Featured
-
-
Article |
 Micrometre-scale single-crystalline borophene on a square-lattice Cu(100) surface
Micrometre-scale single-crystalline borophene on a square-lattice Cu(100) surface
Borophene, a two-dimensional boron sheet, can adopt a variety of polymorphic structures that are predicted to possess interesting and potentially useful electronic properties. Micrometre-scale single-crystal borophene domains have now been grown on a square-lattice Cu(100) surface. The resulting boron sheets feature a rectangular unit cell, intrinsic stripe modulations and an unusual electron band structure.
- Rongting Wu
- , Stephen Eltinge
- & Ivan Božović
-
News & Views |
 Defogging the view through a milling jar
Defogging the view through a milling jar
Innovations in instrumentation together with new strategies of data collection and processing have been shown to solve the problem of data quality for time-resolved in situ X-ray diffraction studies on ball milling, opening new horizons in mechanochemistry.
- Elena Boldyreva
-
News & Views |
 Solid potential
Solid potential
Small-molecule drug discovery and development is limited by the ability of chemists to readily synthesize and purify new compounds with suitable chemical diversity. Now, a new twist on solid-phase chemical synthesis has enabled rapid and simplified synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant small molecules.
- Mark S. Kerr
- & Kevin P. Cole
-
Article |
 Automated synthesis of prexasertib and derivatives enabled by continuous-flow solid-phase synthesis
Automated synthesis of prexasertib and derivatives enabled by continuous-flow solid-phase synthesis
Although strategies for the automated assembly of compounds of pharmaceutical relevance is a growing field of research, the synthesis of small-molecule pharmacophores remains a predominantly manual process. Now, an automated six-step synthesis of prexasertib is achieved by multistep solid-phase chemistry in a continuous-flow fashion using a chemical recipe file that enables automated scaffold modification through both early and late-stage diversification.
- Chenguang Liu
- , Jiaxun Xie
- & Jie Wu
-
Article |
 Dynamic covalent chemistry enables formation of antimicrobial peptide quaternary assemblies in a completely abiotic manner
Dynamic covalent chemistry enables formation of antimicrobial peptide quaternary assemblies in a completely abiotic manner
Despite advances in peptide synthesis techniques, explicit control over the quaternary structure of synthetic peptides has remained elusive. Now, the dynamic covalent chemistry of hydrazide- and aldehyde-containing peptides has now been shown to enable the formation of unique quaternary structures with topological diversity. Using this method, oligomers were assembled into complex structures showing dramatic enhancements of antimicrobial effectiveness versus Staphylococcus Aureus.
- James F. Reuther
- , Justine L. Dees
- & Eric V. Anslyn
-
Article |
 Tyrosine sulfation modulates activity of tick-derived thrombin inhibitors
Tyrosine sulfation modulates activity of tick-derived thrombin inhibitors
Tyrosine sulfation strongly enhances the inhibition of thrombin by the tick-derived anticoagulants madanin-1 and chimadanin. Protein chemical synthesis and structural studies have revealed a mode of inhibition that is unprecedented among cysteine-free anticoagulant proteins. This inhibition occurs through the recognition of the highly basic exosite II of thrombin.
- Robert E. Thompson
- , Xuyu Liu
- & Richard J. Payne
-
Article |
 Flow chemistry and polymer-supported pseudoenantiomeric acylating agents enable parallel kinetic resolution of chiral saturated N-heterocycles
Flow chemistry and polymer-supported pseudoenantiomeric acylating agents enable parallel kinetic resolution of chiral saturated N-heterocycles
Parallel kinetic resolution (PKR) of N-heterocycles via asymmetric acylation has been achieved using quasienantiomers of polymer supported hydroxamic acid reagents. Flow techniques provide physical separation of the reagents, establishing a practical implementation of PKR. The enantioenriched amide products can be readily deprotected to reveal the desired amine without detectable epimerization.
- Imants Kreituss
- & Jeffrey W. Bode
-
Article |
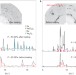 Synthesis and stability of xenon oxides Xe2O5 and Xe3O2 under pressure
Synthesis and stability of xenon oxides Xe2O5 and Xe3O2 under pressure
The reactivity of the noble gases—a notoriously inert group—at high pressures is intriguing. Now, two xenon oxides with unusual stoichiometries, Xe2O5 and Xe3O2, have been synthesized above 78 GPa and predicted to be stable above 50 GPa, indicating that xenon is more reactive than previously thought.
- Agnès Dewaele
- , Nicholas Worth
- & Tetsuo Irifune
-
News & Views |
 The quest for new functionality
The quest for new functionality
Building on our understanding of the chemical bond, advances in synthetic chemistry, and large-scale computation, materials design has now become a reality. From a pool of 400 unknown compositions, 15 new compounds have been realized that adopt the predicted structures and properties.
- Aron Walsh
-
Article |
 Prediction and accelerated laboratory discovery of previously unknown 18-electron ABX compounds
Prediction and accelerated laboratory discovery of previously unknown 18-electron ABX compounds
A method to predict the stability, structure and properties of as-yet-unreported materials has been devised. For 18-valence electron ABX materials, 15 such ‘missing’ compounds identified to be thermodynamically stable were successfully synthesized, and showed crystal structures and properties in good agreement with the predicted ones.
- Romain Gautier
- , Xiuwen Zhang
- & Alex Zunger
-
Article |
 The synthesis, crystal structure and charge-transport properties of hexacene
The synthesis, crystal structure and charge-transport properties of hexacene
Crystals of hexacene prepared from a monoketone precursor are found to be stable up to 300 °C in the dark, but readily decompose when exposed to light. An organic-field transistor made with a single crystal of hexacene was found to have superior properties to one made from pentacene under analogous conditions.
- Motonori Watanabe
- , Yuan Jay Chang
- & Tahsin J. Chow
-
Article |
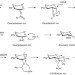 Chiral-auxiliary-mediated 1,2-cis-glycosylations for the solid-supported synthesis of a biologically important branched α-glucan
Chiral-auxiliary-mediated 1,2-cis-glycosylations for the solid-supported synthesis of a biologically important branched α-glucan
The difficulty in the stereoselective introduction of 1,2-cis-glycosides is a major stumbling block in the solid-supported synthesis of oligosaccharides. Now, this has been achieved for a biologically important glucoside containing multiple 1,2-cis-glycosidic linkages with complete anomeric control by using glycosyl donors having a participating (S)-(phenylthiomethyl)benzyl chiral auxiliary at C-2.
- Thomas J. Boltje
- , Jin-Hwan Kim
- & Geert-Jan Boons

 In situ multiscale probing of the synthesis of a Ni-rich layered oxide cathode reveals reaction heterogeneity driven by competing kinetic pathways
In situ multiscale probing of the synthesis of a Ni-rich layered oxide cathode reveals reaction heterogeneity driven by competing kinetic pathways