Featured
-
-
Article |
 Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Copper-based and iron-based compounds exhibit an interplay between magnetism and superconductivity. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional oxide heterostructures, where a spatially varying superconducting order is demonstrated at the EuO/KTaO3 interface.
- Xiangyu Hua
- , Zimeng Zeng
- & Xianhui Chen
-
News & Views |
 Through the slopes of a light-induced phase transition
Through the slopes of a light-induced phase transition
The integration of theory and experiment makes possible tracking the slow evolution of a photodoped Mott insulator to a distinct non-equilibrium metallic phase under the influence of electron-lattice coupling.
- Denitsa R. Baykusheva
-
Article |
 Picosecond volume expansion drives a later-time insulator–metal transition in a nano-textured Mott insulator
Picosecond volume expansion drives a later-time insulator–metal transition in a nano-textured Mott insulator
During a photoinduced phase transition, electronic rearrangements are usually faster than lattice ones. Time-resolved measurements now show that the insulator-to-metal transition in a thin-film Mott insulator is preceded by lattice reconfiguration.
- Anita Verma
- , Denis Golež
- & Andrej Singer
-
Article |
 Observation of possible excitonic charge density waves and metal–insulator transitions in atomically thin semimetals
Observation of possible excitonic charge density waves and metal–insulator transitions in atomically thin semimetals
The mechanism of charge density wave formation has been hard to explain due to accompanying structural distortions. Now low-dimensional HfTe2 is revealed to host a purely electronic exitonic charge density wave driven by reduced screening effects.
- Qiang Gao
- , Yang-hao Chan
- & Peng Chen
-
News & Views |
 Electron spin finds a fresh excitation
Electron spin finds a fresh excitation
The Kondo effect — the screening of an impurity spin by conduction electrons — is a fundamental many-body effect. However, recent experiments combined with simulations have caused a long-standing model system for the single-atom Kondo effect to fail.
- Jörg Kröger
- & Takashi Uchihashi
-
Research Briefing |
 Competing electron solids and electron fluids in the moiré atomic limit
Competing electron solids and electron fluids in the moiré atomic limit
Local thermodynamic measurements of a twisted transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructure reveal competition between unconventional charge order and Hofstadter states. This results from the presence of both flat and dispersive electronic bands, whose energetic ordering can be experimentally tuned.
-
Article |
 Scaling behaviour and control of nuclear wrinkling
Scaling behaviour and control of nuclear wrinkling
Wrinkling of cell nuclei is associated with disease. During development, the nucleus behaves like a sheet of paper and the wrinkling amplitude can be manipulated without changing its pattern.
- Jonathan A. Jackson
- , Nicolas Romeo
- & Jasmin Imran Alsous
-
Article |
 Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
The boson peak refers to an excess in the phonon density of states seen in three-dimensional amorphous materials. Helium-atom scattering experiments have now revealed a boson peak in a two-dimensional material, too, at a frequency similar to that of the bulk material.
- Martin Tømterud
- , Sabrina D. Eder
- & Bodil Holst
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional Shiba lattices as a possible platform for crystalline topological superconductivity
Two-dimensional Shiba lattices as a possible platform for crystalline topological superconductivity
One-dimensional chains of magnetic adatoms on the surface of a superconductor have been claimed to host topological states. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional systems.
- Martina O. Soldini
- , Felix Küster
- & Titus Neupert
-
Article |
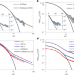 Signature of collective elastic glass physics in surface-induced long-range tails in dynamical gradients
Signature of collective elastic glass physics in surface-induced long-range tails in dynamical gradients
Large-system molecular dynamics simulations of films of glass-forming polymers reveal spatially long-range tails of interface-driven gradients of the glass transition temperature, suggestive of a combined local caging and long-range collective elasticity origin of relaxation and vitrification in glass-forming liquids.
- Asieh Ghanekarade
- , Anh D. Phan
- & David S. Simmons
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional long-range uniaxial order in three-dimensional active fluids
Two-dimensional long-range uniaxial order in three-dimensional active fluids
Bulk active fluids are unstable because activity destroys long-range ordering. Now, a model of 3D active liquids shows that stable states can form at fluid–fluid surfaces.
- Ananyo Maitra
-
News & Views |
 Freeze in or breeze out
Freeze in or breeze out
Phase-change processes, such as condensation or freezing, are known to compromise a surface’s water-repelling capability. It now turns out that tuning the freezing conditions can enable the spontaneous expulsion of water droplets.
- Jonathan B. Boreyko
-
Article |
 Polymorphic crystalline wetting layers on crystal surfaces
Polymorphic crystalline wetting layers on crystal surfaces
Premelting refers to the formation of a thin liquid film on a crystal’s surface before it properly melts. Now, a similar mechanism is shown to occur before solid–solid transitions in colloidal crystals: the formation of a polymorphic crystalline layer.
- Xipeng Wang
- , Bo Li
- & Yilong Han
-
News & Views |
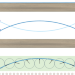 Nanoscale spin waves get excited
Nanoscale spin waves get excited
Disturbances in the orientation of magnetization in a magnet can propagate as spin waves or magnons. A design that makes it possible to optically excite nanoscale spin waves offers a route to developing miniaturized spin-based devices.
- Akashdeep Kamra
- & Lina G. Johnsen
-
Article |
 Antiferromagnetic metal phase in an electron-doped rare-earth nickelate
Antiferromagnetic metal phase in an electron-doped rare-earth nickelate
Films of the correlated oxide NdNiO3 form a metallic antiferromagnetic phase that can be identified using electrical currents, raising the prospect of applications in spintronics.
- Qi Song
- , Spencer Doyle
- & Julia A. Mundy
-
Article |
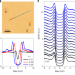 Evidence for chiral superconductivity on a silicon surface
Evidence for chiral superconductivity on a silicon surface
Adatoms on the surface of silicon can create two-dimensional superconductivity, the order parameter symmetry of which is currently not known. Now, evidence suggests it might be a topological chiral d-wave state.
- F. Ming
- , X. Wu
- & H. H. Weitering
-
Letter |
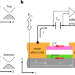 Laughlin charge pumping in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Laughlin charge pumping in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Quantized charge pumping is a hallmark of topological phases. Now, this effect is observed in the quantum anomalous Hall regime.
- Minoru Kawamura
- , Masataka Mogi
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
News & Views |
 Intercalation tailors superconductors
Intercalation tailors superconductors
Making monolayer superconductors creates interesting effects, but often decreases the transition temperature compared to 3D materials. Instead, intercalating molecules into a layered superconductor tailors the superconductivity with fewer trade-offs.
- Mark T. Edmonds
-
Article |
 Charge mosaics on contact-electrified dielectrics result from polarity-inverting discharges
Charge mosaics on contact-electrified dielectrics result from polarity-inverting discharges
Under certain conditions, contact electrification can lead to heterogeneous surface charge distributions—charge mosaics. Experiments and theory now show that these arise from electrostatic discharges between disjoining surfaces.
- Yaroslav I. Sobolev
- , Witold Adamkiewicz
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article |
 Exact solutions for the wrinkle patterns of confined elastic shells
Exact solutions for the wrinkle patterns of confined elastic shells
Wrinkling happens because of mechanical instabilities arising from length mismatches. A theory now describes wrinkling in confined elastic shells and is expected to be relevant for the controlled design of complex wrinkle patterns.
- Ian Tobasco
- , Yousra Timounay
- & Eleni Katifori
-
Letter |
 Coherence enhancement of solid-state qubits by local manipulation of the electron spin bath
Coherence enhancement of solid-state qubits by local manipulation of the electron spin bath
Nitrogen vacancy centres close to the surface of diamonds are a key component of quantum sensing technologies. Using an atomic force microscope to manipulate the surface electrostatic environment can significantly improve the sensing performance.
- Wentian Zheng
- , Ke Bian
- & Ying Jiang
-
Letter |
 Topology-driven surface patterning of liquid spheres
Topology-driven surface patterning of liquid spheres
The isotropy of a spherical droplet’s surface causes uniform distribution of adsorbed molecules. However, wrapping the droplet by a crystalline monolayer induces structural defects, enabling temperature-controllable positioning of adsorbates.
- Subhomoy Das
- , Alexander V. Butenko
- & Eli Sloutskin
-
Letter |
 Intrinsic magnetism in superconducting infinite-layer nickelates
Intrinsic magnetism in superconducting infinite-layer nickelates
Measurements of four different infinite-layer nickelates show that magnetic behaviour coexists with superconductivity. This is different from what is seen in cuprates, giving a strong distinction between the two classes of oxide superconductors.
- Jennifer Fowlie
- , Marios Hadjimichael
- & Andreas Suter
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous charging affects the motion of sliding drops
Spontaneous charging affects the motion of sliding drops
The sliding of a water drop on a surface is traditionally described by taking flow within the drop and contact-line friction into account. Now, evidence shows that electric forces can also substantially affect water-on-surface sliding dynamics.
- Xiaomei Li
- , Pravash Bista
- & Hans-Jürgen Butt
-
Article |
 Cyclotron resonance overtones and near-field magnetoabsorption via terahertz Bernstein modes in graphene
Cyclotron resonance overtones and near-field magnetoabsorption via terahertz Bernstein modes in graphene
Electrons in an external magnetic field absorb electromagnetic radiation via cyclotron resonance. Deviations from this behaviour in the form of overtone resonances due to ultraslow magnetoplasmonic excitations are now reported for graphene.
