Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Deuterated compounds are used in many applications such as mass-spectrometry standards, drugs or in organic light-emitting diodes. Now, hydrogen-activated homogeneous pincer complex catalysts can be used to perform selective alkene deuteration with the cheapest available deuterium source, D2O.
- Anika Tarasewicz
- & Volker Derdau
-
News & Views |
 Isolating intermediates
Isolating intermediates
Noyori-type catalysts and inorganic bases are frequently used together for homogeneous hydrogenation, but key intermediates have not yet been isolated. Now, the structure and reactivity of a long-postulated intermediate — the alkali metal amidate complex — have been reported through experimental and computational studies.
- Pavel A. Dub
-
Article |
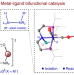 Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Noyori-type hydrogenation catalysts consist of an N–H moiety coordinated to a metal centre. Now, a metal-hydride amidate complex (HMn–NLi) has been isolated and found to have superior reactivity and catalytic performance compared with the corresponding HMn–NH complex, highlighting the superiority of M/NM′ bifunctional catalysis over the classic M/NH bifunctional catalysis for hydrogenation reactions.
- Yujie Wang
- , Shihan Liu
- & Qiang Liu
-
In Your Element |
 Shapeshifting xantphos
Shapeshifting xantphos
Lukas Veth and Paweł Dydio discuss the importance of ligands in transition metal catalysis, looking at the success story of xantphos and why it should earn the title of ‘privileged ligand’.
- Lukas Veth
- & Paweł Dydio
-
Article |
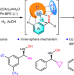 Nickel-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes
Nickel-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes
The asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes to chiral hydroxylamines is a long-standing challenge because of the labile N–O bond and inert C=N bond. Now, it has been shown that this reaction can be catalysed with a chiral nickel complex, and the weak interactions between catalyst and substrate are found to play a crucial role.
- Bowen Li
- , Jianzhong Chen
- & Wanbin Zhang
-
Article |
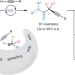 Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
A general copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of diverse racemic tertiary alkyl halides with terminal alkynes has been developed, forging all-carbon quaternary stereocentres. Key to the success is the rational design of chiral anionic N,N,N-ligands tailor-made for the computationally predicted outer-sphere radical group transfer pathway.
- Fu-Li Wang
- , Chang-Jiang Yang
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article |
 General synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high metal loading using graphene quantum dots
General synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high metal loading using graphene quantum dots
Transition-metal single-atom catalysts display excellent activity per metal atom site, but suffer from low metal atom densities (typically less than 5 wt% or 1 at.%), which limits their overall catalytic performance. Now, the use of a graphene-quantum-dot primary support, later interweaved into a carbon matrix, has enabled the synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high transition-metal atom loadings of up to 40 wt% or 3.84 at.%.
- Chuan Xia
- , Yunrui Qiu
- & Haotian Wang
-
Article |
 Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Generating stable single-atom catalysts is far from straightforward and can involve complicated preparation procedures. Now, mononuclear gold oxo-clusters formed in alkaline solutions through a facile one-pot synthesis are shown to catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reaction to methyl formate and hydrogen. The intrinsic activity is the same for both supported and unsupported gold catalysts.
- Sufeng Cao
- , Ming Yang
- & Maria Flytzani-Stephanopoulos
-
Article |
 The formation of all-cis-(multi)fluorinated piperidines by a dearomatization–hydrogenation process
The formation of all-cis-(multi)fluorinated piperidines by a dearomatization–hydrogenation process
Despite their huge potential in medicinal chemistry, current approaches for the synthesis of fluorinated piperidines are often impractical. A straightforward process for the rhodium-catalysed dearomatization–hydrogenation of fluoropyridines has now been described. This strategy enables the highly diastereoselective formation of a variety of all-cis-(multi)fluorinated piperidines and the study of their conformational behaviour.
- Zackaria Nairoukh
- , Marco Wollenburg
- & Frank Glorius
-
Article |
 Catalytic dehydrogenative decarboxyolefination of carboxylic acids
Catalytic dehydrogenative decarboxyolefination of carboxylic acids
A direct conversion of carboxylic acids to alpha-olefins without the need for a stoichiometric additive has now been reported. The transformation is enabled by a dual cobalt/iridium proton-reduction–photoredox catalyst system, and can proceed on abundant fatty acids as well as on complex carboxylic acids.
- Xiang Sun
- , Junting Chen
- & Tobias Ritter
-
News & Views |
 N-doping goes sp-hybridized
N-doping goes sp-hybridized
Specific forms of nitrogen doping can endow carbon-based metal-free materials with electrocatalytic activity. Now, introducing sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms into some acetylenic sites of ultra-thin graphdiyne — a highly π-conjugated lamellar carbon allotrope — has led to excellent oxygen reduction reaction activity.
