News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
A transient perturbation of transcriptional silencing mediated by Polycomb proteins is sufficient to induce an epigenetic cancer cell fate in Drosophila in the absence of driver mutations.
- V. Parreno
- , V. Loubiere
- & G. Cavalli
-
Nature Podcast |
 Pregnancy’s effect on ‘biological’ age, polite birds, and the carbon cost of home-grown veg
Pregnancy’s effect on ‘biological’ age, polite birds, and the carbon cost of home-grown veg
We round up some recent stories from the Nature Briefing.
- Benjamin Thompson
- , Noah Baker
- & Flora Graham
-
Article |
 Targeting DCAF5 suppresses SMARCB1-mutant cancer by stabilizing SWI/SNF
Targeting DCAF5 suppresses SMARCB1-mutant cancer by stabilizing SWI/SNF
DCAF5 has a quality-control function for SWI/SNF complexes and promotes the degradation of incompletely assembled SWI/SNF complexes in the absence of SMARCB1.
- Sandi Radko-Juettner
- , Hong Yue
- & Charles W. M. Roberts
-
News |
 Pregnancy advances your ‘biological’ age — but giving birth turns it back
Pregnancy advances your ‘biological’ age — but giving birth turns it back
Carrying a baby creates some of the same epigenetic patterns on DNA seen in older people.
- Saima Sidik
-
Article
| Open Access Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
In Caenorhabditis tropicalis, selective expression of genetic alleles from one parent but not the other can arise from maternally inherited small transcripts acting via the PIWI-interacting RNA host defence pathway.
- Pinelopi Pliota
- , Hana Marvanova
- & Alejandro Burga
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
A multidimensional proteomics analysis of the interactions between around 2,000 nuclear proteins and over 80 modified dinucleosomes representing promoter, enhancer and heterochromatin states provides insights into how chromatin states are decoded by chromatin readers.
- Saulius Lukauskas
- , Andrey Tvardovskiy
- & Till Bartke
-
Article
| Open Access Durable and efficient gene silencing in vivo by hit-and-run epigenome editing
Durable and efficient gene silencing in vivo by hit-and-run epigenome editing
Experiments in mice show that designed epigenome editors that contain domains of transcriptional repressors can enable stable epigenetic silencing of Pcsk9, a gene with a role in cholesterol homeostasis, without inducing DNA breaks.
- Martino Alfredo Cappelluti
- , Valeria Mollica Poeta
- & Angelo Lombardo
-
Nature Podcast |
 Could this one-time ‘epigenetic’ treatment control cholesterol?
Could this one-time ‘epigenetic’ treatment control cholesterol?
Regulating gene expression lowers blood cholesterol in mice, and how the Universe’s cosmic fog was lifted.
- Nick Petrić Howe
-
News |
 ‘Epigenetic’ editing cuts cholesterol in mice
‘Epigenetic’ editing cuts cholesterol in mice
Changes to chemical tags on DNA in mice dial down the activity of a gene without cuts to the genome.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms of action and resistance in histone methylation-targeted therapy
Mechanisms of action and resistance in histone methylation-targeted therapy
The mechanisms of action and resistance of valemetostat, an EZH1–EZH2 dual inhibitor, in patients with adult T cell leukaemia/lymphoma who initially responded but later showed disease progression are explored.
- Makoto Yamagishi
- , Yuta Kuze
- & Kaoru Uchimaru
-
Article
| Open Access WNT signalling control by KDM5C during development affects cognition
WNT signalling control by KDM5C during development affects cognition
The demethylase KDM5C, mutations in which often lead to intellectual disability, is identified as a crucial player in regulating the precise timing of neurodevelopment together with the WNT signalling pathway.
- Violetta Karwacki-Neisius
- , Ahram Jang
- & Yang Shi
-
Technology Feature |
 Super-speedy sequencing puts genomic diagnosis in the fast lane
Super-speedy sequencing puts genomic diagnosis in the fast lane
Streamlined workflows for DNA and RNA sequencing are helping clinicians to deliver prompt, targeted care to people in days — or even hours.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Nature Video |
 Why human brain cells grow so slowly
Why human brain cells grow so slowly
Some human neurons take years to reach maturity; an epigenetic ‘brake’ could be responsible.
- Shamini Bundell
-
News & Views |
 Gene expression of single cells mapped in tissue sections
Gene expression of single cells mapped in tissue sections
A tool that tags individual cells in a tissue with a unique barcode means that the gene-expression profile of each cell can be plotted in its original location. This allows spatial information to be captured at single-cell resolution.
- Patrik L. Ståhl
-
News & Views Forum |
 Cellular atlases of the entire mouse brain
Cellular atlases of the entire mouse brain
In a huge collaborative effort, millions of cells in the mouse brain have been mapped in detail. Two scientists examine the resulting wealth of insights into gene regulation in brain cells, neuronal connections and how our own brains evolved.
- Maria Antonietta Tosches
- & Heather J. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
A single-cell multiomics analysis of over 200,000 cells of the primary motor cortex of human, macaque, marmoset and mouse shows that divergence of transcription factor expression corresponds to species-specific epigenome landscapes, and conserved and divergent gene regulatory features are reflected in the evolution of the three-dimensional genome.
- Nathan R. Zemke
- , Ethan J. Armand
- & Bing Ren
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
A study describes the molecular basis of sexual development of Toxoplasma gondii entirely in vitro, demonstrating the role and interaction of AP2XII-1 and AP2XI-2 in the developmental program of this protozoan parasite.
- Ana Vera Antunes
- , Martina Shahinas
- & Mohamed-Ali Hakimi
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain
Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain
Methylome-based clustering and cross-modality integration with companion datasets from the BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network enabled the construction of a 3D multi-omic genome atlas of the adult mouse brain featuring thousands of cell-type-specific profiles.
- Hanqing Liu
- , Qiurui Zeng
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
Article
| Open Access MSL2 ensures biallelic gene expression in mammals
MSL2 ensures biallelic gene expression in mammals
After loss of MSL2, a class of dosage-sensitive genes transitions from biallelic to monoallelic expression, whereby one allele remains active, retaining active histone modifications and transcription factor binding, and the other allele is silenced, exhibiting loss of promoter–enhancer contacts and the acquisition of DNA methylation.
- Yidan Sun
- , Meike Wiese
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article |
 Asymmetric distribution of parental H3K9me3 in S phase silences L1 elements
Asymmetric distribution of parental H3K9me3 in S phase silences L1 elements
The epigenetic modification H3K9me3 is asymmetrically partitioned at long interspersed nuclear element retrotransposons for their silencing in S phase, a newly discovered mechanism that is mediated by the HUSH complex and the DNA polymerase Pol ε.
- Zhiming Li
- , Shoufu Duan
- & Zhiguo Zhang
-
Article |
 TNRC18 engages H3K9me3 to mediate silencing of endogenous retrotransposons
TNRC18 engages H3K9me3 to mediate silencing of endogenous retrotransposons
Trinucleotide-repeat-containing 18 (TNRC18), which has poorly understood functions, is now identified as an H3K9me3-specific reader that silences endogenous retroviruses.
- Shuai Zhao
- , Jiuwei Lu
- & Gang Greg Wang
-
News & Views |
 Master regulator of a mosquito X chromosome discovered
Master regulator of a mosquito X chromosome discovered
In organisms with X and Y chromosomes, gene expression must be equalized between the sexes. A protein that causes upregulation of gene expression of the X chromosome in male mosquitoes has been discovered.
- Maggie P. Lauria Sneideman
- & Victoria H. Meller
-
Article
| Open Access The sex-specific factor SOA controls dosage compensation in Anopheles mosquitoes
The sex-specific factor SOA controls dosage compensation in Anopheles mosquitoes
A newly identified gene, sex chromosome activation (SOA), is a master regulator of dosage compensation in Anopheles gambiae.
- Agata Izabela Kalita
- , Eric Marois
- & Claudia Isabelle Keller Valsecchi
-
Research Briefing |
 A way to wipe a cell’s memory
A way to wipe a cell’s memory
Cells that have been artificially reprogrammed into states similar to embryonic stem cells — known as induced pluripotent stem cells — can bear a memory of their previous history. An innovative method that incorporates a step mimicking early development yields pluripotent cells that more closely resemble those in embryos, both on a molecular and functional level.
-
Article |
 RNA polymerase II associates with active genes during DNA replication
RNA polymerase II associates with active genes during DNA replication
Protein complexes containing RNA polymerase II and immature RNA are associated with active genes immediately after replication, suggesting that transmission of active transcriptional states to daughter cells may not require any additional epigenetic bookmarks.
- Tyler K. Fenstermaker
- , Svetlana Petruk
- & Alexander Mazo
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse modes of H3K36me3-guided nucleosomal deacetylation by Rpd3S
Diverse modes of H3K36me3-guided nucleosomal deacetylation by Rpd3S
Structural and biochemical studies of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpd3 small complex in free and H3K36me3 nucleosome-bound states reveal multiple nucleosome-binding modes and provide insights into mechanisms underlying epigenetic regulation by histone modification.
- Haipeng Guan
- , Pei Wang
- & Haitao Li
-
Article
| Open Access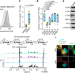 A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation
A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation
Cellular uptake of copper(ii) by CD44 has a key role in regulating cellular plasticity via copper(ii)-dependent downstream signalling events.
- Stéphanie Solier
- , Sebastian Müller
- & Raphaël Rodriguez
-
Article |
 Large-scale mapping and mutagenesis of human transcriptional effector domains
Large-scale mapping and mutagenesis of human transcriptional effector domains
A high throughput recruitment assay testing the transcriptional activity of more than 100,000 protein fragments tiling across most human chromatin regulators and transcription factors maps the locations and strengths of activation, repression and bifunctional domains, and identifies the sequences necessary for these functions.
- Nicole DelRosso
- , Josh Tycko
- & Lacramioara Bintu
-
Article |
 Basis of the H2AK119 specificity of the Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase
Basis of the H2AK119 specificity of the Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) in complex with the H2AK119ub1 nucleosome provides insight into how the substrate specificity of PR-DUB is achieved.
- Weiran Ge
- , Cong Yu
- & Rui-Ming Xu
-
News & Views |
 Inheritance of epigenetic DNA marks studied in new mouse model
Inheritance of epigenetic DNA marks studied in new mouse model
There is debate about how epigenetic marks, such as methyl groups on DNA, can be passed down from parent to offspring. A mouse model involving targeted DNA methylation will better equip researchers to study this process.
- Serge McGraw
- & Sarah Kimmins
-
Research Briefing |
 Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Cells in which the whole genome has been doubled do not upscale protein synthesis to cope with the increase in DNA. Instead, a shortage of proteins that regulate the packing of DNA in the nucleus leads to poor segregation of DNA structures, which eventually contributes to the development of cancer.
-
Research Briefing |
 Gene expression and epigenetic regulation co-mapped in brain tissues
Gene expression and epigenetic regulation co-mapped in brain tissues
Gene expression and features of the DNA–protein complex chromatin were mapped together at high spatial resolution in tissue sections of the mouse or human brain. This spatially resolved technology enables the examination of the spatio-temporal dynamics and regulation of gene expression in complex mammalian tissues.
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome doubling drives oncogenic loss of chromatin segregation
Whole-genome doubling drives oncogenic loss of chromatin segregation
Whole-genome doubling induces the loss of segregation of chromatin compartments, and can lead to tumour-promoting epigenetic and transcriptional modifications.
- Ruxandra A. Lambuta
- , Luca Nanni
- & Elisa Oricchio
-
Article
| Open Access H3K4me3 regulates RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pause-release
H3K4me3 regulates RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pause-release
Acute loss of H3K4me3 does not have detectable effects on transcriptional initiation, but leads to a widespread decrease in transcriptional output, an increase in RNA polymerase II pausing and slower elongation
- Hua Wang
- , Zheng Fan
- & Kristian Helin
-
Technology Feature |
 Innovative technologies crowd the short-read sequencing market
Innovative technologies crowd the short-read sequencing market
With a dizzying range of strategies available, laboratories must weigh up their options to find the best fit for their projects
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Article |
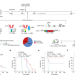 TET2 guards against unchecked BATF3-induced CAR T cell expansion
TET2 guards against unchecked BATF3-induced CAR T cell expansion
Disruption of TET2 increases the antitumour efficacy of CAR T cells, but establishes an epigenetic state that is prone to hyperproliferation and accumulation of secondary mutations.
- Nayan Jain
- , Zeguo Zhao
- & Michel Sadelain
-
Obituary |
 C. David Allis (1951–2023)
C. David Allis (1951–2023)
Biologist who revolutionized the chromatin and gene-expression field.
- Sharon Dent
- & Shiv Grewal
-
Article
| Open Access Inheritance of paternal DNA damage by histone-mediated repair restriction
Inheritance of paternal DNA damage by histone-mediated repair restriction
In Caenorhabditis elegans, paternal exposure to ionizing radiation results in HIS-24 and HPL-1-dependent genome instability phenotypes, causing embryonic lethality in the offspring.
- Siyao Wang
- , David H. Meyer
- & Björn Schumacher
-
Technology Feature |
 Which single-cell analysis tool is best? Scientists offer advice
Which single-cell analysis tool is best? Scientists offer advice
In the fast-paced field of single-cell biology, studies that compare methods can help scientists to pick the right technique for their research.
- Amber Dance
-
Article |
 Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Results are presented that indicate that alterations to gene regulatory three-dimensional architecture are a critical mechanism that enables structural variant-based oncogene activation in cancer genomes and sheds light on the essential elements for such gene activation events.
- Zhichao Xu
- , Dong-Sung Lee
- & Jesse R. Dixon
-
News |
 How the Great Depression shaped people’s DNA
How the Great Depression shaped people’s DNA
Epigenetics study finds that children born during the historic recession have markers of accelerated ageing later in life.
- Freda Kreier
-
Research Briefing |
 How flowering plants compact their sperm DNA
How flowering plants compact their sperm DNA
It has not been clear how sperm DNA is compacted in the pollen of flowering plants. Research has now revealed that sperm chromatin, which is a complex of DNA and proteins, is packaged by a special histone protein that spontaneously aggregates in a phenomenon known as phase separation.
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
H2B.8 is identified as a histone variant that mediates a newly described mechanism of transcription-compatible chromatin condensation in flowering plant sperm cells.
- Toby Buttress
- , Shengbo He
- & Xiaoqi Feng
-
News & Views |
 SARS-CoV-2 mimics a host protein to bypass defences
SARS-CoV-2 mimics a host protein to bypass defences
It emerges that the SARS-CoV-2 virus has evolved to mimic one of the histone proteins that package DNA in the cell nucleus. This mimicry leads to disrupted gene transcription and a diminished antiviral response.
- Lisa Thomann
- & Volker Thiel
-
Article |
 SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry
SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry
The SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8 functions as a mimic of histone H3 to disrupt host cell epigenetic regulation.
- John Kee
- , Samuel Thudium
- & Erica Korb
-
Article |
 Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose signalling via TOR controls growth and differentiation through regulation of genome-wide histone methylation via FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE).
- Ruiqiang Ye
- , Meiyue Wang
- & Jen Sheen
-
News & Views |
 Two-layer design protects genes from mutations in their enhancers
Two-layer design protects genes from mutations in their enhancers
Gene expression is regulated by clusters of regulatory DNA sequences called enhancers. Basic design principles that protect enhancer networks against the harmful effects of genetic mutations have now been elucidated.
- Ran Elkon
- & Reuven Agami
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
The structures of single COOLAIR RNA isoforms change in abundance and shape in response to external conditions; structural mutation of these isoforms altered FLC expression and flowering time, consistent with a regulatory role of the COOLAIR structure in FLC transcription.
- Minglei Yang
- , Pan Zhu
- & Yiliang Ding
-
Review Article |
 Inflammatory memory and tissue adaptation in sickness and in health
Inflammatory memory and tissue adaptation in sickness and in health
A Review on inflammatory memory in non-immune cells of different epithelia and neurons, and the potential mechanisms controlling these epigenetic memories and their implications in human health and disease.
- Shruti Naik
- & Elaine Fuchs

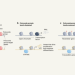 Tumours form without genetic mutations
Tumours form without genetic mutations