Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma is a malignancy that continues to be associated with a dismal prognosis, and a better understanding of the disease biology is required to improve early detection and treatment strategies. In this Review, the authors describe key scientific and clinical advances made in this area over the past 5 years, encompassing novel insights into the tumour stroma and immune microenvironment, promising progress in developing liquid biopsy approaches for diagnosis and monitoring, clinical translation of molecularly targeted therapies, emerging immunotherapies and reassessment of the potential role of liver transplantation.
- Sumera I. Ilyas
- , Silvia Affo
- & Gregory J. Gores
-
Research Highlight |
Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab shows promise in MSI-H/dMMR solid tumours
- Peter Sidaway
-
Review Article |
 Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
The incidence of early-onset forms of many cancers (defined as cancers diagnosed in individuals <50 years of age) has increased in a number of countries over the past several decades. The underlying reasons for this apparent increase probably include greater use of screening programmes, but also changing patterns in early-life exposures. In this Review, the authors describe the emerging global increase in the incidence of early-onset cancers and suggest changes that might address this situation.
- Tomotaka Ugai
- , Naoko Sasamoto
- & Shuji Ogino
-
Review Article |
 New treatment strategies for advanced-stage gastrointestinal stromal tumours
New treatment strategies for advanced-stage gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) is the most common form of sarcoma and has become a paradigm of precision medicine owing to the fact that almost all patients harbour one of several known molecule drivers, most of which can be targeted therapeutically. Nevertheless, novel therapeutic strategies are required to overcome the intrinsic resistance of certain subtypes of GIST to existing treatments as well as the acquired resistance that eventually arises in initially sensitive subtypes. This Review describes the biology of GIST, the evolution of the current treatments for this cancer, and the emerging therapeutic agents and approaches that might overcome the remaining clinical challenges.
- Lillian R. Klug
- , Homma M. Khosroyani
- & Michael C. Heinrich
-
Review Article |
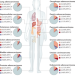 The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC proto-oncogenes are among the most commonly activated proteins in human cancer, yet the clinical efficacy of MYC-targeted agents remains to be demonstrated. The authors of this Review describe how activation of the MYC pathway affects cancer cells as well as the tumour microenvironment and propose strategies for the therapeutic targeting of MYC-driven cancers.
- Renumathy Dhanasekaran
- , Anja Deutzmann
- & Dean W. Felsher
-
Review Article |
 Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts
Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are inherently linked with cancers and have long been considered attractive therapeutic targets. However, the existence of several CAF subpopulations with substantial phenotypic and functional heterogeneity and plasticity is increasingly recognized. This Review provides an overview of the heterogeneity of CAFs and its implications with regard to the tumour-promoting and tumour-restraining roles of these cells as well as their clinical relevance in terms of prognostic value and therapeutic potential. The authors also provide insights and perspectives on future research and clinical studies involving CAFs.
- Yang Chen
- , Kathleen M. McAndrews
- & Raghu Kalluri
-
Review Article |
 Therapeutic targeting of the hypoxic tumour microenvironment
Therapeutic targeting of the hypoxic tumour microenvironment
Hypoxia is a common feature of tumours, contributes to many of the hallmarks of cancer and influences responses to anticancer therapies. Thus, strategies to eliminate and/or exploit tumour hypoxia have long been explored, although with limited success to date. Herein, the authors describe new insights into hypoxia biology, discuss the implications of these advances for novel hypoxia-directed therapeutic strategies, and review the progress made with longstanding methods for targeting hypoxic tumours.
- Dean C. Singleton
- , Andrew Macann
- & William R. Wilson
-
News & Views |
The ten genes for breast (and ovarian) cancer susceptibility
ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2 and TP53 are all established breast cancer susceptibility genes. Over the past 30 years, many other genes have been proposed as candidates. In these two large studies, the candidacy of several questionable genes has been largely resolved, and a final list of ten genes for breast and, importantly, ovarian cancer risk has emerged.
- William D. Foulkes
-
Review Article |
 Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Chronic inflammation can promote the development of various cancers. In this Review, the current clinical advances in ameliorating inflammation for the prevention or treatment of cancer are highlighted, and the experimental insights into the biological mechanisms supporting current and potential novel anti-inflammatory approaches to the management of cancer are discussed.
