News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Single-component superconductivity in UTe2 at ambient pressure
Single-component superconductivity in UTe2 at ambient pressure
The symmetry of the superconducting order parameter in UTe2 is still debated. Now ultrasound experiments suggest that the order parameter can only have one component.
- Florian Theuss
- , Avi Shragai
- & B. J. Ramshaw
-
Article |
 Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
The hybrid architecture of Andreev spin qubits made using semiconductor–superconductor nanowires means that supercurrents can be used to inductively couple qubits over long distances.
- Marta Pita-Vidal
- , Jaap J. Wesdorp
- & Christian Kraglund Andersen
-
-
-
Article
| Open Access Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes can occur when superconductivity arises in more than one band in a material and represent oscillation of the relative phases of the two superconducting condensates. Now, this mode is observed in Cd3As2, a Dirac semimetal.
- Joseph J. Cuozzo
- , W. Yu
- & Enrico Rossi
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Despite their potential device applications, experimental realizations of proximity-induced Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov states are rare. Now Josephson junctions based on a dilute magnetic topological insulator provide evidence of such a state.
- Pankaj Mandal
- , Soumi Mondal
- & Laurens W. Molenkamp
-
Article |
 Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
A mechanism for the phase transition of charge density wave states via the generation and proliferation of topological defects with opposite phase windings is demonstrated in a heavy-fermion superconductor.
- Anuva Aishwarya
- , Julian May-Mann
- & Vidya Madhavan
-
Article |
 Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Copper-based and iron-based compounds exhibit an interplay between magnetism and superconductivity. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional oxide heterostructures, where a spatially varying superconducting order is demonstrated at the EuO/KTaO3 interface.
- Xiangyu Hua
- , Zimeng Zeng
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
The standard current–phase relation in tunnel Josephson junctions involves a single sinusoidal term, but real junctions are more complicated. The effects of higher Josephson harmonics have now been identified in superconducting qubit devices.
- Dennis Willsch
- , Dennis Rieger
- & Ioan M. Pop
-
News & Views |
 Relaxation of a sensitive superconductor
Relaxation of a sensitive superconductor
Some exotic metals exhibit competing electronic states that can be influenced by small perturbations. Now, a study of a kagome superconductor shows that this competition is exquisitely sensitive to weak strain fields, providing insight into its anomalous electronic properties.
- Stephen D. Wilson
-
News & Views |
Pocket pairs in iron-based materials
Experiments with unprecedented energy and momentum resolution reveal the nature of the pairing symmetry in KFe2As2 and pave the way for a unified theoretical description of unconventional superconductivity in iron-based materials.
- Norman Mannella
-
Article |
 Nodal s± pairing symmetry in an iron-based superconductor with only hole pockets
Nodal s± pairing symmetry in an iron-based superconductor with only hole pockets
High-precision photoemission measurements determine that the superconducting pairing symmetry in KFe2As2 is the same as in other types of iron-based superconductors, despite having different features in the band structure.
- Dingsong Wu
- , Junjie Jia
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Article |
 Edge supercurrent reveals competition between condensates in a Weyl superconductor
Edge supercurrent reveals competition between condensates in a Weyl superconductor
How superconducting states with different order parameter symmetries can interact with each other is not well understood. Now, the edge mode of a Weyl superconductor serves as a probe for competing condensates.
- Stephan Kim
- , Shiming Lei
- & N. P. Ong
-
Article |
 Unconventional superconducting quantum criticality in monolayer WTe2
Unconventional superconducting quantum criticality in monolayer WTe2
Thermoelectric measurements show an unusual form of critical behaviour at the superconducting quantum phase transition in monolayer WTe2.
- Tiancheng Song
- , Yanyu Jia
- & Sanfeng Wu
-
Article |
 Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
A computational method capable of capturing the effects of electronic interactions and scattering can help interpret the vibrational reflectance measurements in superconducting and bad metals.
- Guglielmo Marchese
- , Francesco Macheda
- & Francesco Mauri
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
There is evidence that K3C60 can host a photo-induced superconducting state. Now, resonant excitation at low frequencies allows this phenomenon at room temperature and low pumping fluence.
