Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of a small monomeric Clivia fluorogenic RNA with a large Stokes shift
Structural basis of a small monomeric Clivia fluorogenic RNA with a large Stokes shift
Huang et al. report the tertiary structure of a small monomeric fluorogenic RNA aptamer named Clivia, characterized by a large Stokes shift, revealing the fluorescence activation mechanism and enabling a multivalent design to enhance the fluorescence output at specific dye concentrations.
- Kaiyi Huang
- , Qianqian Song
- & Aiming Ren
-
Article |
 Antibody–peptide conjugates deliver covalent inhibitors blocking oncogenic cathepsins
Antibody–peptide conjugates deliver covalent inhibitors blocking oncogenic cathepsins
Cathepsins are relevant therapeutic targets in cancer and other diseases. Here, the authors developed a different approach to block the activity of cathepsins in specific cellular contexts by combining non-natural peptide inhibitors with antibodies, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects.
- Aaron Petruzzella
- , Marine Bruand
- & Elisa Oricchio
-
News & Views |
 Bump-hole ZDHHCs
Bump-hole ZDHHCs
The ZDHHC family of palmitoyl transferases lipidates numerous protein targets, but the paucity of selective inhibitors has hindered their target profiling. A generalized chemical genetic system can now map the protein targets of individual ZDHHC family members.
- Tong Lan
- & Bryan C. Dickinson
-
News & Views |
 PROTAC-ing tuberculosis
PROTAC-ing tuberculosis
Targeted protein degradation has emerged as a promising approach in drug discovery, harnessing a cell’s intrinsic machinery to eliminate disease-related proteins. Now, a study paves the way to translating this technology into potential anti-mycobacterial therapies, by exploiting the bacterial protein-degradation complex.
- Delia Preti
- , Valentina Albanese
- & Peggy Carla Raffaella Marconi
-
Article |
 Imaging the dynamics of messenger RNA with a bright and stable green fluorescent RNA
Imaging the dynamics of messenger RNA with a bright and stable green fluorescent RNA
Zuo et al. developed a highly bright and stable green fluorescent RNA for robust imaging of the dynamics of messenger RNA in living cells, enabling visualization of nonuniform and distinct distributions of different RNAs throughout stress granules.
- Fangting Zuo
- , Li Jiang
- & Yi Yang
-
Article |
 Transcriptional regulation of living materials via extracellular electron transfer
Transcriptional regulation of living materials via extracellular electron transfer
Engineered living materials harness the computational power of biology to control interesting material properties. Here the authors leverage complex transcriptional regulation of bacterial extracellular electron transfer to control hydrogel cross-linking with Boolean logic.
- Austin J. Graham
- , Gina Partipilo
- & Benjamin K. Keitz
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 A key to unlock ubiquitin ligase function
A key to unlock ubiquitin ligase function
Reliably identifying ubiquitin ligase interactors and substrates has been a persistent challenge in cellular biology. A breakthrough comes in the form of a potent, selective and cell-active chemical probe, shedding light on the intricate functions of a key regulatory enzyme.
- Shaoshuai Xie
- & Gang Li
-
Article |
 A chemical probe to modulate human GID4 Pro/N-degron interactions
A chemical probe to modulate human GID4 Pro/N-degron interactions
Owens et al. reported PFI-7, a selective and potent antagonist of GID4 of the CTLH E3 ligase complex, which enables identification of human GID4 targets. This study provides valuable insights into GID4 functions and a powerful tool for advancing new targeted protein degradation strategies.
- Dominic D. G. Owens
- , Matthew E. R. Maitland
- & Cheryl H. Arrowsmith
-
Article |
 Antibodies expand the scope of angiotensin receptor pharmacology
Antibodies expand the scope of angiotensin receptor pharmacology
A newly developed maternally selective nanobody antagonist against the angiotensin II type I receptor stabilizes the receptor in a hybrid conformation and simultaneously binds with specific small-molecule antagonists.
- Meredith A. Skiba
- , Sarah M. Sterling
- & Andrew C. Kruse
-
News & Views |
 Dodging death
Dodging death
Ferroptosis, a cell death mechanism induced by lipid peroxidation, is pivotal in tumor suppression. A recent study shows that tumor repopulating cells evade ferroptosis and develop resistance to therapy via subverting a lipid metabolism enzyme.
- Yuelong Yan
- & Boyi Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Tumor-repopulating cells evade ferroptosis via PCK2-dependent phospholipid remodeling
Tumor-repopulating cells evade ferroptosis via PCK2-dependent phospholipid remodeling
Phosphorylation of ACSL4 by mitochondria-located metabolic kinase PCK2 is critical to regulating ferroptosis-associated phospholipid remodeling in tumor-repopulating cells that are resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
- Zhe Li
- , Zhi-min Xu
- & Zhuo-wei Liu
-
Review Article |
 Structures, mechanisms and applications of RNA-centric CRISPR–Cas13
Structures, mechanisms and applications of RNA-centric CRISPR–Cas13
CRISPR–Cas13 systems use single-subunit RNA-guided Cas13 effectors for targeted RNA recognition and cleavage. This Review summarizes the recent advances in understanding the structural and mechanistic aspects of Cas13 systems and the diverse applications of these systems in biotechnology and therapeutics.
- Hui Yang
- & Dinshaw J. Patel
-
-
-
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical screening by time-resolved X-ray scattering to discover allosteric probes
Chemical screening by time-resolved X-ray scattering to discover allosteric probes
A discovery pipeline integrating time-resolved HT-SAXS and fragment screening identifies chemical leads targeting exemplary allosteric states of mitochondrial oxidoreductase apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF).
- Chris A. Brosey
- , Todd M. Link
- & John A. Tainer
-
News & Views |
 Pyro(phospho)mania
Pyro(phospho)mania
Understanding the role of pyrophosphorylation requires specific analytical strategies to discriminate it from protein phosphorylation. A custom workflow reveals that nucleolar protein pyrophosphorylation in human cells regulates the transcription of ribosomal DNA.
- Claire E. Eyers
- & Christopher J. Clarke
-
Article |
 Minimizing higher-order aggregation maximizes iron mobilization by small molecules
Minimizing higher-order aggregation maximizes iron mobilization by small molecules
A small-molecule iron mobilizer, FeM-1269, minimally higher-order aggregates in aqueous media and effectively mobilizes iron across a range of concentrations. FeM-1269-promoted iron mobilization restores physiology in animals at well-tolerated doses.
- Andrew D. Blake
- , Jianhua Chao
- & Martin D. Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive protein pyrophosphorylation revealed in human cell lines
Extensive protein pyrophosphorylation revealed in human cell lines
A tailored proteomics workflow to identify endogenous protein pyrophosphorylation in human cells was developed, revealing the dependence of the modification on inositol pyrophosphates and a putative function in rDNA transcription.
- Jeremy A. M. Morgan
- , Arpita Singh
- & Dorothea Fiedler
-
Article |
 Structural basis for α-tubulin-specific and modification state-dependent glutamylation
Structural basis for α-tubulin-specific and modification state-dependent glutamylation
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), kinetic analysis and single-molecule biochemistry reveal how the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 6 (TTLL6) glutamylase binds reads microtubule geometry and modification state of neighboring tubulins, enabling a spatial positive feedback loop for microtubule modification.
- Kishore K. Mahalingan
- , Danielle A. Grotjahn
- & Antonina Roll-Mecak
-
Article |
 UFL1 triggers replication fork degradation by MRE11 in BRCA1/2-deficient cells
UFL1 triggers replication fork degradation by MRE11 in BRCA1/2-deficient cells
The mechanisms of stalled fork degradation in BRCA1/2-deficient cells remain unclear. UFL1, an UFM1-specific E3 ligase, was found to catalyze PTIP UFMylation at lysine 148, promoting stalled fork degradation by the MRE11 nuclease.
- Tian Tian
- , Junliang Chen
- & Ting Liu
-
News & Views |
 Forced rewiring of RTK signaling
Forced rewiring of RTK signaling
Reprogramming intercellular mechanotransduction and signaling pathways is still challenging. A recent advance uses a plug-and-play DNA nanodevice to allow non-mechanosensitive receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) to transmit force-induced cellular signals.
- Ahsan Ausaf Ali
- , Mahmoud Amouzadeh Tabrizi
- & Mingxu You
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of potent inhibitors of α-synuclein aggregation using structure-based iterative learning
Discovery of potent inhibitors of α-synuclein aggregation using structure-based iterative learning
Developing disease-modifying drugs for neurodegenerative diseases has been very challenging. Now a machine learning approach has been used to identify small molecule inhibitors of α-synuclein aggregation, a process implicated in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. Compounds that bind to the catalytic sites on the surface of the aggregates were identified and then progressively optimized into secondary nucleation inhibitors.
- Robert I. Horne
- , Ewa A. Andrzejewska
- & Michele Vendruscolo
-
Meeting Report |
 Bringing chemistry to medicine to redefine the undruggable
Bringing chemistry to medicine to redefine the undruggable
Chemical approaches, such as those that leverage induced proximity, targeted degradation, synthetic gene regulators or protein design offer opportunities to therapeutically target cellular processes that have long been thought of as undruggable. We report on the progress and the potential for transformative collaborations between fields discussed at the 2023 Bringing Chemistry to Medicine symposium at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
- Caitlin D. Deane
- , Marcus Fischer
- & Anang A. Shelat
-
News & Views |
 Peptide vaccines get an OS update
Peptide vaccines get an OS update
Peptide vaccines use antigenic peptide fragments to induce an immune response but are problematic because of the short half-life of peptides. A study now reports thioamide substitution in the peptide backbone as a strategy to enhance resistance to proteolysis and promote binding to the MHC I complex for T cell activation.
- Martin Zacharias
- & Sebastian Springer
-
News & Views |
 LPS gets a fresh trim
LPS gets a fresh trim
Detection of intracellular lipolysaccharide (LPS) activates an immune response initiated by the non-canonical inflammasome. ATGL has now been identified as a negative regulator of this pathway that dampens inflammation by removing LPS’ acyl chains, preventing the activation of inflammatory caspases and cytokines.
- Gemma Banister
- & Dave Boucher
-
Article |
 Engineering APOBEC3A deaminase for highly accurate and efficient base editing
Engineering APOBEC3A deaminase for highly accurate and efficient base editing
Through rational engineering of A3A deaminase, Yang and colleagues have designed CBEs termed haA3A-CBEs, which feature a condensed editing window and minimal off-target effects that are independent of defined sequence contexts and methylation status.
- Lei Yang
- , Yanan Huo
- & Dali Li
-
Article |
 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 dephosphorylates and inhibits TERT for tumor suppression
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 dephosphorylates and inhibits TERT for tumor suppression
TERT was dephosphorylated by the protein phosphatase activity of the gluconeogenic enzyme FBP1, leading to inhibition of TERT nuclear translocation and telomere function. Lipid nanoparticle-delivered FBP1 mRNA blunts tumor growth in mice.
- Min Li
- , Zheng Wang
- & Zhimin Lu
-
News & Views |
 The death gaze of MEDUSA
The death gaze of MEDUSA
Chemogenetic profiling can reveal genetic determinants that coordinate phenotypic responses to therapeutics, along with predicting potential pathways of resistance. A new analytical method for evaluating chemogenetic profiles reveals contributions from death-regulatory genes.
- Jesse D. Gelles
- & Jerry Edward Chipuk
-
-
Article |
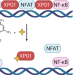 Targeting the chromatin binding of exportin-1 disrupts NFAT and T cell activation
Targeting the chromatin binding of exportin-1 disrupts NFAT and T cell activation
Exportin-1 (XPO1) was identified as the target of small molecules suppressing T cell activation. Selective disruption of the chromatin scaffolding function of XPO1 without blocking nuclear export implicates XPO1 as a target in autoimmunity.
- Yi Fan Chen
- , Maryam Ghazala
- & Drew J. Adams
-
Article |
 Profiling the proximal proteome of the activated μ-opioid receptor
Profiling the proximal proteome of the activated μ-opioid receptor
A proteomics and computational approach was developed to map the proximal proteome of the activated μ-opioid receptor and to extract subcellular location, trafficking and functional partners of G-protein-coupled receptor activity.
- Benjamin J. Polacco
- , Braden T. Lobingier
- & Ruth Hüttenhain
-
Article |
 Global signal peptide profiling reveals principles of selective Sec61 inhibition
Global signal peptide profiling reveals principles of selective Sec61 inhibition
Wenzell et al. developed a massively parallel screening platform to interrogate the sensitivity of signal peptides (SPs) to Sec61 inhibitors. The platform revealed how distinct inhibitors achieve sequence-dependent SP discrimination.
- Nicole A. Wenzell
- , Brian B. Tuch
- & Jack Taunton
-
News & Views |
 Ripping and stitching with copper
Ripping and stitching with copper
BURP-domain proteins belong to an emerging class of autocatalytic copper-containing proteins that modify themselves after synthesis. Now, a report explains how their structure and metal coordination sphere control the installation of crosslinks within the core peptide, and shows how nature leverages mechanistic paradigms to create diversity.
- Ninian J. Blackburn
-
Article |
 Ubiquitin-specific proximity labeling for the identification of E3 ligase substrates
Ubiquitin-specific proximity labeling for the identification of E3 ligase substrates
Huang et al. developed E3-substrate tagging by ubiquitin biotinylation (E-STUB), a proximity labeling-based method for direct identification of ubiquitylated substrates for a given E3 ligase, providing a useful tool for substrate discovery of targeted protein degradation and the understanding of E3 ligase function.
- Hai-Tsang Huang
- , Ryan J. Lumpkin
- & William R. Sellers
-
Article |
 Sulfide oxidation promotes hypoxic angiogenesis and neovascularization
Sulfide oxidation promotes hypoxic angiogenesis and neovascularization
Hypoxia induces ·NO-dependent hydrogen sulfide (H2S) biogenesis by inhibiting the transsulfuration pathway. H2S oxidation promotes endothelial cell proliferation to support neovascularization in tissue injury and tumor xenograft models.
- Roshan Kumar
- , Victor Vitvitsky
- & Ruma Banerjee
-
News & Views |
 Accessing natural vaccine adjuvants
Accessing natural vaccine adjuvants
An integrative approach has now enabled elucidation of the complete biosynthetic pathway of a prominent saponin adjuvant. Reconstruction of the whole biosynthetic pathway in a heterologous host provides new perspectives for the biotechnological supply of this immunostimulant.
- Vincent Courdavault
- & Nicolas Papon
-
Article |
 Functional genomic screens with death rate analyses reveal mechanisms of drug action
Functional genomic screens with death rate analyses reveal mechanisms of drug action
A method called MEDUSA was developed for identifying death regulatory genes in chemo-genetic profiling data, which enables characterization of a previously unappreciated mechanism of death induced by DNA damage in p53-deficient cells.
- Megan E. Honeywell
- , Marie S. Isidor
- & Michael J. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access De novo-designed transmembrane proteins bind and regulate a cytokine receptor
De novo-designed transmembrane proteins bind and regulate a cytokine receptor
The study demonstrates that specific recognition and custom binding geometries can be computationally encoded between protein spans within lipids through designing synthetic transmembrane proteins to functionally regulate a target cytokine receptor.
- Marco Mravic
- , Li He
- & William F. DeGrado
-
News & Views |
 Breaking the deadlock in genetic code expansion
Breaking the deadlock in genetic code expansion
Reprogramming of the genetic code allows the synthesis of proteins using new building blocks, thus opening the door to the development of a wider variety of medicines and biocatalysts; however, it is currently limited to α-amino acids. A new study has now reported the incorporation of β-linked and α,α-disubstituted monomers into a ribosome-synthesized protein.
- Ya-Ming Hou
- & Yuko Nakano
-
Comment |
 Big data and benchmarking initiatives to bridge the gap from AlphaFold to drug design
Big data and benchmarking initiatives to bridge the gap from AlphaFold to drug design
AlphaFold is a breakthrough in protein structure prediction, but limitations in its application to computation- and structure-guided drug discovery remain. As with structure prediction, public-domain data and benchmarking initiatives will be essential to advance the field of computational drug design.
- Matthieu Schapira
- , Levon Halabelian
- & Rachel J. Harding
-
News & Views |
 Dam antidepressants
Dam antidepressants
Kir4.1 potassium channels expressed in astroglial cells critically regulate extracellular potassium concentration in the brain. A new study reports that blocking the flow of potassium ions into astrocytes by inhibiting Kir4.1 induces rapid-onset antidepressive effects in rodents.
- Jerod S. Denton
-
News & Views |
 Hijacking endogenous mRNA for genetic code expansion
Hijacking endogenous mRNA for genetic code expansion
Labeling of endogenous proteins with chemical probes is highly desirable for life science studies. The combination of RNA base editing and site-specific incorporation of non-canonical amino acids allows the introduction of small chemical tags into endogenous proteins in living cells.
- Tomohiro Doura
- , Yuma Matsuoka
- & Shigeki Kiyonaka
-
Article |
 DNA-functionalized artificial mechanoreceptor for de novo force-responsive signaling
DNA-functionalized artificial mechanoreceptor for de novo force-responsive signaling
Yang et al. reported the development of nongenetically engineered artificial mechanoreceptors capable of reprogramming non-mechanoresponsive receptors to sense user-defined force cues, enabling de novo-designed mechanotransduction.
- Sihui Yang
- , Miao Wang
- & Zhou Nie
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial ATP generation is more proteome efficient than glycolysis
Mitochondrial ATP generation is more proteome efficient than glycolysis
Aerobic glycolysis is a hallmark of fast-growing cells, but it is unclear whether glycolysis was selected for its speed. Glycolysis produces ATP slower than respiration (per protein mass) and is beneficial for rendering cells robust to hypoxia.
- Yihui Shen
- , Hoang V. Dinh
- & Joshua D. Rabinowitz
-
News & Views |
 Another KRAS variant trapped
Another KRAS variant trapped
Inhibitors of KRAS G12C have shown that directly targeting RAS is possible, but G12C is only one of many RAS driver mutations. Covalent targeting of another major variant, G12D, raises hope for treating other groups of patients with KRAS-mutant tumors.
- Kenneth Westover
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biophysical chemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical ecology
- Chemical genetics
- Chemical libraries
- Chemical modification
- Chemical tools
- Cheminformatics
- Combinatorial libraries
- Computational chemistry
- DNA
- Drug delivery
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Ion channels
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Mechanism of action
- Membranes
- Metabolic pathways
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Natural products
- Networks and systems biology
- Nucleic acids
- Peptides
- Pharmacology
- Post-translational modifications
- Proteases
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Screening
- Small molecules
- Synthetic biology
- Target identification
- Target validation
- Transporters

 Antibody–peptide conjugates for targeted inhibition of cysteine proteases
Antibody–peptide conjugates for targeted inhibition of cysteine proteases Bacteria lose a pep in their step
Bacteria lose a pep in their step