms. Now, an enzyme promoted α-hydroxyketone rearrangement catalysed by vanadium-dependent haloperoxidases reveals a conserved biosynthetic reaction in this molecular class that further has inspired a concise biomimetic synthesis of naphthomevalin, a prominent member of the napyradiomycin meroterpenes.
- Zachary D. Miles
- , Stefan Diethelm
- & Bradley S. Moore
-
Editorial |
Life, but not as we know it
There are many unanswered questions regarding how the biomolecules and biomechanical processes that define life came to be. A collection of Articles in this issue show how intermediates in RNA synthesis might have formed and how the initiation and evolution of RNA replication might have occurred.
-
Article |
 Ligand-modulated conformational switching in a fully synthetic membrane-bound receptor
Ligand-modulated conformational switching in a fully synthetic membrane-bound receptor
A dynamic foldamer scaffold has now been ligated to a water-compatible, metal-centred binding site and a conformationally responsive fluorophore to form a receptor mimic that inserts into the membrane of artificial vesicles. Binding of specific carboxylate ligands induces a global conformational change that depends on the structure of the ligand, and can be detected via fluorescence.
- Francis G. A. Lister
- , Bryden A. F. Le Bailly
- & Jonathan Clayden
-
Article |
 Unified biomimetic assembly of voacalgine A and bipleiophylline via divergent oxidative couplings
Unified biomimetic assembly of voacalgine A and bipleiophylline via divergent oxidative couplings
The biomimetic syntheses of bipleiophylline, one of the most complex monoterpene indole alkaloids, and voacalgine A, its biosynthetic precursor, have been achieved from pleiocarpamine starting material. The development of a divergent oxidative coupling for the formation of the benzofuro[2,3-b]indolenine and isochromano[3,4-b]indolenine moieties was key to this accomplishment.
- David Lachkar
- , Natacha Denizot
- & Guillaume Vincent
-
News & Views |
 Complex peptides made simple
Complex peptides made simple
Nature oxidizes biosynthetic intermediates into structurally and functionally diverse peptides. An iron-catalysed C–H oxidation mimics this approach in the lab, enabling chemists to synthesize structural analogues with ease.
- Sean Bartlett
- & David R. Spring
-
Article |
 Synthesis of marmycin A and investigation into its cellular activity
Synthesis of marmycin A and investigation into its cellular activity
Marmycin A is an anthraquinone natural product with antiproliferative properties. Now the chemical synthesis of marmycin A—through a Diels–Alder cycloaddition, an Ullmann aromatic amination and a Friedel–Crafts cyclization—has enabled a study of its biological activity. Fluorescence microscopy reveals that marmycin A accumulates in lysosomes and promotes cell death independently of genome targeting.
- Tatiana Cañeque
- , Filipe Gomes
- & Raphaël Rodriguez
-
News & Views |
 Terpenes in tight spaces
Terpenes in tight spaces
The ability of enzymes to direct the synthesis of complex natural products from simple starting materials is epitomized by terpene biosynthesis. Now, a supramolecular catalyst has been shown to mimic some of the reactivity of this process.
- Jeremy J. Roach
- & Ryan A. Shenvi
-
Article |
 Terpene cyclization catalysed inside a self-assembled cavity
Terpene cyclization catalysed inside a self-assembled cavity
A tail-to-head terpene cyclization, which is hard to control in solution, has now been catalysed inside a supramolecular structure. Evidence indicates that a direct isomerization of a geranyl cation to the cisoid-isomer, which so far was considered unlikely in the biosynthesis, is feasible in this system.
- Q. Zhang
- & K. Tiefenbacher
-
-
News & Views |
 Merging the old with the new
Merging the old with the new
The classic organometallic compound ferrocene has been combined with a unique diiron unit in the latest synthetic analogue of an enzyme active site, achieving the three functionalities needed for a working model of diiron hydrogenase, itself of ancient origin.
- Marcetta Y. Darensbourg
- & Ryan D. Bethel
-
Article |
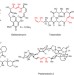 A biomimetic polyketide-inspired approach to small-molecule ligand discovery
A biomimetic polyketide-inspired approach to small-molecule ligand discovery
The design and synthesis of a family of chiral and conformationally constrained oligomers is described. Asymmetric synthesis of the monomers is presented and the preparation of a 160,000-member library of diverse tetramers via split-and-pool methods is discussed. From this library, a non-covalent ligand to the DNA-binding domain of p53 was discovered.
- Claudio Aquino
- , Mohosin Sarkar
- & Glenn C. Micalizio
-
News & Views |
 Communicating chirality
Communicating chirality
Conformational control can be used to transmit information in the form of chirality over relatively long molecular distances and could be the key to the preparation of minimalistic synthetic mimics of biological systems.
- Jonathan Clayden
-
Article |
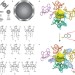 A bioinspired approach for controlling accessibility in calix[4]arene-bound metal cluster catalysts
A bioinspired approach for controlling accessibility in calix[4]arene-bound metal cluster catalysts
The accessibility of catalytically active sites in enzymes is maintained by the surrounding amino acid residues, but in synthetic metal clusters, these sites are typically blocked by the organic groups used to coat them. It has now been shown that the accessibility of gold clusters bound by calixarenes can be controlled by tuning the relative sizes of the metal cores and the ligands.
- Namal de Silva
- , Jeong-Myeong Ha
- & Alexander Katz
-
News & Views |
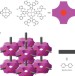 Towards artificial enzymes
Towards artificial enzymes
Despite knowing that the active centres of many metalloprotein enzymes are iron porphyrin 'haem' complexes, chemists find them difficult to imitate. Now, the assembly of haem-like centres into a crystalline, stable, nanoporous array shows promise for biomimetic catalysis.
- Joseph T. Hupp

 Prebiotic synthesis of α-amino acids and orotate from α-ketoacids potentiates transition to extant metabolic pathways
Prebiotic synthesis of α-amino acids and orotate from α-ketoacids potentiates transition to extant metabolic pathways Flinderoles facilitated
Flinderoles facilitated