Featured
-
-
Article |
 Centromeres are dismantled by foundational meiotic proteins Spo11 and Rec8
Centromeres are dismantled by foundational meiotic proteins Spo11 and Rec8
The meiotic proteins Spo11 and Rec8, which ensure meiotic recombination and reductional chromosome segregation, have additional activities that challenge centromere stability by promoting centromeric nucleosome remodelling in both fission yeast and human cells.
- Haitong Hou
- , Eftychia Kyriacou
- & Julia Promisel Cooper
-
Article |
 Nuclear sensing of breaks in mitochondrial DNA enhances immune surveillance
Nuclear sensing of breaks in mitochondrial DNA enhances immune surveillance
Breaks in mitochondrial DNA cause leakage of mitochondrial RNA into the cytoplasm, enhancing immune surveillance and synergizing with nuclear DNA damage to mount a robust type-I interferon immune response.
- Marco Tigano
- , Danielle C. Vargas
- & Agnel Sfeir
-
Technology Feature |
 Closing in on a complete human genome
Closing in on a complete human genome
Advances in sequencing technology mean that scientists are on the verge of finally finishing an end-to-end human genome map.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Article |
 Loop extrusion as a mechanism for formation of DNA damage repair foci
Loop extrusion as a mechanism for formation of DNA damage repair foci
During the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks, cohesin mediates the extrusion of loops of DNA along which phosphorylated H2AX spreads to establish a repair zone.
- Coline Arnould
- , Vincent Rocher
- & Gaëlle Legube
-
News & Views |
 Cells use loop extrusion to weave and tie the genome
Cells use loop extrusion to weave and tie the genome
A study reveals that a process called loop extrusion, which is central to the folding and function of chromosomes, also seems to play a key part in the repair of double-strand DNA breaks.
- Leonid A. Mirny
-
Article |
 Non-coding deletions identify Maenli lncRNA as a limb-specific En1 regulator
Non-coding deletions identify Maenli lncRNA as a limb-specific En1 regulator
The long non-coding RNA locus Maenli controls mouse limb development by regulating En1 activity, and the absence of the homolgous MAENLI locus is associated with severe congenital limb defects in humans.
- Lila Allou
- , Sara Balzano
- & Andrea Superti-Furga
-
Article |
 Elevated NSD3 histone methylation activity drives squamous cell lung cancer
Elevated NSD3 histone methylation activity drives squamous cell lung cancer
The histone H3K36 methyltransferase NSD3, which is associated with the common 8p11–12 chromosomal amplification, is an oncogenic driver in lung squamous cell carcinoma.
- Gang Yuan
- , Natasha M. Flores
- & Or Gozani
-
Article |
 BRCA1 and RNAi factors promote repair mediated by small RNAs and PALB2–RAD52
BRCA1 and RNAi factors promote repair mediated by small RNAs and PALB2–RAD52
Single-stranded, DNA-damage-associated small RNAs generated by a BRCA1–RNA-interference complex promote PALB2–RAD52-mediated DNA repair at transcriptional termination pause sites that contain R-loops and are rich in single-stranded DNA breaks in both quiescent and proliferating cells.
- Elodie Hatchi
- , Liana Goehring
- & David M. Livingston
-
Article |
 Integrated spatial genomics reveals global architecture of single nuclei
Integrated spatial genomics reveals global architecture of single nuclei
Multiplexed imaging of 3,660 chromosomal loci in individual mouse embryonic stem cells by DNA seqFISH+ with immunofluorescence of 17 chromatin marks and subnuclear structures reveals invariant organization of loci within individual cells, and heterogeneous and long-lived distinct combinatorial chromatin states in cellular subpopulations.
- Yodai Takei
- , Jina Yun
- & Long Cai
-
Article |
 METTL3 regulates heterochromatin in mouse embryonic stem cells
METTL3 regulates heterochromatin in mouse embryonic stem cells
Binding of METTL3 to chromatin is enriched over IAP family endogenous retroviral elements in mouse embryonic stem cells, helping to ensure the integrity of heterochromatin at these elements.
- Wenqi Xu
- , Jiahui Li
- & Hongjie Shen
-
Article |
 Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
An ultra-high-throughput multiplex protein–DNA binding assay is used to assess binding of 270 human transcription factors to 95,886 noncoding variants in the human genome, providing data to improve prediction of the effects of noncoding variants on transcription factor binding and thereby increase understanding of molecular pathways involved in diverse human traits and genetic diseases.
- Jian Yan
- , Yunjiang Qiu
- & Bing Ren
-
News & Views |
 A molecular handbook for human development
A molecular handbook for human development
A large-scale, high-resolution cell atlas of gene expression and regulation in human embryos enables innovative investigation of development through multi‑organ and multi‑modal analysis.
