Featured
-
-
Article |
 Genome-wide forward genetic screening to identify receptors and proteins mediating nanoparticle uptake and intracellular processing
Genome-wide forward genetic screening to identify receptors and proteins mediating nanoparticle uptake and intracellular processing
Understanding how cells process nanoparticles is crucial to improve nanomedicine efficacy. Here a genome-wide screening is used to discover proteins that are involved in silica nanoparticle accumulation by cells and shows that different apolipoprotein receptors and proteoglycans mediate their internalization.
- Daphne Montizaan
- , Roberta Bartucci
- & Anna Salvati
-
Article |
 Targeting initial tumour–osteoclast spatiotemporal interaction to prevent bone metastasis
Targeting initial tumour–osteoclast spatiotemporal interaction to prevent bone metastasis
Tumour cell behaviour is an underdeveloped target for cancer intervention. Here the authors report on a spatiotemporal interaction between tumour cells and osteoclasts in initial bone metastases and propose a behaviour-targeting therapy with an in situ physical killing strategy.
- Chenhui Gu
- , Pengfei Chen
- & Xianfeng Lin
-
Article |
 Fine tuning of CpG spatial distribution with DNA origami for improved cancer vaccination
Fine tuning of CpG spatial distribution with DNA origami for improved cancer vaccination
The spacing of ligands presented to cells can have a huge impact on cellular responses. DNA origami is used to block structures to control the distribution of Toll-like receptor ligands and optimize presentation in the activation of dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy.
- Yang C. Zeng
- , Olivia J. Young
- & William M. Shih
-
Article |
 Photothermal therapy of tuberculosis using targeting pre-activated macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles
Photothermal therapy of tuberculosis using targeting pre-activated macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles
Tuberculosis is a major global health issue. Here the authors report Mycobacterium-pre-activated macrophage membrane-coated photothermal nanoparticles for targeted tuberculous granuloma and pathogen dual imaging and antibacterial photothermal therapy.
- Bin Li
- , Wei Wang
- & Yuhui Liao
-
Article |
 Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
Manufacturing complexities, low yield and stability issues have hampered the clinical translation and scaling-up of immunoliposomes to meet the needs of pharmaceutical-grade products. The authors propose a one-step method of incorporating chimeric nanobodies tagged to hydrophobic linkers into liposomes, allowing targeted delivery of small-molecule anti-cancer drugs to tumours.
- Md. Mofizur Rahman
- , Jing Wang
- & Yuan Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular uptake and in vivo distribution of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are protein corona dependent
Cellular uptake and in vivo distribution of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are protein corona dependent
In regenerative medicine, stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are emerging as cell-free nanotherapeutics. Here, the authors show that coating these nanovesicles with blood proteins such as albumin improves their uptake by liver cells, offering a better treatment strategy for liver diseases.
- Revadee Liam-Or
- , Farid N. Faruqu
- & Khuloud T. Al-Jamal
-
Article |
 Augmenting insect olfaction performance through nano-neuromodulation
Augmenting insect olfaction performance through nano-neuromodulation
Insects have been shown to have the ability to detect different chemical agents. Here, the authors present a nanomaterial-assisted neuromodulation strategy to augment the chemosensory abilities of insects via photothermal effect and on-demand neurotransmitter release from cargo-loaded nanovehicles to augment natural sensory function.
- Prashant Gupta
- , Rishabh Chandak
- & Srikanth Singamaneni
-
Article |
 Controlled adsorption of multiple bioactive proteins enables targeted mast cell nanotherapy
Controlled adsorption of multiple bioactive proteins enables targeted mast cell nanotherapy
Proteins absorbed on nanomaterials often lose function due to denaturation. A poly(propylene sulfone) nanoparticle with site-specific dipole relaxation has been reported, which allows proteins to anchor to the nanoparticle without disrupting the hydrogen bonding or structure maintaining the protein functionality.
- Fanfan Du
- , Clayton H. Rische
- & Evan A. Scott
-
Article |
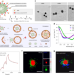 Nanoreceptors promote mutant p53 protein degradation by mimicking selective autophagy receptors
Nanoreceptors promote mutant p53 protein degradation by mimicking selective autophagy receptors
Protein degradation is a powerful tool for a range of applications and therapies. Here, a selective autophagy receptor mimetic against mutant p53 protein is developed to substantially elevate autophagy levels and to recognize and transport mutant proteins for autophagy-mediated degradation and anticancer effect.
- Xiaowan Huang
- , Ziyang Cao
- & Yunjiao Zhang
-
Article |
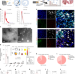 Inhalable extracellular vesicle delivery of IL-12 mRNA to treat lung cancer and promote systemic immunity
Inhalable extracellular vesicle delivery of IL-12 mRNA to treat lung cancer and promote systemic immunity
Cytokine interleukin-12 (IL-12) has potential for tumour suppression yet off-target effects limit potential applications. Here the authors report on the delivery of IL-12 mRNA encapsulated in extracellular vesicles to lungs via inhalation and demonstrate the immunotherapeutic potential of targeted cytokine mRNA therapy.
- Mengrui Liu
- , Shiqi Hu
- & Ke Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Oral nanotherapeutic formulation of insulin with reduced episodes of hypoglycaemia
Oral nanotherapeutic formulation of insulin with reduced episodes of hypoglycaemia
Insulin injections are not ideal and have an increased risk of hypoglycaemia. A preferable oral formulation based on silver sulfide quantum dots coated with a chitosan/glucose polymer is discussed, which has controlled insulin release and reduced risk of hypoglycaemia, and demonstrates applications in rodent and non-human primate models.
- Nicholas J. Hunt
- , Glen P. Lockwood
- & Victoria C. Cogger
-
News & Views |
 Intracerebral fate of engineered nanoparticles
Intracerebral fate of engineered nanoparticles
Organic and inorganic nanoparticles have different clearance mechanisms from the brain resulting in different biological fates and retention times.
- Elizabeth Nance
-
Review Article |
 Strategies for non-viral vectors targeting organs beyond the liver
Strategies for non-viral vectors targeting organs beyond the liver
Nanoparticles naturally accumulate in the liver; this can be a major limitation to any therapy needing delivery to other organs or tissues. Here the authors review the reason for predominant liver uptake and explore different strategies used to target non-viral gene delivery nanoparticles to other organs and tissues.
- Jeonghwan Kim
- , Yulia Eygeris
- & Gaurav Sahay
-
Article |
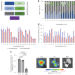 Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs
Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs
Nebulized mRNA delivery has broad therapeutic potential but has proven challenging. Here, the authors report on a modified lipid nanoparticle with improved conditions to allow nebulization and demonstrate its application for delivering mRNA to the lungs.
- Allen Y. Jiang
- , Jacob Witten
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Article |
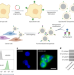 A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering
A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering
Synthetic nanoparticles coated with cell membranes show immune evasion and circulate longer. Here, a genetically engineered cell membrane expressing a SpyCatcher anchor is used as a modular nanotherapeutic drug delivery platform for high-affinity targeting and suppression of ovarian cancer.
- Nishta Krishnan
- , Yao Jiang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Biohybrid nanoparticles for treating arthritis
Biohybrid nanoparticles for treating arthritis
A biohybrid nanoparticle formulation effectively treats rheumatoid arthritis by concurrently providing symptom relief and restoring proper immune function.
- Ronnie H. Fang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
Article |
 Age-associated disparity in phagocytic clearance affects the efficacy of cancer nanotherapeutics
Age-associated disparity in phagocytic clearance affects the efficacy of cancer nanotherapeutics
Here, the authors find a decrease in hepatic phagocytic uptake of nanoparticles in old mice due to age-associated downregulation of the scavenger receptor MARCO, which led to improved tumour delivery and antitumour efficacy of cancer nanomedicine, showing the need to consider age as a factor in therapeutics.
- Yifan Wang
- , Weiye Deng
- & Wen Jiang
-
Article |
 Breaking through the basement membrane barrier to improve nanotherapeutic delivery to tumours
Breaking through the basement membrane barrier to improve nanotherapeutic delivery to tumours
Nanoparticle penetration into tumours is an obstacle to cancer therapeutics. Here the authors show that the tumour vascular basement membrane constitutes a barrier that reduces nanoparticle delivery and demonstrate an immune-driven strategy to overcome the barrier, increasing nanoparticle movement into tumours.
- Qin Wang
- , Qirui Liang
- & Yucai Wang
-
Comment |
The Cancer Moonshot, the role of in vitro models, model accuracy, and the need for validation
Reducing cancer-related deaths can only happen with a better understanding of cancer biology and the development of improved, new therapeutics and delivery mechanisms. Nearly all cancer research is dependent upon the models being used, the model’s accuracy, and appropriate validation and benchmarking. Here the need for such considerations is discussed in line with the goal of the Cancer Moonshot.
- Peter C. Searson
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable multispecific DNA-origami-based T-cell engagers
Programmable multispecific DNA-origami-based T-cell engagers
A synthetic nanocarrier based on DNA origami chassis offers control over valency, orientation and spatial arrangement of antibodies for simultaneously engaging immune signalling pathways, checkpoint inhibition and targeted co-stimulation in anticancer immunotherapy in vivo.
- Klaus F. Wagenbauer
- , Nhi Pham
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Article |
 Close the cancer–immunity cycle by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy
Close the cancer–immunity cycle by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy
Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment is a challenge. A strategy to close the cancer–immunity cycle has been reported by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy to promote tumour elimination and develop antitumour immunity.
- Yuebao Zhang
- , Xucheng Hou
- & Yizhou Dong
-
Article |
 Universal, label-free, single-molecule visualization of DNA origami nanodevices across biological samples using origamiFISH
Universal, label-free, single-molecule visualization of DNA origami nanodevices across biological samples using origamiFISH
Signal amplification through hybridization chain reaction by targeting conserved regions of the M13mp18 bacteriophage-based scaffold sequences is used for in situ imaging of unlabelled DNA origami nanostructures.
- Wendy Xueyi Wang
- , Travis R. Douglas
- & Leo Y. T. Chou
-
Article |
 Transport by circulating myeloid cells drives liposomal accumulation in inflamed synovium
Transport by circulating myeloid cells drives liposomal accumulation in inflamed synovium
PEGylated liposomal accumulation in inflamed regions has mainly been attributed to the enhanced permeation and retention effect. An arthritis model that chemotactically attracted myeloid cells shows that monocytes and neutrophils play an essential role in liposome delivery towards inflamed joints.
- Joke Deprez
- , Rein Verbeke
- & Ine Lentacker
-
Article |
 Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines
Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines
A lipid nanoparticle (LNP) component—an adjuvant lipidoid—is developed to enhance the adjuvanticity of LNPs, which significantly increases the innate and adaptive responses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines with good tolerability in mice.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article |
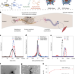 Controlled delivery of a neurotransmitter–agonist conjugate for functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury
Controlled delivery of a neurotransmitter–agonist conjugate for functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury
Here the authors report the delivery of neurotransmitter-conjugated KCC2 agonist using a reactive oxygen species–responsive polymer nanoparticle that can cross the damaged blood–spinal cord barrier and significantly increase recovery after spinal cord injury in vivo.
- Yanming Zuo
- , Jingjia Ye
- & Xuhua Wang
-
Article |
 Non-invasive activation of intratumoural gene editing for improved adoptive T-cell therapy in solid tumours
Non-invasive activation of intratumoural gene editing for improved adoptive T-cell therapy in solid tumours
Cancer resistance to apoptosis can hinder T-cell-based therapies. Here, the authors develop a temperature-sensitive system for the controlled delivery of a Cas9 gene-editing sequence targeting resistance mechanisms HSP70 and BAG3, which with a mild thermal effect increases T-cell delivery and therapeutic outcomes.
- Xiaohong Chen
- , Shuang Wang
- & Yuan Ping
-
Article |
 Tailoring renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin for colorectal cancer-selective drug delivery
Tailoring renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin for colorectal cancer-selective drug delivery
Optimizing the retention of drug delivery nanocarriers for improved cancer therapy has the potential to improve clinical outcomes. Here the authors screen 20 renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin-based nanocarriers for optimized biodistribution and tumour retention, demonstrating application in colorectal cancer models.
- Min-Jun Baek
- , Duy-Thuc Nguyen
- & Dae-Duk Kim
-
News & Views |
 Artificial intelligence assists nanoparticles to enter solid tumours
Artificial intelligence assists nanoparticles to enter solid tumours
Single blood vessel analysis by artificial intelligence (AI) reveals heterogeneous vascular permeability among different tumour types, which is leveraged in rationally designing protein nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems to achieve active trans-endothelial permeability in tumours.
- Lutz Nuhn
-
News & Views |
 Rerouting nanoparticles to bone marrow via neutrophil hitchhiking
Rerouting nanoparticles to bone marrow via neutrophil hitchhiking
Drug delivery to the bone marrow has limited efficiency, hitchhiking on bone marrow homing neutrophils offers a solution.
- Ningqiang Gong
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article |
 Neutrophil hitchhiking for drug delivery to the bone marrow
Neutrophil hitchhiking for drug delivery to the bone marrow
Systemic drug delivery to the bone marrow is limited, currently requiring high doses of drug, increasing the risk of side effects. Here, the authors report on the hitchhiking of drug nanoparticles in neutrophils using their natural homing to the bone marrow for targeted delivery, and demonstrate its application.
- Zhenyu Luo
- , Yichao Lu
- & Jian You
-
Article |
 Artificial-enzymes-armed Bifidobacterium longum probiotics for alleviating intestinal inflammation and microbiota dysbiosis
Artificial-enzymes-armed Bifidobacterium longum probiotics for alleviating intestinal inflammation and microbiota dysbiosis
Approaches to treat inflammatory bowel disease with probiotics or artificial enzymes have advantages and limitations. Here we combine the advantages to overcome the individual limitations by modifying probiotics with artificial enzymes and demonstrate application in treating inflammatory bowel disease.
- Fangfang Cao
- , Lulu Jin
- & Zhengwei Mao
-
News & Views |
 Multidrug nanomedicine
Multidrug nanomedicine
Polymer-based nanomedicines have been engineered to ratiometrically deliver three different drugs to tumors, thereby bridging in vitro–in vivo correlation and producing synergistic therapeutic efficacy in multiple myeloma mouse models.
- Alexandros Marios Sofias
- & Twan Lammers
-
Article |
 Machine-learning-assisted single-vessel analysis of nanoparticle permeability in tumour vasculatures
Machine-learning-assisted single-vessel analysis of nanoparticle permeability in tumour vasculatures
Using genetically tailored protein-based nanoprobes and taking advantage of image-segmentation-based machine learning, a high-throughput assessment of vascular permeability of individual blood vessels in 32 different tumours is quantified. These insights are valuable in developing personalized anticancer nanomedicine therapeutics and strategies modulating vascular permeability to treat tumours.
- Mingsheng Zhu
- , Jie Zhuang
- & Xinglu Huang
-
Article |
 Molecular bottlebrush prodrugs as mono- and triplex combination therapies for multiple myeloma
Molecular bottlebrush prodrugs as mono- and triplex combination therapies for multiple myeloma
Although nanomedicine has shown benefits with respect to soluble drug administration, whether delivery of multiple drugs within the same nanocarrier has advantages over administration of single-drug nanomedicines or combination of free drugs at the same dosage is unclear. Here we use a bottlebrush prodrug platform to show that the delivery of three drugs in a synergistic combination in animal models outperforms other combinatorial approaches for multiple myeloma therapy.
- Alexandre Detappe
- , Hung V.-T. Nguyen
- & Jeremiah A. Johnson
-
Review Article |
 The potential impact of nanomedicine on COVID-19-induced thrombosis
The potential impact of nanomedicine on COVID-19-induced thrombosis
This Review analyses the possibilities that a nanomedicine approach offers to tackle COVID-19-induced thrombosis and the associated challenges.
- Peije Russell
- , Lars Esser
- & Nicolas H. Voelcker
-
Article |
 Selective targeting of visceral adiposity by polycation nanomedicine
Selective targeting of visceral adiposity by polycation nanomedicine
Accumulation of visceral fat, linked to adipocyte expansion and overgrowth, is the most detrimental aspect of obesity, and a major cause of obesity comorbidities. We develop a cationic nanomedicine based on polyamidoamine dendrimers that specifically targets visceral fat and shrinks adipocytes, inhibiting diet-induced obesity and improving metabolic health in murine models.
- Qianfen Wan
- , Baoding Huang
- & Li Qiang
-
Article |
 Targeting Xkr8 via nanoparticle-mediated in situ co-delivery of siRNA and chemotherapy drugs for cancer immunochemotherapy
Targeting Xkr8 via nanoparticle-mediated in situ co-delivery of siRNA and chemotherapy drugs for cancer immunochemotherapy
Downregulation of specific proteins named scramblases might enhance tumour immunosuppression. In this paper the authors first show that the scramblase Xrk8 is overexpressed in tumour cells upon treatment with chemotherapeutics, and then develop a nanomedicine platform for co-delivery of a cancer prodrug and an siRNA directed against the Xrk8 gene, showing therapeutic effect and enhanced immune response in animal tumour models.
- Yuang Chen
- , Yixian Huang
- & Song Li
-
Article |
 Zinc cyclic di-AMP nanoparticles target and suppress tumours via endothelial STING activation and tumour-associated macrophage reinvigoration
Zinc cyclic di-AMP nanoparticles target and suppress tumours via endothelial STING activation and tumour-associated macrophage reinvigoration
Activation of the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) can induce immunity in various cancer therapies, but delivery of STING agonists to tumours is challenging. Now a metal-based polymeric nanoparticle delivers STING agonists to tumours upon disruption of endothelial cells in tumour vasculature and targets tumour-associated macrophages, eliciting anti-tumour immune response in hard-to-treat cancer models.
- Kaiting Yang
- , Wenbo Han
- & Ralph R. Weichselbaum
-
Perspective |
 Nanotechnology-based strategies against SARS-CoV-2 variants
Nanotechnology-based strategies against SARS-CoV-2 variants
This Perspective highlights the role that nanotechnology might play in tackling the rise of new SARS-CoV-2 variants.
- Xiangang Huang
- , Edo Kon
- & Wei Tao
-
Article |
 Nanomedicine platform for targeting activated neutrophils and neutrophil–platelet complexes using an α1-antitrypsin-derived peptide motif
Nanomedicine platform for targeting activated neutrophils and neutrophil–platelet complexes using an α1-antitrypsin-derived peptide motif
While neutrophils are the first line of defence against infections and inflammation, their unrestricted recruitment and constant activation might result in prolonged inflammation and sharpening of specific pathological conditions. Here the authors develop a strategy to specifically target activated, pro-inflammatory neutrophils and neutrophil–platelet complexes to deliver therapeutics in the context of a murine model of venous thrombosis.
- Michelle A. Cruz
- , Dillon Bohinc
- & Evi X. Stavrou
-
Article |
 NAD(H)-loaded nanoparticles for efficient sepsis therapy via modulating immune and vascular homeostasis
NAD(H)-loaded nanoparticles for efficient sepsis therapy via modulating immune and vascular homeostasis
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an immune modulator that was suggested as a potential treatment for sepsis, but its in vivo benefits are contradictory and its low bioavailability as a free drug hampers potential clinical translation. Here the authors show that using a lipid-coated nanoparticle to deliver NAD+ to the cell cytosol can effectively replenish the intracellular content of NAD+ and reduce the extent of the inflammatory response in mouse models of sepsis.
- Mingzhou Ye
- , Yi Zhao
- & Shaoqin Gong
-
Article |
 Cancer immunotherapy based on image-guided STING activation by nucleotide nanocomplex-decorated ultrasound microbubbles
Cancer immunotherapy based on image-guided STING activation by nucleotide nanocomplex-decorated ultrasound microbubbles
Activation of the STING pathway in antigen-presenting cells has been proposed as a strategy to stimulate the adaptive immune response against tumours, but its clinical application is hampered by the instability, low specificity and low cytosolic entry of natural STING agonists. Here the authors present a platform for targeted ultrasound-mediated cytosolic delivery of STING agonists that shows efficacy in different animal tumour models and improves the response to checkpoint blockade therapies.
- Xuefeng Li
- , Sina Khorsandi
- & Jacques Lux
-
Article |
 Enhancing CRISPR/Cas gene editing through modulating cellular mechanical properties for cancer therapy
Enhancing CRISPR/Cas gene editing through modulating cellular mechanical properties for cancer therapy
In vivo delivery of the CRISPR/Cas system is a promising cancer therapy approach, but its efficacy is hampered by low penetrability of nanoparticles in the stiff tumour tissue. Here the authors use dendrimer lipid nanoparticles to couple PD-L1 gene editing with knockdown of FAK, a protein involved in cell adhesion, showing that modulation of the mechanical properties of tumour cells leads to enhanced gene editing and tumour growth inhibition in four different animal models.
- Di Zhang
- , Guoxun Wang
- & Daniel J. Siegwart
-
News & Views |
 Boosting dendritic cell nanovaccines
Boosting dendritic cell nanovaccines
A preclinical study reports a platform for the generation of dendritic cell-derived nanovesicles with enhanced immunostimulatory function, which demonstrate promising antitumoural activity in mouse models and might overcome some of the shortcomings of early-generation dendritic cell nanovaccines.
- Yahya Mohammadzadeh
- & Michele De Palma
-
Review Article |
 Applying lessons learned from nanomedicines to understand rare hypersensitivity reactions to mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
Applying lessons learned from nanomedicines to understand rare hypersensitivity reactions to mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
This perspective analyses the adverse reactions reported for mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in the light of infusion reactions to nanomedicines, which display similar outcomes, suggests possible mechanisms and offers a safety roadmap for vaccine developers.
- Janos Szebeni
- , Gert Storm
- & Marina A. Dobrovolskaia
-
Analysis |
 Nano-enabled pesticides for sustainable agriculture and global food security
Nano-enabled pesticides for sustainable agriculture and global food security
A comprehensive analysis of the key properties of nanopesticides in controlling agricultural pests for crop enhancement shows a much higher efficacy compared with non-nano analogues, also for in-field trials.
- Dengjun Wang
- , Navid B. Saleh
- & Chunming Su
-
Article |
 Subcutaneous nanotherapy repurposes the immunosuppressive mechanism of rapamycin to enhance allogeneic islet graft viability
Subcutaneous nanotherapy repurposes the immunosuppressive mechanism of rapamycin to enhance allogeneic islet graft viability
Orally delivered rapamycin is an immunosuppressant that inhibits islet graft rejection in patients treated for type 1 diabetes, but it suffers from poor bioavailability, inconsistent cellular distribution and adverse reactions. Here the authors show that subcutaneous delivery of rapamycin using a polymersome platform allows for control of the drug’s biodistribution and activity on specific immune cells, which changes its mechanism of action from immunosuppression to tolerance, reduces side effects and enhances anti-inflammatory efficacy.
- Jacqueline A. Burke
- , Xiaomin Zhang
- & Evan A. Scott
-
Article |
 Intrapleural nano-immunotherapy promotes innate and adaptive immune responses to enhance anti-PD-L1 therapy for malignant pleural effusion
Intrapleural nano-immunotherapy promotes innate and adaptive immune responses to enhance anti-PD-L1 therapy for malignant pleural effusion
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is the terminal stage of cancer and the current standard of care for MPE is largely palliative. Here the authors design a liposomal nanoparticle loaded with cyclic dinucleotide for targeted activation of STING signalling in macrophages and dendritic cells and show that, on intrapleural administration, the nanoparticle effectively mitigates the immune cold MPE and significantly augments the checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in a mouse MPE model and clinical patients’ samples.
- Yang Liu
- , Lulu Wang
- & Dawen Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Nanomedicine hitchhikes on neutrophils to the inflamed lung
Nanomedicine hitchhikes on neutrophils to the inflamed lung
Supramolecular arrangement of proteins provides nanoparticles with neutrophil tropism via complement opsonization during an acute inflammation, enabling diagnosis and treatment of acute lung injury.
- Jeonghwan Kim
- & Gaurav Sahay

 Multimodal nanoimmunotherapy engages neutrophils to eliminate Staphylococcus aureus infections
Multimodal nanoimmunotherapy engages neutrophils to eliminate Staphylococcus aureus infections