Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Accessing natural vaccine adjuvants
Accessing natural vaccine adjuvants
An integrative approach has now enabled elucidation of the complete biosynthetic pathway of a prominent saponin adjuvant. Reconstruction of the whole biosynthetic pathway in a heterologous host provides new perspectives for the biotechnological supply of this immunostimulant.
- Vincent Courdavault
- & Nicolas Papon
-
News & Views |
 Friend or foe-maldehyde
Friend or foe-maldehyde
Chemically reactive metabolites such as formaldehyde are often toxic and are proposed to react promiscuously with biomolecules. New work shows that some reactive sites on proteins are uniquely sensitive to formaldehyde, leading to functionally important regulation of protein and cell functions.
- Vicki L. Emms
- , Sara Y. Chothia
- & Richard J. Hopkinson
-
Research Briefing |
 High-throughput engineering of biosynthetic assembly lines
High-throughput engineering of biosynthetic assembly lines
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases produce diverse natural products, including many valuable therapeutics. Although the condensation domains that catalyze peptide bond formation in these multifunctional enzymes have been difficult to engineer, a yeast display system that was developed to screen millions of variants now enables efficient reprogramming of synthetase substrate specificity.
-
Article
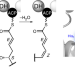
| Open Access Complete biosynthesis of the potent vaccine adjuvant QS-21
Complete biosynthesis of the potent vaccine adjuvant QS-21
Vaccine immunoadjuvants are central to vaccine efficiency. Now, the complete characterization of the biosynthetic pathway of QS-21, a potent immunoadjuvant produced by the Chilean soapbark tree, has been reported. These findings open the door to heterologous production of QS-21 and new-to-nature adjuvants.
- Laetitia B. B. Martin
- , Shingo Kikuchi
- & Anne Osbourn
-
News & Views |
 A new class of macrocyclic peptides
A new class of macrocyclic peptides
Nature has evolved elegant enzymatic strategies to cyclize peptides, resulting in complex macrocyclic compounds with potent biological activities. A study illustrates the diverse chemical versatility of one such remarkable enzyme family, the cytochrome P450 macrocyclases, which form new biaryl crosslinks in ribosomal peptidic natural products.
- Krushnamurthy Pattanayakanahalli Henjarappa
- , Simita Das
- & Nilkamal Mahanta
-
Article |
 Biocatalytic cyclization of small macrolactams by a penicillin-binding protein-type thioesterase
Biocatalytic cyclization of small macrolactams by a penicillin-binding protein-type thioesterase
Macrocyclic peptides are promising scaffolds for chemical tools and potential therapeutics, but their synthesis is currently difficult. Here, the authors report the characterization of Ulm16, a peptide cyclase of the penicillin-binding protein (PBP)-type class of thioesterases, that catalyzes head-to-tail macrolactamization of nonribosmal peptides of 4–6 amino acids in length.
- Zachary L. Budimir
- , Rishi S. Patel
- & Elizabeth I. Parkinson
-
News & Views |
 Mining the noncanonical terpenome
Mining the noncanonical terpenome
Terpenoids bearing carbon skeletons derived from nonisoprene units are rare and considered noncanonical. Now, a genome-mining study has uncovered previously unknown noncanonical C16 terpenes and their biosynthetic pathways from bacteria. The findings suggest that noncanonical terpenoids are diverse and widespread in nature.
- Shaonan Liu
- , Darwin Lara
- & Yang Hai
-
Article |
 Cofactorless oxygenases guide anthraquinone-fused enediyne biosynthesis
Cofactorless oxygenases guide anthraquinone-fused enediyne biosynthesis
Cofactorless oxygenases are rare in nature and natural product biosynthesis. Here the authors describe the biochemical and structural characterization of two such oxygenases catalyzing deformylation, ring cleavage and epoxidation in the biosynthesis of the enediyne natural product tiancimycin A.
- Chun Gui
- , Edward Kalkreuter
- & Ben Shen
-
-
Article |
 Widespread biosynthesis of 16-carbon terpenoids in bacteria
Widespread biosynthesis of 16-carbon terpenoids in bacteria
Almost all terpenoids discovered so far have backbones made up of multiples of five carbon atoms. Here, the authors combine gene mining with biochemical characterization and chemical structure analysis to unveil an extensive class of terpenoids with 16 carbon atoms in bacteria.
- Yao-Tao Duan
- , Aikaterini Koutsaviti
- & Sotirios C. Kampranis
-
Article |
 Hydroxytryptophan biosynthesis by a family of heme-dependent enzymes in bacteria
Hydroxytryptophan biosynthesis by a family of heme-dependent enzymes in bacteria
Tryptophan hydroxylases have only been known from eukaryotes and are involved in the biosynthesis of serotonin or melatonin. Here, the authors characterize a family of bacterial tryptophan hydroxylases that differ markedly from their eukaryotic counterpart in cofactor and catalytic mechanism.
- Xinjie Shi
- , Guiyun Zhao
- & Yi-Ling Du
-
Article |
 A platform for distributed production of synthetic nitrated proteins in live bacteria
A platform for distributed production of synthetic nitrated proteins in live bacteria
A combination of enzyme discovery for nonheme diiron N-monooxygenases, metabolic engineering and genetic code expansion enables the construction of a live bacterial producer of synthetic nitrated proteins containing para-nitro-l-phenylalanine.
- Neil D. Butler
- , Sabyasachi Sen
- & Aditya M. Kunjapur
-
Perspective |
 Repurposing degradation pathways for modular metabolite biosynthesis in nematodes
Repurposing degradation pathways for modular metabolite biosynthesis in nematodes
This Perspective details how genome-wide association studies and metabolomics enabled the discovery of structures, bioactivities and pathways of modular metabolite biosynthesis originates from the ‘hijacking’ of conserved detoxification mechanisms by nematodes.
- Chester J. J. Wrobel
- & Frank C. Schroeder
-
-
Review Article |
 Enzymology of assembly line synthesis by modular polyketide synthases
Enzymology of assembly line synthesis by modular polyketide synthases
A new review article details how new structural insight regarding modular polyketide synthases (PKSs) helps us better understand the organization of catalytic events within a PKS module. The plausible models discussed will likely influence future PKS engineering efforts.
- Martin Grininger
-
-
Article |
 Genome mining for unknown–unknown natural products
Genome mining for unknown–unknown natural products
A new biosynthetic core-forming enzyme, arginine cyclodipeptide synthase (RCDPS), was found to produce cyclo-arginine-Xaa dipeptides via a tRNA-dependent mechanism, and further genome mining using RCDPS as a beacon uncovered new natural products.
- Danielle A. Yee
- , Kanji Niwa
- & Yi Tang
-
News & Views |
 A balancing act
A balancing act
Inspired by nature, a synthetic carbon fixation cycle builds complex molecules directly from CO2. Building metabolism from the ground up requires several innovative advancements — now, a strategy to balance carbon demands in a complex metabolic network is explored.
- Grant M. Landwehr
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic anaplerotic modules for the direct synthesis of complex molecules from CO2
Synthetic anaplerotic modules for the direct synthesis of complex molecules from CO2
Anaplerotic reactions constantly refill metabolic networks with essential intermediates. This concept was adapted to enable a 54-step in vitro biosynthesis of the macrolide backbone of the antibiotic erythromycin from CO2.
- Christoph Diehl
- , Patrick D. Gerlinger
- & Tobias J. Erb
-
Article
| Open Access Probing coenzyme A homeostasis with semisynthetic biosensors
Probing coenzyme A homeostasis with semisynthetic biosensors
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor. A biosensor for visualizing cytosolic and mitochondrial CoA in living cells was developed to address central questions concerning CoA homeostasis.
- Lin Xue
- , Paul Schnacke
- & Kai Johnsson
-
Article |
 Small-molecule inhibition of the archetypal UbiB protein COQ8
Small-molecule inhibition of the archetypal UbiB protein COQ8
Murray et al. identified and characterized a small-molecule inhibitor of human COQ8A, which belongs to the UbiB protein family and is essential for coenzyme Q biosynthesis.
- Nathan H. Murray
- , Christopher R. M. Asquith
- & David J. Pagliarini
-
News & Views |
 Caught in the act
Caught in the act
YcaO enzymes are able to catalyze a diverse set of reactions and have found industrial applications. New biochemical data provide the first direct evidence for the unified reaction mechanism proposed a decade ago and will inform future enzyme engineering efforts.
- Jesko Koehnke
-
-
Article |
 Diene incorporation by a dehydratase domain variant in modular polyketide synthases
Diene incorporation by a dehydratase domain variant in modular polyketide synthases
Polyketides are assembled by modular polyketide synthases and undergo chemical tailoring reactions. A dehydratase domain variant catalyzes two sequential elimination reactions from thioester intermediates to produce conjugated diene modifications.
- Christian Hobson
- , Matthew Jenner
- & Gregory L. Challis
-
Article |
 Bicyclostreptins are radical SAM enzyme-modified peptides with unique cyclization motifs
Bicyclostreptins are radical SAM enzyme-modified peptides with unique cyclization motifs
Bicyclostreptins are peptide natural products in which a macrocyclic β-ether and a heterocyclic sp3–sp3 linkage between a backbone amide nitrogen and an adjacent α-carbon are installed by two radical S-adenosylmethionine metalloenzymes.
