Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access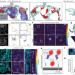 Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
High-speed molecular tracking is integrated with three-dimensional electron microscopy to map the diffusion distribution and ultrastructure of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contact sites, revealing the ability of high-speed single-molecule imaging to map contact site interface structures and corresponding diffusion landscapes.
- Christopher J. Obara
- , Jonathon Nixon-Abell
- & Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
-
Article |
 Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
As well as being the substrate for the lipopolysaccharide transport protein complex comprising LptA–G, lipopolysaccharide binding to Lpt proteins promotes their assembly into a bridge linking the inner and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria.
- Lisa Törk
- , Caitlin B. Moffatt
- & Daniel Kahne
-
Article |
 A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
High-speed atomic force microscopy single-molecule imaging and cryo-EM analysis discover and reveal the structure of a TRPV3 pentamer, providing evidence for a non-canonical pentameric TRP-channel assembly, laying the foundation for new directions in TRP channel research.
- Shifra Lansky
- , John Michael Betancourt
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article
| Open Access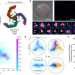 Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
The plasma membrane can expand the blades of the PIEZO1 ion channel, impacting channel activation.
- Eric M. Mulhall
- , Anant Gharpure
- & Ardem Patapoutian
-
Article |
 Extreme dynamics in a biomolecular condensate
Extreme dynamics in a biomolecular condensate
Two highly charged disordered human proteins phase-separate into viscous complex coacervates while retaining their rapid conformational dynamics through pico- to nanosecond exchange of short-lived side-chain interactions.
- Nicola Galvanetto
- , Miloš T. Ivanović
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Article |
 Structural insights into BCDX2 complex function in homologous recombination
Structural insights into BCDX2 complex function in homologous recombination
Analyses of the structure and biochemical properties of the tetrameric complex of RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D and XRCC2 reveal details of its role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks.
- Yashpal Rawal
- , Lijia Jia
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access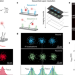 Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
The authors introduce a single-molecule DNA-barcoding method, resolution enhancement by sequential imaging, that improves the resolution of fluorescence microscopy down to the Ångström scale using off-the-shelf fluorescence microscopy hardware and reagents.
- Susanne C. M. Reinhardt
- , Luciano A. Masullo
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article
| Open Access The Smc5/6 complex is a DNA loop-extruding motor
The Smc5/6 complex is a DNA loop-extruding motor
Using single-molecule imaging, the authors show that Smc5/6 forms DNA loops by extrusion, which establishes DNA loop extrusion as a conserved mechanism among eukaryotic SMC complexes.
- Biswajit Pradhan
- , Takaharu Kanno
- & Eugene Kim
-
Article
| Open Access CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is sufficient to block loop extruding cohesin in a DNA tension dependent manner, and induces loop extrusion direction switching and loop shrinkage.
- Iain F. Davidson
- , Roman Barth
- & Jan-Michael Peters
-
Article
| Open Access mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria
mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria
The reaction coordinate of aminoacyl-tRNA movement is altered on the human ribosome and the process is an order of magnitude slower compared with bacteria due to eukaryote-specific structural elements in the human ribosome and in the elongation factor eEF1A.
- Mikael Holm
- , S. Kundhavai Natchiar
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Article
| Open Access CFTR function, pathology and pharmacology at single-molecule resolution
CFTR function, pathology and pharmacology at single-molecule resolution
A structure–function analysis of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator shows its two nucleotide-binding domains dimerize before channel opening, and reveals a mechanism through which conformational changes in the channel regulate chloride conductance.
- Jesper Levring
- , Daniel S. Terry
- & Jue Chen
-
Article |
 Regulation of the mammalian-brain V-ATPase through ultraslow mode-switching
Regulation of the mammalian-brain V-ATPase through ultraslow mode-switching
Single-molecule measurements of synaptic vesicles show that V-ATPases do not pump continuously in time but instead stochastically switch between ultralong-lived proton-pumping, inactive and proton-leaky modes.
- Eleftherios Kosmidis
- , Christopher G. Shuttle
- & Dimitrios Stamou
-
Article
| Open Access Organizing structural principles of the IL-17 ligand–receptor axis
Organizing structural principles of the IL-17 ligand–receptor axis
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of IL-25–IL-17RB–IL-17RA and IL-17A–IL-17RC–IL-17RA complexes show a tip-to-tip architecture, which is a key organizing principle of the IL-17 receptor family.
- Steven C. Wilson
- , Nathanael A. Caveney
- & K. Christopher Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA origami rotary ratchet motor
A DNA origami rotary ratchet motor
A nanoscale rotary motor made of DNA origami, driven by ratcheting and powered by an external electric field, shows the ability to wind up a spring and has mechanical capabilities approaching those of biological motors.
