Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Cooling efficiency in thermoelectric devices decreases considerably at lower temperatures. Now thermoelectric cooling at cryogenic temperatures is directly imaged in a van der Waals semimetal.
- T. Völkl
- , A. Aharon-Steinberg
- & E. Zeldov
-
Article |
 Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Spin polarons, bound states of a doped carrier and a spin flip excitation, are observed in a transition metal moiré bilayer.
- Zui Tao
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Article
| Open Access The interplay of field-tunable strongly correlated states in a multi-orbital moiré system
The interplay of field-tunable strongly correlated states in a multi-orbital moiré system
Heterostructures of transition metal dichalcogenides are known to simulate the triangular-lattice Hubbard model. Now, by combining a monolayer and bilayer of different materials, this idea is extended to multi-orbital Hubbard models.
- Aidan J. Campbell
- , Valerio Vitale
- & Brian D. Gerardot
-
Article |
 Robust continuous time crystal in an electron–nuclear spin system
Robust continuous time crystal in an electron–nuclear spin system
Time crystals spontaneously produce periodic oscillations that are robust to perturbations. A time crystal phase with a long coherence time has now been produced using the electron and nuclear spins of a semiconductor sample.
- A. Greilich
- , N. E. Kopteva
- & M. Bayer
-
Editorial |
 Twenty years of 2D materials
Twenty years of 2D materials
Two-dimensional crystals have revolutionized fundamental research across a staggering range of disciplines. We take stock of the progress gained after twenty years of work.
-
Article |
 Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Quantum-correlated photons typically characterize strongly nonlinear quantum emitters. A two-photon correlation spectroscopy method now provides a powerful probe of weakly nonlinear many-body quantum systems.
- Lorenzo Scarpelli
- , Cyril Elouard
- & Thomas Volz
-
Article |
 Realization of the Haldane Chern insulator in a moiré lattice
Realization of the Haldane Chern insulator in a moiré lattice
The Haldane model is a paradigmatic example of topological behaviour but has not previously been implemented in condensed-matter experiments. Now a moiré bilayer is shown to realize this model with the accompanying quantized transport response.
- Wenjin Zhao
- , Kaifei Kang
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
News & Views |
 When excitons crystallize
When excitons crystallize
Semiconducting dipolar excitons — bound states of electrons and holes — in artificial moiré lattices constitute a promising condensed matter system to explore the phase diagram of strongly interacting bosonic particles.
- Nadine Leisgang
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Time-resolved measurements show that coupling between electrons and phonons in lead halide perovskites can mediate attractive interactions between excitons, although the interaction strength depends on the specific material.
- Nuri Yazdani
- , Maryna I. Bodnarchuk
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
News & Views |
 Spatial correlations of charge noise captured
Spatial correlations of charge noise captured
Measurements of two neighbouring silicon-based qubits show that the charge noise they each experience is correlated, suggesting a common origin. Understanding these correlations is crucial for performing error correction in these systems.
- Łukasz Cywiński
-
Article |
 Strong phonon softening and avoided crossing in aliovalence-doped heavy-band thermoelectrics
Strong phonon softening and avoided crossing in aliovalence-doped heavy-band thermoelectrics
Aliovalent doping affects the electrical properties of semiconductors, but its effect on phonons is unclear. Now, strong softening and deceleration of phonons, causing a significant reduction in lattice thermal conductivity, is reported for Hf-doped NbFeSb.
- Shen Han
- , Shengnan Dai
- & Tiejun Zhu
-
Article |
 Josephson diode effect derived from short-range coherent coupling
Josephson diode effect derived from short-range coherent coupling
The behaviour of a superconductor can be altered by changing its symmetry properties. Coherently coupling two Josephson junctions breaks time-reversal and inversion symmetries, giving rise to a device with a controllable superconducting diode effect.
- Sadashige Matsuo
- , Takaya Imoto
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article |
 Nanoscale electrostatic control in ultraclean van der Waals heterostructures by local anodic oxidation of graphite gates
Nanoscale electrostatic control in ultraclean van der Waals heterostructures by local anodic oxidation of graphite gates
Precise control of electrons in two-dimensional materials has been limited by fabrication techniques for local gates that introduce disorder. Now, a technique allows patterning of sub-100 nm features and fabrication of very clean interfaces.
