Featured
-
-
Article |
 Spectral evidence for Dirac spinons in a kagome lattice antiferromagnet
Spectral evidence for Dirac spinons in a kagome lattice antiferromagnet
A Dirac quantum spin liquid phase is predicted to have a continuum of fractionalized spinon excitations with a Dirac cone dispersion. A spin continuum consistent with this picture has now been observed in neutron scattering measurements.
- Zhenyuan Zeng
- , Chengkang Zhou
- & Shiliang Li
-
Article |
 Single-component superconductivity in UTe2 at ambient pressure
Single-component superconductivity in UTe2 at ambient pressure
The symmetry of the superconducting order parameter in UTe2 is still debated. Now ultrasound experiments suggest that the order parameter can only have one component.
- Florian Theuss
- , Avi Shragai
- & B. J. Ramshaw
-
Article |
 Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
The hybrid architecture of Andreev spin qubits made using semiconductor–superconductor nanowires means that supercurrents can be used to inductively couple qubits over long distances.
- Marta Pita-Vidal
- , Jaap J. Wesdorp
- & Christian Kraglund Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
A successful silicon spin qubit design should be rapidly scalable by benefiting from industrial transistor technology. This investigation of exchange interactions between two FinFET qubits provides a guide to implementing two-qubit gates for hole spins.
- Simon Geyer
- , Bence Hetényi
- & Andreas V. Kuhlmann
-
Research Briefing |
 Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs
Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs
As counterparts to optical frequency combs, magnonic frequency combs could have broad applications if their initiation thresholds were low and the ‘teeth’ of the comb plentiful. Progress has now been made through exploiting so-called exceptional points to enhance the nonlinear coupling between magnons and produce wider magnonic frequency combs.
-
Article |
 Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Frequency combs, which are important for applications in precision spectroscopy, depend on material nonlinearities for their function, which can be hard to engineer. Now an approach combining magnons and exceptional points is shown to be effective.
- Congyi Wang
- , Jinwei Rao
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Irreversible entropy transport enhanced by fermionic superfluidity
Irreversible entropy transport enhanced by fermionic superfluidity
Connecting two superfluid reservoirs leads to both particle and entropy flow between the systems. Now, a direct measurement of the entropy current and production in ultracold quantum gases reveals how superfluidity enhances entropy transport.
- Philipp Fabritius
- , Jeffrey Mohan
- & Tilman Esslinger
-
Article |
 Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
Controlling orbital magnetic moments for applications can be difficult. Now local probes of a kagome material, TbV6Sn6, demonstrate how the spin Berry curvature can produce a large orbital Zeeman effect that can be tuned with a magnetic field.
- Hong Li
- , Siyu Cheng
- & Ilija Zeljkovic
-
Article |
 Room-temperature flexible manipulation of the quantum-metric structure in a topological chiral antiferromagnet
Room-temperature flexible manipulation of the quantum-metric structure in a topological chiral antiferromagnet
Manipulation of the quantum-metric structure to produce topological phenomena has rarely been studied. Now, flexible control of the quantum-metric structure is demonstrated in a topological chiral antiferromagnet at room temperature.
- Jiahao Han
- , Tomohiro Uchimura
- & Shunsuke Fukami
-
-
-
Article |
 Distinct elastic properties and their origins in glasses and gels
Distinct elastic properties and their origins in glasses and gels
As amorphous solids, glasses and gels are similar, but the origins of their different elastic properties are unclear. Simulations now suggest differing free-energy-minimizing pathways: structural ordering for glasses and interface reduction for gels.
- Yinqiao Wang
- , Michio Tateno
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article |
 All-optical seeding of a light-induced phase transition with correlated disorder
All-optical seeding of a light-induced phase transition with correlated disorder
Controlling phase transitions in solids is crucial for many applications. Ultrafast laser pulses have now been shown to enable the energy-efficient generation of structural fluctuations in VO2 by harnessing the correlated disorder in the material.
- Allan S. Johnson
- , Ernest Pastor
- & Simon E. Wall
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Linear topological systems can be characterized using invariants such as the Chern number. This concept can be extended to the nonlinear regime, giving rise to nonlinearity-induced topological phase transitions.
- Kazuki Sone
- , Motohiko Ezawa
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
Perspective |
 Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Although topological photonics has been an active field of research for some time, most studies still focus on the linear optical regime. This Perspective summarizes recent investigations into the nonlinear properties of discrete topological photonic systems.
- Alexander Szameit
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
News & Views |
 At the breaking point
At the breaking point
The shape and trajectory of a crack plays a crucial role in material fracture. High-precision experiments now directly capture this phenomenon, unveiling the intricate 3D nature of cracks.
- Michael D. Bartlett
-
Article |
 Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
The ferromagnet CrVI6 serves as a material platform to demonstrate the topological Kerr effect in two-dimensional magnets. This can be used to identify skyrmions by magneto-optical means.
- Xiaoyin Li
- , Caixing Liu
- & Zhenyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes can occur when superconductivity arises in more than one band in a material and represent oscillation of the relative phases of the two superconducting condensates. Now, this mode is observed in Cd3As2, a Dirac semimetal.
- Joseph J. Cuozzo
- , W. Yu
- & Enrico Rossi
-
Article |
 Multistep topological transitions among meron and skyrmion crystals in a centrosymmetric magnet
Multistep topological transitions among meron and skyrmion crystals in a centrosymmetric magnet
Topological magnetic spin structures such as skyrmions and merons have the potential to be used in magnetic information devices. Now multistep transformations between such structures are demonstrated in a centrosymmetric material.
- H. Yoshimochi
- , R. Takagi
- & S. Seki
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Despite their potential device applications, experimental realizations of proximity-induced Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov states are rare. Now Josephson junctions based on a dilute magnetic topological insulator provide evidence of such a state.
- Pankaj Mandal
- , Soumi Mondal
- & Laurens W. Molenkamp
-
Article |
 Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
A mechanism for the phase transition of charge density wave states via the generation and proliferation of topological defects with opposite phase windings is demonstrated in a heavy-fermion superconductor.
- Anuva Aishwarya
- , Julian May-Mann
- & Vidya Madhavan
-
Article |
 Flexoelectricity-driven toroidal polar topology in liquid-matter helielectrics
Flexoelectricity-driven toroidal polar topology in liquid-matter helielectrics
Exploring and exploiting electric dipole arrangements analogously to what is possible with magnetic spin textures is an emerging prospect. Now a spontaneous toroidal polar topology is observed in ferroelectric liquid crystals.
- Jidan Yang
- , Yu Zou
- & Satoshi Aya
-
Article |
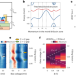 Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
The local electronic structure of interface states between topologically distinct domains is imaged and controlled, allowing visualization of the interplay between strong interactions and non-trivial topology.
- Canxun Zhang
- , Tiancong Zhu
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
Article |
 Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Copper-based and iron-based compounds exhibit an interplay between magnetism and superconductivity. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional oxide heterostructures, where a spatially varying superconducting order is demonstrated at the EuO/KTaO3 interface.
- Xiangyu Hua
- , Zimeng Zeng
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Cooling efficiency in thermoelectric devices decreases considerably at lower temperatures. Now thermoelectric cooling at cryogenic temperatures is directly imaged in a van der Waals semimetal.
- T. Völkl
- , A. Aharon-Steinberg
- & E. Zeldov
-
News & Views |
 Terahertz magnon algebra
Terahertz magnon algebra
Excitation of magnons — quanta of spin-waves — in an antiferromagnet can be used for high-speed data processing. The addition and subtraction of two such modes opens up possibilities for magnon-based information transfer in the terahertz spectral region.
- Brijesh Singh Mehra
- & Dhanvir Singh Rana
-
Article |
 Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Spin polarons, bound states of a doped carrier and a spin flip excitation, are observed in a transition metal moiré bilayer.
- Zui Tao
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
News & Views |
 Metal poles around the bend
Metal poles around the bend
Electric dipoles are common in insulators, but extremely rare in metals. This situation may be about to change, thanks to flexoelectricity.
- Gustau Catalan
-
Article |
 Quantized topological pumping in Floquet synthetic dimensions with a driven dissipative photonic molecule
Quantized topological pumping in Floquet synthetic dimensions with a driven dissipative photonic molecule
Although dissipation is often detrimental to the observation of topological effects, a photonic molecule driven at several incommensurate frequencies is shown to be a candidate system for quantized topological transport in synthetic dimensions.
- Sashank Kaushik Sridhar
- , Sayan Ghosh
- & Avik Dutt
-
Article |
 Quantum transport response of topological hinge modes
Quantum transport response of topological hinge modes
Topologically protected hinge modes could be important for developing quantum devices, but electronic transport through those states has not been demonstrated. Now quantum transport has been shown in gapless topological hinge states.
- Md Shafayat Hossain
- , Qi Zhang
- & M. Zahid Hasan
-
News & Views |
Time in a glass
Ageing is a non-linear, irreversible process that defines many properties of glassy materials. Now, it is shown that the so-called material-time formalism can describe ageing in terms of equilibrium-like properties.
- Beatrice Ruta
- & Daniele Cangialosi
-
News & Views |
 Sound interactions across multiple modes
Sound interactions across multiple modes
Some quantum acoustic resonators possess a large number of phonon modes at different frequencies. Direct interactions between modes similar to those available for photonic devices have now been demonstrated. This enables manipulation of multimode states.
- Audrey Bienfait
-
News & Views |
 Through the slopes of a light-induced phase transition
Through the slopes of a light-induced phase transition
The integration of theory and experiment makes possible tracking the slow evolution of a photodoped Mott insulator to a distinct non-equilibrium metallic phase under the influence of electron-lattice coupling.
- Denitsa R. Baykusheva
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
The standard current–phase relation in tunnel Josephson junctions involves a single sinusoidal term, but real junctions are more complicated. The effects of higher Josephson harmonics have now been identified in superconducting qubit devices.
- Dennis Willsch
- , Dennis Rieger
- & Ioan M. Pop
-
News & Views |
 A strange way to get a strange metal
A strange way to get a strange metal
Some cerium and uranium compounds exhibit unusual transport properties due to localized electron states. Recent experiments demonstrate that quantum interference on frustrated lattices provides an alternative route to this behaviour.
- William R. Meier
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry matters
Symmetry matters
Quantum simulators can provide new insights into the complicated dynamics of quantum many-body systems far from equilibrium. A recent experiment reveals that underlying symmetries dictate the nature of universal scaling dynamics.
- Maximilian Prüfer
-
News & Views |
 A kagome antiferromagnet reaches its quantum plateau
A kagome antiferromagnet reaches its quantum plateau
It has long been predicted that spin-1/2 antiferromagnets on the kagome lattice should feature a series of plateaus in the change of its magnetization under an applied magnetic field. A quantum plateau of this kind has now been observed experimentally.
- Gia-Wei Chern
-
Article
| Open Access Bragg glass signatures in PdxErTe3 with X-ray diffraction temperature clustering
Bragg glass signatures in PdxErTe3 with X-ray diffraction temperature clustering
The existence of Bragg glasses—featuring nearly perfect crystalline order and glassy features—has yet to be experimentally confirmed for disordered charge-density-wave systems. A machine-learning-based experimental study now provides evidence for a Bragg glass phase in the charge density waves of PdxErTe3.
- Krishnanand Mallayya
- , Joshua Straquadine
- & Eun-Ah Kim
-
Article |
 Picosecond volume expansion drives a later-time insulator–metal transition in a nano-textured Mott insulator
Picosecond volume expansion drives a later-time insulator–metal transition in a nano-textured Mott insulator
During a photoinduced phase transition, electronic rearrangements are usually faster than lattice ones. Time-resolved measurements now show that the insulator-to-metal transition in a thin-film Mott insulator is preceded by lattice reconfiguration.
- Anita Verma
- , Denis Golež
- & Andrej Singer
-
News & Views |
 Relaxation of a sensitive superconductor
Relaxation of a sensitive superconductor
Some exotic metals exhibit competing electronic states that can be influenced by small perturbations. Now, a study of a kagome superconductor shows that this competition is exquisitely sensitive to weak strain fields, providing insight into its anomalous electronic properties.
- Stephen D. Wilson
-
Article |
 Dipolar spin wave packet transport in a van der Waals antiferromagnet
Dipolar spin wave packet transport in a van der Waals antiferromagnet
Understanding the mechanism by which magnons—the quanta of spin waves—propagate is important for developing practical devices. Now it is shown that long-range dipole–dipole interactions mediate the propagation in a van der Waals antiferromagnet.
- Yue Sun
- , Fanhao Meng
- & Joseph Orenstein
-
News & Views |
 A quantum collaboration for flat bands
A quantum collaboration for flat bands
Multiple mechanisms can create electrons with reduced kinetic energy in solids. Combining these mechanisms now appears as a promising route to enhancing quantum effects in flat band materials.
- Priscila F. S. Rosa
- & Filip Ronning
-
Article |
 Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Magnons—quanta of spin waves—have potential applications in signal processing technology. But it is challenging to obtain coupling between different magnons. Now a study achieves this by demonstrating nonlinear magnon mixing in an antiferromagnet.
- Zhuquan Zhang
- , Frank Y. Gao
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access Correlated order at the tipping point in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5
Correlated order at the tipping point in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5
The electronic transport properties of charge-ordered kagome metals are controversial. Now careful measurements on unperturbed samples show that previously measured anisotropy in the transport occurs only when external perturbations are present.
- Chunyu Guo
- , Glenn Wagner
- & Philip J. W. Moll
-
News & Views |
 Phonons bend to magnetic fields
Phonons bend to magnetic fields
Phonons do not carry spin or charge, but they can couple to an external magnetic field and cause a sizable transverse thermal gradient. Experiments suggest that phonon handedness is a widespread effect in magnetic insulators with impurities.
- Valentina Martelli
-
Article |
 Phonon chirality from impurity scattering in the antiferromagnetic phase of Sr2IrO4
Phonon chirality from impurity scattering in the antiferromagnetic phase of Sr2IrO4
The thermal Hall effect of phonons does not yet have a definitive explanation. Now a careful study of doped Sr2IrO4 suggests that the mechanism involves the scattering of phonons by impurities embedded in an antiferromagnetic environment.
- A. Ataei
- , G. Grissonnanche
- & L. Taillefer
-
Article
| Open Access The interplay of field-tunable strongly correlated states in a multi-orbital moiré system
The interplay of field-tunable strongly correlated states in a multi-orbital moiré system
Heterostructures of transition metal dichalcogenides are known to simulate the triangular-lattice Hubbard model. Now, by combining a monolayer and bilayer of different materials, this idea is extended to multi-orbital Hubbard models.
- Aidan J. Campbell
- , Valerio Vitale
- & Brian D. Gerardot
-
News & Views |
 Electronic transport probes a hidden state
Electronic transport probes a hidden state
Electronic transport measurements of the anomalous Hall effect can probe properties of a frustrated kagome spin ice that are hidden from conventional thermodynamic and magnetic probes.
- Enke Liu
-
Article |
 Non-Fermi liquid behaviour in a correlated flat-band pyrochlore lattice
Non-Fermi liquid behaviour in a correlated flat-band pyrochlore lattice
Observations of strong electron correlation effects have been mostly confined to compounds containing f orbital electrons. Now, the study of the 3d pyrochlore metal CuV2S4 reveals that similar effects can be induced by flat-band engineering.
- Jianwei Huang
- , Lei Chen
- & Ming Yi
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

 A quantum critical Bose gas of magnons in the quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet YbCl3 under magnetic fields
A quantum critical Bose gas of magnons in the quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet YbCl3 under magnetic fields Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier
Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier Naturally superconducting
Naturally superconducting