- Leah B. Bushin
- , Brett C. Covington
- & Mohammad R. Seyedsayamdost
-
Article |
 Engineering site-selective incorporation of fluorine into polyketides
Engineering site-selective incorporation of fluorine into polyketides
A combination of engineering a fluorine-selective trans-acyltransferase and manipulation of the fluorinated extender unit pool in Escherichia coli enables the production of site-selectively fluorinated erythromycin precursors in vitro in vitroin vitro and in vivo.
- Sasilada Sirirungruang
- , Omer Ad
- & Michelle C. Y. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of saponin defensive compounds in sea cucumbers
Biosynthesis of saponin defensive compounds in sea cucumbers
Sea stars and sea cucumbers biosynthesize protective glycosylated steroids and triterpenes via divergent oxidosqualene cyclases (OSCs) that produce these distinct saponins in different species as well as in different tissues of a single species.
- Ramesha Thimmappa
- , Shi Wang
- & Anne Osbourn
-
Article |
 Mucin O-glycans are natural inhibitors of Candida albicans pathogenicity
Mucin O-glycans are natural inhibitors of Candida albicans pathogenicity
Glycomic profiling of mucosal surfaces identified O-mucin glycoconjugate motifs that regulate Candida albicans virulence. Synthetic analogs based on these glycans suppress fungal filamentation, offering potential for antifungal development.
- Julie Takagi
- , Kazuhiro Aoki
- & Katharina Ribbeck
-
Article |
 Biosynthesis of cyanobacterin, a paradigm for furanolide core structure assembly
Biosynthesis of cyanobacterin, a paradigm for furanolide core structure assembly
Elucidation of the biosynthetic pathway of the γ-butyrolactone core structure of the furanolide natural product cyanobacterin reveals a carbon–carbon bond-forming cascade that features an enzyme catalyzing a Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction.
- Paul M. D’Agostino
- , Catharina J. Seel
- & Tobias A. M. Gulder
-
News & Views |
 Old path, new frontier
Old path, new frontier
The discovery of long-existing terpenoid biosynthetic pathways in soft corals changes the way specialized metabolism in animals is thought about, and opens unprecedented access to the largely untapped treasure trove of medicinal marine natural products.
- Trinh-Don Nguyen
- & Thu-Thuy T. Dang
-
Article |
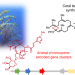 Ancient defensive terpene biosynthetic gene clusters in the soft corals
Ancient defensive terpene biosynthetic gene clusters in the soft corals
Rather than relying on microbial symbionts, certain corals themselves encode terpene cyclases that produce the eunicellane precursor of defensive terpenes, while the sequences of widespread related cyclase genes indicate a potential ancient origin.
- Paul D. Scesa
- , Zhenjian Lin
- & Eric W. Schmidt
-
Article |
 Ancient plant-like terpene biosynthesis in corals
Ancient plant-like terpene biosynthesis in corals
Marine natural products are often made by symbiotic microbes, but octocorals encode their own terpene cyclases that share features with bacterial versions and produce terpenoid precursors, including the coral-exclusive capnellane scaffold.
- Immo Burkhardt
- , Tristan de Rond
- & Bradley S. Moore
-
Article |
 Conformational remodeling enhances activity of lanthipeptide zinc-metallopeptidases
Conformational remodeling enhances activity of lanthipeptide zinc-metallopeptidases
Biochemical and structural characterization of the bifunctional lanthipeptide protease EryP enables identification of a regulatory interdomain calcium-binding site and leads to a strategy to engineer related enzymes for enhanced catalytic activity.
- Chang Zhao
- , Wangjian Sheng
- & Huan Wang
-
-
Article |
 Enzymatic assembly of the salinosporamide γ-lactam-β-lactone anticancer warhead
Enzymatic assembly of the salinosporamide γ-lactam-β-lactone anticancer warhead
Biochemical and structural characterization of a standalone ketosynthase, SalC, reveals that it serves as a critical intramolecular aldolase and β-lactone synthase during biosynthesis of the core of the marine natural product salinosporamide A.
- Katherine D. Bauman
- , Vikram V. Shende
- & Bradley S. Moore
-
Article |
 Convergent evolution of bacterial ceramide synthesis
Convergent evolution of bacterial ceramide synthesis
Elucidation of the bacterial ceramide biosynthetic pathway reveals that it likely evolved independently from the eukaryotic pathway, as bacteria lack homologs for many of the eukaryotic enzymes and the reactions occur in a different order.
- Gabriele Stankeviciute
- , Peijun Tang
- & Eric A. Klein
-
Article |
 An isotopic labeling approach linking natural products with biosynthetic gene clusters
An isotopic labeling approach linking natural products with biosynthetic gene clusters
IsoAnalyst is a mass spectrometry-based parallel stable isotope labeling platform that associates labeling patterns with bioinformatic structure prediction in order to connect natural products to their corresponding biosynthetic gene clusters.
- Catherine S. McCaughey
- , Jeffrey A. van Santen
- & Roger G. Linington
-
News & Views |
 RiPP-ing through the plant kingdom
RiPP-ing through the plant kingdom
An autocatalytic peptide cyclase defines a new subclass of plant ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). This discovery explains the origins of a large family of cyclic peptides and inspires new tools for mining these RiPPs across the plant kingdom.
- Yit-Heng Chooi
-
Article |
 Discovery and biosynthesis of cyclic plant peptides via autocatalytic cyclases
Discovery and biosynthesis of cyclic plant peptides via autocatalytic cyclases
BURP domains within lyciumin precursor peptides serve as autocatalytic peptide cyclases, enabling the discovery of other BURP-domain-derived products and development of a bioinformatic method to mine plants for precursor-peptide-encoding genes.
- Desnor N. Chigumba
- , Lisa S. Mydy
- & Roland D. Kersten
-
Article |
 Biosynthesis of triacsin featuring an N-hydroxytriazene pharmacophore
Biosynthesis of triacsin featuring an N-hydroxytriazene pharmacophore
During the biosynthesis of triacsin, the two N–N bond formation reactions necessary to create the unique N-hydroxytriazene moiety are catalyzed by a glycine-utilizing hydrazine-forming enzyme and a nitrite-utilizing N-nitrosating enzyme.
- Antonio Del Rio Flores
- , Frederick F. Twigg
- & Wenjun Zhang
-
News & Views |
 The core of the matter
The core of the matter
Graspetides are an important class of ribosomal natural products with potent bioactivities. New structural information provides insights into substrate recognition and catalysis, including a rare glimpse into the interactions between a tailoring enzyme and the core of the precursor peptide.
- Jesko Koehnke
-
Article |
 Molecular mechanism underlying substrate recognition of the peptide macrocyclase PsnB
Molecular mechanism underlying substrate recognition of the peptide macrocyclase PsnB
Structural and biochemical analysis of the plesiocin macrocyclase enzyme PsnB revealed that, unlike other ribosomal natural products, the core region of the precursor peptide enhances its interaction with the enzyme via conserved glutamate residues.
- Inseok Song
- , Younghyeon Kim
- & Seokhee Kim
-
Article |
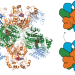 Structures and function of the amino acid polymerase cyanophycin synthetase
Structures and function of the amino acid polymerase cyanophycin synthetase
Structures of three cyanophycin synthetases reveal how the constituent glutathione synthetase and muramyl ligase-like domains cooperate to make cyanophycin, a poly-aspartate chain with arginine residues attached to the sidechains by isopeptide bonds.
- Itai Sharon
- , Asfarul S. Haque
- & T. Martin Schmeing
-
Article |
 Prospecting for natural products by genome mining and microcrystal electron diffraction
Prospecting for natural products by genome mining and microcrystal electron diffraction
Combined use of microcrystal electron diffraction and genome mining for biosynthetic gene clusters enables the rapid structural elucidation of natural products, including a newly discovered 2-pyridone compound and a revised structure of fischerin.
- Lee Joon Kim
- , Masao Ohashi
- & Hosea M. Nelson
-
-
Article |
 Co-occurrence of enzyme domains guides the discovery of an oxazolone synthetase
Co-occurrence of enzyme domains guides the discovery of an oxazolone synthetase
A genome-mining approach targeted to enzyme domains that co-occur in a single protein (CO-ED) facilitates the discovery and characterization of an oxazolone synthetase involved in the biosynthesis of a series of oxazolone-containing natural products.
- Tristan de Rond
- , Julia E. Asay
- & Bradley S. Moore
-
News & Views |
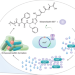 Mining for mouth metabolites
Mining for mouth metabolites
Genome mining of Streptococcus mutans clinical samples led to the identification of a structurally unique polyketide/non-ribosomal peptide, mutanofactin-697, that promotes biofilm formation. This study highlights the unexplored functional potential of secondary metabolites and opens new avenues for inhibiting pathogenic processes.
- Amber M. Scharnow
- & William M. Wuest
-
Article |
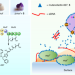 Mutanofactin promotes adhesion and biofilm formation of cariogenic Streptococcus mutans
Mutanofactin promotes adhesion and biofilm formation of cariogenic Streptococcus mutans
The mutanofactin family of lipopeptide natural products, produced by strains of cariogenic Streptococcus mutans, promotes biofilm formation via increased cell-surface hydrophobicity and binding to extracellular DNA.
- Zhong-Rui Li
- , Jin Sun
- & Wenjun Zhang
-

 An antibacterial glove
An antibacterial glove Limonoids on the menu
Limonoids on the menu