- Liam A. Cohen
- , Noah L. Samuelson
- & Andrea F. Young
-
Article |
 Dipole ladders with large Hubbard interaction in a moiré exciton lattice
Dipole ladders with large Hubbard interaction in a moiré exciton lattice
Strong dipole–dipole interactions between excitons in a moiré superlattice create a manifestation of the Bose–Hubbard model with a ground state similar to a Mott insulator.
- Heonjoon Park
- , Jiayi Zhu
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Article |
 Intrinsic spin Hall torque in a moiré Chern magnet
Intrinsic spin Hall torque in a moiré Chern magnet
Switching of magnetic behaviour is one of the main ideas that drives spintronics. Now, magnetic switching via spin-orbit torque is shown in a moiré bilayer, introducing a platform for spintronic applications.
- C. L. Tschirhart
- , Evgeny Redekop
- & A. F. Young
-
News & Views |
 Doped silicon’s challenging behaviour
Doped silicon’s challenging behaviour
Despite its technological importance, there remain gaps in our understanding of silicon’s electronic behaviour, especially at low temperatures. Measurements close to a metal–insulator transition show signs of a collective many-body quantum state.
- Mark Lee
-
Perspective |
 In search of Majorana
In search of Majorana
Majorana zero modes are emergent excitations in topological superconductors. This Perspective introduces the physics of these modes, recaps the recent history of the experimental search for them and discusses the future prognosis for success.
- Sankar Das Sarma
-
Article |
 Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
The quantum critical behaviour of a two-impurity Kondo model variant is observed in a system of hybrid-semiconductor islands that could provide a scalable platform for solid-state quantum simulation
- Winston Pouse
- , Lucas Peeters
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article |
 Ultrafast relaxation of lattice distortion in two-dimensional perovskites
Ultrafast relaxation of lattice distortion in two-dimensional perovskites
The ultrafast structural dynamics in 2D perovskites are an important part of their non-equilibrium properties. Now, their visualization reveals a light-induced reduction in the antiferro-distortion initiated by the electron–hole plasma.
- Hao Zhang
- , Wenbin Li
- & Aditya D. Mohite
-
Article |
 Coherent spin–valley oscillations in silicon
Coherent spin–valley oscillations in silicon
Established methods of controlling silicon spin qubits require high-frequency signals that can be difficult to implement for various reasons. Exploiting the coupling between spin and valley degrees of freedom provides an alternative approach.
- Xinxin Cai
- , Elliot J. Connors
- & John M. Nichol
-
Article |
 Correlated interlayer exciton insulator in heterostructures of monolayer WSe2 and moiré WS2/WSe2
Correlated interlayer exciton insulator in heterostructures of monolayer WSe2 and moiré WS2/WSe2
When independent layers of electrons and holes are in close proximity to each other, their Coulomb interaction allows them to pair into neutral bosons and form an insulating state. This phenomenon is reported in a heterostructure of 2D materials.
- Zuocheng Zhang
- , Emma C. Regan
- & Feng Wang
-
Letter |
 Broken-symmetry states at half-integer band fillings in twisted bilayer graphene
Broken-symmetry states at half-integer band fillings in twisted bilayer graphene
Correlated insulating states are common in twisted bilayer graphene when the density of carriers is close to an integer per moiré unit cell. Now, such states emerge at half-integer fillings and show signs of being spin or charge density waves.
- Saisab Bhowmik
- , Bhaskar Ghawri
- & U. Chandni
-
Letter |
 Dipolar excitonic insulator in a moiré lattice
Dipolar excitonic insulator in a moiré lattice
A heterostructure supports the equilibrium bound states of an electron and hole—excitons—that strongly interact with each other. This provides a platform for the quantum simulation of bosonic lattice models.
