Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A key to unlock ubiquitin ligase function
A key to unlock ubiquitin ligase function
Reliably identifying ubiquitin ligase interactors and substrates has been a persistent challenge in cellular biology. A breakthrough comes in the form of a potent, selective and cell-active chemical probe, shedding light on the intricate functions of a key regulatory enzyme.
- Shaoshuai Xie
- & Gang Li
-
Article
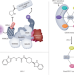
| Open Access Chemical screening by time-resolved X-ray scattering to discover allosteric probes
Chemical screening by time-resolved X-ray scattering to discover allosteric probes
A discovery pipeline integrating time-resolved HT-SAXS and fragment screening identifies chemical leads targeting exemplary allosteric states of mitochondrial oxidoreductase apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF).
- Chris A. Brosey
- , Todd M. Link
- & John A. Tainer
-
Article |
 Minimizing higher-order aggregation maximizes iron mobilization by small molecules
Minimizing higher-order aggregation maximizes iron mobilization by small molecules
A small-molecule iron mobilizer, FeM-1269, minimally higher-order aggregates in aqueous media and effectively mobilizes iron across a range of concentrations. FeM-1269-promoted iron mobilization restores physiology in animals at well-tolerated doses.
- Andrew D. Blake
- , Jianhua Chao
- & Martin D. Burke
-
-
Article |
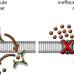
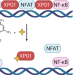 Targeting the chromatin binding of exportin-1 disrupts NFAT and T cell activation
Targeting the chromatin binding of exportin-1 disrupts NFAT and T cell activation
Exportin-1 (XPO1) was identified as the target of small molecules suppressing T cell activation. Selective disruption of the chromatin scaffolding function of XPO1 without blocking nuclear export implicates XPO1 as a target in autoimmunity.
- Yi Fan Chen
- , Maryam Ghazala
- & Drew J. Adams
-
Comment |
 Big data and benchmarking initiatives to bridge the gap from AlphaFold to drug design
Big data and benchmarking initiatives to bridge the gap from AlphaFold to drug design
AlphaFold is a breakthrough in protein structure prediction, but limitations in its application to computation- and structure-guided drug discovery remain. As with structure prediction, public-domain data and benchmarking initiatives will be essential to advance the field of computational drug design.
- Matthieu Schapira
- , Levon Halabelian
- & Rachel J. Harding
-
News & Views |
 Dam antidepressants
Dam antidepressants
Kir4.1 potassium channels expressed in astroglial cells critically regulate extracellular potassium concentration in the brain. A new study reports that blocking the flow of potassium ions into astrocytes by inhibiting Kir4.1 induces rapid-onset antidepressive effects in rodents.
- Jerod S. Denton
-
News & Views |
 Another KRAS variant trapped
Another KRAS variant trapped
Inhibitors of KRAS G12C have shown that directly targeting RAS is possible, but G12C is only one of many RAS driver mutations. Covalent targeting of another major variant, G12D, raises hope for treating other groups of patients with KRAS-mutant tumors.
- Kenneth Westover
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-release alkylation of Asp12 enables mutant selective targeting of K-Ras-G12D
Strain-release alkylation of Asp12 enables mutant selective targeting of K-Ras-G12D
Development of a malolactone electrophile that contains sufficient ring strain to counteract the weak nucleophilicity of aspartate enables covalent targeting of K-Ras-G12D, which is commonly found in pancreatic cancers.
- Qinheng Zheng
- , Ziyang Zhang
- & Kevan M. Shokat
-
News & Views |
 Friend or foe-maldehyde
Friend or foe-maldehyde
Chemically reactive metabolites such as formaldehyde are often toxic and are proposed to react promiscuously with biomolecules. New work shows that some reactive sites on proteins are uniquely sensitive to formaldehyde, leading to functionally important regulation of protein and cell functions.
- Vicki L. Emms
- , Sara Y. Chothia
- & Richard J. Hopkinson
-
Article
| Open Access In situ analysis of osmolyte mechanisms of proteome thermal stabilization
In situ analysis of osmolyte mechanisms of proteome thermal stabilization
A proteome-wide thermal profiling study of osmolyte action on E. coli and human proteins within the cellular milieu reveals mechanisms of protein thermal stabilization by osmolytes and in situ behavior of intrinsically disordered proteins.
- Monika Pepelnjak
- , Britta Velten
- & Paola Picotti
-
Article |
 Antiviral drug recognition and elevator-type transport motions of CNT3
Antiviral drug recognition and elevator-type transport motions of CNT3
Structural, functional and computational studies uncover the molecular details of antiviral drug recognition and membrane translocation by a concentrative nucleoside transporter.
