Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Random-access wide-field mesoscopy for centimetre-scale imaging of biodynamics with subcellular resolution
Random-access wide-field mesoscopy for centimetre-scale imaging of biodynamics with subcellular resolution
Random-access wide-field mesoscopy enables the imaging of in vivo biodynamics in mice over an area of 160 mm2 and at a subcellular spatial resolution of about 2 μm.
- Ruheng Shi
- , Xinyue Chen
- & Lingjie Kong
-
Article |
 Mid-infrared wide-field nanoscopy
Mid-infrared wide-field nanoscopy
Wide-field mid-infrared photothermal imaging is developed to supress the resolution degradation caused by photo-thermal heat diffusion. By employing a single-objective synthetic-aperture imaging with synchronized subnanosecond mid-infrared and visible light sources, spatial resolution of 120 nm is obtained.
- Miu Tamamitsu
- , Keiichiro Toda
- & Takuro Ideguchi
-
News & Views |
 Illuminating cancer with sonoafterglow
Illuminating cancer with sonoafterglow
Ultrasound-induced luminescence in trianthracene derivative-based nanoparticles enables tumour imaging and immunological profiling in a variety of in vivo models.
- Cheng Xu
- & Kanyi Pu
-
News & Views |
 Single protein imaging with holography
Single protein imaging with holography
A non-common-path interferometric scheme enables holographic detection of single proteins of mass 90 kDa and estimation of single-protein polarizability.
- Chia-Lung Hsieh
-
News & Views |
 Mechanical anisotropy with Brillouin spectroscopy in one shot
Mechanical anisotropy with Brillouin spectroscopy in one shot
Brillouin light scattering anisotropy microscopy affords single-shot collection of angle-resolved phonon dispersion, enabling the mapping of mechanical anisotropies in living matter with a frequency resolution of 10 MHz and a spatial resolution of 2 µm.
- Yogeshwari S. Ambekar
- & Giuliano Scarcelli
-
Review Article |
 In vivo NIR-II fluorescence imaging for biology and medicine
In vivo NIR-II fluorescence imaging for biology and medicine
A review of NIR-II fluorescence imaging is presented, with a focus on fluorophores, probes and imaging techniques.
- Feifei Wang
- , Yeteng Zhong
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 In vivo ultrasound-induced luminescence molecular imaging
In vivo ultrasound-induced luminescence molecular imaging
Ultrasound-induced luminescence enables in vivo molecular imaging of tumours and lymph nodes with spatial resolution of 1.46 mm.
- Youjuan Wang
- , Zhigao Yi
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article |
 Super-resolved FRET and co-tracking in pMINFLUX
Super-resolved FRET and co-tracking in pMINFLUX
Super-resolution pMINFLUX microscopy is combined with FRET and enables co-tracking of two fluorophores without photoswitching.
- Fiona Cole
- , Jonas Zähringer
- & Philip Tinnefeld
-
Article |
 A wireless optoelectronic probe to monitor oxygenation in deep brain tissue
A wireless optoelectronic probe to monitor oxygenation in deep brain tissue
A wireless optoelectronic probe integrates a microscale light-emitting diode and a photodetector coated with oxygen-sensitive dyes to monitor the partial pressure of oxygen in the deep brain of freely moving mice.
- Xue Cai
- , Haijian Zhang
- & Xing Sheng
-
Article |
 Brillouin light scattering anisotropy microscopy for imaging the viscoelastic anisotropy in living cells
Brillouin light scattering anisotropy microscopy for imaging the viscoelastic anisotropy in living cells
Single-shot angle-resolved Brillouin light scattering microscopy enables spatiotemporal mapping of mechanical anisotropy in living cells with a spatial resolution below 2 µm and precision in the Brillouin frequency shift of 10 MHz.
- Hamid Keshmiri
- , Domagoj Cikes
- & Kareem Elsayad
-
Review Article |
 Label-free biomedical optical imaging
Label-free biomedical optical imaging
This Review covers a comparison between various label-free biomedical imaging techniques, their advantages over label-based methods and relevant applications.
- Natan T. Shaked
- , Stephen A. Boppart
- & Jürgen Popp
-
News & Views |
 Event-based super-resolution microscopy
Event-based super-resolution microscopy
Event-based detectors, which respond to local changes in light intensity rather than producing images, enable super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy with sensitivity and resolution comparable to conventional methods.
- Ian M. Dobbie
-
Article |
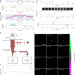 Event-based vision sensor for fast and dense single-molecule localization microscopy
Event-based vision sensor for fast and dense single-molecule localization microscopy
Event-based sensors enable super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy with comparable quality and resolution to traditional scientific cameras, while also overcoming the limitations of high-density imaging.
- Clément Cabriel
- , Tual Monfort
- & Ignacio Izeddin
-
News & Views |
 Deconvolution enhances fluctuation detection
Deconvolution enhances fluctuation detection
The introduction of a two-step deconvolution workflow maximizes the detection of fluorescence in fluctuation-based super-resolution imaging, enabling a square millimetre field of view to be captured in as little as ten minutes.
- David Baddeley
-
Article
| Open Access Single multimode fibre for in vivo light-field-encoded endoscopic imaging
Single multimode fibre for in vivo light-field-encoded endoscopic imaging
Spatial-frequency tracking adaptive beacon light-field encoded endoscopy enables imaging through a single multimode fibre under bending and twisting. In vivo imaging with subcellular resolution is demonstrated in mice models.
- Zhong Wen
- , Zhenyu Dong
- & Qing Yang
-
Article |
 Bond-selective fluorescence imaging with single-molecule sensitivity
Bond-selective fluorescence imaging with single-molecule sensitivity
Two-photon excitation with mid- and near-infrared pulses encodes bond selectivity in fluorescence imaging. Single-molecule imaging and spectroscopy is demonstrated on individual fluorophores as well as various labelled biological targets.
- Haomin Wang
- , Dongkwan Lee
- & Lu Wei
-
Article |
 Parallelized computational 3D video microscopy of freely moving organisms at multiple gigapixels per second
Parallelized computational 3D video microscopy of freely moving organisms at multiple gigapixels per second
3D-RAPID, a scalable computational microscope using 54 cameras, records 3D topographic videos of freely moving organisms over an area of 135 cm2 at a spatial resolution of tens of micrometres and at a throughput exceeding 5 gigapixels per second.
- Kevin C. Zhou
- , Mark Harfouche
- & Roarke Horstmeyer
-
Article |
 Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent molecules by photothermal relaxation localization microscopy
Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent molecules by photothermal relaxation localization microscopy
Photothermal relaxation localization microscopy allows super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent targets by leveraging spatial-dependent heat dissipation in photothermal microscopy. Individual lipid droplets and their distribution in living cells are imaged at spatial resolutions down to 120 nm.
- Pengcheng Fu
- , Wanlin Cao
- & Delong Zhang
-
Article |
 Artificial confocal microscopy for deep label-free imaging
Artificial confocal microscopy for deep label-free imaging
A laser scanning microscope equipped with quantitative phase imaging is trained with a neural network to perform artificial confocal microscopy
- Xi Chen
- , Mikhail E. Kandel
- & Gabriel Popescu
-
Article |
 Six-dimensional single-molecule imaging with isotropic resolution using a multi-view reflector microscope
Six-dimensional single-molecule imaging with isotropic resolution using a multi-view reflector microscope
A multi-view reflector microscope based on polarization modulation and pupil splitting enables single-molecule orientation-localization microscopy with precisions of 10.9 nm and 2.0°.
- Oumeng Zhang
- , Zijian Guo
- & Matthew D. Lew
-
Article
| Open Access Stain-free identification of cell nuclei using tomographic phase microscopy in flow cytometry
Stain-free identification of cell nuclei using tomographic phase microscopy in flow cytometry
The accurate identification of the three-dimensional quantitative shape of a cell nucleus is now possible without fluorescent staining by applying computational segmentation to refractive index tomograms recorded in the flow cytometry mode.
- Daniele Pirone
- , Joowon Lim
- & Pietro Ferraro
-
News & Views |
 Bubbles clear the way for imaging
Bubbles clear the way for imaging
Ultrasound-induced gas bubbles in tissue can temporarily minimize optical scattering, enabling laser light to be focused at greater depth for higher-resolution imaging.
- Paul Beard
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
News & Views |
 The diamond voltage microscope
The diamond voltage microscope
The demonstration that diamond nitrogen–vacancy centre technology can optically detect voltages with an impressive sensitivity could bring new opportunities for investigating neurobiology.
- Milos Nesladek
- & Micha E. Spira
-
Article |
 Deep laser microscopy using optical clearing by ultrasound-induced gas bubbles
Deep laser microscopy using optical clearing by ultrasound-induced gas bubbles
Optical clearing based on ultrasound-induced gas bubbles offers new opportunities for deeper laser scanning microscopy of biological tissue.
- Haemin Kim
- , Sangyeon Youn
- & Jin Ho Chang
-
Obituary |
 In memory of Gabriel Popescu
In memory of Gabriel Popescu
Gabriel Popescu passed away in June 2022. He will be remembered as a creative leader in biophotonics, with pioneering contributions to quantitative phase imaging and spectroscopy, an engaging collaborator and a dear friend.
- Natan T. Shaked
- , YongKeun Park
- & Peter T. C. So
-
News & Views |
 Spectroscopy finds chiral phonons
Spectroscopy finds chiral phonons
The chiral nature of phonons in crystals of biomolecules is identified by terahertz spectroscopy, paving the way to a better understanding of biochemical processes.
- Minkyu Kim
- & Vladimir V. Tsukruk
-
Article |
 Chiral phonons in microcrystals and nanofibrils of biomolecules
Chiral phonons in microcrystals and nanofibrils of biomolecules
Chiral phonons—long-range lattice vibrations with rotational motion of atoms—are observed by terahertz chiroptical spectroscopy in biocrystals. Terahertz circular dichroism peaks between 0.2 and 2.0 THz clearly identify the chirality of these phonons in various microcrystalline and nanofibrils of biomolecules.
- Won Jin Choi
- , Keiichi Yano
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
News & Views |
 Reconstruction-free positron emission imaging
Reconstruction-free positron emission imaging
Measurement of the arrival times of annihilation photons in a detector with greater precision is opening the way to new direct forms of tomographic positron emission imaging that do not require back-projection-based reconstruction techniques.
- Suleman Surti
- & Joel S. Karp
-
Review Article |
 Speed scaling in multiphoton fluorescence microscopy
Speed scaling in multiphoton fluorescence microscopy
This Review summarizes the latest state-of-the-art technologies for high-speed multiphoton (fluorescence) microscopy, especially at kilohertz 2D frame rate, and 3D video rate or beyond—a speed regime that was generally inconceivable until very recently, as well as the prospects and challenges of these emerging technologies.
- Jianglai Wu
- , Na Ji
- & Kevin K. Tsia
-
Article |
 Ultrafast timing enables reconstruction-free positron emission imaging
Ultrafast timing enables reconstruction-free positron emission imaging
Positron emission imaging without tomographic reconstruction is demonstrated. A Cherenkov radiation detector detects gamma rays produced by positron–electron annihilation. The position of a positron source is determined with a precision of 4.8 mm.
- Sun Il Kwon
- , Ryosuke Ota
- & Simon R. Cherry
-
Correspondence |
 Open-source browser-based software simplifies fluorescence correlation spectroscopy data analysis
Open-source browser-based software simplifies fluorescence correlation spectroscopy data analysis
- Dominic Waithe
-
Obituary |
 In memory of Arthur Ashkin
In memory of Arthur Ashkin
Radiation pressure exerted by light was a lifelong passion for Arthur Ashkin. He foresaw that light pressure could do useful work and invented the optical tweezers that can trap microscopic objects, from small ‘living things’ down to individual atoms.
- René-Jean Essiambre
-
News & Views |
 Exploiting sound and noise
Exploiting sound and noise
A correlation method that combines ultrasound and fluorescence enables imaging in strongly scattering environments.
- Allard P. Mosk
-
Article |
 Photochemical upconversion of near-infrared light from below the silicon bandgap
Photochemical upconversion of near-infrared light from below the silicon bandgap
Photochemical upconversion of light with photon energy below the silicon bandgap has remained elusive, but the feat has now been demonstrated using PbS semiconductor nanocrystals and violanthrone.
- Elham M. Gholizadeh
- , Shyamal K. K. Prasad
- & Timothy W. Schmidt
-
Article |
 Monitoring contractility in cardiac tissue with cellular resolution using biointegrated microlasers
Monitoring contractility in cardiac tissue with cellular resolution using biointegrated microlasers
The incorporation of microsphere lasers into heart cells allows all-optical recording of cardiac contraction with cellular resolution. [This summary has been amended from ‘microdisk’ to ‘microsphere’ lasers.]
- Marcel Schubert
- , Lewis Woolfson
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article |
 Harmonic optical tomography of nonlinear structures
Harmonic optical tomography of nonlinear structures
A tomographiac approach to second-harmonic-generation imaging on nonlinear structures is demonstrated, with experiments and three-dimensional reconstructions on a beta-barium borate crystal and various biological specimens performed.
- Chenfei Hu
- , Jeffrey J. Field
- & Gabriel Popescu
-
News & Views |
 Optically sensing neural activity without imaging
Optically sensing neural activity without imaging
Advanced computational imaging techniques have the potential to extract neural activity patterns from scattered data without reconstructing images.
- Gordon Wetzstein
- & Isaac Kauvar
-
Article |
 Structured illumination microscopy using a photonic chip
Structured illumination microscopy using a photonic chip
The use of a photonic integrated circuit to both hold a biological sample and generate the necessary light patterns for structured illumination microscopy promises convenient super-resolution imaging.
- Øystein Ivar Helle
- , Firehun Tsige Dullo
- & Balpreet Singh Ahluwalia
-
Article |
 Fluorescence imaging through dynamic scattering media with speckle-encoded ultrasound-modulated light correlation
Fluorescence imaging through dynamic scattering media with speckle-encoded ultrasound-modulated light correlation
Combining the advantages of ultrasound and light for fluorescence imaging, an imaging technique termed fluorescence and ultrasound-modulated light correlation, or FLUX, that leverages the dynamic nature of the medium is reported to uniquely resolve fluorophore distribution even when the speckles decorrelate fast.
- Haowen Ruan
- , Yan Liu
- & Changhuei Yang
-
News & Views |
 Dark field on a chip
Dark field on a chip
Dark-field microscopy is a widely used imaging method that emphasizes sharp edges and other small features, but typically requires specialized microscope components. Researchers have now engineered special substrates that enable dark-field microscopy using simple bright-field microscopes.
- Mikhail A. Kats
-
Letter |
 Readout of fluorescence functional signals through highly scattering tissue
Readout of fluorescence functional signals through highly scattering tissue
By exploiting low-contrast fluctuating speckle patterns from extended fluorescence sources using an advanced signal-processing algorithm, functional signals through highly scattering tissues can be extracted.
- Claudio Moretti
- & Sylvain Gigan
-
Letter |
 Luminescent surfaces with tailored angular emission for compact dark-field imaging devices
Luminescent surfaces with tailored angular emission for compact dark-field imaging devices
A luminescent photonic substrate with a controlled angular emission profile is introduced and its ability to generate high-contrast dark-field images of micrometre-sized living organisms is demonstrated using standard optical microscopy equipment.
- Cécile A. C. Chazot
- , Sara Nagelberg
- & Mathias Kolle
-
Article |
 Snapshot photoacoustic topography through an ergodic relay for high-throughput imaging of optical absorption
Snapshot photoacoustic topography through an ergodic relay for high-throughput imaging of optical absorption
A low-cost high-throughput photoacoustic imaging based on an ergodic relay coupled with a single-element ultrasonic transducer that can capture a wide-field image with only a single laser shot is demonstrated.
- Yang Li
- , Lei Li
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
News & Views |
 Video-rate gigapixel imaging of the brain
Video-rate gigapixel imaging of the brain
A wide-field system that can perform video-rate imaging of the entire area of the brain of an awake mouse is aiding the study of neurones, epilepsy and the immune system.
- Gail McConnell
-
Article |
 Optical coherence refraction tomography
Optical coherence refraction tomography
By synthesizing undistorted cross-sectional image reconstructions from multiple conventional images acquired with angular diversity, optical coherence refraction tomography offers greater than threefold improvement in lateral resolution and speckle reduction in imaging tissue ultrastructure, and reconstructs the tissue’s internal refractive index distribution.
- Kevin C. Zhou
- , Ruobing Qian
- & Joseph A. Izatt
-
News & Views |
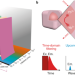 Overcoming the colour barrier
Overcoming the colour barrier
High-efficiency, time-domain, near-infrared fluorophores provide multiplexed colour channels for distinct deep bioimaging.
- Shoujun Zhu
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article |
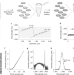 Wavelength-encoded laser particles for massively multiplexed cell tagging
Wavelength-encoded laser particles for massively multiplexed cell tagging
Intracellular laser particles based on silica-coated semiconductor microcavities with distinct emission wavelengths allow real-time tracking of thousands of cells in a tumour model.
- Nicola Martino
- , Sheldon J. J. Kwok
- & Seok-Hyun Yun
-
Article |
 Video-rate imaging of biological dynamics at centimetre scale and micrometre resolution
Video-rate imaging of biological dynamics at centimetre scale and micrometre resolution
Video-rate imaging of the brains of awake mice with a field of view of 10 × 12 mm2 and a spatial resolution of 1.2 µm is accomplished.
- Jingtao Fan
- , Jinli Suo
- & Qionghai Dai
-
News & Views |
 Photonic amyloids
Photonic amyloids
Emerging data reveal that amyloid fibrils possess intrinsic photonic activity, showing luminescence over a wide range of the electromagnetic spectrum from the ultraviolet to the near-infrared.
- Per Hammarström
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Electrochemically controlled blinking of fluorophores for quantitative STORM imaging
Electrochemically controlled blinking of fluorophores for quantitative STORM imaging