- Jie Gu
- , Liguo Ma
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Letter |
 Mott insulator of strongly interacting two-dimensional semiconductor excitons
Mott insulator of strongly interacting two-dimensional semiconductor excitons
A semiconductor platform for experimentally investigating the multiorbital Bose–Hubbard model with long-range interactions is demonstrated. The interactions between the excitons are strong enough to reach the Mott insulator regime.
- Camille Lagoin
- , Stephan Suffit
- & François Dubin
-
Article |
 Witnessing quantum correlations in a nuclear ensemble via an electron spin qubit
Witnessing quantum correlations in a nuclear ensemble via an electron spin qubit
Atoms in a semiconductor can have non-zero nuclear spins, creating a large ensemble with many quantum degrees of freedom. An electron spin coupled to the nuclei of a semiconductor quantum dot can witness the creation of entanglement within the ensemble.
- Dorian A. Gangloff
- , Leon Zaporski
- & Mete Atatüre
-
-
News & Views |
 Models and mountains
Models and mountains
A microscopy technique allows the identification of parameters in a paradigmatic model of condensed-matter physics.
- Isabel Guillamón
-
Letter |
 Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
The Hubbard model describes many fascinating phenomena, but relating it to complicated quantum materials is difficult. Now, atomic-resolution measurements can estimate the interaction parameters that appear in the model for real materials.
- Hongyuan Li
- , Shaowei Li
- & Feng Wang
-
-
-
Article |
 Quantum sensing of a coherent single spin excitation in a nuclear ensemble
Quantum sensing of a coherent single spin excitation in a nuclear ensemble
A single excitation in a semiconductor nuclear spin ensemble is detected with parts-per-million accuracy using the coupling between the ensemble and an electron-spin quantum dot.
- D. M. Jackson
- , D. A. Gangloff
- & M. Atatüre
-
News & Views |
When silicon is like a cuprate
Recent advances in spectroscopy give access to the decay time of excitations in disordered insulating silicon close to the metal–insulator transition, revealing similarities to high-temperature cuprate superconductors.
- Eduardo Miranda
-
Article |
 Electrically tunable correlated and topological states in twisted monolayer–bilayer graphene
Electrically tunable correlated and topological states in twisted monolayer–bilayer graphene
Stacking a monolayer and bilayer of graphene, with a small twist angle between them, creates a tunable platform where the physics of both twisted bilayer graphene and twisted double bilayer graphene can be realized.
- Shaowen Chen
- , Minhao He
- & Matthew Yankowitz
-
Letter |
 Symmetry breaking in twisted double bilayer graphene
Symmetry breaking in twisted double bilayer graphene
Transport measurements show that spontaneous symmetry breaking plays a crucial role in the correlated insulating and metallic states in twisted double bilayer graphene.
- Minhao He
- , Yuhao Li
- & Matthew Yankowitz
-
Article |
 Strong coupling and pressure engineering in WSe2–MoSe2 heterobilayers
Strong coupling and pressure engineering in WSe2–MoSe2 heterobilayers
High-quality WSe2–MoSe2 heterostructures support strong coupling between the two layers, which is associated with tight hybridization and effective charge separation. In these structures, the bands of the interlayer excitons can be pressure-engineered.
- Juan Xia
- , Jiaxu Yan
- & Zexiang Shen
-
Letter |
 Continuous monitoring of a trapped superconducting spin
Continuous monitoring of a trapped superconducting spin
A quasiparticle in Andreev levels was coupled to a superconducting microwave resonator and its spin was monitored in real time. This has potential applications in the readout of superconducting spin qubits and measurements of Majorana fermions.
- M. Hays
- , V. Fatemi
- & M. H. Devoret
-
Letter |
 Spin phase diagram of the interacting quantum Hall liquid
Spin phase diagram of the interacting quantum Hall liquid
The spin polarization of a quantum Hall system is determined by a spin-resolved tunnelling method. This technique shows a substantial regime where the weakly interacting composite fermion picture is not valid.
- H. M. Yoo
- , K. W. Baldwin
- & R. C. Ashoori
-
Letter |
 Emergence of criticality through a cascade of delocalization transitions in quasiperiodic chains
Emergence of criticality through a cascade of delocalization transitions in quasiperiodic chains
The localization properties of waves in the quasiperiodic chains described by the Aubry–André model and Fibonacci model are investigated. Passing from one model to the other, the system develops a cascade of delocalization transitions.
- V. Goblot
- , A. Štrkalj
- & O. Zilberberg
-
Letter |
 Strong photon coupling to the quadrupole moment of an electron in a solid-state qubit
Strong photon coupling to the quadrupole moment of an electron in a solid-state qubit
Coupling of the quadrupole moment of an electron in a triple quantum dot to photons has been predicted to be a good platform for reducing the effect of charge noise on the decoherence time of a qubit. Here, the authors create such a coupling.
- J. V. Koski
- , A. J. Landig
- & T. Ihn
-
Article |
 Photon-assisted tunnelling of zero modes in a Majorana wire
Photon-assisted tunnelling of zero modes in a Majorana wire
Majorana bound states at the end of nanowires may be used for quantum computation if they can be coupled sufficiently strongly. Here, the Copenhagen lab show strong and tunable coupling, a step along the road towards devices.
- David M. T. van Zanten
- , Deividas Sabonis
- & Charles M. Marcus
-
News & Views |
 Correlated insulator by the slice
Correlated insulator by the slice
A layer-by-layer study of TaSe2 shows how this material becomes increasingly insulating as it thins to a monolayer. Scanning tunnelling microscopy reveals the electronic correlations underlying this insulator with atomic resolution.
- Katharina J. Franke
- & Felix von Oppen
-
Letter |
 Solids of quantum Hall skyrmions in graphene
Solids of quantum Hall skyrmions in graphene
The authors use spin waves to demonstrate that charged quantum Hall skyrmions exist away from integer filling. They also see evidence of several fractional skyrmion states.
- H. Zhou
- , H. Polshyn
- & A. F. Young
-
Letter |
 Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid in the edge channels of a quantum spin Hall insulator
Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid in the edge channels of a quantum spin Hall insulator
Scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy study of the conductive edge state in a two-dimensional topological insulator reveals the interplay of topology and electronic correlations.
- R. Stühler
- , F. Reis
- & R. Claessen
-
Letter |
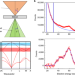 Vibrational spectroscopy at atomic resolution with electron impact scattering
Vibrational spectroscopy at atomic resolution with electron impact scattering
Conventional on-axis electron energy-loss spectroscopy can detect vibrational modes in crystals and amorphous solids at atomic resolution by isolating the specific signal from the background signal and the dipole contributions.
- Kartik Venkatraman
- , Barnaby D. A. Levin
- & Peter A. Crozier
-
Letter |
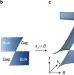 Photonic Weyl points due to broken time-reversal symmetry in magnetized semiconductor
Photonic Weyl points due to broken time-reversal symmetry in magnetized semiconductor
Photonic Weyl points—topologically chiral singularity points in three-dimensional momentum space—have been realized in a homogeneous non-reciprocal material without a crystal lattice structure.
- Dongyang Wang
- , Biao Yang
- & Shuang Zhang
-
News & Views |
A needle in a moiré stack
Spatially resolved measurements of twisted bilayer graphene reveal more details of the strongly correlated electrons.
- Adina Luican-Mayer
-
Letter |
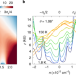 Large linear-in-temperature resistivity in twisted bilayer graphene
Large linear-in-temperature resistivity in twisted bilayer graphene
Transport measurements on twisted bilayer graphene show that a large linear-in-temperature increase in resistivity exists for many twist angles. This may have implications for the mechanism of superconductivity in this material.
- Hryhoriy Polshyn
- , Matthew Yankowitz
- & Andrea F. Young
-
Letter |
 Pairing states of composite fermions in double-layer graphene
Pairing states of composite fermions in double-layer graphene
It is shown that composite fermions in the fractional quantum Hall regime form paired states in double-layer graphene. Pairing between layers gives a phase similar to an exciton condensate and pairing within a layer may lead to non-abelian states.
- J. I. A. Li
- , Q. Shi
- & C. R. Dean

 Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier
Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier Topological breakdown
Topological breakdown Another twist in the tale
Another twist in the tale