- Jiajie Hou
- , Michael Karin
- & Beicheng Sun
-
-
Review Article |
 Tumour budding in solid cancers
Tumour budding in solid cancers
Tumour budding is hypothesized to reflect the invasive and metastatic capacities of cancers and is accordingly associated with unfavourable patient outcomes. Herein, Lugli and colleagues describe the pathobiological characteristics of this phenomenon, including its associations with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and features of the tumour microenvironment, and review the evidence demonstrating the value of tumour budding as a prognostic biomarker across various solid cancers.
- Alessandro Lugli
- , Inti Zlobec
- & Iris D. Nagtegaal
-
Review Article |
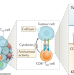 Tissue-resident memory T cells in breast cancer control and immunotherapy responses
Tissue-resident memory T cells in breast cancer control and immunotherapy responses
TRM cells have a role in peripheral immune surveillance in several organs. The presence of TRM cells in the immune infiltrate is also associated with improved outcomes in patients with several solid tumour types, and these cells might have a role in the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. In this Review, the authors describe the available date on the role of TRM cells in patients with breast cancer
- Ann Byrne
- , Peter Savas
- & Sherene Loi
-
Review Article |
 Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer
Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer
Neutrophils accumulate in the circulation of patients with cancer, and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a widely used biomarker. However, the effects of neutrophils on tumour development and progression, and the efficacy of therapies, remain relatively unknown. In this Review, the authors draw on data from animal models and patients with cancer to provide an overview of the effects of neutrophils in cancer.
- Merav E. Shaul
- & Zvi G. Fridlender
-
Review Article |
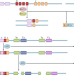 Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in DLBCL
Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in DLBCL
Approximately 50% of patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are cured with chemotherapy. However, patients with relapsed and/or refractory DLBCL have few other treatment options. In this Review, the authors describe emerging data on genetically targeted therapies for patients with DLBCL and how these might improve patient outcomes.
- Yi Miao
- , L. Jeffrey Medeiros
- & Ken H. Young
-
-
News & Views |
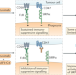 Myeloid immune-checkpoint inhibition enters the clinical stage
Myeloid immune-checkpoint inhibition enters the clinical stage
The first-in-human study of anti-CD47 antibodies blocking CD47–SIRPα interactions in combination with rituximab in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma shows encouraging clinical responses accompanied with mild levels of toxicity. Inhibition of the CD47–SIRPα interaction might provide a generic method of promoting the effects of antitumour antibodies in a variety of cancer types. This reveals, for the first time, an innate immune checkpoint as a bona fide target for therapy.
- Timo K. van den Berg
- & Thomas Valerius
-
Review Article |
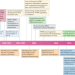 NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
TRK fusion proteins are pathognomonic in certain rare tumour types and present in a small subset of diverse cancer types, including some common cancers; TRK inhibitors have promising efficacy in the treatment of these cancers, in a histology-agnostic manner. In this Review, the biology of TRK signalling and TRK fusions, strategies to target these drivers, the unique safety profile of TRK inhibitors and mechanisms of and strategies to overcome acquired resistance to these agents are discussed.
- Emiliano Cocco
- , Maurizio Scaltriti
- & Alexander Drilon
-
Review Article |
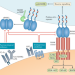 Roles of the RANKL–RANK axis in antitumour immunity — implications for therapy
Roles of the RANKL–RANK axis in antitumour immunity — implications for therapy
Intriguing evidence suggests that expression of RANK or RANKL by various cells of the tumour microenvironment modulates the anticancer immune response. Herein, the authors review this evidence, discuss the current preclinical and clinical data supporting a potential of RANKL inhibition to improve anticancer immunotherapy and describe hypothetical immune-related mechanisms of action.
- Elizabeth Ahern
- , Mark J. Smyth
- & Michele W. L. Teng
-
Review Article |
 Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs — an update
Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs — an update
Evidence of the functional roles of non-coding RNAs in cancer is expanding, and the potential of these RNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers is increasingly recognized. Herein, the authors review the recent developments in these areas and provide compendiums of circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs that have promise as diagnostic and prognostic cancer biomarkers.
- Simone Anfossi
- , Anna Babayan
- & George A. Calin
-
News & Views |
How to eliminate gastric cancer-related death worldwide?
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is effective in preventing gastric cancer, even in patients with advanced pre-neoplastic lesions (gastric atrophy and/or intestinal metaplasia). We must now focus on how to accomplish the goal of eliminating gastric cancer-related death worldwide; strategies for screening and treatment of gastric neoplasia (primary prevention) and post-treatment surveillance (secondary prevention) are discussed herein.
- Yoshio Yamaoka
-
News & Views |
Does nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer still exist?
After almost 20 years of negative trials of novel therapies for patients with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC), two androgen receptor antagonists have shown favourable outcomes in phase III trials involving patients with high-risk nmCRPC. Herein, the history of nmCRPC and clinical trials in this disease setting are discussed and a perspective on molecular imaging and clinical management of nmCRPC is offered.
- Celestia S. Higano
-
Review Article |
 The emerging clinical relevance of genomics in cancer medicine
The emerging clinical relevance of genomics in cancer medicine
Developments in genomic sequencing technologies have enabled increasing amounts of information on the genomes of individual cancers to be revealed. At the same time, increasing numbers of therapies targeting specific genomic alterations are being made available, necessitating the use of genomics to diagnose and treat patients with cancer. In this Review, the authors describe the emerging clinical relevance of genomics in oncology, in addition to the many challenges that currently preclude routine clinical use.
- Michael F. Berger
- & Elaine R. Mardis
-
-
Review Article |
 Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
The PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway has key roles in tumorigenesis and is dysregulated in most cancers. Consequently, numerous drugs that target key nodes of this pathway have been developed, although few of these agents have been approved for the treatment of cancer. Herein, the authors review the current experience with anticancer therapies that target the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway, discuss the challenges that have limited the clinical translation of these agents, and provide perspectives for the future development of these drugs.
- Filip Janku
- , Timothy A. Yap
- & Funda Meric-Bernstam
-
Review Article |
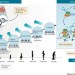 Epigenome-based cancer risk prediction: rationale, opportunities and challenges
Epigenome-based cancer risk prediction: rationale, opportunities and challenges
The development of cancer involves several epigenomic alterations, and the presence of certain alterations before the development of cancer is associated with cancer risk. In this Review, the authors describe the potential of epigenomics-based assays to predict an individual's risk of cancer, including discussions of technical, practical and societal issues regarding the implementation of such assays.
- Martin Widschwendter
- , Allison Jones
- & Nora Pashayan
-
Review Article |
 Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer
Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer
The interleukin-6 (IL-6)/Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway is aberrantly hyperactivated in many types of cancer, and such hyperactivation is generally associated with a poor clinical prognosis. In this Review, the authors describe the clinical potential of agents designed to inhibit the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway, either alone or in combination with other agents, in patients with cancer.
- Daniel E. Johnson
- , Rachel A. O'Keefe
- & Jennifer R. Grandis
-
-
Review Article |
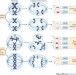 Determinants and clinical implications of chromosomal instability in cancer
Determinants and clinical implications of chromosomal instability in cancer
Aberrant chromosomal architecture is one of the most common features of cancer and can often lead to chromosomal instability (CIN). In this Review, the authors describe the role of CIN in the development and progression of cancer and the potential to target the therapeutic vulnerabilities created by this process.
- Laurent Sansregret
- , Bart Vanhaesebroeck
- & Charles Swanton
-
Review Article |
 Perioperative events influence cancer recurrence risk after surgery
Perioperative events influence cancer recurrence risk after surgery
Despite the achievement of locoregional control, a third of patients undergoing surgery for cancer will have disease recurrence. In this Review, the authors describe the potential to optimize the outcomes of patients with cancer by minimizing inflammation and activation of the sympathetic nervous system in the perioperative period, which is often achievable with simple and cost-effective changes in patient-management strategies.