- Nicholas J. Wright
- , Feng Zhang
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
News & Views |
 Sinking the carrier
Sinking the carrier
Transporters and channels have strong potential as drug targets, but drug discovery targeting these membrane-embedded molecules is challenging. Fragment-based ligand discovery combined with chemical proteomics offers a promising solution to the search for inhibitors of solute transporter family members.
- Noriko Toyama-Sorimachi
-
Review Article |
 Host–microbiome orchestration of the sulfated metabolome
Host–microbiome orchestration of the sulfated metabolome
Sulfated compounds produced collaboratively by the microbiome and the host have important biological functions. This Review highlights the production of select sulfated carbohydrates, amino acid derivatives and steroidal metabolites and discusses their influence on health. The Review also explore potential roles of sulfated molecules in disease detection, prevention and treatment.
- Gabriel D. D’Agostino
- , Snehal N. Chaudhari
- & A. Sloan Devlin
-
News & Views |
 A new twist to increase ion flow
A new twist to increase ion flow
The K+ ion channel KCNQ2 modulates neuronal excitability and is targeted by retigabine, an anti-epileptic drug that enhances the probability of channel opening. New activators have now been discovered to increase unitary conductance through an unprecedented mechanism.
- Jun Chen
- & Michael C. Sanguinetti
-
Article |
 Covalent inhibition of pro-apoptotic BAX
Covalent inhibition of pro-apoptotic BAX
A disulfide tethering screen identified a molecule that covalently interacts with pro-apoptotic BAX at C126, inhibiting its activation.
- Matthew W. McHenry
- , Peiwen Shi
- & Loren D. Walensky
-
News & Views |
 Ironing out the mitochondria
Ironing out the mitochondria
Screening of a chemical library identifies a novel ferroptosis inhibitor that directly interferes with the formation of intracellular membrane contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria (ERMCS), commonly referred to as mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs).
- Junsheng Chen
- , Tadashi Makio
- & Thomas Simmen
-
Article |
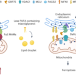 CGI1746 targets σ1R to modulate ferroptosis through mitochondria-associated membranes
CGI1746 targets σ1R to modulate ferroptosis through mitochondria-associated membranes
A small molecule, CGI1746, was identified to block ferroptosis acting through the sigma-1 receptor, a chaperone primarily at endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria contacts to mediate calcium transfer.
- Zili Zhang
- , Hong Zhou
- & Qing Zhong
-
Article |
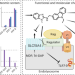 Chemoproteomic development of SLC15A4 inhibitors with anti-inflammatory activity
Chemoproteomic development of SLC15A4 inhibitors with anti-inflammatory activity
Integrated chemoproteomic development of selective small-molecule SLC15A4 inhibitors and their functional characterization establish SLC15A4 as a druggable target for autoimmune conditions.
- Tzu-Yuan Chiu
- , Daniel C. Lazar
- & Christopher G. Parker
-
Article |
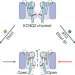 A small-molecule activation mechanism that directly opens the KCNQ2 channel
A small-molecule activation mechanism that directly opens the KCNQ2 channel
Identification of a small molecule (Ebio1) reveals a unique activation mechanism for the KCNQ2 potassium channel. Ebio1 induces a twist-to-open movement in the S6 helices, creating an extended channel gate with enhanced conductance.
- Shaoying Zhang
- , Demin Ma
- & Huaiyu Yang
-
Article |
 Enhanced mapping of small-molecule binding sites in cells
Enhanced mapping of small-molecule binding sites in cells
A chemoproteomic workflow was developed to determine the interaction sites of photoaffinity probes in cells, enabling the identification of diverse binding pockets and providing evidence of their tractability to small-molecule action.
- Jacob M. Wozniak
- , Weichao Li
- & Christopher G. Parker
-
News & Views |
 In search of chemical rationales
In search of chemical rationales
Small molecules and drugs are not homogenously distributed across cells, and are instead enriched in distinct subcellular compartments and membraneless biomolecular condensates. A new study lays out the path to identifying chemical features or ‘rationales’ that confer condensate-selective partitioning of small molecules.
- Aseem Z. Ansari
-
Article
| Open Access Protein-based bandpass filters for controlling cellular signaling with chemical inputs
Protein-based bandpass filters for controlling cellular signaling with chemical inputs
Development of chemically responsive bandpass filters mimics the signal-processing abilities of electronic circuits in mammalian cells by responding to chemical concentrations within a specific range and rejecting ones outside that range.
- Sailan Shui
- , Leo Scheller
- & Bruno E. Correia
-
Article
| Open Access Checkpoint kinase 2 controls insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
Checkpoint kinase 2 controls insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
A chemical screen identified a small molecule inhibitor of CHEK2 that boosts insulin secretion in human β cells, including those from both healthy and type 2 diabetic human islets, as well as in diabetic mouse models and cynomolgus macaques.
- Angie Chi Nok Chong
- , J. Jeya Vandana
- & Shuibing Chen
-
Article |
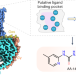 Structure of GPR101–Gs enables identification of ligands with rejuvenating potential
Structure of GPR101–Gs enables identification of ligands with rejuvenating potential
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the GPR101–Gs complex reveals the mechanism for its constitutive activity and facilitates the screening and identification of GPR101 ligands with rejuvenating potential.
- Zhao Yang
- , Jun-Yan Wang
- & Jin-Peng Sun
-
News & Views |
 Affinity for both sides
Affinity for both sides
DNA-encoded libraries are a powerful tool to identify novel chemical inducers of proximity such as targeted protein degraders, even without a known binder for the target protein.
- Andrea Testa
-
Article |
 Live-cell target engagement of allosteric MEKi on MEK–RAF/KSR–14-3-3 complexes
Live-cell target engagement of allosteric MEKi on MEK–RAF/KSR–14-3-3 complexes
Development of live-cell target engagement approaches to query MEK-bound binary and ternary complexes reveals the distinct pharmacology of clinical MEK inhibitors at specific assemblies composed of MEK, RAF, KSR and 14-3-3.
- William M. Marsiglia
- , Arthur Chow
- & Arvin C. Dar
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical proteomics reveals the target landscape of 1,000 kinase inhibitors
Chemical proteomics reveals the target landscape of 1,000 kinase inhibitors
Chemical proteomics profiling of 1,183 kinase inhibitors from past drug discovery projects revealed a large number of reasonably selective compounds for several kinases such as SYK and CK2.
- Maria Reinecke
- , Paul Brear
- & Bernhard Kuster
-
Article |
 Targeting ROS production through inhibition of NADPH oxidases
Targeting ROS production through inhibition of NADPH oxidases
NOXs are vital ROS-producing enzymes with roles in cell function and cancer. Here the authors combine computational and experimental methods to validate inhibitors for human NOX enzymes, opening avenues for redox biology-related cancer drug development.
- Joana Reis
- , Christoph Gorgulla
- & Andrea Mattevi
-
News & Views |
 A new road to STING activation
A new road to STING activation
Activation of STING-dependent signal transduction results in adaptive immune responses that promote antitumor immunity. A recent study has identified a small-molecule STING agonist that functions by binding to a newly discovered ligandable site to induce high-order STING oligomerization.
- Ariana Sulpizio
- & Luke L. Lairson
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of human STING by a molecular glue-like compound
Activation of human STING by a molecular glue-like compound
A cell-based phenotypic screen led to the discovery of compounds called NVS-STGs, which bind to the N-terminal domain of STING and act as a molecular glue to induce higher-order oligomerization and activation.
- Jie Li
- , Stephen M. Canham
- & Yan Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Design principles for cyclin K molecular glue degraders
Design principles for cyclin K molecular glue degraders
Detailed analysis of the structure–activity relationship for cyclin K degraders reveals diverse compounds that acquire glue activity through simultaneous binding to the CDK12 kinase pocket and engagement of several key DDB1 interfacial residues.
- Zuzanna Kozicka
- , Dakota J. Suchyta
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
-
-
News & Views |
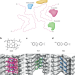 Chemical targeting of amyloids
Chemical targeting of amyloids
Cryo-EM structures of chemical-compound-bound α-synuclein amyloid fibrils shed light on the mechanism by which small molecules bind to cross-beta-sheet amyloid structures, opening the gateway to rational drug design for targeting pathological amyloid assemblies.
- Javier Garcia-Pardo
- & Salvador Ventura
-
-
News & Views |
 Brassinosteroids en route
Brassinosteroids en route
Brassinosteroid (BR) hormones promote root growth by controlling meristem size and cell elongation, but the mechanism of BR transport remains elusive. A new study shows that BR precursors move via intercellular pores called plasmodesmata to modulate BR cellular levels and their signaling functions.
- Yoselin Benitez-Alfonso
- & Ana I. Caño-Delgado
-
Article |
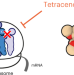 Tetracenomycin X sequesters peptidyl-tRNA during translation of QK motifs
Tetracenomycin X sequesters peptidyl-tRNA during translation of QK motifs
Biochemical and structural analyses reveal how tetracenomycin X inhibits bacterial translation in a context-dependent manner that relies primarily on the presence of Gln-Lys motifs in the nascent polypeptide chain.
- Elodie C. Leroy
- , Thomas N. Perry
- & C. Axel Innis
-
News & Views |
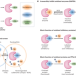 Flipping the polarity switch
Flipping the polarity switch
A new platform for screening nucleophilic-fragment-based covalent ligands enables the identification and targeting of ligandable sulfenic acid sites, setting the stage for exploration of nucleophile-directed probe and drug development.
- Daniel W. Bak
-
Article |
 Nucleophilic covalent ligand discovery for the cysteine redoxome
Nucleophilic covalent ligand discovery for the cysteine redoxome
Chemoproteomics reveals a vast expanse of ligandable cysteine sulfenic acids in the human proteome, highlighting the utility of nucleophilic small molecules in the fragment-based covalent ligand discovery pipeline.
- Ling Fu
- , Youngeun Jung
- & Kate S. Carroll
-
Article |
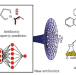 Deep learning-guided discovery of an antibiotic targeting Acinetobacter baumannii
Deep learning-guided discovery of an antibiotic targeting Acinetobacter baumannii
Using a neural network trained on bacterial growth inhibition data, in silico prediction of molecules with activity against Acinetobacter baumannii led to the identification of the narrow-spectrum abaucin, which perturbs lipoprotein trafficking.
- Gary Liu
- , Denise B. Catacutan
- & Jonathan M. Stokes
-
News & Views |
 Metabolic regulation of epigenetic drug resistance
Metabolic regulation of epigenetic drug resistance
A drug-resistance mechanism emphasizes the dependence of epigenetic signaling on acetyl-CoA.
- Nathaniel W. Snyder
- & Jordan L. Meier
-
Article |
 Acetyl-CoA biosynthesis drives resistance to histone acetyltransferase inhibition
Acetyl-CoA biosynthesis drives resistance to histone acetyltransferase inhibition
A resistance mechanism for a class of drugs targeting histone acetyltransferase inhibitors was identified where metabolic rewiring creates high concentrations of acetyl-CoA that outcompete drug-target engagement.
- Timothy R. Bishop
- , Chitra Subramanian
- & Michael A. Erb
-
News & Views |
 A goldilocks amount of H3K27me3
A goldilocks amount of H3K27me3
A study of drug-resistant lymphomas with hypermorphic mutations in PRC2 has identified a ‘methylation index’ by which cancer cells maintain optimal H3K27me3 levels for survival, emphasizing the importance of understanding how tumors adapt to changes in chromatin and to drug-resistance mutations.
- Tyler J. Reich
- & Peter W. Lewis
-
Article |
 Drug addiction unveils a repressive methylation ceiling in EZH2-mutant lymphoma
Drug addiction unveils a repressive methylation ceiling in EZH2-mutant lymphoma
Profiling the resistance landscape to PRC2 inhibitors in EZH2-mutant lymphoma with CRISPR-suppressor scanning reveals drug addiction mutations and a repressive methylation ceiling. Surpassing the ceiling with SETD2 inhibition halts lymphoma growth.
- Hui Si Kwok
- , Allyson M. Freedy
- & Brian B. Liau
-
Article |
 Remodeling oncogenic transcriptomes by small molecules targeting NONO
Remodeling oncogenic transcriptomes by small molecules targeting NONO
Integrated phenotypic screening and activity-based protein profiling identifies small molecules that decrease the expression of oncogenic transcription factors and suppress cancer cell growth by covalently targeting the RNA-binding protein NONO.
- Stefan G. Kathman
- , Seong Joo Koo
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
-
Article |
 Depletion of creatine phosphagen energetics with a covalent creatine kinase inhibitor
Depletion of creatine phosphagen energetics with a covalent creatine kinase inhibitor
A first-in-class covalent inhibitor of creatine phosphagen energetics was developed that induced toxicity in creatine kinase-dependent AML cell lines and regulated proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophages.
- Narek Darabedian
- , Wenzhi Ji
- & Edward T. Chouchani
-
Article |
 A selective small-molecule STAT5 PROTAC degrader capable of achieving tumor regression in vivo
A selective small-molecule STAT5 PROTAC degrader capable of achieving tumor regression in vivo
A potent and selective degrader was developed that depletes STAT5 in cells and mouse tissues, exerts cell growth inhibition in cells with activated STAT5 and induces tumor regression in mouse models.
- Atsunori Kaneshige
- , Longchuan Bai
- & Shaomeng Wang
-

 Linked to death
Linked to death Phasing out death
Phasing out death Degrade the RNA
Degrade the RNA