Featured
-
-
Article |
 Mechanical confinement regulates cartilage matrix formation by chondrocytes
Mechanical confinement regulates cartilage matrix formation by chondrocytes
The mechanical properties of biomaterials affect cell growth through mechanotransduction signals. Here, hydrogels with fast stress relaxation were developed and showed increased cartilage matrix formation by cartilage cells compared to slow relaxation hydrogels.
- Hong-pyo Lee
- , Luo Gu
- & Ovijit Chaudhuri
-
News & Views |
 When tissues collide
When tissues collide
Quantitative analysis of colliding cell monolayers reveals surprising wave phenomena involving contractility, jamming and activation of epithelial cells.
- Ulrich S. Schwarz
- & Falko Ziebert
-
News & Views |
 Sticking around vessels
Sticking around vessels
A study demonstrates that controlled integrin binding on a biomaterial was capable of promoting vascular cell sprouting and formation of a non-leaky blood vessel network in a healthy and diseased state.
- Michael R. Blatchley
- & Sharon Gerecht
-
Article |
 Flexible shape-memory scaffold for minimally invasive delivery of functional tissues
Flexible shape-memory scaffold for minimally invasive delivery of functional tissues
Cardiac repair usually requires highly invasive interventional procedures. Here, the authors develop an injectable shape-memory cardiac patch and demonstrated its applicability in a myocardial infarction model.
- Miles Montgomery
- , Samad Ahadian
- & Milica Radisic
-
Article |
 Hydrogels with precisely controlled integrin activation dictate vascular patterning and permeability
Hydrogels with precisely controlled integrin activation dictate vascular patterning and permeability
Ligand–integrin binding is essential for cell and tissue growth. Here, controlled integrin binding on a hyaluronic acid hydrogel was shown to promote endothelial cell sprouting in vitro and vessel network formation in vivo.
- Shuoran Li
- , Lina R. Nih
- & Tatiana Segura
-
Article |
 Tension stimulation drives tissue formation in scaffold-free systems
Tension stimulation drives tissue formation in scaffold-free systems
The application of tension in a self-assembled articular-cartilage model leads to the formation of tissue with tensile properties similar to those of native tissue.
- Jennifer K. Lee
- , Le W. Huwe
- & Kyriacos A. Athanasiou
-
Article |
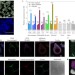 Colony stimulating factor-1 receptor is a central component of the foreign body response to biomaterial implants in rodents and non-human primates
Colony stimulating factor-1 receptor is a central component of the foreign body response to biomaterial implants in rodents and non-human primates
By studying the immune responses of animals to different types of biomaterial implants, colony stimulating factor-1 receptor is revealed as an important mediator of the foreign body reaction and a possible target for fibrosis inhibition.
- Joshua C. Doloff
- , Omid Veiseh
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Letter |
 Self-organized amniogenesis by human pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic implantation-like niche
Self-organized amniogenesis by human pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic implantation-like niche
The control of biophysical cues during the culture of human pluripotent stem cells on biomaterial substrates can be used to replicate the in vivo amniogenic environment and direct in vitro generation of early human amniotic tissue.
- Yue Shao
- , Kenichiro Taniguchi
- & Jianping Fu
-
Article |
 Collagen intrafibrillar mineralization as a result of the balance between osmotic equilibrium and electroneutrality
Collagen intrafibrillar mineralization as a result of the balance between osmotic equilibrium and electroneutrality
A new model for collagen intrafibrillar mineralization shows the need for a balance between osmotic equilibrium and electroneutrality to establish Gibbs–Donnan equilibrium.
- Li-na Niu
- , Sang Eun Jee
- & Franklin R. Tay
-
Letter |
 Instrumented cardiac microphysiological devices via multimaterial three-dimensional printing
Instrumented cardiac microphysiological devices via multimaterial three-dimensional printing
Heart-on-a-chip devices with integrated strain gauges for direct readout of tissue contractile strength allow for multiplexed drug-dose experiments and studies of functional maturation of cardiac tissue.
- Johan U. Lind
- , Travis A. Busbee
- & Kevin K. Parker
-
Article |
 Complete prevention of blood loss with self-sealing haemostatic needles
Complete prevention of blood loss with self-sealing haemostatic needles
The penetration of tissues with syringe needles is a common clinical practice that inevitably results in blood loss at the puncture site. This blood loss can now be eliminated using self-sealing haemostatic needles.
- Mikyung Shin
- , Sung-Gurl Park
- & Haeshin Lee
-
Article |
 Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing
Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing
Calcium ions play a vital role in enabling synaptic plasticity in biological systems. The dynamic behaviour of these ions has now been emulated in a metal atom diffusion-based memristor.
- Zhongrui Wang
- , Saumil Joshi
- & J. Joshua Yang
-
Article |
 Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
The blood clearance mechanism, by the liver, of administered hard nanomaterials is reported in relation to blood flow dynamics, organ microarchitecture and cellular phenotype.
- Kim M. Tsoi
- , Sonya A. MacParland
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article |
 N-cadherin adhesive interactions modulate matrix mechanosensing and fate commitment of mesenchymal stem cells
N-cadherin adhesive interactions modulate matrix mechanosensing and fate commitment of mesenchymal stem cells
N-cadherin can alter how the stiffening extracellular microenvironment is interpreted by mesenchymal stem cells, leading to subsequent changes in downstream cell proliferation and differentiation.
- Brian D. Cosgrove
- , Keeley L. Mui
- & Robert L. Mauck
-
Article |
 Local triple-combination therapy results in tumour regression and prevents recurrence in a colon cancer model
Local triple-combination therapy results in tumour regression and prevents recurrence in a colon cancer model
A hydrogel patch delivering a combination of gene, drug and phototherapy leads to complete tumour remission and the absence of tumour recurrence in a colon cancer mouse model.
- João Conde
- , Nuria Oliva
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Review Article |
 Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin
Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin
This Review discusses the materials and electronic requirements for flexible sensors and electronic systems to mimic the mechanical and sensing properties of natural skin, with the goal of providing artificial prostheses with sensing capabilities.
- Alex Chortos
- , Jia Liu
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article |
 Heterogeneous silicon mesostructures for lipid-supported bioelectric interfaces
Heterogeneous silicon mesostructures for lipid-supported bioelectric interfaces
A biocompatible and biodegradable mesostructured form of silicon is used to make lipid-bilayer-supported bioelectric interfaces that can optically modulate the electrophysiology of single dorsal root ganglia neurons.
- Yuanwen Jiang
- , João L. Carvalho-de-Souza
- & Bozhi Tian
-
News & Views |
 Scalable vascularized implants
Scalable vascularized implants
Biodegradable and perfusable scaffolds enable the fabrication of implantable, millimetre-scale cardiac and hepatic tissue models.
- Ying Zheng
- & Meredith A. Roberts
-
News & Views |
 Signals from within
Signals from within
A regenerative cardiac patch with integrated freestanding electrodes allows the electrical stimulation and recording of cardiomyocyte growth and activity, with on-demand drug delivery.
- Milica Radisic
-
Article |
 Bioresorbable silicon electronics for transient spatiotemporal mapping of electrical activity from the cerebral cortex
Bioresorbable silicon electronics for transient spatiotemporal mapping of electrical activity from the cerebral cortex
Arrays of bioresorbable, highly doped silicon electrodes with multiplexing capabilities are used as electrocorticography sensors to perform in vivo, reliable acute and chronic recordings for up to one month before dissolving in the body.
- Ki Jun Yu
- , Duygu Kuzum
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Paramagnetic fluorinated nanoemulsions for sensitive cellular fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging
Paramagnetic fluorinated nanoemulsions for sensitive cellular fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging
New paramagnetic fluorinated nanoemulsions significantly enhance the detection sensitivity of MRI compared with alternative fluorine-19 tracers.
- Alexander A. Kislukhin
- , Hongyan Xu
- & Eric T. Ahrens
-
Article |
 Engineered hybrid cardiac patches with multifunctional electronics for online monitoring and regulation of tissue function
Engineered hybrid cardiac patches with multifunctional electronics for online monitoring and regulation of tissue function
Integrating multifunctional electronics with engineered cardiac patches enables the recording of cellular electrical activities, and on-demand provision of electrical stimulation and release of drugs.
- Ron Feiner
- , Leeya Engel
- & Tal Dvir
-
Article |
 Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-on-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis
Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-on-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis
Biodegradable, perfusable scaffolds are able to generate both in vitro cardiac and hepatic vascularized tissue models and in vivo implants for direct surgical anastomosis.
- Boyang Zhang
- , Miles Montgomery
- & Milica Radisic
-
Article |
 Defined three-dimensional microenvironments boost induction of pluripotency
Defined three-dimensional microenvironments boost induction of pluripotency
The confinement imposed by the three-dimensional microenvironment promotes the induction of pluripotency in somatic cells through an accelerated mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and increased epigenetic remodelling.
- Massimiliano Caiazzo
- , Yuya Okawa
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Article |
 Microstructural heterogeneity directs micromechanics and mechanobiology in native and engineered fibrocartilage
Microstructural heterogeneity directs micromechanics and mechanobiology in native and engineered fibrocartilage
Tissue-engineered constructs with non-fibrous, proteoglycan-rich microdomains match the microstructural, micromechanical and mechanobiological properties of native fibrocartilaginous tissue.
- Woojin M. Han
- , Su-Jin Heo
- & Dawn M. Elliott
-
-
Article |
 Self-assembled RNA-triple-helix hydrogel scaffold for microRNA modulation in the tumour microenvironment
Self-assembled RNA-triple-helix hydrogel scaffold for microRNA modulation in the tumour microenvironment
Tissue-adhesive scaffolds made by the conjugation of RNA triple helices to dendrimers lead to ∼90% shrinkage of tumours two weeks after implantation in a triple-negative breast cancer mouse model.
- João Conde
- , Nuria Oliva
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Article |
 A magnetic protein biocompass
A magnetic protein biocompass
A polymeric protein complex consisting of a newly identified magnetoreceptor protein and known magnetoreception-related photoreceptor cryptochromes exhibits spontaneous alignment in magnetic fields.
- Siying Qin
- , Hang Yin
- & Can Xie
-
-
News & Views |
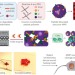 Enzymatically crosslinked scaffolds
Enzymatically crosslinked scaffolds
Microgel particle precursors bearing peptide substrates for human enzymes crosslink in wound sites to produce bioactive scaffolds in situ that rapidly recruit cells and promote dermal healing.
- David W. Grainger
-
News & Views |
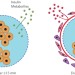 Larger is stealthier
Larger is stealthier
Implanted spheres with a diameter larger than 1.5 mm escape fibrotic responses, thereby extending the survival time of the encapsulated therapeutic cells.
- Ruud A. Bank
-
-
Commentary |
 Tracking gene and cell fate for therapeutic gain
Tracking gene and cell fate for therapeutic gain
The preclinical intersection of molecular imaging and gene- and cell-based therapies will enable more informed and effective clinical translation. We discuss how imaging can monitor cell and gene fate and function in vivo and overcome barriers associated with these therapies.
- Nigel G. Kooreman
- , Julia D. Ransohoff
- & Joseph C. Wu
-
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
News & Views |
 Towards the void
Towards the void
Cells at the edges of migrating epithelial sheets pull themselves towards unfilled space regardless of their direction of motion.
- Eric R. Dufresne
- & Martin A. Schwartz
-
News & Views |
 Differential stickiness
Differential stickiness
Technologies to isolate colonies of human pluripotent stem cells from other cell types in a high-throughput manner are lacking. A microfluidic-based approach that exploits differences in the adhesion strength between these cells and a substrate may soon fill the gap.
- Oscar J. Abilez
- & Joseph C. Wu
-
News & Views |
 Keeping track
Keeping track
Assessing when cell death occurs following in vivo transplantation of stem cells is challenging. Now, pH-sensitive hydrogel capsules containing arginine-based liposomes are shown to act as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, allowing cell death to be monitored within the capsules.
- Keren Ziv
- & Sanjiv S. Gambhir
-
Article |
 Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Microneedle arrays coated with a pH-sensitive releasable layer act as an intradermal delivery system for polyelectrolyte films containing bioactive molecules for DNA vaccination. The implanted films co-deliver DNA, transfection agents and adjuvants, promoting local transfection and generating immune responses that can be tuned from days to weeks.
- Peter C. DeMuth
- , Younjin Min
- & Darrell J. Irvine
-
News & Views |
 Perfusable vascular networks
Perfusable vascular networks
A rapid vascular casting approach that uses carbohydrate glass as a sacrificial template allows tissues to be built that can be kept alive for longer in the laboratory until needed for transplantation.
- Gabor Forgacs
-
News & Views |
 Loaded-up microsponges
Loaded-up microsponges
Self-assembled microsponges of hairpin RNA polymers achieve, with one thousand times lower concentration, the same degree of gene silencing in tumour-carrying mice as conventional nanoparticle-based siRNA delivery vehicles.
- Wade W. Grabow
- & Luc Jaeger
-
News & Views |
 Charged for success
Charged for success
DNA-complexated cationic polymers with reduced charge density, high molecular weight and increased hydrophobicity show a lack of detectable cytotoxicity and efficiently deliver the apoptosis-inducing TRAIL gene to transplanted tumours in mice.
- Enrico Mastrobattista
- & Wim E. Hennink
-
Article |
 Biodegradable poly(amine-co-ester) terpolymers for targeted gene delivery
Biodegradable poly(amine-co-ester) terpolymers for targeted gene delivery
Many synthetic polymer nanoparticles used for non-viral gene delivery contain excess cations on their surface, which makes the particles cytotoxic and the delivery of genes inefficient. Terpolymers with a low charge density, high molecular weight and increased hydrophobicity are now shown to have minimal toxicity, and to efficiently deliver the apoptosis-inducing TRAIL gene to transplanted tumours in mice.
- Jiangbing Zhou
- , Jie Liu
- & W. Mark Saltzman
-
News & Views |
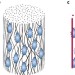 Noodle gels for cells
Noodle gels for cells
Heating and cooling of peptide amphiphile suspensions converts disorganized nanofibres into liquid-crystalline nanofibre bundles that gel on addition of salts. The noodle-shaped strings of gel can entrap and align cells.
- Timothy J. Deming
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Sequential bottom-up assembly of mechanically stabilized synthetic cells by microfluidics
Sequential bottom-up assembly of mechanically stabilized synthetic cells by microfluidics Assembled using DNA glue
Assembled using DNA glue