Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
-
-
Article |
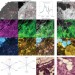 Stain-free histopathology by programmable supercontinuum pulses
Stain-free histopathology by programmable supercontinuum pulses
A single-source multimodal nonlinear optical imaging system has been developed to probe different endogenous biomolecules. Rapid, stain-free imaging of fresh tissue specimens is possible with short turnaround times for disease diagnosis.
- Haohua Tu
- , Yuan Liu
- & Stephen A. Boppart
-
Letter |
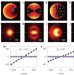 Removing orientation-induced localization biases in single-molecule microscopy using a broadband metasurface mask
Removing orientation-induced localization biases in single-molecule microscopy using a broadband metasurface mask
A custom-designed metamaterial mask helps improve the accuracy of microscopy of single fluorescent molecules.
- Mikael P. Backlund
- , Amir Arbabi
- & W. E. Moerner
-
News & Views |
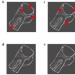 Super-resolution fight club
Super-resolution fight club
A 2016 competition to find the optimum software for 3D single-molecule localization microscopy will help practitioners choose the best tool for the job and spur further developments in the field.
- Seamus Holden
- & Daniel Sage
-
Commentary |
 Standardizing the resolution claims for coherent microscopy
Standardizing the resolution claims for coherent microscopy
The definition and reporting of spatial resolution for coherent imaging methods varies widely in the imaging community. We advocate the use of a standard spoke-pattern imaging target and the mandatory inclusion of information about underlying a priori assumptions.
- Roarke Horstmeyer
- , Rainer Heintzmann
- & Changhuei Yang
-
Article |
 Coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy with multiple off states
Coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy with multiple off states
By exploiting a second off state of a reversibly switchable fluorophore, a general approach that can reduce photobleaching and enhance resolution of coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy has been demonstrated.
- Johann G. Danzl
- , Sven C. Sidenstein
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Letter |
 Optical control of excitation waves in cardiac tissue
Optical control of excitation waves in cardiac tissue
Optogenetics makes it possible for dynamic patterns of visible light to control the behaviour of excitation waves in heart cells.
- Rebecca A. B. Burton
- , Aleksandra Klimas
- & Gil Bub
-
-
News & Views |
 Probing hyperbolic polaritons
Probing hyperbolic polaritons
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons confined to the subdiffraction limit exhibit encouragingly long lifetimes and group velocities as slow as 0.002c. Researchers use a time-resolved set-up sensitive to nanometre-scale optical fields to shed light on the exciting optical properties of hyperbolic materials.
- Joshua D. Caldwell
- , Igor Vurgaftman
- & Joseph G. Tischler
-
Letter |
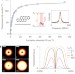 Optical nanoscopy with excited state saturation at liquid helium temperatures
Optical nanoscopy with excited state saturation at liquid helium temperatures
Based on optical saturation of the excited state of single fluorescent molecules with a doughnut-shaped beam, sub-10-nm-resolution optical microscopy at cryogenic temperatures is achieved.
- B. Yang
- , J.-B. Trebbia
- & B. Lounis
-
Article |
 Direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection
Direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection
Researchers exploit direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy and dedicated detection of super-critical-angle fluorescence emission to enable direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection.
- N. Bourg
- , C. Mayet
- & S. Lévêque-Fort
-
News & Views |
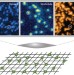 Fermions under the microscope
Fermions under the microscope
The observation of individual atoms with single-lattice-site resolution has proved to be an enormously powerful detection method for optical lattice-based quantum simulators. Such a technique has now been demonstrated with fermionic atoms.
- Christian Groß
-
-
Review Article |
 Chemically sensitive bioimaging with coherent Raman scattering
Chemically sensitive bioimaging with coherent Raman scattering
Coherent Raman imaging techniques have evolved to become powerful tools for biomedical imaging without the need for labelling.
- Charles H. Camp Jr
- & Marcus T. Cicerone
-
Article |
 Imaging deep within a scattering medium using collective accumulation of single-scattered waves
Imaging deep within a scattering medium using collective accumulation of single-scattered waves
Using the collective accumulation of single-scattered waves, scientists manage to image deep within a scattering medium, achieving an imaging depth 11.5 times the scattering mean free path and a near-diffraction-limit resolution of 1.5 µm.
- Sungsam Kang
- , Seungwon Jeong
- & Wonshik Choi
-
-
News & Views |
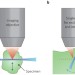 Bringing the living brain into focus
Bringing the living brain into focus
A fast scanning light-sheet microscope that produces multicolour, dynamic images of living tissue could provide fresh insights into the brain's neural circuits.
- Alexander D. Corbett
- & Gil Bub
-
Article |
 Swept confocally-aligned planar excitation (SCAPE) microscopy for high-speed volumetric imaging of behaving organisms
Swept confocally-aligned planar excitation (SCAPE) microscopy for high-speed volumetric imaging of behaving organisms
A swept light-sheet microscopy scheme allows volumetric imaging of living samples at high speed.
- Matthew B. Bouchard
- , Venkatakaushik Voleti
- & Elizabeth M. C. Hillman
-
-
Review Article |
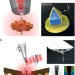 Mapping nanoscale light fields
Mapping nanoscale light fields
Recent developments in probe-based near-field microscopy are reviewed, including techniques for determining the phase, amplitude and separate components of the electric and magnetic field.
- N. Rotenberg
- & L. Kuipers
-
News & Views |
 Celebrating optical nanoscopy
Celebrating optical nanoscopy
The award of this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry to the pioneers of various optical schemes capable of achieving super-resolution and single-molecule detection is recognition of a revolution in optical imaging.
- Michel Orrit
-
Editorial |
Photonics dominates Nobel Prizes
Awards for blue LEDs and super-resolution microscopy announced.
-
Letter |
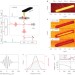 Ultrafast multi-terahertz nano-spectroscopy with sub-cycle temporal resolution
Ultrafast multi-terahertz nano-spectroscopy with sub-cycle temporal resolution
The authors demonstrate ultrabroadband time-resolved THz spectroscopy on a single InAs nanowire with 10 nm spatial resolution and sub-100 fs time resolution.
- M. Eisele
- , T. L. Cocker
- & R. Huber
-
Letter |
 Chemical composition mapping with nanometre resolution by soft X-ray microscopy
Chemical composition mapping with nanometre resolution by soft X-ray microscopy
A soft X-ray ptychography approach can now image 5-nm-sized objects. Chemical component distributions in the delithiation of LiFePO4 nanoplates — a process relevant for energy storage — links structural defects to chemical phase propagation.
- David A. Shapiro
- , Young-Sang Yu
- & Howard A. Padmore
-
-
Article |
 Non-invasive single-shot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlations
Non-invasive single-shot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlations
Diffraction-limited imaging in a variety of complex media is realized based on analysis of speckle correlations in light captured using a camera phone.
- Ori Katz
- , Pierre Heidmann
- & Sylvain Gigan
-
Article |
 High-speed coherent Raman fingerprint imaging of biological tissues
High-speed coherent Raman fingerprint imaging of biological tissues
A high-resolution, broadband imaging system based on coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy performs rapid, chemically specific imaging of biological tissue. It employs three-colour excitation and operates across the entire biological window.
- Charles H. Camp Jr
- , Young Jong Lee
- & Marcus T. Cicerone
-
Commentary |
 Resolving a misconception about structured illumination
Resolving a misconception about structured illumination
Applying structured illumination microscopy to coherent imaging modalities such as scattering does not yield any additional information beyond that provided by oblique illumination. It thus yields no resolution enhancement over the Abbe diffraction limit, which was derived precisely for that case.
- Kai Wicker
- & Rainer Heintzmann
-
-
Letter |
 Isotropic three-dimensional super-resolution imaging with a self-bending point spread function
Isotropic three-dimensional super-resolution imaging with a self-bending point spread function
By exploiting a self-bending point spread function based on Airy beams, a three-dimensional super-resolution fluorescence imaging is realized. A three-dimensional localization precision in the range 10–15 nm was obtained at an imaging depth of 3 µm from ∼2,000 photons per localization.
- Shu Jia
- , Joshua C. Vaughan
- & Xiaowei Zhuang
-
News & Views |
 White-light diffraction tomography
White-light diffraction tomography
A clever extension to a classic phase-contrast microscope allows speckle-free three-dimensional quantitative phase imaging of living cells in a tomographic imaging mode.
- Arno Bouwens
- & Theo Lasser
-
-
Letter |
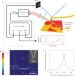 Tip-enhanced infrared nanospectroscopy via molecular expansion force detection
Tip-enhanced infrared nanospectroscopy via molecular expansion force detection
Mid-infrared spectroscopy with nanometre spatial resolution is highly desired for materials and life sciences applications. A nanoscale mid-infrared spectrometer is demonstrated that detects mechanical forces exerted by molecules on an atomic force microscope tip upon light excitation. It operates under ambient conditions with a high sensitivity and a spatial resolution of better than 25 nm.
- Feng Lu
- , Mingzhou Jin
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Article |
 Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a robust fibre laser source
Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a robust fibre laser source
A dual-wavelength fibre laser source has been developed for stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. It is precisely tunable over the entire high-wavenumber region of Raman spectra, where most stimulated Raman scattering imaging is performed. Imaging speeds of up to 1 frame s−1 with shot-noise-limited sensitivity were achieved.
- Christian W. Freudiger
- , Wenlong Yang
- & Khanh Q. Kieu
-
Article |
 White-light diffraction tomography of unlabelled live cells
White-light diffraction tomography of unlabelled live cells
The three-dimensional structures of transparent objects, such as living cells, are captured by an imaging technique that uses white-light illumination and diffraction tomography to collect a stack of phase-based images.
- Taewoo Kim
- , Renjie Zhou
- & Gabriel Popescu
-
Letter |
 Metal-induced energy transfer for live cell nanoscopy
Metal-induced energy transfer for live cell nanoscopy
A means for localizing fluorescent molecules over distances of hundreds of nanometres exploits the energy transfer between a donor molecule and surface plasmons on a metal film. The technique is demonstrated by using it to profile the membranes of living cells.
- Alexey I. Chizhik
- , Jan Rother
- & Jörg Enderlein
-
-
News & Views |
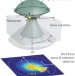 Scattering in focus
Scattering in focus
Sustaining the ongoing revolution in optical microscopy will require gaining detailed insight into the optical fields in focal spots. Researchers have developed an elegant method for mapping the full electric vector field using just a metal nanosphere on a glass substrate.
- L. Kuipers
-
Letter |
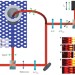 Simultaneous measurement of nanoscale electric and magnetic optical fields
Simultaneous measurement of nanoscale electric and magnetic optical fields
Simultaneous detection of electric and magnetic fields with a subwavelength resolution is achieved by a near-field scanning approach. Additionally, theoretical considerations provide guidelines for designing probes sensitive to specific desired combinations of electric- and magnetic-field components.
- B. le Feber
- , N. Rotenberg
- & L. Kuipers
-
-
Letter |
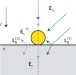 Nanointerferometric amplitude and phase reconstruction of tightly focused vector beams
Nanointerferometric amplitude and phase reconstruction of tightly focused vector beams
An easily implementable reconstruction scheme is demonstrated for determining the full vectorial amplitude and relative phase distributions of highly confined electromagnetic fields with subwavelength resolution from a single-scan measurement. This scheme will help improve microscopy and nanoscopy techniques.
- Thomas Bauer
- , Sergej Orlov
- & Gerd Leuchs
-
Review Article |
 Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy
Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy
This Review discusses recent advances, and identifies challenges and opportunities regarding the use of fibre lasers in nonlinear bioimaging.
- C. Xu
- & F. W. Wise
-
Letter |
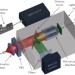 Enhanced two-photon excited fluorescence from imaging agents using true thermal light
Enhanced two-photon excited fluorescence from imaging agents using true thermal light
Excitation with thermal light from a superluminescent diode is shown to yield enhanced fluorescence from both quantum dots and dyes, potentially enabling higher-sensitivity biological imaging.
- Andreas Jechow
- , Michael Seefeldt
- & Ralf Menzel
-
Letter |
 Digitally synthesized beat frequency multiplexing for sub-millisecond fluorescence microscopy
Digitally synthesized beat frequency multiplexing for sub-millisecond fluorescence microscopy
A confocal fluorescence microscopy scheme that maps the image to the radiofrequency spectrum by beating together two optical fields offers enhanced read-out speeds at kilohertz frame rates. It provides a new way for observing dynamic phenomena in cells.
- Eric D. Diebold
- , Brandon W. Buckley
- & Bahram Jalali
-
-
News & Views |
 Beyond the realm of fluorescence
Beyond the realm of fluorescence
Using a pump–probe technique, scientists have experimentally demonstrated a nonlinear imaging scheme that permits the super-resolution imaging of nonfluorescent samples, making it promising for use with unstained specimens.
- Rainer Heintzmann
-
Letter |
 Far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species with subdiffraction resolution
Far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species with subdiffraction resolution
A scheme for overcoming the diffraction limit in the far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species is demonstrated. This technique, which is based on the spatially controlled saturation of electronic absorption, may enable the super-resolution imaging of nanomaterials and non-fluorescent chromophores.
- Pu Wang
- , Mikhail N. Slipchenko
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
News & Views |
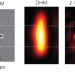 Label-free nanoscopy of living cells
Label-free nanoscopy of living cells
A holographic microscope capable of dynamically imaging unstained living cells at resolutions beyond the diffraction limit could prove extremely useful for studying biological cells.
- Gary Brooker
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atomic force microscopy
- Ca2+ imaging
- Confocal microscopy
- Cryoelectron microscopy
- Interference microscopy
- Light-sheet microscopy
- Multiphoton microscopy
- Phase-contrast microscopy
- Polarization microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
- Scanning probe microscopy
- Super-resolution microscopy
- Total internal reflection microscopy
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Transmission light microscopy
- Wide-field fluorescence microscopy

 Improved time resolution
Improved time resolution Artwork analysis
Artwork analysis Saturable plasmon scattering
Saturable plasmon scattering Magnetic mapping
Magnetic mapping