- Yao Zheng
- & Shi-Zhang Qiao
-
Article |
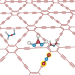 Few-layer graphdiyne doped with sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms at acetylenic sites for oxygen reduction electrocatalysis
Few-layer graphdiyne doped with sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms at acetylenic sites for oxygen reduction electrocatalysis
Heteroatom doping is a widely used modification method for carbon-based catalysts. Now, chemically defined sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms have been selectively introduced to the acetylene groups in ultrathin graphdiynes, resulting in good catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic media.
- Yasong Zhao
- , Jiawei Wan
- & Dan Wang
-
News & Views |
 Popping up to the surface
Popping up to the surface
Merging the advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts is a useful strategy for creating improved catalytic systems. Now, a concept has been developed that uses single Pd atoms — supported within liquid alloy droplets — that emerge from the droplet subsurface and interior to react with molecules approaching from the gas phase.
- Günther Rupprechter
-
Article |
 Gallium-rich Pd–Ga phases as supported liquid metal catalysts
Gallium-rich Pd–Ga phases as supported liquid metal catalysts
Creating systems that merge some of the advantages of both heterogeneous and molecular catalysis is a useful approach to developing improved catalysts. Following this strategy, a liquid mixture of gallium and palladium supported on porous glass has now been shown to form an active catalyst for alkane dehydrogenation that is resistant to coke formation and is thus highly stable.
- N. Taccardi
- , M. Grabau
- & P. Wasserscheid
-
News & Views |
 Eight irons hit the right spin
Eight irons hit the right spin
After remaining elusive for 40 years, 'Kochi's complex', a key intermediate in iron-catalysed cross-coupling, has finally been pinned down, and its structure comes as something of a surprise.
- Robin B. Bedford
-
Article |
 New ligands for nickel catalysis from diverse pharmaceutical heterocycle libraries
New ligands for nickel catalysis from diverse pharmaceutical heterocycle libraries
Pharmaceutical compound libraries are an essential part of drug discovery and the screening of libraries for new drug leads is routine. It has now been shown that these heterocycle-rich, diverse libraries can also be used for ligand discovery. The discovery and application of several new ligands to nickel-catalysed cross-electrophile coupling is demonstrated.
- Eric C. Hansen
- , Dylan J. Pedro
- & Daniel J. Weix
-
Article |
 Mass-selected nanoparticles of PtxY as model catalysts for oxygen electroreduction
Mass-selected nanoparticles of PtxY as model catalysts for oxygen electroreduction
The widespread use of fuel cells requires improved catalysts to reduce oxygen efficiently at the cathode. It is shown that model, well-characterized size-selected PtxY nanoparticles can be synthesized by the gas aggregation technique, and that they are highly active for this reaction.
- Patricia Hernandez-Fernandez
- , Federico Masini
- & Ib Chorkendorff
-
News & Views |
 An aminated reaction
An aminated reaction
Selective conversion of C–H bonds into C–N bonds to form N-heterocycles would streamline the synthesis of these important structural motifs. Now, an iron(II) catalyst has been developed that can transform alkyl azides into cyclic secondary amines by controlling the iron imido intermediate to react only with the nearby aliphatic C–H bond.
- Tom G. Driver
-
-
News & Views |
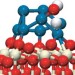 Electronic perturbations
Electronic perturbations
Oxide materials typically used as supports for the active metal nanoparticles of heterogeneous catalysts are known to influence catalytic activity through strong metal–support interactions. Researchers have now revealed electronic interactions between platinum and ceria that go well beyond known effects and lead to excellent catalytic activity.
- Charles T. Campbell
-
News & Views |
 Access granted
Access granted
Enzymes keep their catalytic reactivity under fine control, letting appropriate molecules approach their active sites to perform reactions. Now, studies of calixarenes attached to gold clusters to emulate this behaviour in synthetic systems suggest that the key to accessibility could be a matter of the relative sizes of ligands and metal clusters.
- Graham J. Hutchings
-
News & Views |
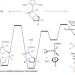 The mechanics of metathesis
The mechanics of metathesis
Olefin metathesis is a flexible and efficient method for making carbon–carbon bonds and has found widespread application in academia and industry. Now, a detailed mechanistic study looking at key catalytic intermediates offers new insight into this reaction, and may prove useful in the development of more active and selective catalysts.
- Jennifer A. Love
-
Research Highlights |
 Stable and able
Stable and able
A stable water-oxidation catalyst containing a cobalt oxide core has been made.
- Neil Withers

 An air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst for diverse reactivity
An air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst for diverse reactivity Supra selectivity
Supra selectivity