- Anna-Katharina Pumm
- , Wouter Engelen
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Article |
 eIF5B and eIF1A reorient initiator tRNA to allow ribosomal subunit joining
eIF5B and eIF1A reorient initiator tRNA to allow ribosomal subunit joining
Single-molecule spectroscopy and structural studies were used to examine the dynamics of association of eIF1A and eIF5B with the human translation initiation complex and their role in presenting tRNA to the complex to initiate translation.
- Christopher P. Lapointe
- , Rosslyn Grosely
- & Joseph D. Puglisi
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear mechanics of human mitotic chromosomes
Nonlinear mechanics of human mitotic chromosomes
A method that uses a combination of optical trapping, fluorescence microscopy and microfluidics to analyse the internal structure of chromosomes shows that there is a distinct nonlinear stiffening of the chromosome in response to tension.
- Anna E. C. Meijering
- , Kata Sarlós
- & Gijs J. L. Wuite
-
Article
| Open Access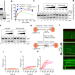 HELQ is a dual-function DSB repair enzyme modulated by RPA and RAD51
HELQ is a dual-function DSB repair enzyme modulated by RPA and RAD51
HELQ is differentially regulated by RAD51, which stimulates helicase activity, and RPA, which inhibits helicase activity and stimulates annealing.
- Roopesh Anand
- , Erika Buechelmaier
- & Simon J. Boulton
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of early translocation events on the ribosome
Structural basis of early translocation events on the ribosome
Cryo-electron microscopy and single-molecule fluorescence methods are used to elucidate the mechanism of early translocation events on the bacterial ribosome.
- Emily J. Rundlet
- , Mikael Holm
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Article |
 cAMP binding to closed pacemaker ion channels is non-cooperative
cAMP binding to closed pacemaker ion channels is non-cooperative
Direct monitoring of individual cAMP molecules binding to HCN ion channels reveals the binding dynamics underlying the distinct physiological responses of ion channel isoforms.
- David S. White
- , Sandipan Chowdhury
- & Baron Chanda
-
Article |
 Localization atomic force microscopy
Localization atomic force microscopy
A localization algorithm is applied to datasets obtained with conventional and high-speed atomic force microscopy to increase image resolution beyond the limits set by the radius of the tip used.
- George R. Heath
- , Ekaterina Kots
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article |
 Integrated spatial genomics reveals global architecture of single nuclei
Integrated spatial genomics reveals global architecture of single nuclei
Multiplexed imaging of 3,660 chromosomal loci in individual mouse embryonic stem cells by DNA seqFISH+ with immunofluorescence of 17 chromatin marks and subnuclear structures reveals invariant organization of loci within individual cells, and heterogeneous and long-lived distinct combinatorial chromatin states in cellular subpopulations.
- Yodai Takei
- , Jina Yun
- & Long Cai
-
Article |
 DNA surface exploration and operator bypassing during target search
DNA surface exploration and operator bypassing during target search
Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer and real-time confocal laser tracking with fluorescence correlation spectroscopy together characterize how individual lac repressor molecules bypass operator sites while exploring the DNA surface at microsecond timescales.
- Emil Marklund
- , Brad van Oosten
- & Sebastian Deindl
-
Article |
 DNA-loop extruding condensin complexes can traverse one another
DNA-loop extruding condensin complexes can traverse one another
Single-molecule visualization shows that condensin—a motor protein that extrudes DNA in one direction only—can encounter and pass a second condensin molecule to form a new type of DNA loop that gathers DNA from both sides.
- Eugene Kim
- , Jacob Kerssemakers
- & Cees Dekker
-
Article |
 Selective loading and processing of prespacers for precise CRISPR adaptation
Selective loading and processing of prespacers for precise CRISPR adaptation
Cas1–Cas2 selects precursor prespacers from DNA fragments in a length- and PAM-sequence-dependent manner, and these precursors are trimmed by DnaQ exonucleases to enable integration into the CRISPR locus in the correct orientation.
- Sungchul Kim
- , Luuk Loeff
- & Chirlmin Joo
-
Article |
 Processive extrusion of polypeptide loops by a Hsp100 disaggregase
Processive extrusion of polypeptide loops by a Hsp100 disaggregase
A combination of optical tweezers and fluorescent-particle tracking is used to dissect the dynamics of the Hsp100 disaggregase ClpB, and show that the processive extrusion of polypeptide loops is the mechanistic basis of its activity.
- Mario J. Avellaneda
- , Kamila B. Franke
- & Sander J. Tans
-
Article |
 Quantifying secondary transport at single-molecule resolution
Quantifying secondary transport at single-molecule resolution
Imaging of substrate transport by individual MhsT transporters, members of the neurotransmitter:sodium symporter family of secondary transporters, at single- and multi-turnover resolution reveals that the rate-limiting step varies with the identity of the transported substrate.