- Felicia Kuperwaser
- & Itai Yanai
-
Article |
 Tracking break-induced replication shows that it stalls at roadblocks
Tracking break-induced replication shows that it stalls at roadblocks
A method of tracking break-induced replication reveals the details of this repair process and shows that it can be impaired by certain genomic elements and by transcription.
- Liping Liu
- , Zhenxin Yan
- & Anna Malkova
-
Research Highlight |
 Ground-breaking films show RNA’s complex curves take shape
Ground-breaking films show RNA’s complex curves take shape
Experimental data and predictive algorithms combine to reveal the essential biomolecule’s shape-shifting.
-
Article |
 m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of endogenous retroviruses
m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of endogenous retroviruses
A CRISPR screen in mouse embryonic stem cells shows that transcripts derived from endogenous retroviruses are destabilized by m6A RNA methylation.
- Tomasz Chelmicki
- , Emeline Roger
- & Deborah Bourc’his
-
Article |
 Loop extrusion mediates physiological Igh locus contraction for RAG scanning
Loop extrusion mediates physiological Igh locus contraction for RAG scanning
Long-distance V(D)J recombination is facilitated by contraction of the Igh locus and linear RAG scanning along chromatin, both driven by cohesin-mediated loop extrusion, which allows recombination of widely separated gene segments to occur.
- Hai-Qiang Dai
- , Hongli Hu
- & Frederick W. Alt
-
Article |
 Molecular basis of nucleosomal H3K36 methylation by NSD methyltransferases
Molecular basis of nucleosomal H3K36 methylation by NSD methyltransferases
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the nucleosome-bound NSD2 and NSD3 histone methyltransferases reveal the molecular basis of their histone modification activity, and show how mutations in these proteins can lead to oncogenesis.
- Wanqiu Li
- , Wei Tian
- & Zhanxin Wang
-
Article |
 Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
A high-throughput, chromosome-wide analysis of DNA looping reveals its contribution to the organization of chromatin, and provides insight into how nucleosomes are deposited and organised de novo.
- Aakash Basu
- , Dmitriy G. Bobrovnikov
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article |
 Small-molecule inhibitors of human mitochondrial DNA transcription
Small-molecule inhibitors of human mitochondrial DNA transcription
Inhibitors of mitochondrial transcription that target human mitochondrial RNA polymerase provide a chemical biology tool for studying the role of mitochondrial DNA expression in a wide range of pathologies.
- Nina A. Bonekamp
- , Bradley Peter
- & Nils-Göran Larsson
-
Article |
 Anti-tumour immunity induces aberrant peptide presentation in melanoma
Anti-tumour immunity induces aberrant peptide presentation in melanoma
Tryptophan depletion in melanoma cells after prolonged treatment with interferon-γ (IFNγ) results in ribosomal frameshifting and the production of aberrant peptides that can be presented to T cells and induce an immune response.
- Osnat Bartok
- , Abhijeet Pataskar
- & Reuven Agami
-
Book Review |
 Women of the Nobel factory share their stories
Women of the Nobel factory share their stories
From sequencing to stardom — alumnae of the Laboratory of Molecular Biology reflect on how they succeeded in science.
- Georgina Ferry
-
Article |
 H1 histones control the epigenetic landscape by local chromatin compaction
H1 histones control the epigenetic landscape by local chromatin compaction
Experiments using a conditional triple-knockout mouse strain show that histone H1 regulates the activity of chromatin domains by controlling chromatin compaction, genome architecture and histone methylation.
- Michael A. Willcockson
- , Sean E. Healton
- & Arthur I. Skoultchi
-
Article |
 Histone H1 loss drives lymphoma by disrupting 3D chromatin architecture
Histone H1 loss drives lymphoma by disrupting 3D chromatin architecture
Mutations in histone H1 induce the remodelling of chromatin architecture to a more relaxed state, which leads to malignant transformation through changes in histone modifications and the expression of stem cell genes.
- Nevin Yusufova
- , Andreas Kloetgen
- & Ari M. Melnick
-
Article |
 Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision
Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision
Expression of three Yamanaka transcription factors in mouse retinal ganglion cells restores youthful DNA methylation patterns, promotes axon regeneration after injury, and reverses vision loss in a mouse model of glaucoma and in aged mice, suggesting that mammalian tissues retain a record of youthful epigenetic information that can be accessed to improve tissue function.
- Yuancheng Lu
- , Benedikt Brommer
- & David A. Sinclair
-
Article |
 TRF2-mediated telomere protection is dispensable in pluripotent stem cells
TRF2-mediated telomere protection is dispensable in pluripotent stem cells
Depletion of TRF2—an essential mediator of telomere protection in most mammalian cells—in mouse embryonic stem cells activates a compensatory transcriptional program that renders TRF2 dispensable for their survival and proliferation.
- Marta Markiewicz-Potoczny
- , Anastasia Lobanova
- & Eros Lazzerini Denchi
-
Article |
 TRF2-independent chromosome end protection during pluripotency
TRF2-independent chromosome end protection during pluripotency
Experiments in mouse pluripotent embryonic and epiblast stem cells show that TRF2 is dispensable for telomere protection specifically specifically in the pluripotent cells that form during early embryonic development, when cells form T-loops independently of this protein.
- Phil Ruis
- , David Van Ly
- & Simon J. Boulton
-
Article |
 A map of cis-regulatory elements and 3D genome structures in zebrafish
A map of cis-regulatory elements and 3D genome structures in zebrafish
A comprehensive map of transcriptomes, cis-regulatory elements, heterochromatin structure, the methylome and 3D genome organization in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) enables identification of species-specific and evolutionarily conserved regulatory features, and provides a foundation for modelling studies on human disease and development.
- Hongbo Yang
- , Yu Luan
- & Feng Yue
-
Career Feature |
 How to shift into COVID-19 research
How to shift into COVID-19 research
Scientists who aren’t virologists or vaccinologists can still make crucial contributions to the global effort to battle SARS-CoV-2.
- Amy DePaul
-
Article |
 Structure and function of virion RNA polymerase of a crAss-like phage
Structure and function of virion RNA polymerase of a crAss-like phage
The RNA polymerase from the crAss-like bacteriophage phi14:2, which is translocated into the host cell with phage DNA and transcribes early phage genes, is structurally most similar to eukaryotic RNA interference polymerases, suggesting that the latter have a phage origin.
- Arina V. Drobysheva
- , Sofia A. Panafidina
- & Maria L. Sokolova
-
Article |
 Structural basis for the final steps of human 40S ribosome maturation
Structural basis for the final steps of human 40S ribosome maturation
Studies of five cryo-electron microscopy structures reveal the composition and conformational progression in the final maturation events of human 40S ribosomal subunit assembly.
- Michael Ameismeier
- , Ivo Zemp
- & Roland Beckmann
-
Article |
 RNA nucleation by MSL2 induces selective X chromosome compartmentalization
RNA nucleation by MSL2 induces selective X chromosome compartmentalization
Dosage compensation in Drosophila involves nucleation of the dosage compensation complex at the X chromosome by MSL2 and the non-coding RNA roX.
- Claudia Isabelle Keller Valsecchi
- , M. Felicia Basilicata
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article |
 A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing
A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing
Expression profiling on 75,000 single cells creates a comprehensive cell atlas of the human lung that includes 41 out of 45 previously known cell types and 14 new ones.
- Kyle J. Travaglini
- , Ahmad N. Nabhan
- & Mark A. Krasnow
-
Article |
 Persistent transcriptional programmes are associated with remote memory
Persistent transcriptional programmes are associated with remote memory
The authors identify long-lasting transcriptional programmes in neurons and glia that are associated with the storage of a remote memory.
- Michelle B. Chen
- , Xian Jiang
- & Thomas C. Südhof
-
News & Views |
 DNA-binding proteins meet their mismatch
DNA-binding proteins meet their mismatch
Mismatches are alterations in DNA that prevent the bases on each strand of the double helix from aligning correctly. It emerges that mismatches can bend DNA into favourable conformations for binding by proteins.
- Kale Kundert
- & James S. Fraser
-
Article |
 DNA mismatches reveal conformational penalties in protein–DNA recognition
DNA mismatches reveal conformational penalties in protein–DNA recognition
A high-throughput assay that introduces mismatched base pairs into the DNA sequence shows that mismatches can increase transcription factor binding affinity by prepaying some of the energetic cost of distorting the DNA.
- Ariel Afek
- , Honglue Shi
- & Raluca Gordân
-
News & Views |
 Demystifying the D-loop during DNA recombination
Demystifying the D-loop during DNA recombination
Homologous recombination is a mechanism for DNA repair that enables the exchange of genetic information between DNA molecules. Structural analysis reveals how the protein RecA orchestrates this process.
- Upasana Roy
- & Eric C. Greene
-
Article |
 RAD51-dependent recruitment of TERRA lncRNA to telomeres through R-loops
RAD51-dependent recruitment of TERRA lncRNA to telomeres through R-loops
Telomeric-repeat-containing RNA is recruited to telomeres by a mechanism that involves the DNA recombinase RAD51 and the formation of DNA–RNA hybrids, or R-loops—a process similar to that involved in homology-directed DNA repair.
- Marianna Feretzaki
- , Michaela Pospisilova
- & Joachim Lingner
-
Article |
 Mechanism of strand exchange from RecA–DNA synaptic and D-loop structures
Mechanism of strand exchange from RecA–DNA synaptic and D-loop structures
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the bacterial recombination protein RecA with DNA, and of RecA–D-loop complexes, provide insights into the double-stranded DNA opening, homology search and strand-exchange processes of homologous recombination.
- Haijuan Yang
- , Chun Zhou
- & Nikola P. Pavletich
-
Article |
 Innovations present in the primate interneuron repertoire
Innovations present in the primate interneuron repertoire
Single-nucleus RNA-sequencing analyses of brain from humans, macaques, marmosets, mice and ferrets reveal diverse ways that interneuron populations have changed during evolution.
- Fenna M. Krienen
- , Melissa Goldman
- & Steven A. McCarroll
-
Article |
 Repeat expansions confer WRN dependence in microsatellite-unstable cancers
Repeat expansions confer WRN dependence in microsatellite-unstable cancers
In cells with microsatellite instability, expanded TA-dinucleotide repeats form cruciform structures that stall replication forks and cause chromosome shattering in the absence of the WRN helicase.
- Niek van Wietmarschen
- , Sriram Sridharan
- & André Nussenzweig
-
Article |
 Structure of nucleosome-bound DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B
Structure of nucleosome-bound DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B
Catalytically inactive DNMT3B3 is crucial in de novo CpG methylation of DNA, interacting with the nucleosome core to orient catalytically active DNMT3A2 so that it can bind to nearby linker DNA.
- Ting-Hai Xu
- , Minmin Liu
- & Peter A. Jones
-
Article |
 Bridging of DNA breaks activates PARP2–HPF1 to modify chromatin
Bridging of DNA breaks activates PARP2–HPF1 to modify chromatin
The PARP2–HPF1 histone-modifying complex bridges two nucleosomes to align broken DNA ends for ligation, initiating conformational changes that activate PARP2 and enable DNA damage repair.
- Silvija Bilokapic
- , Marcin J. Suskiewicz
- & Mario Halic
-
Article |
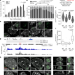 A protein assembly mediates Xist localization and gene silencing
A protein assembly mediates Xist localization and gene silencing
A protein condensate formed by multivalent interactions between the long non-coding RNA Xist and specific RNA-binding proteins drives the compartmentalization required to perpetuate gene silencing on the inactive X chromosome.
- Amy Pandya-Jones
- , Yolanda Markaki
- & Kathrin Plath
-
Article |
 Identification of the human DPR core promoter element using machine learning
Identification of the human DPR core promoter element using machine learning
A machine learning approach shows that the downstream core promoter region (DPR) is widely used in human gene promoters, and that many promoters contain either a DPR or a TATA box, but not both.
- Long Vo ngoc
- , Cassidy Yunjing Huang
- & James T. Kadonaga
-
Article |
 The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2
The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2
A high-resolution map of coding regions in the SARS-CoV-2 genome enables the identification of 23 unannotated open reading frames and quantification of the expression of canonical viral open reading frames.
- Yaara Finkel
- , Orel Mizrahi
- & Noam Stern-Ginossar
-
Article |
 C. elegans interprets bacterial non-coding RNAs to learn pathogenic avoidance
C. elegans interprets bacterial non-coding RNAs to learn pathogenic avoidance
Exposing Caenorhabditis elegans to non-coding small RNAs from pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces avoidance behaviours in treated worms and their progeny, which reveals how C. elegans discriminates between bacterial species in its microbial environment.
- Rachel Kaletsky
- , Rebecca S. Moore
- & Coleen T. Murphy
-
Article |
 Epigenetic gene silencing by heterochromatin primes fungal resistance
Epigenetic gene silencing by heterochromatin primes fungal resistance
Fission yeast grown in sublethal levels of caffeine develop heterochromatin-dependent epimutations conferring unstable heritable gene silencing that conveys resistance to caffeine, while remaining genetically wild type.
- Sito Torres-Garcia
- , Imtiyaz Yaseen
- & Robin C. Allshire
-
News Feature |
 The coronavirus is mutating — does it matter?
The coronavirus is mutating — does it matter?
Different SARS-CoV-2 strains haven’t yet had a major impact on the course of the pandemic, but they might in future.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article |
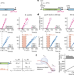 Functionally uncoupled transcription–translation in Bacillus subtilis
Functionally uncoupled transcription–translation in Bacillus subtilis
In Bacillus subtilis, unlike in Escherichia coli, transcription and translation of genes are not tightly coupled, and pioneering ribosomes lag substantially behind RNA polymerases.
- Grace E. Johnson
- , Jean-Benoît Lalanne
- & Gene-Wei Li
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cell division
- Chromatin
- Chromosomes
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- DNA damage and repair
- DNA metabolism
- DNA recombination
- DNA replication
- Epigenetics
- Non-coding RNAs
- Nuclear organization
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- Riboswitches
- Ribozymes
- RNA metabolism
- RNAi
- Single-molecule biophysics
- Transcription
- Transcriptomics
- Translation
- Transposition

 The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity
The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity