News Feature |
Featured
-
-
Outlook |
 Neurobiology: Rise of resilience
Neurobiology: Rise of resilience
Stress can have a negative influence on the human brain, but increasingly it is the ability to withstand severe stress that is the focus of research.
- Anthony King
-
News & Views |
 A new methyl mark on messengers
A new methyl mark on messengers
The presence of an N1 methyl group on adenine bases in DNA and RNA was thought to be a form of damage. Results now show that it also occurs at specific sites in messenger RNAs, where it affects protein expression. See Article p.441
- Anna M. Kietrys
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
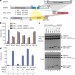 Structural basis for activity regulation of MLL family methyltransferases
Structural basis for activity regulation of MLL family methyltransferases
Crystal structures of the SET domains of MLL3 and a mutant MLL1 either unbound or complexed with domains from RBBP5 and ASH2L are determined; a combination of structural, biochemical and computational analyses reveals a two-step activation mechanism of MLL family proteins, which may be relevant for other histone methyltransferases.
- Yanjing Li
- , Jianming Han
- & Ming Lei
-
Article |
 The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA
Here the m1A modification is discovered in messenger RNA and mapped at the transcriptome-wide level; the modification is conserved, dynamic, accumulates in structured regions around translation initiation sites upstream of the first splice site, and correlates with higher protein expression.
- Dan Dominissini
- , Sigrid Nachtergaele
- & Chuan He
-
Research Highlights |
On–off switch for obesity
-
News & Views |
 Bet on drug resistance
Bet on drug resistance
Inhibitors of the BET bromodomain proteins are promising cancer therapeutics, but tumour cells are likely to become resistant to these drugs. Anticipated mechanisms of resistance have now been described. See Letter p.413
- Jeff Settleman
-
News & Views |
 Oncogene brought into the loop
Oncogene brought into the loop
Analysis of the 3D structure of DNA in tumour cells reveals how mutations in the IDH1 gene, and associated changes in methyl groups attached to DNA, elevate the expression of cancer-promoting genes. See Letter p.110
- Matthew R. Grimmer
- & Joseph F. Costello
-
Letter |
 Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas
Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas
An epigenetic mechanism in which gain-of-function IDH mutations promote gliomagenesis by disrupting chromosomal topology is presented, with IDH mutations causing the binding sites of the methylation-sensitive insulator CTCF to become hypermethylated; disruption of a CTCF boundary near the glioma oncogene PDGFRA allows a constitutive enhancer to contact and activate the oncogene aberrantly.
- William A. Flavahan
- , Yotam Drier
- & Bradley E. Bernstein
-
Letter |
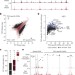 Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1
Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1
The relationship between DNA methylation and transcription factor binding was studied across the genome in mouse embryonic stem cells-the study reveals that the transcription factor NRF1 is methylation-sensitive and how physiological binding of NRF1 relies on local removal of DNA methylation.
- Silvia Domcke
- , Anaïs Flore Bardet
- & Dirk Schübeler
-
Outlook |
 Genome editing: 4 big questions
Genome editing: 4 big questions
Despite the popularity of genome-editing techniques, researchers are still grappling with the known unknowns of the technologies. Here are four of their most pressing questions.
- Will Tauxe
-
Outlook |
 Epigenetics: The genome unwrapped
Epigenetics: The genome unwrapped
Epigeneticists are harnessing genome-editing technologies to tackle a central question hanging over the community — does their field matter?
- Heidi Ledford
-
Outlook |
 Genetics: Relative risk
Genetics: Relative risk
Mutations in BRCA genes predispose women to cancer, but outside influences shape the ultimate risk.
- Moises Velasquez-Manoff
-
Letter |
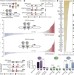 Transcriptional regulators form diverse groups with context-dependent regulatory functions
Transcriptional regulators form diverse groups with context-dependent regulatory functions
A large-scale enhancer complementation assay assessing the activating or repressing contributions of over 800 Drosophila transcription factors and cofactors to combinatorial enhancer control reveals a more complex picture than expected, with many factors having diverse regulatory functions that depend on the enhancer context.
- Gerald Stampfel
- , Tomáš Kazmar
- & Alexander Stark
-
Outlook |
 Collaborations: Mining the motherlodes
Collaborations: Mining the motherlodes
Collaboration and competition are spurring on major '-omic' projects.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Letter |
 Structural insight into substrate preference for TET-mediated oxidation
Structural insight into substrate preference for TET-mediated oxidation
In DNA demethylation, human TET proteins are evolutionarily tuned to be less reactive towards 5hmC and facilitate its generation as a potentially stable mark for regulatory functions.
- Lulu Hu
- , Junyan Lu
- & Yanhui Xu
-
Social Selection |
 Preprints called on to support controversial talks
Preprints called on to support controversial talks
Scientists on social media grapple with the idea of posting preprints of provocative research presented at meetings.
- Rachel Becker
-
News & Views |
 Mediating transcription and RNA export
Mediating transcription and RNA export
The finding that the Mediator protein complex contributes to messenger RNA export from the nucleus in yeast adds to a growing list of roles for the complex in regulating transcriptional processes.
- Jonathan D. Rubin
- & Dylan J. Taatjes
-
Letter |
 BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitors that target bromodomain chromatin readers such as BRD4 are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, in a MLL–AF9 mouse leukaemia model, resistance to BET inhibitors is shown to emerge from leukaemia stem cells, and be partly due to increased Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
- Chun Yew Fong
- , Omer Gilan
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
News & Views |
 The karma of oil palms
The karma of oil palms
Despite their clonal origin, some oil palm trees develop fruits that give almost no oil. It emerges that the number of methyl groups attached to a DNA region called Karma determine which plants are defective. See Letter p.533
- Jerzy Paszkowski
-
Letter |
 Loss of Karma transposon methylation underlies the mantled somaclonal variant of oil palm
Loss of Karma transposon methylation underlies the mantled somaclonal variant of oil palm
The oil palm fruit ‘mantled’ abnormality is a somaclonal variant that markedly reduces yield; here, a genome-wide DNA methylation analysis finds that hypomethylation of a single Karma family retrotransposon embedded in a homeotic gene intron is common to all mantled clones and is associated with aberrant splicing and termination of the gene transcript, and that loss of methylation predicts a loss of oil palm yield.
- Meilina Ong-Abdullah
- , Jared M. Ordway
- & Robert A. Martienssen
-
News & Views |
 Mutant p53 and chromatin regulation
Mutant p53 and chromatin regulation
The finding that genes encoding enzymes that modify histone proteins are among the targets of certain mutant forms of the p53 protein sheds light on how these mutations cause cancer beyond p53 inactivation. See Article p.206
- Carol Prives
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
News & Views |
 Salvaging the genome
Salvaging the genome
Overexpression of the enzyme cytidine deaminase allows the incorporation of abnormally modified nucleotides into DNA, leading to cell death. This discovery might point the way to treating some cancers. See Letter p.114
- Sharanya Sivanand
- & Kathryn E. Wellen
-
Letter |
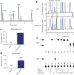 CDA directs metabolism of epigenetic nucleosides revealing a therapeutic window in cancer
CDA directs metabolism of epigenetic nucleosides revealing a therapeutic window in cancer
Enzymes of the nucleotide salvage pathway are shown to have substrate selectivity that protects newly synthesized DNA from random incorporation of epigenetically modified forms of cytosine; a subset of cancer cell lines that overexpress cytidine deaminase (CDA) are sensitive to treatment with 5hmdC or 5fdC (oxidized forms of 5-methyl-cytosine), which leads to DNA damage and cell death, indicating the chemotherapeutic potential of these nucleoside variants for CDA-overexpressing cancers.
- Melania Zauri
- , Georgina Berridge
- & Skirmantas Kriaucionis
-
Letter |
 Molecular basis for 5-carboxycytosine recognition by RNA polymerase II elongation complex
Molecular basis for 5-carboxycytosine recognition by RNA polymerase II elongation complex
Structural and biochemical studies of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) assembled on DNA containing 5-carboxycytosine reveals that Pol II can sense the oxidized methylation state of DNA and transiently slows down during transcription.
- Lanfeng Wang
- , Yu Zhou
- & Dong Wang
-
Letter |
 Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation
Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation
Genome-wide chromosome conformation capture analysis in C. elegans reveals that the dosage compensation complex, a condensin complex, remodels the X chromosomes of hermaphrodites into a sex-specific topology distinct from autosomes while regulating gene expression chromosome-wide.
- Emily Crane
- , Qian Bian
- & Barbara J. Meyer
-
Letter
| Open Access Human body epigenome maps reveal noncanonical DNA methylation variation
Human body epigenome maps reveal noncanonical DNA methylation variation
As part of the Epigenome Roadmap Project, genome-wide maps of DNA methylation and transcriptomes together with genomic DNA sequencing of 18 different primary human tissue types from 4 individuals are presented; analysis reveals widespread differential methylation of CG sites between tissues, and the presence of non-CG methylation in adult tissues.
- Matthew D. Schultz
- , Yupeng He
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
Research Highlights |
 Mammary cells have a memory
Mammary cells have a memory
-
Letter |
 The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3
The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3
The mechanisms by which Xist, a long non-coding RNA, silences one X chromosome in female mammals are unknown; here a mass spectrometry-based approach is developed to identify several proteins that interact directly with Xist, including the transcriptional repressor SHARP that is required for transcriptional silencing through the histone deacetylase HDAC3.
- Colleen A. McHugh
- , Chun-Kan Chen
- & Mitchell Guttman
-
Research Highlights |
CRISPR controls gene expression
-
Research Highlights |
Methylation makes the brain female
-
Books & Arts |
 Books in brief
Books in brief
Daniel Cressey reviews five of the week's best science picks.
- Daniel Cressey
-
News & Views |
 RNA interference hangs by a thread
RNA interference hangs by a thread
The Paf1 protein complex in fission yeast has been found to protect protein-coding genes from inhibition by RNA-mediated silencing of transcription, by stimulating the release of nascent transcripts from DNA. See Letter p.248
- Mikel Zaratiegui
-
Letter |
 The Paf1 complex represses small-RNA-mediated epigenetic gene silencing
The Paf1 complex represses small-RNA-mediated epigenetic gene silencing
The fission yeast is shown to have a mechanism to prevent small RNAs from inducing heterochromatin and epigenetic gene silencing; this protective model involves the highly conserved Paf1 complex, which is known to promote transcription and processing of pre-mRNA, and protects protein-coding genes from unwanted silencing by spurious transcripts.
- Katarzyna Maria Kowalik
- , Yukiko Shimada
- & Marc Bühler
-
Letter |
 Disruption of DNA-methylation-dependent long gene repression in Rett syndrome
Disruption of DNA-methylation-dependent long gene repression in Rett syndrome
Rett syndrome is caused by mutation of the MECP2 gene that codes for a protein that binds methylated DNA; this study reveals that MeCP2 affects the expression of long genes, which often serve neuronal functions.
- Harrison W. Gabel
- , Benyam Kinde
- & Michael E. Greenberg
-
News |
 Epigenome: The symphony in your cells
Epigenome: The symphony in your cells
A slew of papers reveals the chemical tweaks to DNA in a wealth of different cells — as explained with the help of a small orchestra.
- Kerri Smith
-
Nature Video |
 Epigenome: The symphony in your cells
Epigenome: The symphony in your cells
-
Editorial |
Beyond the genome
Studies of the epigenomic signatures of many healthy and diseased human tissues could provide crucial information to link genetic variation and disease.
-
News & Views |
 Roadmap for regulation
Roadmap for regulation
A package of papers investigates the functional regulatory elements in genomes that have been obtained from human tissue samples and cell lines. The implications of the project are presented here from three viewpoints. See Articles p.317, p.331, p.337 & p.344 and Letters p.350, p.355, p.360 & p.365
- Casey E. Romanoski
- , Christopher K. Glass
- & Genevieve Almouzni
-
Letter
| Open Access Integrative analysis of haplotype-resolved epigenomes across human tissues
Integrative analysis of haplotype-resolved epigenomes across human tissues
As part of the Epigenome Roadmap project, this study uses a chromosome-spanning haplotype reconstruction strategy to construct haplotype-resolved epigenomic maps for a diverse set of human tissues; the maps reveal extensive allelic biases in chromatin state and transcription, which vary across individuals due to genetic backgrounds.
- Danny Leung
- , Inkyung Jung
- & Bing Ren
-
Letter |
 An epigenome-wide association study of total serum immunoglobulin E concentration
An epigenome-wide association study of total serum immunoglobulin E concentration
A survey of epigenetic associations between serum immunoglobulin E concentrations indicating allergy and methylation at CpG islands in families and a population sample has revealed associations at 36 loci that harbour genes encoding proteins including eosinophil products and phospholipid inflammatory mediators.
- Liming Liang
- , Saffron A. G. Willis-Owen
- & William O. C. M. Cookson
-
Letter |
 Super-enhancers delineate disease-associated regulatory nodes in T cells
Super-enhancers delineate disease-associated regulatory nodes in T cells
A study of the super-enhancer landscape in three mouse T-helper lymphocyte subsets identifies nodes that have key roles in cell identity, with the locus encoding Bach2, a key negative regulator of effector differentiation, emerging as the most prominent T-cell super-enhancer.
- Golnaz Vahedi
- , Yuka Kanno
- & John J. O’Shea
-
Letter |
 Genomic profiling of DNA methyltransferases reveals a role for DNMT3B in genic methylation
Genomic profiling of DNA methyltransferases reveals a role for DNMT3B in genic methylation
Genome-wide localization and activity analysis of the de novo DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B in mouse embryonic stem cells identifies overlapping and individual targeting preferences to the genome, including a role for DNMT3B in gene body methylation.
- Tuncay Baubec
- , Daniele F. Colombo
- & Dirk Schübeler
-
Letter |
 TRIM37 is a new histone H2A ubiquitin ligase and breast cancer oncoprotein
TRIM37 is a new histone H2A ubiquitin ligase and breast cancer oncoprotein
The RING finger protein TRIM37 is encoded by a gene that is amplified in certain breast cancers, but its function is unknown; here, it is shown to mono-ubiquitinate histone H2A and repress gene expression, and to function as a breast cancer oncoprotein.
- Sanchita Bhatnagar
- , Claude Gazin
- & Michael R. Green
-
Letter |
 Structural insight into autoinhibition and histone H3-induced activation of DNMT3A
Structural insight into autoinhibition and histone H3-induced activation of DNMT3A
A working model for histone H3-induced dynamic regulation of the de novo DNA methyltransferase.
- Xue Guo
- , Ling Wang
- & Yanhui Xu
-
Letter |
 Tyrosine phosphorylation of histone H2A by CK2 regulates transcriptional elongation
Tyrosine phosphorylation of histone H2A by CK2 regulates transcriptional elongation
A conserved tyrosine residue, Tyr 57, of histone H2A is phosphorylated by an unsuspected tyrosine kinase activity of casein kinase 2, influencing a series of histone marks associated with active transcription and regulating transcription elongation.
- Harihar Basnet
- , Xue B. Su
- & Michael G. Rosenfeld
-
Letter |
 Epigenetic reprogramming that prevents transgenerational inheritance of the vernalized state
Epigenetic reprogramming that prevents transgenerational inheritance of the vernalized state
The Arabidopsis thaliana floral repressor FLC is epigenetically silenced by prolonged cold in a process called vernalization and then is reactivated before the completion of seed development; a histone demethylase, ELF6, is now shown to be involved in reactivating FLC in reproductive tissues, allowing the resetting of FLC expression and thus the requirement for vernalization in each generation.
- Pedro Crevillén
- , Hongchun Yang
- & Caroline Dean
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional interference by antisense RNA is required for circadian clock function
Transcriptional interference by antisense RNA is required for circadian clock function
The transcriptions of frq sense and antisense RNAs are mutually inhibitory and form a double negative feedback loop required for robust and sustained circadian rhythmicity: antisense transcription inhibits sense expression by causing chromatin modifications and premature transcription termination.
- Zhihong Xue
- , Qiaohong Ye
- & Yi Liu
-
Letter |
 A long noncoding RNA protects the heart from pathological hypertrophy
A long noncoding RNA protects the heart from pathological hypertrophy
Here, a long noncoding RNA, termed Mhrt, is identified in the loci of myosin heavy chain (Myh) genes in mice and shown to be capable of suppressing cardiomyopathy in the animals, as well as being repressed in diseased human hearts.
- Pei Han
- , Wei Li
- & Ching-Pin Chang
-
Letter |
 Antifungal drug resistance evoked via RNAi-dependent epimutations
Antifungal drug resistance evoked via RNAi-dependent epimutations
The human fungal pathogen Mucor circinelloides develops spontaneous resistance to an antifungal drug both through mutation and through a newly identified epigenetic RNA-mediated pathway; RNA interference is spontaneously triggered to silence the fkbA gene, giving rise to drug-resistant epimutants that revert to being drug-sensitive once again when grown in the absence of drug.
- Silvia Calo
- , Cecelia Shertz-Wall
- & Joseph Heitman

 CRISPR: gene editing is just the beginning
CRISPR: gene editing is just the beginning