- E. Rowe
- , B. Yuan
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Comment |
 Evolution of superconducting diodes
Evolution of superconducting diodes
Efficient superconducting diodes can be designed according to established physics. However, emerging concepts must be united with known mechanisms in order to unlock functionality in rectification and frequency conversion.
- P. J. W. Moll
- & V. B. Geshkenbein
-
Article |
 Bogoliubov quasiparticle on the gossamer Fermi surface in electron-doped cuprates
Bogoliubov quasiparticle on the gossamer Fermi surface in electron-doped cuprates
Observation of a faint Fermi surface inside the pseudogap of an electron-doped cuprate suggests that Cooper pairing is mediated by antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations.
- Ke-Jun Xu
- , Qinda Guo
- & Zhi-Xun Shen
-
News & Views |
 Three is the optimal number
Three is the optimal number
A trilayer copper oxide superconductor, which exhibits the highest superconducting critical temperature as a function of the number of copper–oxygen planes, is shown to have unusual doped hole distribution and interaction between the planes.
- Atsushi Fujimori
-
Article |
 Electronic origin of high superconducting critical temperature in trilayer cuprates
Electronic origin of high superconducting critical temperature in trilayer cuprates
Measurements of the electronic structure of a trilayer cuprate superconductor suggest that its high critical temperature is explained by the different doping levels of the layers. The combination of underdoped inner layer and overdoped outer layers supports superconductivity.
- Xiangyu Luo
- , Hao Chen
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Editorial |
 Party like it’s LK-99
Party like it’s LK-99
Claims of a room-temperature, ambient-pressure superconductor recently kicked up a storm on social media. As the dust settles, we take stock of what this experience can teach us.
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of finite-momentum pairing in a centrosymmetric bilayer
Evidence of finite-momentum pairing in a centrosymmetric bilayer
Cooper pairs that form with finite centre-of-mass momentum are rare. Now there is evidence that this can happen below the Pauli limit in a bilayer material.
- Dong Zhao
- , Lukas Debbeler
- & Jurgen Smet
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity from a melted insulator in Josephson junction arrays
Superconductivity from a melted insulator in Josephson junction arrays
Predictions of a quantum superconductor–insulator transition in Josephson junction arrays are not always borne out by experiments. Unexpectedly large thermal effects may explain why.
- S. Mukhopadhyay
- , J. Senior
- & A. P. Higginbotham
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional Shiba lattices as a possible platform for crystalline topological superconductivity
Two-dimensional Shiba lattices as a possible platform for crystalline topological superconductivity
One-dimensional chains of magnetic adatoms on the surface of a superconductor have been claimed to host topological states. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional systems.
- Martina O. Soldini
- , Felix Küster
- & Titus Neupert
-
News & Views |
 A qubit tames its environment
A qubit tames its environment
A real qubit is not an isolated unitary quantum system but is subject to noise from its environment. An experiment has now turned this interaction on its head, controlling the environment using the qubit itself.
- Bayan Karimi
- & Jukka P. Pekola
-
News & Views |
 Trapped magnetic flux in superconducting hydrides
Trapped magnetic flux in superconducting hydrides
Hydrides are promising for harnessing high-temperature superconductivity, albeit with the need of extreme pressures. New experimental protocols establish a magnetic route to detect and study superconductivity compatible with high-pressure devices.
- Swee K. Goh
- , Wei Zhang
- & King Yau Yip
-
Article |
 The emergence of global phase coherence from local pairing in underdoped cuprates
The emergence of global phase coherence from local pairing in underdoped cuprates
How the superconducting state emerges from a Mott insulator in cuprate superconductors is still not fully understood. Now, the spatial extent of a chequerboard charge order with internal stripes is shown to be crucial.
- Shusen Ye
- , Changwei Zou
- & Yayu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic flux trapping in hydrogen-rich high-temperature superconductors
Magnetic flux trapping in hydrogen-rich high-temperature superconductors
Measurements of the trapped magnetic flux in hydrides at high pressure provide further evidence that these materials are superconducting at high temperatures.
