Featured
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Optimizing the safety of antibody–drug conjugates for patients with solid tumours
Optimizing the safety of antibody–drug conjugates for patients with solid tumours
Advances in technology have enabled the development of several novel antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) with encouraging clinical activity in patients with advanced-stage solid tumours. Indications for these therapies are expanding rapidly to earlier lines of therapy. Nonetheless, the toxicities of these various agents are not trivial and can be fatal, even in patients with early stage disease. In this Review, the authors summarize the toxicities of ADCs in patients with solid tumours both as monotherapies and in combination with other agents and discuss various ongoing research efforts attempting to optimize the therapeutic index of these agents.
- Paolo Tarantino
- , Biagio Ricciuti
- & Sara M. Tolaney
-
Review Article |
 Emerging evidence for adapting radiotherapy to immunotherapy
Emerging evidence for adapting radiotherapy to immunotherapy
Radiotherapy has several key attributes that make it an attractive combination partner for immunotherapy; however, numerous clinical trials investigating the combination of these two treatment modalities have failed to demonstrate clear improvements in patient outcomes. In this Review, Galluzzi and colleagues discuss the evidence indicating that radiotherapy administered according to standard schedules and target volumes might impair immune fitness and, therefore, propose that adaptation of the radiotherapy regimens to immunotherapy (and not vice versa) might synergistically enhance the antitumour immune response to achieve meaningful clinical benefits.
- Lorenzo Galluzzi
- , Molykutty J. Aryankalayil
- & Silvia C. Formenti
-
Perspective |
 Circulating tumour cells for early detection of clinically relevant cancer
Circulating tumour cells for early detection of clinically relevant cancer
The authors of this Perspective propose that, with further improvement in detection efficiency, circulating tumour cells (CTCs), which are released early during cancer development, have the potential to be used for the early detection of clinically relevant, aggressive cancers. Thus, use of CTCs as diagnostic biomarkers might improve outcomes by enabling the identification of cancers at a stage at which they are more amenable to treatment while avoiding overtreatment of patients with indolent tumours.
- Rachel Lawrence
- , Melissa Watters
- & Yong-Jie Lu
-
Review Article |
 Early stage gastric adenocarcinoma: clinical and molecular landscapes
Early stage gastric adenocarcinoma: clinical and molecular landscapes
Long-term survival rates of patients with gastric cancer remain low, particularly in Western countries. This lack of progress, among other aspects, is likely to reflect a focus on empirical approaches that fail to account for the heterogeneity of gastric cancers. In this Review, the authors summarize the available evidence on the management of patients with early stage gastric cancers, with an emphasis on understanding the underlying biology in order to improve the outcomes in patients with these historically difficult-to-treat tumours.
- Yuki Hirata
- , Ayesha Noorani
- & Jaffer A. Ajani
-
Comment |
The FDA’s latest draft guidance on accelerated approvals — one step forward, two steps back?
The FDA Accelerated Approval pathway, which has been pivotal in enabling early access to new oncology drugs over the past three decades, has recently come under increased scrutiny. New draft guidance published in March 2023 offers several possible solutions to improve this pathway, with the ultimate goal of improving outcomes for patients with cancer, but might also have important limitations.
- David J. Benjamin
- & Mark P. Lythgoe
-
-
Research Highlight |
Venetoclax–obinutuzumab combinations are effective in fit patients with CLL
- Diana Romero
-
Review Article |
 Mitigating long-term and delayed adverse events associated with cancer treatment: implications for survivorship
Mitigating long-term and delayed adverse events associated with cancer treatment: implications for survivorship
The effective management of treatment-related events remains an unmet need in oncology. The authors of this Review discuss the underlying biological mechanisms, risk factors, most commonly used pharmacological and non-pharmacological management strategies, and clinical practice guidelines for the most common long-term (continuing beyond treatment) and late or delayed (following treatment) adverse events associated with chemotherapy and other anticancer treatments.
- Maryam B. Lustberg
- , Nicole M. Kuderer
- & Gary H. Lyman
-
Review Article |
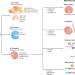 The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer
The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer
Dysregulation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most prevalent internal modification in eukaryotic mRNA, is common in various cancer types. The authors of this Review provide an overview of the mechanisms of m6A-dependent RNA regulation, summarize current knowledge of their pathological effects and potential utility as biomarkers in cancer, and describe ongoing efforts to develop small-molecule inhibitors of oncogenic m6A modifiers.
- Xiaolan Deng
- , Ying Qing
- & Jianjun Chen
-
-
Review Article |
 Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma is a malignancy that continues to be associated with a dismal prognosis, and a better understanding of the disease biology is required to improve early detection and treatment strategies. In this Review, the authors describe key scientific and clinical advances made in this area over the past 5 years, encompassing novel insights into the tumour stroma and immune microenvironment, promising progress in developing liquid biopsy approaches for diagnosis and monitoring, clinical translation of molecularly targeted therapies, emerging immunotherapies and reassessment of the potential role of liver transplantation.
- Sumera I. Ilyas
- , Silvia Affo
- & Gregory J. Gores
-
-
Comment |
 National value-based pricing negotiation for oncology drugs — lessons from China
National value-based pricing negotiation for oncology drugs — lessons from China
Between 2016 and 2022, 83 previously approved oncology drugs were covered and reimbursed in China through a value-based pricing negotiation programme, which resulted in substantial price cuts but did not improve the correlation between drug cost and clinical benefit. Herein, we call for an improved, transparent value-based pricing model to better account for high-value innovation in oncology drugs.
- Jing Yuan
- , Minghui Li
- & Z. Kevin Lu
-
-
-
Review Article |
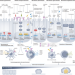 Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer development and therapy
Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer development and therapy
Emerging data indicate a central role for the microbiota in all aspects of colorectal cancer (CRC). Despite this general consensus, understanding the role of specific components of the microbiota in such a way that enables the development of clinical interventions or tools to inform clinical decision-making has thus far proved challenging. In this Review, the authors summarize the role of the microbiota in CRC, including in prevention, in interactions with treatment and as a source of novel biomarkers.
- Chi Chun Wong
- & Jun Yu
-
-
Review Article |
 Personalizing neoadjuvant immune-checkpoint inhibition in patients with melanoma
Personalizing neoadjuvant immune-checkpoint inhibition in patients with melanoma
Neoadjuvant immune-checkpoint inhibition is a promising emerging treatment strategy that potentially enables patients with a good response to initial therapy to avoid further treatment and the associated toxicity risks, while also identifying those who might require treatment escalation. In this Review, the authors describe treatment personalization strategies based on the initial response to one or more neoadjuvant immune-checkpoint inhibitors and consider the potential to expand this approach beyond patients with melanoma.
- Minke W. Lucas
- , Judith M. Versluis
- & Christian U. Blank
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Improving outcomes in patients with oesophageal cancer
Improving outcomes in patients with oesophageal cancer
Oesophageal cancer is one of the most common malignancies worldwide and is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. In this Review, the authors highlight advances made across the disease continuum that have improved the management and outcomes of patients with oesophageal cancer. These advances include an increased understanding of the disease biology, improvements in screening, the development of minimally invasive endoscopic monitoring and management technologies, refinement of surgical techniques and perioperative management, and novel radiotherapy and systemic therapy approaches. Continual multidisciplinary efforts across all these aspects of care will further improve patient outcomes.
- Manish A. Shah
- , Nasser Altorki
- & Julian A. Abrams
-
Review Article |
 Understanding the activity of antibody–drug conjugates in primary and secondary brain tumours
Understanding the activity of antibody–drug conjugates in primary and secondary brain tumours
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) have demonstrated efficacy in patients with various cancers, although their antitumour activity in the central nervous system (CNS) might be limited by the blood–brain barrier. In this Review, the authors describe the available clinical data emphasizing the heterogeneous activity of ADCs against primary or secondary brain tumours and ongoing clinical trials in this area. In addition, they discuss physical, biological and molecular determinants of the CNS activity of ADCs, as well as potential strategies to improve delivery of these agents to brain tumours.
- Maximilian J. Mair
- , Rupert Bartsch
- & Matthias Preusser
-
-
Review Article |
 Long-term outcomes following CAR T cell therapy: what we know so far
Long-term outcomes following CAR T cell therapy: what we know so far
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have dramatically improved the outcomes of patients with certain relapsed and/or refractory haematological malignancies. Owing to the promising short-term survival outcomes achieved, long-term data on both safety and survival are becoming increasingly relevant. In this Review, the authors describe the available long-term follow-up data from early studies testing the safety and efficacy of receiving CAR T cells targeting CD19 as well as more recent data on BCMA-targeted CAR T cells in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma.
- Kathryn M. Cappell
- & James N. Kochenderfer
-
Comment |
Envisioning trans-inclusive and trans-specific cancer care
Transgender patients are a marginalized group for whom current standards of oncology have yet to be optimized. In this Comment, we highlight opportunities for transgender-inclusive and transgender-specific practices across the cancer care continuum and identify evidence gaps that will need to be filled to attain optimal care for transgender populations.
- Elle Lett
- , Joannie M. Ivory
- & Mya L. Roberson
-
-
News & Views |
Combination immunomodulation for immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-associated myocarditis
Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-associated myocarditis has a high fatality rate, warranting the development of more-effective treatment strategies. Herein, we discuss a recent report of a series of patients who were managed using a novel approach that involved personalized abatacept dosing, ruxolitinib and close respiratory monitoring, which was associated with low mortality.
- Douglas B. Johnson
- & Alexander M. Menzies
-
Comment |
Navigating approval pathways for immunotherapy in NSCLC: should criteria be revised?
Recent FDA reviews of cemiplimab and sintilimab combined with chemotherapy for patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer reached discordant outcomes, as cemiplimab was approved and sintilimab was rejected. The applications share many serious faults, including neither serving an unmet need nor enrolling any patients from the USA. We argue that the FDA criteria should be more transparent and consistent; moreover, the historical policy of the FDA to abstain from consideration of the cost of a drug perpetuates a crisis in oncology care and should be re-examined.
- Aakash Desai
- , Caleb J. Smith
- & Howard Jack West
-
Research Highlight |
 Adding immune-checkpoint inhibitors to chemotherapy extends survival in endometrial cancer
Adding immune-checkpoint inhibitors to chemotherapy extends survival in endometrial cancer
- Diana Romero
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention
Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention
Globally, gastric cancer is a common and highly fatal cancer with two anatomical subtypes, non-cardia and cardia gastric cancer. Helicobacter pylori causes almost 90% of distal gastric cancers worldwide. The authors of this Review summarize the current epidemiology of gastric cancer and the evidence and implications of primary and secondary prevention efforts.
- Aaron P. Thrift
- , Theresa Nguyen Wenker
- & Hashem B. El-Serag
-
Review Article |
 Neoadjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer
Neoadjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer
Advances in surgical technique and chemotherapy regimens have improved the survival outcomes of patients with pancreatic cancer, although these remain dismal relative to most other solid tumours. Attempts to further improve outcomes have led to increasing research interest in neoadjuvant therapy, which is beginning to improve the outcomes of certain subgroups of patients. In this Review, the authors provide an overview of the various neoadjuvant therapy approaches for patients with pancreatic cancer, including discussions of several promising future research directions
- Christoph Springfeld
- , Cristina R. Ferrone
- & John Neoptolemos
-
Research Highlight |
Recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: hyperfractionation of IMRT improves outcomes
- David Killock
-
News & Views |
Precision oncology for KRASG12C-mutant colorectal cancer
Allele-specific inhibitors of KRASG12C are approved in non-small-cell lung cancer. Herein, we discuss recent results from the phase I/II KRYSTAL-1 trial of adagrasib alone and in combination with cetuximab in patients with KRASG12C-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. The combination had promising efficacy and, if confirmed in later-phase trials, concomitant inhibition of EGFR and KRASG12C will present a new paradigm in precision oncology.
- Federica Di Nicolantonio
- & Alberto Bardelli
-
Review Article |
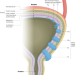 Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice
Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice
Bladder cancer is among the ten most common cancers worldwide and therefore constitutes a substantial health-care burden. This Review summarizes the global trends in bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and describes the main risk factors associated with bladder cancer occurrence and outcomes. The implications, challenges and opportunities of these epidemiological trends for public health and clinical practice are also discussed.
- Lisa M. C. van Hoogstraten
- , Alina Vrieling
- & Lambertus A. Kiemeney
-
Review Article |
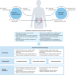 Functional precision oncology using patient-derived assays: bridging genotype and phenotype
Functional precision oncology using patient-derived assays: bridging genotype and phenotype
Genomics-based precision medicine has improved the outcomes of patients with certain types of cancers, although most do not derive benefit. Here, the authors describe the development of functional patient-specific assays, including those based on organoids, spheroids and explants, and how clinical implementation of these models might extend the benefits of precision medicine to a much broader range of patients.
- Allard W. J. van Renterghem
- , Joris van de Haar
- & Emile E. Voest
-
-
News & Views |
 TNT and local recurrence in the RAPIDO trial — untangling the puzzle
TNT and local recurrence in the RAPIDO trial — untangling the puzzle
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy offers a pragmatic alternative to the difficulties associated with delivering timely adjuvant chemotherapy in rectal cancer. Enthusiasm for administering neoadjuvant therapy to all patients with locally advanced rectal cancer is based on data from several phase III trials. Data from the RAPIDO trial are a critical component of this evidence.
- Robert Glynne-Jones
- & James Hollingshead
-
Research Highlight |
Radiotherapy can be omitted for older patients with low-risk disease
- Peter Sidaway
-
-
Comment |
Approvals in 2022: overall survival, dose optimization, new approvals and beyond
In 2022, the FDA approved numerous new drug and biologic agents, including targeted small molecules, immunotherapeutics, a gene therapy and a radiopharmaceutical. Several drug development challenges were also addressed, and key focus areas for the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence included ongoing monitoring of the Accelerated Approval programme and drug dose optimization.
- Deepti Telaraja
- , Nicole Gormley
- & Richard Pazdur
-
Research Highlight |
 Sublobar resection is non-inferior to lobectomy in very early stage NSCLC
Sublobar resection is non-inferior to lobectomy in very early stage NSCLC
- Diana Romero
-
Review Article |
 Rare molecular subtypes of lung cancer
Rare molecular subtypes of lung cancer
Lung cancers harbouring ‘rare’ alterations (defined as those with a prevalence of <5% of oncogene-driven lung cancers) can be detected in around a third of all oncogene-driven lung cancers and are diagnosed in thousands of patients each year. Advances in our understanding of tumour biology, diagnosis and the development of novel therapies are enabling increasing use of specific therapies targeting these alterations. In this Review, the authors provide an overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of patients with lung cancers harbouring these rare alterations. The importance of expedited drug approval pathways and cooperation between multiple stakeholders is also emphasized.
- Guilherme Harada
- , Soo-Ryum Yang
- & Alexander Drilon

 Antigen presentation in cancer — mechanisms and clinical implications for immunotherapy
Antigen presentation in cancer — mechanisms and clinical implications for immunotherapy From ASCO 2023
From ASCO 2023 ROAR brings in a new histology-agnostic approval for rare cancers
ROAR brings in a new histology-agnostic approval for rare cancers Mortality is similar with active monitoring
Mortality is similar with active monitoring