Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Chemoproteomic discovery of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of WRN helicase
Chemoproteomic discovery of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of WRN helicase
VVD-133214, a clinical-stage, covalent allosteric inhibitor of the helicase WRN, was well tolerated in mice and led to robust tumour regression in multiple microsatellite-instability-high colorectal cancer cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models.
- Kristen A. Baltgalvis
- , Kelsey N. Lamb
- & Todd M. Kinsella
-
Article |
 Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
A synthetic proteome-scale strategy enables the identification of a diverse range of human proteins that can induce the degradation or stabilization of a target protein in a proximity-dependent way.
- Juline Poirson
- , Hanna Cho
- & Mikko Taipale
-
Article |
 Oxidative cyclization reagents reveal tryptophan cation–π interactions
Oxidative cyclization reagents reveal tryptophan cation–π interactions
Global profiling of hyper-reactive tryptophan sites across whole proteomes using tryptophan chemical ligation by cyclization (Trp-CLiC) reveals a systematic map of tryptophan residues that participate in cation–π interactions, including functional sites that can regulate protein-mediated phase-separation processes.
- Xiao Xie
- , Patrick J. Moon
- & Christopher J. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
A multidimensional proteomics analysis of the interactions between around 2,000 nuclear proteins and over 80 modified dinucleosomes representing promoter, enhancer and heterochromatin states provides insights into how chromatin states are decoded by chromatin readers.
- Saulius Lukauskas
- , Andrey Tvardovskiy
- & Till Bartke
-
News |
 Are your organs ageing well? The blood holds clues
Are your organs ageing well? The blood holds clues
One organ in a person’s body can age faster than the rest — with implications for health and mortality.
- Max Kozlov
-
Article
| Open Access The social and structural architecture of the yeast protein interactome
The social and structural architecture of the yeast protein interactome
A protein interaction network constructed with data from high-throughput affinity enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry provides a highly saturated yeast interactome with 31,004 interactions, including low-abundance complexes, membrane protein complexes and non-taggable protein complexes.
- André C. Michaelis
- , Andreas-David Brunner
- & Matthias Mann
-
Technology Feature |
 Soft-landing methods aim to simplify structural biology
Soft-landing methods aim to simplify structural biology
Linking mass spectrometry with cryo-electron microscopy could transform understanding of complex protein structures — if scientists can show that samples remain intact when they hit their target.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Comparisons of phenotypic and genetic association with protein levels from Icelandic and UK Biobank cohorts show that using multiple analysis platforms and stratifying populations by ancestry improves the detection of associations and allows the refinement of their location within the genome.
- Grimur Hjorleifsson Eldjarn
- , Egil Ferkingstad
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Rare variant associations with plasma protein levels in the UK Biobank
Rare variant associations with plasma protein levels in the UK Biobank
A set of three papers in Nature reports a new proteomics resource from the UK Biobank and initial analysis of common and rare genetic variant associations with plasma protein levels.
- Ryan S. Dhindsa
- , Oliver S. Burren
- & Slavé Petrovski
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
The Pharma Proteomics Project generates the largest open-access plasma proteomics dataset to date, offering insights into trans protein quantitative trait loci across multiple biological domains, and highlighting genetic influences on ligand–receptor interactions and pathway perturbations across a diverse collection of cytokines and complement networks.
- Benjamin B. Sun
- , Joshua Chiou
- & Christopher D. Whelan
-
Article |
 Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
A scalable total synthesis of portimines enables structural reassignment of portimine B and in-depth functional evaluation of portimine A, revealing that portimine A induces translation inhibition selectively in human cancer cells and is efficacious in vivo tumour-clearance models.
- Junchen Tang
- , Weichao Li
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
 A cross-species proteomic map reveals neoteny of human synapse development
A cross-species proteomic map reveals neoteny of human synapse development
A study presents a cross-species proteomic map of synapse development in neocortex and reveals that the human postsynaptic density assembly develops two to three times slower than that in macaques and mice.