- V. S. Minkov
- , V. Ksenofontov
- & M. I. Eremets
-
Editorial |
 Strive towards sustainability
Strive towards sustainability
Exacerbated by the impacts of climate change and the recent energy crisis, concentrated efforts towards more sustainable research have become matters of urgency, in particular for large-scale accelerator complexes and light sources.
-
Article |
 Dirac revivals drive a resonance response in twisted bilayer graphene
Dirac revivals drive a resonance response in twisted bilayer graphene
Phase transitions during which electrons recover their Dirac nature are shown to produce a spin resonance response that allows the characterization of spin and valley couplings in twisted bilayer graphene.
- Erin Morissette
- , Jiang-Xiazi Lin
- & J. I. A. Li
-
Article |
 Unidirectional electron–phonon coupling in the nematic state of a kagome superconductor
Unidirectional electron–phonon coupling in the nematic state of a kagome superconductor
The observation of unidirectional electron–phonon coupling in a kagome lattice material suggests a strong link between superconductivity and the nematic state in that class of materials.
- Ping Wu
- , Yubing Tu
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article |
 Interdependent superconducting networks
Interdependent superconducting networks
Interdependent networks display many interesting properties, but have not been studied in laboratory experiments because of the lack of a platform that manifests appropriate couplings. Now, a network of disordered superconductors accomplishes this.
- I. Bonamassa
- , B. Gross
- & S. Havlin
-
Article |
 Thermalization and dynamics of high-energy quasiparticles in a superconducting nanowire
Thermalization and dynamics of high-energy quasiparticles in a superconducting nanowire
The performance of superconducting devices is affected by the generation and relaxation of excitations called quasiparticles. A scanning tunnelling microscope can controllably inject quasiparticles so their dynamics can be better understood.
- T. Jalabert
- , E. F. C. Driessen
- & C. Chapelier
-
News & Views |
 Probes to entropy flow in strange metals
Probes to entropy flow in strange metals
The discovery of an unexpectedly large thermoelectric response in a 2D material establishes its power to probe the entropy carried by its charge carriers in the hotly debated strange metal phase.
- Lu Li
- & Dechen Zhang
-
Article |
 Quantum phase diagram of high-pressure hydrogen
Quantum phase diagram of high-pressure hydrogen
It is very challenging to model hydrogen at high pressures and low temperatures because quantum effects become significant. A state-of-the-art numerical study shows that these effects cause important changes to the predicted phase diagram.
- Lorenzo Monacelli
- , Michele Casula
- & Francesco Mauri
-
Letter |
 Unidirectional coherent quasiparticles in the high-temperature rotational symmetry broken phase of AV3Sb5 kagome superconductors
Unidirectional coherent quasiparticles in the high-temperature rotational symmetry broken phase of AV3Sb5 kagome superconductors
The charge density wave state in kagome superconductors is not fully understood. Now, evidence suggests that the rotational symmetry of the lattice is broken before coherence of unidirectional quasiparticles is established at a lower temperature.
- Hong Li
- , He Zhao
- & Ilija Zeljkovic
-
Perspective |
 In search of Majorana
In search of Majorana
Majorana zero modes are emergent excitations in topological superconductors. This Perspective introduces the physics of these modes, recaps the recent history of the experimental search for them and discusses the future prognosis for success.
- Sankar Das Sarma
-
Article |
 Evidence for chiral superconductivity on a silicon surface
Evidence for chiral superconductivity on a silicon surface
Adatoms on the surface of silicon can create two-dimensional superconductivity, the order parameter symmetry of which is currently not known. Now, evidence suggests it might be a topological chiral d-wave state.
- F. Ming
- , X. Wu
- & H. H. Weitering
-
Research Briefing |
 Characterizing the helical Andreev states of a second-order topological insulator
Characterizing the helical Andreev states of a second-order topological insulator
Measurements of the switching supercurrent statistics of a superconducting quantum interference device based on bismuth, a second-order topological insulator, reveal that excited Andreev states are surprisingly long-lived. This protection can be attributed to the splitting of the Andreev pairs carrying the supercurrent along separate crystal hinges of opposite helicities.