- D. A. Bandurin
- , E. Mönch
- & S. D. Ganichev
-
-
Article |
 Nanoscale Turing patterns in a bismuth monolayer
Nanoscale Turing patterns in a bismuth monolayer
Macroscale patterns seen in biological systems such as animal coats or skin can be described by Turing’s reaction–diffusion theory. Now Turing patterns are shown to also exist in bismuth monolayers, an exemplary nanoscale atomic system.
- Yuki Fuseya
- , Hiroyasu Katsuno
- & Aharon Kapitulnik
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 No pressure, you have time
No pressure, you have time
Surface scientists love a good vacuum. The reason for this is captured by the work of Irving Langmuir and the little-known unit bearing his name, explains Daniel Payne.
- Daniel T. Payne
-
Letter |
 A hydrodynamic instability drives protein droplet formation on microtubules to nucleate branches
A hydrodynamic instability drives protein droplet formation on microtubules to nucleate branches
Branching microtubule nucleation plays a major part in cellular processes driving eukaryotic cell division. A combination of microscopy approaches and hydrodynamic theory is used to show how the condensed protein TPX2 on a microtubule reorganizes according to the Rayleigh–Plateau instability.
- Sagar U. Setru
- , Bernardo Gouveia
- & Sabine Petry
-
Article |
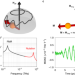 Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial dynamics are observed in a ferromagnet. Specifically, a nutation is seen on top of the usual spin precession that has a lifetime on the order of 10 picoseconds.
- Kumar Neeraj
- , Nilesh Awari
- & Stefano Bonetti
-
Article |
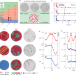 Morphology selection kinetics of crystallization in a sphere
Morphology selection kinetics of crystallization in a sphere
The authors investigate the role of spherical confinement and curvature-induced topological defects on the crystallization of charged colloids. They conclude that crystallization in spherical confinement is due to a combination of thermodynamics and kinetic pathways.
- Yanshuang Chen
- , Zhenwei Yao
- & Peng Tan
-
Letter |
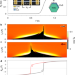 Zero-bias peaks at zero magnetic field in ferromagnetic hybrid nanowires
Zero-bias peaks at zero magnetic field in ferromagnetic hybrid nanowires
By incorporating a ferromagnetic layer in their superconductor–semiconductor nanowire hybrid device, Vaitiekėnas et al. show that zero-bias peaks—potential Majorana bound states—can be induced without an external magnetic field.
- S. Vaitiekėnas
- , Y. Liu
- & C. M. Marcus
-
Letter |
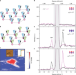 Direct observation of two-dimensional magnons in atomically thin CrI3
Direct observation of two-dimensional magnons in atomically thin CrI3
Magnons are collective excitations that dictate many of a magnet’s low-temperature properties. By means of Raman scattering, the magnon spectra of CrI3 are measured in the monolayer limit.
- John Cenker
- , Bevin Huang
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Article |
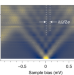 Resonant Andreev reflections probed by photon-assisted tunnelling at the atomic scale
Resonant Andreev reflections probed by photon-assisted tunnelling at the atomic scale
Scanning tunnelling microscopy is enhanced by microwave radiation that allows photon-assisted tunnelling processes. This technique is demonstrated on impurity states in a superconductor.
- Olof Peters
- , Nils Bogdanoff
- & Katharina J. Franke
-
Article |
 Mechanochemical symmetry breaking during morphogenesis of lateral-line sensory organs
Mechanochemical symmetry breaking during morphogenesis of lateral-line sensory organs
Symmetry breaking is essential for polarization of cells and generation of left–right body asymmetry. Here the authors investigate the arrangement of hair cells in zebrafish and show that mirror-symmetric patterns arise from a combination of biochemical and mechanical symmetry-breaking events.
- A. Erzberger
- , A. Jacobo
- & A. J. Hudspeth
-
Letter |
 Moiré engineering of electronic phenomena in correlated oxides
Moiré engineering of electronic phenomena in correlated oxides
Moiré engineering has rapidly gained currency as a means to manipulate electronic states of matter in van der Waals heterostructures. Now, the feat is achieved in epitaxially grown oxide heterostructures, thus opening up fresh opportunities for strongly correlated electronic systems.
- Xinzhong Chen
- , Xiaodong Fan
- & Changgan Zeng
-
Letter |
 Proximity-induced superconducting gap in the quantum spin Hall edge state of monolayer WTe2
Proximity-induced superconducting gap in the quantum spin Hall edge state of monolayer WTe2
One way of producing Majorana fermions for topological quantum computing is to induce superconductivity in other topological states. Here, the proximity effect does this for the quantum spin Hall effect state in a 2D material.