- Jonathan G. Hiller
- , Nicholas J. Perry
- & Erica K. Sloan
-
-
Review Article |
 Fusions in solid tumours: diagnostic strategies, targeted therapy, and acquired resistance
Fusions in solid tumours: diagnostic strategies, targeted therapy, and acquired resistance
A wide range of gene fusions have been detected in solid tumours, and the products of these fusions, some of which result in constitutive activation of kinase signalling, can be targeted using tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. However, the development of acquired resistance is almost inevitable. In this Review, the authors describe strategies used to diagnose and treat patients with fusion-positive cancers.
- Alison M. Schram
- , Matthew T. Chang
- & Alexander Drilon
-
Research Highlight |
 Conditional selection determines the pathways of cancer evolution
Conditional selection determines the pathways of cancer evolution
- David Killock
-
-
Review Article |
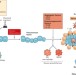 The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment
The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment
Virtually all successful treatments of cancer either create, restore or enhance the antitumour immune response. Therefore, the specific features of the immune microenvironment, both before and after treatment, are important determinants of patients' outcomes. In this Review, the authors describe the influence of the immunological characteristics of the tumour microenvironment on responses to treatment in patients with a variety of cancers.
- Wolf H. Fridman
- , Laurence Zitvogel
- & Guido Kroemer
-
News & Views |
Novel molecular subtypes of cervical cancer — potential clinical consequences
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network recently published the most comprehensive, multi-omic molecular characterization of cervical cancers performed to date. The data reveal novel disease subtypes, and provide new insights into the aetiology and pathogenesis of cervical cancer. Importantly, the information obtained has potentially major clinical implications.
- Chris J. L. M. Meijer
- & Renske D. M. Steenbergen
-
Review Article |
 EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications
EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications
According to the cancer stem cell (CSC) paradigm, a minor subpopulation of cancer cells with stem-cell properties predominantly underlies tumour progression, therapy resistance, and disease recurrence. Notably, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is implicated in these processes, and CSCs typically show markers of EMT-programme activation. Herein, the authors outline our current understanding of the links between the EMT programme, the CSC phenotype, metastasis, and drug resistance, and discuss the potential for therapeutic targeting of these facets of tumour biology.
- Tsukasa Shibue
- & Robert A. Weinberg
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas — implications for classification and therapy
Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas — implications for classification and therapy
In 2016, a revised WHO classification of glioma was published, in which molecular data and traditional histological information are incorporated into integrated diagnoses. Herein, the authors highlight the developments in our understanding of the molecular genetics of gliomas that underlie this classification, and review the current landscape of molecular biomarkers used in the classification of disease subtypes. In addition, they discuss how these advances can promote the development of novel pathogenesis-based therapeutic approaches, paving the way to precision medicine.
- Guido Reifenberger
- , Hans-Georg Wirsching
- & Michael Weller
-
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Genetic signature might spare 100,000 women annually from chemotherapy
Genetic signature might spare 100,000 women annually from chemotherapy
- David Killock
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
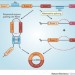 Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
In a paper published recently in Cell, Guarnerio et al. suggest that circular RNAs derived from cancer-associated chromosomal translocations have an oncogenic role; however, the experimental approach that the authors used was inadequate to generate sufficient evidence to prove this role, calling their study into question.
- Carlo M. Croce
-
-
Opinion |
Counselling framework for moderate-penetrance cancer-susceptibility mutations
The use of multigene panels for the assessment of cancer susceptibility is expanding rapidly in clinical practice. The appropriate management of individuals harbouring moderate-penetrance genetic variants in individuals referred for clinical testing is unclear. The authors of this Perspectives article provide a framework for clinical decision-making pending the development of a sufficient evidence base to document the clinical utility of the interventions for individuals with inherited moderate-penetrance gene mutations associated with an increased risk of cancer.
- Nadine Tung
- , Susan M. Domchek
- & Mark E. Robson

 The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer
The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer Intravesical therapy goes viral
Intravesical therapy goes viral CSF DNA provides a snapshot of the glioma genome
CSF DNA provides a snapshot of the glioma genome Pan-cancer genomic analyses uncover molecular drivers
Pan-cancer genomic analyses uncover molecular drivers Genomic and immunological features predict a response
Genomic and immunological features predict a response JAK — opening the door to acquired resistance
JAK — opening the door to acquired resistance