-
Research Briefing |
 A quantitative description of high-temperature superconductivity
A quantitative description of high-temperature superconductivity
The critical temperature of a high-temperature superconductor was systematically tuned using an ionic-liquid gating technique. Measurements of this system revealed a universal quantitative relationship between superconductivity and the strange-metal state, which gives insight into the mechanism responsible for high-temperature superconductivity.
-
Article |
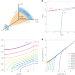 Interplay between superconductivity and the strange-metal state in FeSe
Interplay between superconductivity and the strange-metal state in FeSe
Superconductivity can emerge from a strange-metal state, but the exact relationship between them is unknown. Now, quantitative measurements reveal the dependence of resistivity in the strange metal on the superconducting transition temperature.
- Xingyu Jiang
- , Mingyang Qin
- & Zhongxian Zhao
-
Article |
 Long-lived Andreev states as evidence for protected hinge modes in a bismuth nanoring Josephson junction
Long-lived Andreev states as evidence for protected hinge modes in a bismuth nanoring Josephson junction
Second-order topological insulators feature helical one-dimensional states located at crystal hinges. Running a supercurrent through such systems is now shown to lead to long-lived excited Andreev pairs due to their separation along hinges with opposite helicity.
- A. Bernard
- , Y. Peng
- & S. Guéron
-
Perspective |
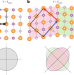 Nematicity and nematic fluctuations in iron-based superconductors
Nematicity and nematic fluctuations in iron-based superconductors
Recent experiments utilizing strain have shed light on the role of electronic nematicity in determining the properties of unconventional superconductors. This Perspective reviews these developments and discusses open questions.
- Anna E. Böhmer
- , Jiun-Haw Chu
- & Ming Yi
-
Article
| Open Access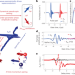 Quantum coherence tomography of light-controlled superconductivity
Quantum coherence tomography of light-controlled superconductivity
Multidimensional coherent spectroscopy measurements in iron-based superconductors demonstrate how the coupling between a superconductor and strong light pulses can drive the transition into a non-equilibrium superconducting state with distinct collective modes.
- L. Luo
- , M. Mootz
- & J. Wang
-
Article |
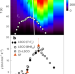 Spin fluctuations associated with the collapse of the pseudogap in a cuprate superconductor
Spin fluctuations associated with the collapse of the pseudogap in a cuprate superconductor
Various features of the behaviour in the cuprates near where the pseudogap collapses are caused by quantum fluctuations. Now, neutron scattering experiments suggest that very-low-energy collective spin excitations are the cause.
- M. Zhu
- , D. J. Voneshen
- & S. M. Hayden
-
News & Views |
 A highly anisotropic polymorph
A highly anisotropic polymorph
Superconductivity with an anisotropy is revealed in a layered material. This result points towards a version of superconductivity where spin–orbit interactions produce a material that is resilient to external magnetic fields.
- Joseph Falson
-
Article |
 Spin–orbit–parity coupled superconductivity in atomically thin 2M-WS2
Spin–orbit–parity coupled superconductivity in atomically thin 2M-WS2
A form of superconductivity where strong spin–orbit coupling combines with topological band inversions to produce strong robustness against magnetic fields is shown in a few-layer transition metal dichalcogenide.
- Enze Zhang
- , Ying-Ming Xie
- & Shaoming Dong
-
News & Views |
 Intercalation tailors superconductors
Intercalation tailors superconductors
Making monolayer superconductors creates interesting effects, but often decreases the transition temperature compared to 3D materials. Instead, intercalating molecules into a layered superconductor tailors the superconductivity with fewer trade-offs.
- Mark T. Edmonds
-
Letter
| Open Access Electrons with Planckian scattering obey standard orbital motion in a magnetic field
Electrons with Planckian scattering obey standard orbital motion in a magnetic field
Electrons in the non-superconducting state of cuprates can exhibit unusual transport behaviour. Now, analysis of experimental data shows that the magnetoresistance in this state is conventional, but influenced by an anisotropic scattering rate.
- Amirreza Ataei
- , A. Gourgout
- & Louis Taillefer

 Elastic response reveals the pairing symmetry
Elastic response reveals the pairing symmetry Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier
Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier Naturally superconducting
Naturally superconducting