- Felix Lüpke
- , Dacen Waters
- & Benjamin M. Hunt
-
Letter |
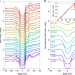 Atomic line defects and zero-energy end states in monolayer Fe(Te,Se) high-temperature superconductors
Atomic line defects and zero-energy end states in monolayer Fe(Te,Se) high-temperature superconductors
Bound states at zero energy are observed at the ends of a line defect formed of atomic vacancies on the surface of a high-temperature superconductor. This indicates the possible presence of Majorana modes.
- Cheng Chen
- , Kun Jiang
- & Jian Wang
-
Letter |
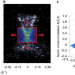 Spectromicroscopic measurement of surface and bulk band structure interplay in a disordered topological insulator
Spectromicroscopic measurement of surface and bulk band structure interplay in a disordered topological insulator
The authors develop a high-spatial-resolution photoemission technique to show variation of the energy of the Dirac point of approximately 50 meV. They also find an interplay between bulk and surface states.
- Erica Kotta
- , Lin Miao
- & L. Andrew Wray
-
Article |
 Strong correlations and orbital texture in single-layer 1T-TaSe2
Strong correlations and orbital texture in single-layer 1T-TaSe2
The electrons that contribute to the Mott insulator state in single-layer 1T-TaSe2 are shown to also have a rich variation in their orbital occupation. As more layers are added, both the insulating state and orbital texture weaken.
- Yi Chen
- , Wei Ruan
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
News & Views |
 Model oddity
Model oddity
A model fluid comprising rotating magnetic particles behaves according to the equations of hydrodynamics, but for a few key differences due to broken mirror symmetry. The resulting active chiral fluid is characterized by parity-odd Hall viscosity.
- Alexander Abanov
-
Letter |
 Disorder-induced multifractal superconductivity in monolayer niobium dichalcogenides
Disorder-induced multifractal superconductivity in monolayer niobium dichalcogenides
Disorder present in monolayer NbSe2 is found to be able to enhance its superconductivity. A systematic study reveals the origin—disorder-induced multifractality of the electron wavefunctions strengthens the local interactions.
- Kun Zhao
- , Haicheng Lin
- & Shuai-Hua Ji
-
Letter |
 Magnetic resonance imaging of single atoms on a surface
Magnetic resonance imaging of single atoms on a surface
The authors demonstrate that individual atoms on a surface can be detected and distinguished from each other with subångström resolution using the electron spin resonance.
- Philip Willke
- , Kai Yang
- & Christopher P. Lutz
-
Article |
 Scaling laws indicate distinct nucleation mechanisms of holes in the nuclear lamina
Scaling laws indicate distinct nucleation mechanisms of holes in the nuclear lamina
The structural integrity of a cell’s nucleus is maintained by a polymer network known as the nuclear lamina. A simple biophysical theory reveals two regimes by which this network can rupture, depending on the structure of the nuclear envelope.
- Dan Deviri
- , Charlotte R. Pfeifer
- & Samuel A. Safran
-
Article |
 Strain-tunable magnetism at oxide domain walls
Strain-tunable magnetism at oxide domain walls
Ferromagnetism is observed at ferroelastic domain walls in strontium titanate and its heterostructures with other oxides. Applying strain can reverse the magnetism. This suggests the possibility of device engineering using domain walls.
- D. V. Christensen
- , Y. Frenkel
- & B. Kalisky
-
Article |
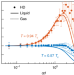 The Goldstone mode and resonances in the fluid interfacial region
The Goldstone mode and resonances in the fluid interfacial region
Accurately capturing both microscopic and mesoscopic properties of fluid–gas interfaces is a long-standing challenge. Now, a microscopic theory of correlation functions that can be scaled up to explain mesoscopic surface tension phenomena is put forward.
- A. O. Parry
- & C. Rascón
-
Letter |
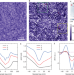 Visualization of the periodic modulation of Cooper pairing in a cuprate superconductor
Visualization of the periodic modulation of Cooper pairing in a cuprate superconductor
A periodic pattern of Cooper pairs is observed at the atomic scale and is shown to be correlated with the local strength of the superconductivity. This reveals a new interplay between different ordered states in the cuprates.
- Wei Ruan
- , Xintong Li
- & Yayu Wang
-
Letter |
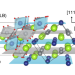 Complex magnetic order in nickelate slabs
Complex magnetic order in nickelate slabs
Surprising phenomena are known to occur when magnetic systems are confined to low-dimensional geometries. A resonant X-ray scattering study of NdNiO3 slabs reveals a crossover between different magnetic ground states as a function of thickness.
- M. Hepting
- , R. J. Green
- & E. Benckiser

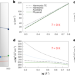 Bending rigidity, sound propagation and ripples in flat graphene
Bending rigidity, sound propagation and ripples in flat graphene All the colours of the rainbow
All the colours of the rainbow Slippy nitty-gritty
Slippy nitty-gritty