Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemically controlled blinking of fluorophores for quantitative STORM imaging
Electrochemically controlled blinking of fluorophores for quantitative STORM imaging
Electrochemical control of the switching of fluorophores in stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (EC-STORM) enables the counting of single fluorophores as well as cell imaging with improved spatial resolution and reduced artefacts compared with traditional STORM.
- Ying Yang
- , Yuanqing Ma
- & J. Justin Gooding
-
Article |
 Mid-infrared wide-field nanoscopy
Mid-infrared wide-field nanoscopy
Wide-field mid-infrared photothermal imaging is developed to supress the resolution degradation caused by photo-thermal heat diffusion. By employing a single-objective synthetic-aperture imaging with synchronized subnanosecond mid-infrared and visible light sources, spatial resolution of 120 nm is obtained.
- Miu Tamamitsu
- , Keiichiro Toda
- & Takuro Ideguchi
-
Article |
 Super-resolved FRET and co-tracking in pMINFLUX
Super-resolved FRET and co-tracking in pMINFLUX
Super-resolution pMINFLUX microscopy is combined with FRET and enables co-tracking of two fluorophores without photoswitching.
- Fiona Cole
- , Jonas Zähringer
- & Philip Tinnefeld
-
Article |
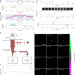 Event-based vision sensor for fast and dense single-molecule localization microscopy
Event-based vision sensor for fast and dense single-molecule localization microscopy
Event-based sensors enable super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy with comparable quality and resolution to traditional scientific cameras, while also overcoming the limitations of high-density imaging.
- Clément Cabriel
- , Tual Monfort
- & Ignacio Izeddin
-
News & Views |
 Deconvolution enhances fluctuation detection
Deconvolution enhances fluctuation detection
The introduction of a two-step deconvolution workflow maximizes the detection of fluorescence in fluctuation-based super-resolution imaging, enabling a square millimetre field of view to be captured in as little as ten minutes.
- David Baddeley
-
Article
| Open Access Single multimode fibre for in vivo light-field-encoded endoscopic imaging
Single multimode fibre for in vivo light-field-encoded endoscopic imaging
Spatial-frequency tracking adaptive beacon light-field encoded endoscopy enables imaging through a single multimode fibre under bending and twisting. In vivo imaging with subcellular resolution is demonstrated in mice models.
- Zhong Wen
- , Zhenyu Dong
- & Qing Yang
-
News & Views |
 Tracking nanoscopic motion with minima of light
Tracking nanoscopic motion with minima of light
Two papers in Science demonstrate tracking of the stepping motion of the kinesin motor protein with nanometric spatial precision and sub-millisecond temporal resolution by using MINFLUX, a highly photon-efficient single-molecule localization technique.
- Fernando D. Stefani
-
Article |
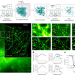 Enhanced detection of fluorescence fluctuations for high-throughput super-resolution imaging
Enhanced detection of fluorescence fluctuations for high-throughput super-resolution imaging
Super-resolution imaging based on autocorrelation with two-step deconvolution (SACD) enables recording super-resolution images with 128-nm spatial resolution over a field of view of 2.0 mm × 1.4 mm within a 10-min acquisition time.
- Weisong Zhao
- , Shiqun Zhao
- & Haoyu Li
-
Correspondence |
 Open-source tools enable accessible and advanced image scanning microscopy data analysis
Open-source tools enable accessible and advanced image scanning microscopy data analysis
- Alessandro Zunino
- , Eli Slenders
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution photothermal microscopy
Super-resolution photothermal microscopy
A photothermal microscopy technique overcomes the diffraction limit by exploiting the spatiotemporal dynamics of heat dissipation within the imaging volume, offering new opportunities for super-resolution, bond-selective and label-free imaging of biological targets.
- Zhilun Zhao
- & Wei Min
-
Article |
 Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent molecules by photothermal relaxation localization microscopy
Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent molecules by photothermal relaxation localization microscopy
Photothermal relaxation localization microscopy allows super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent targets by leveraging spatial-dependent heat dissipation in photothermal microscopy. Individual lipid droplets and their distribution in living cells are imaged at spatial resolutions down to 120 nm.
- Pengcheng Fu
- , Wanlin Cao
- & Delong Zhang
-
Article |
 Six-dimensional single-molecule imaging with isotropic resolution using a multi-view reflector microscope
Six-dimensional single-molecule imaging with isotropic resolution using a multi-view reflector microscope
A multi-view reflector microscope based on polarization modulation and pupil splitting enables single-molecule orientation-localization microscopy with precisions of 10.9 nm and 2.0°.
- Oumeng Zhang
- , Zijian Guo
- & Matthew D. Lew
-
Article
| Open Access MINSTED fluorescence localization and nanoscopy
MINSTED fluorescence localization and nanoscopy
A stimulated-emission-depletion-based fluorescence localization and super-resolution microscopy concept that is capable of attaining a spatial resolution down at the size scale of the fluorophores themselves and a localization precision of 1–3 nm in standard deviation is reported.
- Michael Weber
- , Marcel Leutenegger
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article |
 Nanometric axial localization of single fluorescent molecules with modulated excitation
Nanometric axial localization of single fluorescent molecules with modulated excitation
Adapting the amplitude-modulated light detection and ranging approach to super-resolution microscopy offers a typical axial localization precision of 6.8 nm over the entire field of view and the axial capture range, enabling imaging of biological samples by up to several micrometres in depth.
- Pierre Jouchet
- , Clément Cabriel
- & Sandrine Lévêque-Fort
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution microscopy on a photonic chip
Super-resolution microscopy on a photonic chip
Using a photonic chip to generate the patterns of light needed for structured illumination microscopy could reduce the cost and complexity of super-resolution imaging.
- Sara Abrahamsson
-
Article |
 Structured illumination microscopy using a photonic chip
Structured illumination microscopy using a photonic chip
The use of a photonic integrated circuit to both hold a biological sample and generate the necessary light patterns for structured illumination microscopy promises convenient super-resolution imaging.
- Øystein Ivar Helle
- , Firehun Tsige Dullo
- & Balpreet Singh Ahluwalia
-
News & Views |
 Graphene boost
Graphene boost
Using graphene as the ‘metal’ layer improves the localization accuracy of metal-induced energy transfer by nearly tenfold.
- Margarida M. Barroso
-
Article |
 Higher-order coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy realizes label-free super-resolution vibrational imaging
Higher-order coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy realizes label-free super-resolution vibrational imaging
Higher-order (fifth and seventh order) coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy is demonstrated to break the diffraction limit for label-free super-resolution vibrational imaging for live cells such as HeLa and buccal cells.
- Li Gong
- , Wei Zheng
- & Zhiwei Huang
-
Article |
 High external-efficiency nanofocusing for lens-free near-field optical nanoscopy
High external-efficiency nanofocusing for lens-free near-field optical nanoscopy
A two-step sequential broadband nanofocusing technique offers an external efficiency of ~50% over nearly all the visible range on a fibre-coupled plasmonic nanowire probe. Its integration with a scanning tunnelling microscope realizes lens-free tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with 1 nm spatial resolution.
- Sanggon Kim
- , Ning Yu
- & Ruoxue Yan
-
-
Letter |
 Super-resolution retinal imaging using optically reassigned scanning laser ophthalmoscopy
Super-resolution retinal imaging using optically reassigned scanning laser ophthalmoscopy
The implementation of optically reassigned scanning laser ophthalmoscopy enables in vivo photon reassignment super-resolution imaging and high-resolution imaging of living human retinal cone photoreceptor cells without adaptive optics or chemical dilation of the eye.
- Theodore B. DuBose
- , Francesco LaRocca
- & Joseph A. Izatt
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution with quantum light
Super-resolution with quantum light
Quantum correlations from photon antibunching enhance the resolution of image scanning microscopy in biological imaging by twofold, four times beyond the diffraction limit.
- Andrew Forbes
- & Valeria Rodriguez-Fajardo
-
Article |
 Super-resolution enhancement by quantum image scanning microscopy
Super-resolution enhancement by quantum image scanning microscopy
Characterizing not only the fluorescence intensity but also the inherent quantum correlations of the fluorescent photon stream can enhance the spatial resolution of image scanning microscopy up to twofold, a fourfold improvement over the diffraction limit.
- Ron Tenne
- , Uri Rossman
- & Dan Oron
-
-
-
News & Views |
 The super-resolution debate
The super-resolution debate
In the quest for nanoscopy with super-resolution, consensus from the imaging community is that super-resolution is not always needed and that scientists should choose an imaging technique based on their specific application.
- Rachel Won
-
Article |
 Combined multi-plane phase retrieval and super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging for 4D cell microscopy
Combined multi-plane phase retrieval and super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging for 4D cell microscopy
By combining the sensitivity and high temporal resolution of phase imaging with the specificity and high spatial resolution of fluorescence microscopy, a 4D microscope is demonstrated that visualizes in three dimensions the fast cellular processes in living cells at up to 200 Hz.
- A. Descloux
- , K. S. Grußmayer
- & T. Lasser
-
News & Views |
 Exploring a hidden world
Exploring a hidden world
The science of superoscillations and the creation of local regions of light on a subwavelength scale is attracting attention for new forms of super-resolution microscopy and stiffer optical traps.
- Oliver Graydon
-
-
Article |
 Chip-based wide field-of-view nanoscopy
Chip-based wide field-of-view nanoscopy
Nanoscopy on a chip makes it possible to perform super-resolution imaging of biological specimens with a wide field-of-view.
- Robin Diekmann
- , Øystein I. Helle
- & Balpreet S. Ahluwalia
-
Article |
 Background suppression in fluorescence nanoscopy with stimulated emission double depletion
Background suppression in fluorescence nanoscopy with stimulated emission double depletion
Stimulated emission double depletion addresses the issue of background in super-resolution imaging and quantitative microscopy through implementation of a two-pulse sequence in a modified stimulated emission depletion set-up. The measured background intensity is removed from each voxel in the acquired images thanks to time-resolved detection.
- Peng Gao
- , Benedikt Prunsche
- & G. Ulrich Nienhaus
-
Letter |
 Super-resolution imaging of multiple cells by optimized flat-field epi-illumination
Super-resolution imaging of multiple cells by optimized flat-field epi-illumination
An epi-illumination system based on microlens arrays enables field-independent imaging of multiple cells with nanoscale resolution and large field of views.
- Kyle M. Douglass
- , Christian Sieben
- & Suliana Manley
-
Letter |
 Multicolour localization microscopy by point-spread-function engineering
Multicolour localization microscopy by point-spread-function engineering
Multicolour tracking and super-resolution imaging is made possible by the use of a new design of optical phase mask.
- Yoav Shechtman
- , Lucien E. Weiss
- & W. E. Moerner
-
Letter |
 Removing orientation-induced localization biases in single-molecule microscopy using a broadband metasurface mask
Removing orientation-induced localization biases in single-molecule microscopy using a broadband metasurface mask
A custom-designed metamaterial mask helps improve the accuracy of microscopy of single fluorescent molecules.
- Mikael P. Backlund
- , Amir Arbabi
- & W. E. Moerner
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution fight club
Super-resolution fight club
A 2016 competition to find the optimum software for 3D single-molecule localization microscopy will help practitioners choose the best tool for the job and spur further developments in the field.
- Seamus Holden
- & Daniel Sage
-
Article |
 Coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy with multiple off states
Coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy with multiple off states
By exploiting a second off state of a reversibly switchable fluorophore, a general approach that can reduce photobleaching and enhance resolution of coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy has been demonstrated.
- Johann G. Danzl
- , Sven C. Sidenstein
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Letter |
 Optical nanoscopy with excited state saturation at liquid helium temperatures
Optical nanoscopy with excited state saturation at liquid helium temperatures
Based on optical saturation of the excited state of single fluorescent molecules with a doughnut-shaped beam, sub-10-nm-resolution optical microscopy at cryogenic temperatures is achieved.
- B. Yang
- , J.-B. Trebbia
- & B. Lounis
-
Article |
 Direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection
Direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection
Researchers exploit direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy and dedicated detection of super-critical-angle fluorescence emission to enable direct optical nanoscopy with axially localized detection.
- N. Bourg
- , C. Mayet
- & S. Lévêque-Fort
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Celebrating optical nanoscopy
Celebrating optical nanoscopy
The award of this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry to the pioneers of various optical schemes capable of achieving super-resolution and single-molecule detection is recognition of a revolution in optical imaging.
- Michel Orrit
-
Editorial |
Photonics dominates Nobel Prizes
Awards for blue LEDs and super-resolution microscopy announced.
-
Commentary |
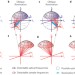 Resolving a misconception about structured illumination
Resolving a misconception about structured illumination
Applying structured illumination microscopy to coherent imaging modalities such as scattering does not yield any additional information beyond that provided by oblique illumination. It thus yields no resolution enhancement over the Abbe diffraction limit, which was derived precisely for that case.
- Kai Wicker
- & Rainer Heintzmann
-
Letter |
 Isotropic three-dimensional super-resolution imaging with a self-bending point spread function
Isotropic three-dimensional super-resolution imaging with a self-bending point spread function
By exploiting a self-bending point spread function based on Airy beams, a three-dimensional super-resolution fluorescence imaging is realized. A three-dimensional localization precision in the range 10–15 nm was obtained at an imaging depth of 3 µm from ∼2,000 photons per localization.
- Shu Jia
- , Joshua C. Vaughan
- & Xiaowei Zhuang
-
Letter |
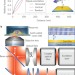 Metal-induced energy transfer for live cell nanoscopy
Metal-induced energy transfer for live cell nanoscopy
A means for localizing fluorescent molecules over distances of hundreds of nanometres exploits the energy transfer between a donor molecule and surface plasmons on a metal film. The technique is demonstrated by using it to profile the membranes of living cells.
- Alexey I. Chizhik
- , Jan Rother
- & Jörg Enderlein
-
News & Views |
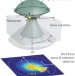 Scattering in focus
Scattering in focus
Sustaining the ongoing revolution in optical microscopy will require gaining detailed insight into the optical fields in focal spots. Researchers have developed an elegant method for mapping the full electric vector field using just a metal nanosphere on a glass substrate.
- L. Kuipers
-
Letter |
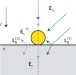 Nanointerferometric amplitude and phase reconstruction of tightly focused vector beams
Nanointerferometric amplitude and phase reconstruction of tightly focused vector beams
An easily implementable reconstruction scheme is demonstrated for determining the full vectorial amplitude and relative phase distributions of highly confined electromagnetic fields with subwavelength resolution from a single-scan measurement. This scheme will help improve microscopy and nanoscopy techniques.
- Thomas Bauer
- , Sergej Orlov
- & Gerd Leuchs
-
News & Views |
 Beyond the realm of fluorescence
Beyond the realm of fluorescence
Using a pump–probe technique, scientists have experimentally demonstrated a nonlinear imaging scheme that permits the super-resolution imaging of nonfluorescent samples, making it promising for use with unstained specimens.
- Rainer Heintzmann
-
Letter |
 Far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species with subdiffraction resolution
Far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species with subdiffraction resolution
A scheme for overcoming the diffraction limit in the far-field imaging of non-fluorescent species is demonstrated. This technique, which is based on the spatially controlled saturation of electronic absorption, may enable the super-resolution imaging of nanomaterials and non-fluorescent chromophores.
- Pu Wang
- , Mikhail N. Slipchenko
- & Ji-Xin Cheng

 Super-resolved snapshot hyperspectral imaging of solid-state quantum emitters for high-throughput integrated quantum technologies
Super-resolved snapshot hyperspectral imaging of solid-state quantum emitters for high-throughput integrated quantum technologies Intracellular movies
Intracellular movies