- Gabriel A. Fitzgerald
- , Daniel S. Terry
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Letter |
 eIF5B gates the transition from translation initiation to elongation
eIF5B gates the transition from translation initiation to elongation
Single-molecule dynamics reveal that the GTPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF5B serves as a kinetic checkpoint for the transition from translation initiation to elongation.
- Jinfan Wang
- , Alex G. Johnson
- & Joseph D. Puglisi
-
Letter |
 Rotation tracking of genome-processing enzymes using DNA origami rotors
Rotation tracking of genome-processing enzymes using DNA origami rotors
ORBIT (origami-rotor-based imaging and tracking) is used to track the DNA rotation that results from DNA unwinding by RecBCD helicase and transcription by RNAP at a single-molecule scale and millisecond time resolution.
- Pallav Kosuri
- , Benjamin D. Altheimer
- & Xiaowei Zhuang
-
Letter |
 Associating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structures with states on the virus observed by smFRET
Associating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structures with states on the virus observed by smFRET
Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer imaging of conformational states of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimers on intact virus and of trimers used in previous structural studies reveal the latter as downstream—rather than pre-triggered—conformations.
- Maolin Lu
- , Xiaochu Ma
- & Walther Mothes
-
Letter |
 Directionality of dynein is controlled by the angle and length of its stalk
Directionality of dynein is controlled by the angle and length of its stalk
The motility of dynein towards the minus end of the microtubule is controlled by the length and angle of the coiled-coil stalk that connects the motor to the microtubule.
- Sinan Can
- , Samuel Lacey
- & Ahmet Yildiz
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36
Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36
A mechanism for the unfolding of guanine-rich DNA ‘quadruplexes’ by helicases is suggested, based on the structure of a DNA-bound helicase.
- Michael C. Chen
- , Ramreddy Tippana
- & Adrian R. Ferré-D’Amaré
-
Article |
 Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
A high-affinity complex of histone H1 and prothymosin-α reveals an unexpected interaction mechanism, where the large opposite net charge enables the two proteins to remain highly disordered even in the complex.
- Alessandro Borgia
- , Madeleine B. Borgia
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Letter |
 The cryo-electron microscopy structure of huntingtin
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of huntingtin
The structure of huntingtin in complex with an interactor is determined to an overall resolution of 4 Å, paving the way for improved understanding of the cellular functions of this protein.
- Qiang Guo
- , Bin Huang
- & Stefan Kochanek
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement
Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement
Cryo-electron microscopy and single-molecule studies reveal that the adaptors BICDR1 and HOOK3 recruit two dynein molecules to dynactin and thereby increase the force and speed of the dynein–dynactin microtubule motor.
- Linas Urnavicius
- , Clinton K. Lau
- & Andrew P. Carter
-
Article |
 Dynamics of P-type ATPase transport revealed by single-molecule FRET
Dynamics of P-type ATPase transport revealed by single-molecule FRET
Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer is used to identify the rate-limiting step and new intermediates in the conformational cycle of the Listeria monocytogenes calcium transporter LMCA1.
- Mateusz Dyla
- , Daniel S. Terry
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Letter |
 Single-molecule imaging reveals receptor–G protein interactions at cell surface hot spots
Single-molecule imaging reveals receptor–G protein interactions at cell surface hot spots
G-protein-coupled receptors and their G protein partners are studied by single-molecule imaging in living cells, which reveals hot spots on the cell membrane where receptors and G proteins interact and signal.
- Titiwat Sungkaworn
- , Marie-Lise Jobin
- & Davide Calebiro
-
Article |
 BRCA1–BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing
BRCA1–BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing
The tumour suppressor complex BRCA1–BARD1, which facilitates the generation of a single-stranded DNA template during homologous recombination, also binds to the recombinase RAD51 and enhances its function.
- Weixing Zhao
- , Justin B. Steinfeld
- & Patrick Sung
-
Letter |
 Enhanced proofreading governs CRISPR–Cas9 targeting accuracy
Enhanced proofreading governs CRISPR–Cas9 targeting accuracy
A new engineered version of SpCas9, called HypaCas9, displays enhanced accuracy of editing without significant loss of efficiency at the desired target.
- Janice S. Chen
- , Yavuz S. Dagdas
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Article |
 Single-molecule analysis of ligand efficacy in β2AR–G-protein activation
Single-molecule analysis of ligand efficacy in β2AR–G-protein activation
Single-molecule FRET imaging provides insights into the allosteric link between the ligand-binding and G-protein nucleotide-binding pockets of the β2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR) and improved understanding of the G-protein activation mechanism.
- G. Glenn Gregorio
- , Matthieu Masureel
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Letter |
 Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver
Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver
Single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization is performed to identify several landmark genes in the liver and their level of expression in single-cell RNA sequencing is used to spatially reconstruct the zonation of all liver genes.
- Keren Bahar Halpern
- , Rom Shenhav
- & Shalev Itzkovitz
-
Letter |
 Cascading MutS and MutL sliding clamps control DNA diffusion to activate mismatch repair
Cascading MutS and MutL sliding clamps control DNA diffusion to activate mismatch repair
MutS and MutL—the highly conserved core proteins responsible for the repair of mismatched DNA—form sequential stable sliding clamps that together modulate one-dimensional diffusion along the DNA and, with MutH, facilitate the search for a distant excision initiation site.
- Jiaquan Liu
- , Jeungphill Hanne
- & Richard Fishel
-
Letter |
 Alternative modes of client binding enable functional plasticity of Hsp70
Alternative modes of client binding enable functional plasticity of Hsp70
Hsp70 binds unfolded protein segments in its groove, but can also bind and stabilize folded protein structures, owing to its moveable lid, with ATP hydrolysis and co-chaperones allowing control of these contrasting effects.
- Alireza Mashaghi
- , Sergey Bezrukavnikov
- & Sander J. Tans
-
Letter |
 Reconstruction of bacterial transcription-coupled repair at single-molecule resolution
Reconstruction of bacterial transcription-coupled repair at single-molecule resolution
Single-molecule assays show that the recruitment of UvrA and UvrAB to Mfd–RNA polymerase complex formed on a DNA lesion arrests the translocating complex and causes its dissolution.
- Jun Fan
- , Mathieu Leroux-Coyau
- & Terence R. Strick
-
Letter |
 Sliding sleeves of XRCC4–XLF bridge DNA and connect fragments of broken DNA
Sliding sleeves of XRCC4–XLF bridge DNA and connect fragments of broken DNA
A combination of single-molecule techniques shows that the repair proteins XRCC4 and XLF form heteromeric mobile sleeve-like complexes that can bridge and hold together fragments of broken DNA.
- Ineke Brouwer
- , Gerrit Sitters
- & Gijs J. L. Wuite
-
Letter |
 Super-resolution imaging reveals distinct chromatin folding for different epigenetic states
Super-resolution imaging reveals distinct chromatin folding for different epigenetic states
Using super-resolution imaging to directly observe the three-dimensional organization of Drosophila chromatin at a scale spanning sizes from individual genes to entire gene regulatory domains, the authors find that transcriptionally active, inactive and Polycomb-repressed chromatin states each have a distinct spatial organisation.
- Alistair N. Boettiger
- , Bogdan Bintu
- & Xiaowei Zhuang
-
Letter |
 Real-time observation of the initiation of RNA polymerase II transcription
Real-time observation of the initiation of RNA polymerase II transcription
A single-molecule optical tweezer assay is developed to monitor transcription initiation in eukaryotic RNA polymerase II in real-time, making use of a highly purified preinitiation complex (PIC) from yeast; observations show that a large bubble is opened up in the DNA template during initiation, driven by the TFIIH helicase that forms part of the PIC, along with synthesis of an extended transcript before the transition from transcription initiation into elongation.
- Furqan M. Fazal
- , Cong A. Meng
- & Steven M. Block
-
Letter |
 Replisome speed determines the efficiency of the Tus−Ter replication termination barrier
Replisome speed determines the efficiency of the Tus−Ter replication termination barrier
The Tus–Ter termination site of Escherichia coli is not completely efficient in stopping DNA replication, with about half of replisomes bypassing this blockade; here the speed of the replication machinery is shown to determine the outcome of the encounter between the replisome and Tus–Ter.
- Mohamed M. Elshenawy
- , Slobodan Jergic
- & Samir M. Hamdan
-
Letter |
 Conformational dynamics of a class C G-protein-coupled receptor
Conformational dynamics of a class C G-protein-coupled receptor
smFRET is used to probe the activation mechanism of two full-length mammalian glutamate receptors, revealing that the extracellular ligand-binding domains of these G-protein-coupled receptors interconvert between three confirmations (resting, activated and a short-lived intermediate state), and that the efficacy of an orthosteric agonist correlates with the degree of occupancy of the active state.
- Reza Vafabakhsh
- , Joshua Levitz
- & Ehud Y. Isacoff
-
Letter |
 Defining fundamental steps in the assembly of the Drosophila RNAi enzyme complex
Defining fundamental steps in the assembly of the Drosophila RNAi enzyme complex
The assembly of single Drosophila RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs) is reconstituted using seven purified proteins, revealing that chaperones help stabilize the interaction of the protein heterodimer Dicer-2–R2D2 bound to the short interfering RNA with Ago2.
- Shintaro Iwasaki
- , Hiroshi M. Sasaki
- & Yukihide Tomari

 Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor
Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor