Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Vortices produced and studied in electron fluids
Vortices produced and studied in electron fluids
Swirling vortices have been directly observed in a flow of electric current for the first time. Unlike conventional viscous fluids, collective fluid-like behaviour in this case is not caused by particle–particle collisions, but results from a previously unidentified mechanism involving single electrons scattering from material surfaces at small angles.
-
News & Views |
 Topology turns the crank on a magnetoelectric switch
Topology turns the crank on a magnetoelectric switch
A mechanism resembling a crankshaft switches the electric polarization of a material in response to changes in an applied magnetic field. The resulting four-state switch is linked to the material’s intriguing topology.
- Wei Ren
- & Laurent Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access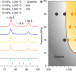 Coherent interfaces govern direct transformation from graphite to diamond
Coherent interfaces govern direct transformation from graphite to diamond
The discovery of graphite–diamond hybrid carbon, Gradia, which consists of graphite and diamond nanodomains interlocked through coherent interfaces, clarifies the long-standing mystery of how graphite turns into diamond.
- Kun Luo
- , Bing Liu
- & Yongjun Tian
-
Article |
 Topologically protected magnetoelectric switching in a multiferroic
Topologically protected magnetoelectric switching in a multiferroic
The electric polarization of a multiferroic is reversed by the application and subsequent removal of a magnetic field, resulting in topologically protected unidirectional magnetoelectric switching.
- Louis Ponet
- , S. Artyukhin
- & Andrei Pimenov
-
News & Views |
 Layered material soaks up molecules to form an electron sieve
Layered material soaks up molecules to form an electron sieve
A simple method for incorporating molecules into the gaps of stacked semimetallic materials through immersion offers an efficient way of filtering electrons, which could be useful for information-storage technologies.
- Xi Ling
-
Article |
 Chiral molecular intercalation superlattices
Chiral molecular intercalation superlattices
By intercalating layered 2D atomic crystals with selected chiral molecules, a new class of chiral molecular intercalation superlattices is reported, demonstrating highly ordered structures and achieving high tunnelling magnetoresistance and spin polarization ratios.
- Qi Qian
- , Huaying Ren
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
News & Views |
 Crystalline order offers access to high speeds for organic transistors
Crystalline order offers access to high speeds for organic transistors
A transistor fabricated from the crystalline phase of an organic semiconductor material could provide a path to improved switching speeds — rivalling those of devices built from inorganic materials such as silicon.
- Julie Euvrard
- & Barry P. Rand
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering topological states in atom-based semiconductor quantum dots
Engineering topological states in atom-based semiconductor quantum dots
Precision-engineered devices consisting of a linear array of ten quantum dots are used to realize both the trivial and topological phases of the many-body Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model.
- M. Kiczynski
- , S. K. Gorman
- & M. Y. Simmons
-
Article |
 Evidence for unconventional superconductivity in twisted trilayer graphene
Evidence for unconventional superconductivity in twisted trilayer graphene
High-resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy are used to provide evidence for unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene.
- Hyunjin Kim
- , Youngjoon Choi
- & Stevan Nadj-Perge
-
Research Briefing |
 A step closer to atom lasers that stay on
A step closer to atom lasers that stay on
Continuous amplification of coherent matter waves has been demonstrated, allowing an exotic state of matter called a Bose–Einstein condensate to be maintained indefinitely. This set-up is the matter-wave analogue of an optical laser enclosed by fully reflective mirrors, and it could have uses in both applied and fundamental physics.
-
News & Views |
 Nanoscale map shows how interfaces impede vibrations
Nanoscale map shows how interfaces impede vibrations
The collective vibrations of atoms at the interface between two semiconducting materials have been imaged with nanometre-scale resolution. Their dynamics depends sensitively on the abruptness of the boundary.
- Fredrik S. Hage
-
Article |
 Ordered and tunable Majorana-zero-mode lattice in naturally strained LiFeAs
Ordered and tunable Majorana-zero-mode lattice in naturally strained LiFeAs
An ordered Majorana-zero-mode lattice in naturally strained LiFeAs is reported, formed by vortices pinned to charge density wave stripes, and with density and geometry tunable by application of an external magnetic field.
- Meng Li
- , Geng Li
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale imaging of phonon dynamics by electron microscopy
Nanoscale imaging of phonon dynamics by electron microscopy
A method for mapping phonon momenta reveals non-equilibrium phonon dynamics at nanoscale interfaces enabling study of actual nanodevices and aiding understanding of heat dissipation near nanoscale hotspots.
- Chaitanya A. Gadre
- , Xingxu Yan
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Observation of Cooper pairs in a mesoscopic two-dimensional Fermi gas
Observation of Cooper pairs in a mesoscopic two-dimensional Fermi gas
Precise control over the quantum state of a two-dimensional Fermi gas together with single-particle-resolved fluorescence imaging enables the direct observation of the formation of Cooper pairs at the Fermi surface.
- Marvin Holten
- , Luca Bayha
- & Selim Jochim
-
Article |
 Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Detection of an axial Higgs mode by quantum pathway interference reveals an unconventional charge density wave phase in RTe3.
- Yiping Wang
- , Ioannis Petrides
- & Kenneth S. Burch
-
News & Views |
 Multilayer 2D insulator shows promise for post-silicon electronics
Multilayer 2D insulator shows promise for post-silicon electronics
A method has been developed for fabricating thin films of the 2D insulator hexagonal boron nitride with a uniform crystal orientation. The advance makes this material a key contender for replacing silica substrates in future electronics.
- Soo Ho Choi
- & Soo Min Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing the symmetry-protected Haldane phase in Fermi–Hubbard ladders
Realizing the symmetry-protected Haldane phase in Fermi–Hubbard ladders
A ladder-like arrangement of an ultracold gas of lithium atoms trapped in an optical lattice enables the observation of a symmetry-protected topological phase.
- Pimonpan Sompet
- , Sarah Hirthe
- & Immanuel Bloch
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian chiral phononics through optomechanically induced squeezing
Non-Hermitian chiral phononics through optomechanically induced squeezing
Time-reversal symmetry breaking is combined with non-Hermitian dynamics in an optomechanical system with squeezing interactions to produce chirality in the system, and a non-Hermitian Aharonov–Bohm effect is observed.
- Javier del Pino
- , Jesse J. Slim
- & Ewold Verhagen
-
Perspective |
 Strongly correlated electron–photon systems
Strongly correlated electron–photon systems
The control of light–matter interactions as a way to manipulate and synthesize strongly correlated quantum matter is discussed, highlighting a field termed ‘strongly correlated electron–photon science’.
- Jacqueline Bloch
- , Andrea Cavalleri
- & Angel Rubio
-
Article |
 Polariton Bose–Einstein condensate from a bound state in the continuum
Polariton Bose–Einstein condensate from a bound state in the continuum
Using a patterned waveguide, a Bose–Einstein condensate of polaritons is realized in a bound state in the continuum, with a low condensation threshold density that occurs at a dispersion saddle point.
- V. Ardizzone
- , F. Riminucci
- & D. Sanvitto
-
Article |
 Observation of ultracold atomic bubbles in orbital microgravity
Observation of ultracold atomic bubbles in orbital microgravity
Bubbles of ultracold atoms have been created, observed and characterized at the NASA Cold Atom Lab onboard the International Space Station, made possible by the microgravity environment of the laboratory.
- R. A. Carollo
- , D. C. Aveline
- & N. Lundblad
-
Article
| Open Access Materials synthesis at terapascal static pressures
Materials synthesis at terapascal static pressures
Pressures of up to 900 gigapascals (9 million atmospheres) are achieved in a laser-heated double-stage diamond cell, enabling the synthesis of Re7N3, and materials characterization is performed in situ using single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
- Leonid Dubrovinsky
- , Saiana Khandarkhaeva
- & Natalia Dubrovinskaia
-
Article |
 Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers in a gold–graphene–gold heterostructure is demonstrated, and used to create a logic gate for application in lightwave electronics.
- Tobias Boolakee
- , Christian Heide
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Imaging tunable quantum Hall broken-symmetry orders in graphene
Imaging tunable quantum Hall broken-symmetry orders in graphene
Three tunable quantum Hall broken-symmetry states in charge-neutral graphene are identified by visualizing their lattice-scale order with scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy.
- Alexis Coissard
- , David Wander
- & Benjamin Sacépé
-
Article |
 One-dimensional Luttinger liquids in a two-dimensional moiré lattice
One-dimensional Luttinger liquids in a two-dimensional moiré lattice
A tuneable platform using twisted WTe2 stacks is described in which an electronic phase in the two-dimensional moiré lattice array is shown to resemble one-dimensional Luttinger liquids.
- Pengjie Wang
- , Guo Yu
- & Sanfeng Wu
-
Research Highlight |
 Pressure prods an elusive superconductor to emerge at last
Pressure prods an elusive superconductor to emerge at last
A high-pressure, high-heat method produces a long-sought crystal.
-
Article |
 The field-free Josephson diode in a van der Waals heterostructure
The field-free Josephson diode in a van der Waals heterostructure
A Josephson diode is made by fabricating an inversion symmetry breaking van der Waals heterostructure of NbSe2/Nb3Br8/NbSe2, demonstrating that even without a magnetic field, the junction can be superconducting with a positive current but resistive with a negative current.
- Heng Wu
- , Yaojia Wang
- & Mazhar N. Ali
-
Article |
 Observation of a linked-loop quantum state in a topological magnet
Observation of a linked-loop quantum state in a topological magnet
A study combining spectroscopy and mathematical topology reports the observation of linked node loops in a quantum magnet, with properties suggesting a Seifert bulk–boundary correspondence.
- Ilya Belopolski
- , Guoqing Chang
- & M. Zahid Hasan
-
Article |
 Light-induced ferromagnetism in moiré superlattices
Light-induced ferromagnetism in moiré superlattices
A study reveals light as a new dynamic knob to control ferromagnetic order in moiré superlattices.
- Xi Wang
- , Chengxin Xiao
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
News & Views |
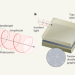 A detector that can learn the fingerprint of light
A detector that can learn the fingerprint of light
The polarization, wavelength and power of a light wave can be simultaneously identified by a compact device made from twisted layers of carbon atoms — with a little help from an artificial neural network.
- Justin C. W. Song
- & Yidong Chong
-
Article |
 Perovskite–organic tandem solar cells with indium oxide interconnect
Perovskite–organic tandem solar cells with indium oxide interconnect
A thin low-loss indium oxide interconnect layer grown by atomic layer deposition enables perovskite–organic hybrid tandem solar cells with a high open-circuit voltage and a high power conversion efficiency.
- K. O. Brinkmann
- , T. Becker
- & T. Riedl
-
Article |
 Catalogue of flat-band stoichiometric materials
Catalogue of flat-band stoichiometric materials
A catalogue of the naturally occurring three-dimensional stoichiometric materials with flat bands around the Fermi level provides a powerful search engine for future theoretical and experimental studies.
- Nicolas Regnault
- , Yuanfeng Xu
- & B. Andrei Bernevig
-
Article |
 Emergence of Fermi arcs due to magnetic splitting in an antiferromagnet
Emergence of Fermi arcs due to magnetic splitting in an antiferromagnet
Magnetic splitting in an antiferromagnetic state of cubic NdBi gives rise to Fermi arcs with bands that have opposing curvature.
- Benjamin Schrunk
- , Yevhen Kushnirenko
- & Adam Kaminski
-
Article
| Open Access Flat-surface-assisted and self-regulated oxidation resistance of Cu(111)
Flat-surface-assisted and self-regulated oxidation resistance of Cu(111)
The fabrication of copper thin films with ultraflat surfaces and only occasional mono-atomic steps, which show semi-permanent resistance to oxidation over long periods, is reported and the mechanism explained using first-principles calculations.
- Su Jae Kim
- , Yong In Kim
- & Se-Young Jeong
-
Article |
 Steady Floquet–Andreev states in graphene Josephson junctions
Steady Floquet–Andreev states in graphene Josephson junctions
Using continuous microwave application without substantial heating, Floquet–Andreev states in graphene Josephson junctions are realized, and their energy spectra are measured directly by superconducting tunnelling spectroscopy.
- Sein Park
- , Wonjun Lee
- & Gil-Ho Lee
-
Article |
 Structure of the moiré exciton captured by imaging its electron and hole
Structure of the moiré exciton captured by imaging its electron and hole
Imaging the electron and hole that bind to form interlayer excitons in a 2D moiré material enables direct measurement of its diameter and indicates the localization of its centre of mass.
- Ouri Karni
- , Elyse Barré
- & Keshav M. Dani
-
Article |
 High-density switchable skyrmion-like polar nanodomains integrated on silicon
High-density switchable skyrmion-like polar nanodomains integrated on silicon
Two types of skyrmion-like polar nanodomain are observed in oxide bilayers transferred onto silicon, and these nanodomains, with distinct resistive behaviour, can be converted to each other under an external electric field.
- Lu Han
- , Christopher Addiego
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Review Article |
 Progress and prospects in magnetic topological materials
Progress and prospects in magnetic topological materials
Recent theoretical and experimental progress in identifying and understanding magnetic topological materials is reviewed, highlighting the antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4 and the ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co3Sn2S2, and future research directions are discussed.
- B. Andrei Bernevig
- , Claudia Felser
- & Haim Beidenkopf
-
Article |
 Evidence for a single-layer van der Waals multiferroic
Evidence for a single-layer van der Waals multiferroic
Multiple complementary optical signatures confirm the persistence of ferroelectricity and inversion-symmetry-breaking magnetic order down to monolayer NiI2, introducing the physics of type-II multiferroics into the area of van der Waals materials.
- Qian Song
- , Connor A. Occhialini
- & Riccardo Comin
-
Article |
 Scaling of the strange-metal scattering in unconventional superconductors
Scaling of the strange-metal scattering in unconventional superconductors
Precise quantitative scaling laws are observed between the normalized T-linear coefficient and Tc among copper oxides, pnictides and a class of organic superconductors, suggesting a common underlying physics at work in these unconventional superconductors.
- Jie Yuan
- , Qihong Chen
- & Zhongxian Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Electrons go loopy in a family of superconductors
Electrons go loopy in a family of superconductors
Measurements indicate that electrons move in loops between the atoms of an intriguing class of superconducting material. Such dynamics breaks key symmetries of the crystal lattice — suggesting the material hosts a rare state of matter.
- Morten H. Christensen
- & Turan Birol
-
Article |
 Ferroelectric incommensurate spin crystals
Ferroelectric incommensurate spin crystals
Analysing the structure of a PbTiO3 epitaxial layer sandwiched between SrRuO3 electrodes led to observation of a topology with two periodic modulations that form an incommensurate polar crystal, providing an analogue to incommensurate spin crystals.
- Dorin Rusu
- , Jonathan J. P. Peters
- & Marin Alexe
-
Article |
 Time-reversal symmetry-breaking charge order in a kagome superconductor
Time-reversal symmetry-breaking charge order in a kagome superconductor
An investigation of muon spin relaxation shows time-reversal symmetry-breaking charge order, intertwined with correlated superconductivity, due to orbital currents in the kagome superconductor KV3Sb5.
- C. Mielke III
- , D. Das
- & Z. Guguchia
-
Article |
 Charge-density-wave-driven electronic nematicity in a kagome superconductor
Charge-density-wave-driven electronic nematicity in a kagome superconductor
Charge-density-wave-driven electronic nematicity that occurs well below the charge-density-wave transition temperature is reported in the kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5.
- Linpeng Nie
- , Kuanglv Sun
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article |
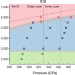 Superionic iron alloys and their seismic velocities in Earth’s inner core
Superionic iron alloys and their seismic velocities in Earth’s inner core
Molecular dynamics simulations show that the light elements hydrogen, oxygen and carbon become highly diffusive like liquid in solid iron under the inner-core conditions, leading to a reduction in the seismic velocities.
- Yu He
- , Shichuan Sun
- & Ho-kwang Mao
-
Article |
 Real-space visualization of intrinsic magnetic fields of an antiferromagnet
Real-space visualization of intrinsic magnetic fields of an antiferromagnet
Real-space visualization of the magnetic fields in antiferromagnetic haematite is achieved using atomic-resolution differential phase contrast scanning transmission electron microscopy in a magnetic-field-free environment.
- Yuji Kohno
- , Takehito Seki
- & Naoya Shibata
-
News & Views |
 Lost magnetism pinned on atomic rotations
Lost magnetism pinned on atomic rotations
Crystal-lattice vibrations reveal the mechanism by which laser pulses can strip a metal of its magnetism. The vibrations absorb the angular momentum of electrons in a sample, allowing it to demagnetize.
- Georg Woltersdorf
-
Review Article |
 Reproducibility in the fabrication and physics of moiré materials
Reproducibility in the fabrication and physics of moiré materials
The essential properties of moiré materials and the progress and latest developments in the field are reviewed, and their fabrication and physics are discussed from a reproducibility perspective.
- Chun Ning Lau
- , Marc W. Bockrath
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article |
 Fluctuation-induced quantum friction in nanoscale water flows
Fluctuation-induced quantum friction in nanoscale water flows
The quantum contribution to friction enables the rationalization of the peculiar friction properties of water on carbon surfaces, and in particular the radius dependence of slippage in carbon nanotubes.
- Nikita Kavokine
- , Marie-Laure Bocquet
- & Lydéric Bocquet
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

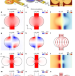 Direct observation of vortices in an electron fluid
Direct observation of vortices in an electron fluid