- Li Wang
- , Kaifang Pang
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein
-
Article
| Open Access A viral ADP-ribosyltransferase attaches RNA chains to host proteins
A viral ADP-ribosyltransferase attaches RNA chains to host proteins
Bacteriophage T4 uses an enzyme known as ADP-ribosyltransferase ModB to modify the translational apparatus of bacteria it infects, not only by ADP-ribosylating proteins, but also by attaching entire RNA chains in a process known as RNAylation.
- Maik Wolfram-Schauerte
- , Nadiia Pozhydaieva
- & Katharina Höfer
-
News |
 Dementia risk linked to blood-protein imbalance in middle age
Dementia risk linked to blood-protein imbalance in middle age
Abnormal levels of certain proteins — many of which have roles outside the brain — could be an early hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease or similar conditions.
- Lilly Tozer
-
News Feature |
 AI tools are designing entirely new proteins that could transform medicine
AI tools are designing entirely new proteins that could transform medicine
Digital art techniques can now devise custom, working biomolecules on demand.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Outlook |
 Disrupting protein folding to tackle cancer
Disrupting protein folding to tackle cancer
Intermediate states show promise as drug targets.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Article
| Open Access Astrocyte–neuron subproteomes and obsessive–compulsive disorder mechanisms
Astrocyte–neuron subproteomes and obsessive–compulsive disorder mechanisms
Analyses of the proteomes of astrocytes and neurons in a cell-specific and subcompartment-specific manner reveal distinct roles for these cell types that are relevant to obsessive–compulsive disorder and perhaps other brain disorders.
- Joselyn S. Soto
- , Yasaman Jami-Alahmadi
- & Baljit S. Khakh
-
Article |
 Tracking chromatin state changes using nanoscale photo-proximity labelling
Tracking chromatin state changes using nanoscale photo-proximity labelling
A proximity labelling-based approach for mapping nuclear protein–protein interactions is described that could advance epigenetic drug discovery.
- Ciaran P. Seath
- , Antony J. Burton
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Research Briefing |
 Genome-based scores predict thousands of molecular traits in humans
Genome-based scores predict thousands of molecular traits in humans
Genetic scores for predicting levels of several types of biomolecule have been developed and validated in people of diverse ancestries, and used to uncover insights into disease biology. An open resource to disseminate these scores, OmicsPred, will enable researchers to predict various molecular traits from genetic profiles in their own data sets.
-
Research Briefing |
 A census of complexes formed by mitochondrial proteins
A census of complexes formed by mitochondrial proteins
Mitochondria are intracellular organelles that contain a large set of proteins to help them produce energy, among other functions. A systematic analysis reveals how mitochondrial proteins are organized into complexes and assemblies, facilitating the identification of the molecular mechanisms and pathways that underlie the organelle’s many functions.
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
An analysis of MitCOM—a comprehensive resource for the identification, organization and interaction of mitochondrial machineries and pathways in yeast—identifies a constitutive pathway for the removal of preproteins.
- Uwe Schulte
- , Fabian den Brave
- & Thomas Becker
-
Career Column |
 ‘Moms in Proteomics’ pushes for change
‘Moms in Proteomics’ pushes for change
A need for community drove Jennifer Geddes-McAlister to found a network for mothers in science. Here’s what she learnt.
- Jennifer Geddes-McAlister
-
News |
 AlphaFold’s new rival? Meta AI predicts shape of 600 million proteins
AlphaFold’s new rival? Meta AI predicts shape of 600 million proteins
Microbial molecules from soil, seawater and human bodies are among the planet’s least understood.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Spotlight |
 Using proteins to test for COVID antibodies
Using proteins to test for COVID antibodies
Working at a research hospital allows Fridtjof Lund-Johansen to test the effectiveness of vaccines in people with compromised immune systems.
- Helen Santoro
-
News |
 Scientists are using AI to dream up revolutionary new proteins
Scientists are using AI to dream up revolutionary new proteins
Huge advances in artificial intelligence mean researchers can design completely original molecules in seconds instead of months.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Nature Index |
 Four rising stars who are reshaping nanoscience
Four rising stars who are reshaping nanoscience
From nano-filters for tackling water pollution to protein fingerprinting that treats disease, these researchers are making their mark on the field.
- Gemma Conroy
- & Benjamin Plackett
-
Editorial |
 How AlphaFold can realize AI’s full potential in structural biology
How AlphaFold can realize AI’s full potential in structural biology
To make the most of artificial intelligence, data and software must be freely shared, and computational, theoretical and experimental researchers must work together closely.
-
News |
 ‘The entire protein universe’: AI predicts shape of nearly every known protein
‘The entire protein universe’: AI predicts shape of nearly every known protein
DeepMind’s AlphaFold tool has determined the structures of around 200 million proteins.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article |
 Deciphering the immunopeptidome in vivo reveals new tumour antigens
Deciphering the immunopeptidome in vivo reveals new tumour antigens
A newly developed genetically engineered mouse model enables the analysis of specific antigen presentation in vivo, providing insights into the tumour immunopeptidome and cancer progression.
- Alex M. Jaeger
- , Lauren E. Stopfer
- & Tyler Jacks
-
Research Briefing |
 A hybrid control model for the eukaryotic cell cycle
A hybrid control model for the eukaryotic cell cycle
The organizational principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle have yet to be pinned down, and two opposing models have been put forward. Genetic and proteomics analyses in a model eukaryote, fission yeast, reveal that the cell cycle is organized through a hybrid of both models, although the contribution of one strongly outweighs the other.
-
Article
| Open Access Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
The core cell cycle is largely driven by increasing total CDK activity together with minor differences in the substrate specificity of the CDKs initiating DNA replication and mitosis.
- Souradeep Basu
- , Jessica Greenwood
- & Paul Nurse
-
Article |
 Defining mitochondrial protein functions through deep multiomic profiling
Defining mitochondrial protein functions through deep multiomic profiling
A multiomics resource characterizing human mitochondrial proteins enables identification of biological functions and supports genetic diagnosis of mitochondrial pathologies.
- Jarred W. Rensvold
- , Evgenia Shishkova
- & David J. Pagliarini
-
Article
| Open Access Rixosomal RNA degradation contributes to silencing of Polycomb target genes
Rixosomal RNA degradation contributes to silencing of Polycomb target genes
The rixosome associates with Polycomb repressive complexes and chromatin and has a role in silencing of Polycomb target gene expression in human cells via degradation of nascent RNA transcripts.
- Haining Zhou
- , Chad B. Stein
- & Danesh Moazed
-
Article
| Open Access Tryptophan depletion results in tryptophan-to-phenylalanine substitutants
Tryptophan depletion results in tryptophan-to-phenylalanine substitutants
Tryptophan depletion, which occurs in tumours, results in in-frame translation across tryptophan-encoding codons by phenylalanine substitution.
- Abhijeet Pataskar
- , Julien Champagne
- & Reuven Agami
-
Technology Feature |
 Single-cell proteomics takes centre stage
Single-cell proteomics takes centre stage
Deducing the full protein complement of individual cells has long played second fiddle to transcriptomics. That’s about to change.
- Jeffrey M. Perkel
-
Article
| Open Access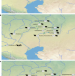 Dairying enabled Early Bronze Age Yamnaya steppe expansions
Dairying enabled Early Bronze Age Yamnaya steppe expansions
Analysis of ancient proteins suggests that Early Bronze Age dairying and horse domestication catalysed eastern Yamnaya migrations.
- Shevan Wilkin
- , Alicia Ventresca Miller
- & Nicole Boivin
-
News & Views |
 Protein pile-up plays havoc in ageing nematode worms
Protein pile-up plays havoc in ageing nematode worms
An analysis in ageing nematode worms reveals reductions in the tagging of certain proteins for clearance. This can lead to the accumulation of unnecessary proteins, in turn impairing cellular and tissue function.
- Bart P. Braeckman
-
Editorial |
 Artificial intelligence in structural biology is here to stay
Artificial intelligence in structural biology is here to stay
Machine learning will transform our understanding of protein folding. And it’s essential that all data be open.
-
News |
 Single chip tests thousands of enzyme mutations at once
Single chip tests thousands of enzyme mutations at once
The technique vastly speeds up understanding of how the proteins function and how to target drugs.
- Sara Reardon
-
News |
 DeepMind’s AI predicts structures for a vast trove of proteins
DeepMind’s AI predicts structures for a vast trove of proteins
AlphaFold neural network produced a ‘totally transformative’ database of more than 350,000 structures from Homo sapiens and 20 model organisms.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Outlook |
 Turning transient structures into drug targets
Turning transient structures into drug targets
Start-up Sibylla Biotech has developed a drug-discovery platform to look for protein folding intermediates to target therapeutically.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Article |
 A proximity-dependent biotinylation map of a human cell
A proximity-dependent biotinylation map of a human cell
A proximity-dependent biotinylation technique defines the location of more than 4,000 proteins in a human cell, and almost 36,000 proximal interactions between proteins, including those at the interface of the mitochondria and ER.
- Christopher D. Go
- , James D. R. Knight
- & Anne-Claude Gingras
-
Article |
 Multilevel proteomics reveals host perturbations by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV
Multilevel proteomics reveals host perturbations by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV
Multi-omics profiling of effects of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV on A549, a lung-derived human cell line, produces a dataset enabling identification of common and virus-specific mechanisms of infection.
- Alexey Stukalov
- , Virginie Girault
- & Andreas Pichlmair
-
Article |
 Spatiotemporal dissection of the cell cycle with single-cell proteogenomics
Spatiotemporal dissection of the cell cycle with single-cell proteogenomics
Spatial and temporal variations among individual human cell proteomes are comprehensively mapped across the cell cycle using proteomic imaging and transcriptomics.
- Diana Mahdessian
- , Anthony J. Cesnik
- & Emma Lundberg
-
Article |
 Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms
Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms
Inhibition of YBX1, a downstream target of the Janus kinase JAK2, sensitizes myeloproliferative neoplasm cells to JAK and could provide a means to eradicate such cells in human haematopoietic cancers.
- Ashok Kumar Jayavelu
- , Tina M. Schnöder
- & Florian H. Heidel
-
Outlook |
 The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The limitations of genomic data have led to a deeper exploration of transcriptomic and proteomic data in cancer.
- Simon Makin
-
Article |
 Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Bulk RNA sequencing of organs and plasma proteomics at different ages across the mouse lifespan is integrated with data from the Tabula Muris Senis, a transcriptomic atlas of ageing mouse tissues, to describe organ-specific changes in gene expression during ageing.
- Nicholas Schaum
- , Benoit Lehallier
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Article |
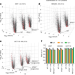 Systematic quantitative analysis of ribosome inventory during nutrient stress
Systematic quantitative analysis of ribosome inventory during nutrient stress
During nutrient stress, ribosomal protein abundance is regulated primarily by translational and non-autophagic degradative mechanisms, but ribosome density per cell is largely maintained by reductions in cell volume and rates of cell division.
- Heeseon An
- , Alban Ordureau
- & J. Wade Harper
-
Article |
 The proteome landscape of the kingdoms of life
The proteome landscape of the kingdoms of life
An advanced proteomics workflow is used to identify 340,000 proteins from 100 taxonomically diverse species, providing a comparative view of proteomes across the evolutionary range.
- Johannes B. Müller
- , Philipp E. Geyer
- & Matthias Mann

 A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan