Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Frequency combs, which are important for applications in precision spectroscopy, depend on material nonlinearities for their function, which can be hard to engineer. Now an approach combining magnons and exceptional points is shown to be effective.
- Congyi Wang
- , Jinwei Rao
- & Wei Lu
-
Article |
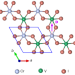 Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
The ferromagnet CrVI6 serves as a material platform to demonstrate the topological Kerr effect in two-dimensional magnets. This can be used to identify skyrmions by magneto-optical means.
- Xiaoyin Li
- , Caixing Liu
- & Zhenyu Zhang
-
Article |
 Terahertz-field-driven magnon upconversion in an antiferromagnet
Terahertz-field-driven magnon upconversion in an antiferromagnet
Inducing coherent interactions between distinct magnon modes—collective excitations of magnetic order—has been challenging. A canted antiferromagnet has demonstrated coherent magnon upconversion induced by terahertz laser pulses.
- Zhuquan Zhang
- , Frank Y. Gao
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access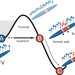 False vacuum decay via bubble formation in ferromagnetic superfluids
False vacuum decay via bubble formation in ferromagnetic superfluids
The transition from a metastable state to the ground state in classical many-body systems is mediated by bubble nucleation. This transition has now been experimentally observed in a quantum setting using coupled atomic superfluids.
- A. Zenesini
- , A. Berti
- & G. Ferrari
-
Article |
 Room-temperature long-range ferromagnetic order in a confined molecular monolayer
Room-temperature long-range ferromagnetic order in a confined molecular monolayer
Realizing robust ferromagnetic order in two dimensions is challenging as an underlying crystalline framework is normally required. Now room-temperature ferromagnetism is demonstrated in a two-dimensional honeycomb self-assembly of confined molecules.
- Yuhua Liu
- , Haifeng Lv
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
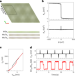 Intrinsic spin Hall torque in a moiré Chern magnet
Intrinsic spin Hall torque in a moiré Chern magnet
Switching of magnetic behaviour is one of the main ideas that drives spintronics. Now, magnetic switching via spin-orbit torque is shown in a moiré bilayer, introducing a platform for spintronic applications.
- C. L. Tschirhart
- , Evgeny Redekop
- & A. F. Young
-
Letter |
 Anomalous Hall effect at half filling in twisted bilayer graphene
Anomalous Hall effect at half filling in twisted bilayer graphene
The anomalous Hall effect can signify that a material has a spontaneous magnetic order. Now, twisted bilayer graphene shows this effect at half filling, suggesting that the ground state is valley-polarized.
- Chun-Chih Tseng
- , Xuetao Ma
- & Matthew Yankowitz
-
Article |
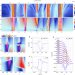 Chern mosaic and Berry-curvature magnetism in magic-angle graphene
Chern mosaic and Berry-curvature magnetism in magic-angle graphene
Topological states characterized by Chern numbers are usually considered to be the global properties of a material. Now a spatial patchwork of different Chern insulator states is imaged in twisted bilayer graphene.
- Sameer Grover
- , Matan Bocarsly
- & Eli Zeldov
-
Letter |
 Cascade of isospin phase transitions in Bernal-stacked bilayer graphene at zero magnetic field
Cascade of isospin phase transitions in Bernal-stacked bilayer graphene at zero magnetic field
The flat portions of the band structure in bilayer graphene are shown to support interaction-driven symmetry-broken states, similar to moiré heterostructures.
- Sergio C. de la Barrera
- , Samuel Aronson
- & Raymond Ashoori
-
Letter |
 Coherent spin-wave transport in an antiferromagnet
Coherent spin-wave transport in an antiferromagnet
Ultrashort light pulses generate nanometre-scale wavepackets of magnons that propagate coherently and at high speed in an antiferromagnet. This pushes antiferromagnetic magnonics forward as a future platform for information processing.
- J. R. Hortensius
- , D. Afanasiev
- & A. D. Caviglia
-
Letter |
 Experimental observation of vortex rings in a bulk magnet
Experimental observation of vortex rings in a bulk magnet
Three-dimensional structures of vortex loops in a bulk micromagnet GdCo2 have been observed using X-ray magnetic nanotomography. The cross-section of these loops consists of a vortex–antivortex pair stabilized by the dipolar interaction.
- Claire Donnelly
- , Konstantin L. Metlov
- & Sebastian Gliga
-
Article |
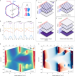 Electrically tunable correlated and topological states in twisted monolayer–bilayer graphene
Electrically tunable correlated and topological states in twisted monolayer–bilayer graphene
Stacking a monolayer and bilayer of graphene, with a small twist angle between them, creates a tunable platform where the physics of both twisted bilayer graphene and twisted double bilayer graphene can be realized.
- Shaowen Chen
- , Minhao He
- & Matthew Yankowitz
-
Article |
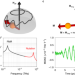 Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial dynamics are observed in a ferromagnet. Specifically, a nutation is seen on top of the usual spin precession that has a lifetime on the order of 10 picoseconds.
- Kumar Neeraj
- , Nilesh Awari
- & Stefano Bonetti
-
Letter |
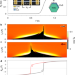 Zero-bias peaks at zero magnetic field in ferromagnetic hybrid nanowires
Zero-bias peaks at zero magnetic field in ferromagnetic hybrid nanowires
By incorporating a ferromagnetic layer in their superconductor–semiconductor nanowire hybrid device, Vaitiekėnas et al. show that zero-bias peaks—potential Majorana bound states—can be induced without an external magnetic field.
- S. Vaitiekėnas
- , Y. Liu
- & C. M. Marcus
-
Letter |
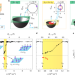 Bloch ferromagnetism of composite fermions
Bloch ferromagnetism of composite fermions
Composite fermions can be tuned to very low effective density in a clean two-dimensional electron gas, which allows the formation of a Bloch ferromagnet.
- Md Shafayat Hossain
- , Tongzhou Zhao
- & M. Shayegan
-
Letter |
 High-temperature quantum anomalous Hall regime in a MnBi2Te4/Bi2Te3 superlattice
High-temperature quantum anomalous Hall regime in a MnBi2Te4/Bi2Te3 superlattice
A three-dimensional topological magnetic superlattice structure exhibits the quantum anomalous Hall effect when the Fermi energy is tuned into the correct energy window.
- Haiming Deng
- , Zhiyi Chen
- & Lia Krusin-Elbaum
-
Letter |
 Direct observation of two-dimensional magnons in atomically thin CrI3
Direct observation of two-dimensional magnons in atomically thin CrI3
Magnons are collective excitations that dictate many of a magnet’s low-temperature properties. By means of Raman scattering, the magnon spectra of CrI3 are measured in the monolayer limit.
- John Cenker
- , Bevin Huang
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
News & Views |
 A magnetic field boost for superconductors
A magnetic field boost for superconductors
High-magnetic-field experiments on the recently discovered unconventional superconductor UTe2 are consistent with p-wave pairing arising while time-reversal symmetry is broken. In turn, this suggests that this material is a candidate for a chiral superconductor that may be exploited for topological quantum computing.
- Marc Janoschek
-
News & Views |
 Order! Order!!
Order! Order!!
The ferromagnetism of iron has been known for millennia. Now a rotational form of spontaneous crystallographic ordering has been discovered. This touches upon fundamental questions about the relation between symmetry, structure and order in matter.
- Manfred Fiebig
-
Article |
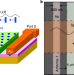 Magnon–fluxon interaction in a ferromagnet/superconductor heterostructure
Magnon–fluxon interaction in a ferromagnet/superconductor heterostructure
A spectral study on a ferromagnet/superconductor heterostructure reveals the interaction between the spin-wave excitations in a magnetically ordered system (magnons) and the magnetic flux quanta formed in a superconductor (fluxons).
- O. V. Dobrovolskiy
- , R. Sachser
- & A. V. Chumak
-
Letter |
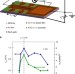 Direct evidence of ferromagnetism in a quantum anomalous Hall system
Direct evidence of ferromagnetism in a quantum anomalous Hall system
Long-range ferromagnetic order in co-doped topological insulator thin films and their typical ferromagnetic domain behaviour is directly evidenced by low-temperature magnetic force microscopy.
- Wenbo Wang
- , Yunbo Ou
- & Weida Wu
-
Letter |
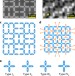 Classical topological order in the kinetics of artificial spin ice
Classical topological order in the kinetics of artificial spin ice
Experiments on the Shakti geometry of artificial spin ice show that its low-energy excitations are topologically protected, and that an emergent classical topological order influences the ergodicity and equilibration of this nanomagnetic system.
- Yuyang Lao
- , Francesco Caravelli
- & Peter Schiffer
-
Article |
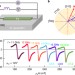 Emergence of anisotropic Gilbert damping in ultrathin Fe layers on GaAs(001)
Emergence of anisotropic Gilbert damping in ultrathin Fe layers on GaAs(001)
The Gilbert damping constant, a fundamental parameter to describe magnetization dynamics, is an isotropic scalar for most magnetic materials. Now, at a metal/semiconductor interface, the emergence of anisotropic magnetic damping has been observed.
- L. Chen
- , S. Mankovsky
- & C. H. Back
-
-
-
Article |
 Exploring the ferromagnetic behaviour of a repulsive Fermi gas through spin dynamics
Exploring the ferromagnetic behaviour of a repulsive Fermi gas through spin dynamics
Can short-range repulsion alone bring a system into the ferromagnetic phase? The question is explored by investigating the spin dynamics in a resonantly interacting ultracold Fermi gas, and a Stoner-like ferromagnetic instability is observed.
- G. Valtolina
- , F. Scazza
- & G. Roati
-
Commentary |
 Deliberate exotic magnetism via frustration and topology
Deliberate exotic magnetism via frustration and topology
Introduced originally to mimic the unusual, frustrated behaviour of spin ice pyrochlores, artificial spin ice can be realized in odd, dedicated geometries that open the door to new manifestations of a higher level of frustration.
- Cristiano Nisoli
- , Vassilios Kapaklis
- & Peter Schiffer
-
Letter |
 Real-time confinement following a quantum quench to a non-integrable model
Real-time confinement following a quantum quench to a non-integrable model
Confinement plays an important role in many-body physics from high energy to condensed matter. New results show that it strongly affects the non-equilibrium dynamics after a quantum quench with possible implications from ultracold atoms to QCD.
- Marton Kormos
- , Mario Collura
- & Pasquale Calabrese
-
Article |
 Supercurrent in a room-temperature Bose–Einstein magnon condensate
Supercurrent in a room-temperature Bose–Einstein magnon condensate
Studies of supercurrent phenomena, such as superconductivity and superfluidity, are usually restricted to cryogenic temperatures, but evidence suggests that a magnon supercurrent can be excited in a Bose–Einstein magnon condensate at room temperature.
- Dmytro A. Bozhko
- , Alexander A. Serga
- & Burkard Hillebrands
-
Letter |
 Ultra-low magnetic damping of a metallic ferromagnet
Ultra-low magnetic damping of a metallic ferromagnet
Materials with low magnetic damping are important for a range of applications but are typically insulating, which limits their use. Thanks to a unique feature of the band structure, similar levels of damping can now be achieved in a metallic alloy.
- Martin A. W. Schoen
- , Danny Thonig
- & Justin M. Shaw
-
Letter |
 Controllable 0–π Josephson junctions containing a ferromagnetic spin valve
Controllable 0–π Josephson junctions containing a ferromagnetic spin valve
Josephson junctions incorporating ferromagnetic spin valves are shown to be switchable between the 0 and π states, opening up interesting wider implications for possible devices.
- E. C. Gingrich
- , Bethany M. Niedzielski
- & Norman O. Birge
-
Article |
 Long-range p–d exchange interaction in a ferromagnet–semiconductor hybrid structure
Long-range p–d exchange interaction in a ferromagnet–semiconductor hybrid structure
Exchange interactions are typically short-ranged as they depend on wavefunction overlap, but a long-ranged exchange is now seen in a hybrid ferromagnet–semiconductor system, which may be mediated by elliptically polarized phonons.
- V. L. Korenev
- , M. Salewski
- & M. Bayer
-
-
Letter |
 Modulated magnetism in PrPtAl
Modulated magnetism in PrPtAl
A comprehensive experimental investigation of a PrPtAl single crystal concludes that it displays modulated magnetic order driven by quantum critical phenomena.
- Gino Abdul-Jabbar
- , Dmitry A. Sokolov
- & Andrew D. Huxley
-
Letter |
 Dynamics and inertia of skyrmionic spin structures
Dynamics and inertia of skyrmionic spin structures
Understanding the motion of magnetic skyrmions is essential if they are to be used as information carriers in devices. It is now shown that topological confinement endows the skyrmions with an unexpectedly large mass, which plays a key role in their dynamics.
- Felix Büttner
- , C. Moutafis
- & S. Eisebitt
-
-
News & Views |
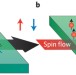 SHE's electric
SHE's electric
The origins of the spin Hall effect are difficult to probe, largely because experiments typically characterize electrons near the Fermi surface. Quantum tunnelling spectroscopy now provides access to its energy dependence.
- Kyoung-Whan Kim
- & Hyun-Woo Lee
-
Letter |
 Spin Hall effect tunnelling spectroscopy
Spin Hall effect tunnelling spectroscopy
The spin Hall effect, which arises from the spin–orbit interaction, is expected to be energy dependent, but experiments typically only characterize electrons near the Fermi surface. A tunnelling spectroscopy method has now been developed to probe the energy dependence.
- Luqiao Liu
- , Ching-Tzu Chen
- & J. Z. Sun
-
-
News & Views |
 Giving directions
Giving directions
The Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction — the mechanism behind weak ferromagnetism — has been difficult to probe experimentally. Now, significant progress is reported that has important implications for a wide range of magnetic phenomena.
- Chong Der Hu
-
Letter |
 Measuring the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in a weak ferromagnet
Measuring the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in a weak ferromagnet
Oxygen-mediated superexchange (or Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya) interactions result in weak ferromagnetism in oxides. A method based on the interference of synchrotron X-ray radiation is now shown to enable the determination of the sign of the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in the prototypical weak ferromagnet iron borate.
- V. E. Dmitrienko
- , E. N. Ovchinnikova
- & M. I. Katsnelson
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic moments under stress
Magnetic moments under stress
Most multiferroic materials are antiferromagnets, yet ferromagnetism can be induced in bismuth ferrite by substrate-induced strain. Strain is now shown to afford useful control of the orientation of magnetic moments in the multiferroics.
- Annemieke M. Mulders
-
Article |
 Fractional spinon excitations in the quantum Heisenberg antiferromagnetic chain
Fractional spinon excitations in the quantum Heisenberg antiferromagnetic chain
Magnetic excitations, or spinons, in a quasi-one-dimensional quantum magnet are investigated in an inelastic neutron-scattering experiment. The measurements confirm the existence of theoretically predicted higher-order spinons.
- Martin Mourigal
- , Mechthild Enderle
- & Henrik M. Rønnow
-
News & Views |
 Graphene gets molecules into order
Graphene gets molecules into order
Small metal-free organic molecules on an epitaxial graphene monolayer are shown to receive a local magnetic moment from the substrate. This magnetic moment survives when many molecules combine to form a layer, with some indication of long-range ferromagnetic order.
- Friedrich Reinert
-
Letter |
 Dirac-fermion-mediated ferromagnetism in a topological insulator
Dirac-fermion-mediated ferromagnetism in a topological insulator
Doping a topological insulator with manganese makes it magnetic. Moreover, decreasing the concentration of Dirac fermions in a Mn-doped topological insulator with an electric field increases the strength of its magnetic characteristics—a trait that could be valuable to the use of topological insulators in the development of spintronics.
- Joseph G. Checkelsky
- , Jianting Ye
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Letter |
 Equal-spin Andreev reflection and long-range coherent transport in high-temperature superconductor/half-metallic ferromagnet junctions
Equal-spin Andreev reflection and long-range coherent transport in high-temperature superconductor/half-metallic ferromagnet junctions
The penetration of a superconducting current from a superconductor into a half-metallic ferromagnet is usually forbidden. Resonances in the conductance spectra of superconductor/half-metal heterostructures suggest this restriction is lifted by the occurrence of unconventional equal-spin Andreev reflection.
- C. Visani
- , Z. Sefrioui
- & Javier E. Villegas
-
Article |
 Spin and valley quantum Hall ferromagnetism in graphene
Spin and valley quantum Hall ferromagnetism in graphene
The extra states sometimes observed in graphene’s quantum Hall characteristics have been presumed to be the result of broken SU(4) symmetry. Magnetotransport measurements of high-quality graphene in a tilted magnetic field finally prove this is indeed the case.
- A. F. Young
- , C. R. Dean
- & P. Kim
-
Article |
 Electric-field-induced ferromagnetic resonance excitation in an ultrathin ferromagnetic metal layer
Electric-field-induced ferromagnetic resonance excitation in an ultrathin ferromagnetic metal layer
Ferromagnetic resonance excitations offer a means to coherently manipulate the spin dynamics of spintronic devices and systems. A demonstration of the ability to control these excitations with electric fields alone could drastically reduce the power consumption of these devices.
- Takayuki Nozaki
- , Yoichi Shiota
- & Yoshishige Suzuki
-
Article |
 Experimental observation of the optical spin transfer torque
Experimental observation of the optical spin transfer torque
Spin transfer torque—the transfer of angular momentum from a spin-polarized current to a ferromagnet’s magnetization—has already found commercial application in memory devices, but the underlying physics is still not fully understood. Researchers now demonstrate the crucial role played by the polarization of the laser light that generates the current; a subtle effect only evident when isolated from other influences such as heating.
- P. Němec
- , E. Rozkotová
- & T. Jungwirth

 Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs
Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs