Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Efferocytosis in atherosclerosis
Efferocytosis in atherosclerosis
In this Review, Adkar and Leeper describe the mechanisms of programmed cell death and efferocytosis, discuss how efferocytosis becomes impaired in atherosclerosis and other cardiometabolic diseases, and suggest potential strategies to target these pathways for the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Shaunak S. Adkar
- & Nicholas J. Leeper
-
Review Article |
 Targeting immune cell recruitment in atherosclerosis
Targeting immune cell recruitment in atherosclerosis
In this Review, the authors discuss the receptors, ligands and interactors that regulate immune cell recruitment in atherosclerosis, describe mechanisms that promote the resolution of inflammation in atherosclerotic lesions, and highlight potential strategies to target these pathways for the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Yvonne Döring
- , Emiel P. C. van der Vorst
- & Christian Weber
-
Review Article |
 Uncovering atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by PET imaging
Uncovering atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by PET imaging
In this Review, van Leent and colleagues provide an overview of current PET imaging approaches for assessment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, as well as of whole-body PET applications; discuss the link between imaging readouts and atherosclerotic plaque pathology; and highlight promising developments in PET systems and radiotracer synthesis.
- Alexander Maier
- , Abraham J. P. Teunissen
- & Mandy M. T. van Leent
-
Research Highlight |
A newly identified gut hormone suppresses cholesterol production in the liver
A new study identifies a hormone that is secreted by the gut in response to cholesterol absorption and can inhibit cholesterol synthesis in the liver, which prevents an increase in circulating cholesterol levels.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Tools of the Trade |
 Long-read sequencing provides insights into genetic influence
Long-read sequencing provides insights into genetic influence
In this Tools of the Trade article, Trivett discusses the potential of long-read sequencing in generating high-quality reference genomes of animal models of cardiovascular disease.
- Cara Trivett
-
Review Article |
 Protein glycosylation in cardiovascular health and disease
Protein glycosylation in cardiovascular health and disease
Protein glycosylation is vital to the regulation of cell function, and changes in this post-translational modification underlie many disease processes. In this Review, Chatham and Patel discuss how protein glycosylation contributes to normal cardiovascular function and its role in cardiovascular disease, identifying important knowledge gaps and areas for future research.
- John C. Chatham
- & Rakesh P. Patel
-
Review Article |
 Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in ischaemic heart disease
Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in ischaemic heart disease
Non-coding RNAs are implicated in the pathophysiology of ischaemic heart disease and heart failure. In this Review, Caporali and colleagues examine the biology of these molecules and discuss the potential of non-coding RNAs for translation to the clinic as biomarkers and therapeutics in adverse cardiac remodelling leading to ischaemic heart failure.
- Andrea Caporali
- , Maryam Anwar
- & Costanza Emanueli
-
Tools of the Trade |
 Imaging cAMP nanodomains in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes
Imaging cAMP nanodomains in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes
In this Tools of the Trade article, Charrière describes the FluoStep FRET-based biosensor used for high-resolution imaging of cAMP nanodomains that are involved in intracellular signalling in cardiomyocytes.
- Camille Charrière
-
Tools of the Trade |
 Modelling pre-eclampsia and its cardiovascular effects
Modelling pre-eclampsia and its cardiovascular effects
In this Tools of the Trade article, Olivera describes a rat model of pre-elampsia that has been instrumental for investigating potential long-term cardiovascular effects in offspring.
- Sol Olivera
- & Delyth Graham
-
Journal Club |
Tackling inflammation in atherosclerosis
Shoaran and Maffia recount how our understanding of the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis has evolved and highlight the study by Göran Hansson and colleagues that provided the first hint of the involvement of the adaptive immune response in atherosclerosis.
- Mohsen Shoaran
- & Pasquale Maffia
-
Journal Club |
Cardiac memory: a phenomenon with important clinical implications
Rebecca Gilchrist discusses the study that demonstrated the long-term modulation of ventricular repolarization by the sequence of electrical activation in the human heart and established the concept of cardiac memory.
- Rebecca J. Gilchrist
-
Review Article |
 Iron deficiency and supplementation in heart failure
Iron deficiency and supplementation in heart failure
In this Review, Lakhal-Littleton and Cleland use the latest understanding of iron homeostasis to evaluate existing and emerging markers of iron status, describe the reciprocal relationship between iron status and heart failure, and mechanistically examine the benefits of oral and intravenous iron replacement therapies.
- Samira Lakhal-Littleton
- & John G. F. Cleland
-
Review Article |
 Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Fredman and Serhan discuss the role of specialized pro-resolving mediators, a superfamily of endogenous signalling lipids that mediate resolution of inflammation processes in atherosclerosis, and appraise the therapeutic potential of specialized pro-resolving mediators for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, and the resolution of uncontrolled vascular inflammation.
- Gabrielle Fredman
- & Charles N. Serhan
-
Review Article |
 Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension
Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension
In this Review, Guzik and colleagues discuss immune and inflammatory mechanisms of hypertension, including upstream regulators and downstream effectors as well as the complex interplay between the immune system, blood pressure regulation and end-organ damage, which can help to identify new targets for therapeutic interventions.
- Tomasz J. Guzik
- , Ryszard Nosalski
- & Grant R. Drummond
-
Review Article |
 RNA-binding proteins in cardiovascular biology and disease: the beat goes on
RNA-binding proteins in cardiovascular biology and disease: the beat goes on
In this Review, the authors discuss the latest insights on RNA-binding proteins and RNA biology and appraise them in the context of cardiovascular research, summarizing the progress in our understanding of the involvement of RNA-binding proteins in cardiac biology and disease.
- Mirko Völkers
- , Thomas Preiss
- & Matthias W. Hentze
-
Research Highlight |
Base editing therapy corrects long QT syndrome in mice
Gene therapy involving adenine base editing can correct a pathogenic variant in the Scn5a gene and alleviate arrhythmia phenotypes in a mouse model of long QT syndrome type 3.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Long non-coding RNAs in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure: functions, mechanisms and clinical prospects
Long non-coding RNAs in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure: functions, mechanisms and clinical prospects
In this Review, Mably and Wang summarize the expression, functions and molecular mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in cardiac hypertrophy and failure. The authors also discuss lncRNAs as novel targets for the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.
- John D. Mably
- & Da-Zhi Wang
-
Research Highlight |
Disrupting a cell-specific miRNA–CXCR4 interaction is atheroprotective in mice
An approach that increases the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in vascular cells by targeting a microRNA-based repressive pathway attenuates atherosclerosis in mice and promotes atheroprotective functions in human and mouse vascular cells in vitro.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
 Patisiran is beneficial for the treatment of TTR cardiac amyloidosis
Patisiran is beneficial for the treatment of TTR cardiac amyloidosis
Treatment with the small interfering RNA patisiran preserves functional capacity and improves health status and quality of life in patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis, according to data from the 12-month double-blind period of the ongoing APOLLO-B trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases
The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases
The NLRP3 inflammasome can sense cardiac ischaemic and non-ischaemic injury, amplify the inflammatory response and induce inflammatory cell death. In this Review, Toldo and Abbate describe the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in numerous cardiac pathologies and summarize evidence on the use of agents targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome and related cytokines.
- Stefano Toldo
- & Antonio Abbate
-
Research Highlight |
 SARS-CoV-2 infects macrophages in coronary atherosclerotic plaques
SARS-CoV-2 infects macrophages in coronary atherosclerotic plaques
SARS-CoV-2 infects macrophages, especially lipid-laden foam cells, in coronary atherosclerotic plaques in patients with COVID-19; this infection initiates a strong proatherogenic inflammatory response, which might contribute to the ischaemic cardiovascular complications in these patients.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Sirtuin 2 protects against cardiac ageing
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin 2 is a key protective mediator against cardiac ageing, according to a study in non-human primates.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Metabolic reprogramming unlocks the regenerative potential of the heart
The metabolic maturation of mammalian cardiomyocytes that occurs during the early postnatal period shapes the epigenetic landscape of cardiomyocytes and creates a barrier for cell division, but reversing this remodelling process can restore the reparative capacity of the heart in mice, according to a study published in Nature.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Comment |
 Cardiovascular benefits of fermented foods and beverages: still up for debate
Cardiovascular benefits of fermented foods and beverages: still up for debate
Despite the high consumption of fermented foods and beverages worldwide, their role in a healthy diet is still up for debate. Some fermented beverages have been demonstrated to protect against cardiovascular disease, but many aspects of the effects of fermented foods on cardiovascular health are uncertain. Better-designed studies are warranted.
- Ramon Estruch
- & Rosa M. Lamuela-Raventós
-
Review Article |
 Effects of lifestyle factors on leukocytes in cardiovascular health and disease
Effects of lifestyle factors on leukocytes in cardiovascular health and disease
In this Review, Swirski and co-workers discuss how lifestyle factors modulate haematopoiesis and leukocyte migration in the context of cardiovascular homeostasis and disease, with particular focus on the role of the nervous system as the key executor connecting environmental influences to leukocyte behaviour.
- Henrike Janssen
- , Laura L. Koekkoek
- & Filip K. Swirski
-
Review Article |
 The menopausal transition period and cardiovascular risk
The menopausal transition period and cardiovascular risk
The menopausal transition period, which begins with irregular menstrual cycles and ends with the final menstrual period, is associated with an increase in cardiovascular risk. In this Review, Mehta and Manson describe the metabolic and cardiovascular changes that occur during the menopausal transition period and summarize the evidence on the use of targeted interventions to slow the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Jaya M. Mehta
- & JoAnn E. Manson
-
Review Article |
 Immunomodulation and immunopharmacology in heart failure
Immunomodulation and immunopharmacology in heart failure
In this Review, the authors discuss the clinical and experimental data on immunomodulatory effects of evidence-based treatments for heart failure and their primary mechanisms of action, and highlight potential therapeutic targets and opportunities for the development and application of novel immunomodulatory treatments for heart failure.
- George Markousis-Mavrogenis
- , Lukas Baumhove
- & Peter van der Meer
-
Research Highlight |
 Age-induced senescence impairs the neurovascular interface in the heart
Age-induced senescence impairs the neurovascular interface in the heart
An interaction between blood vessels and nerve fibres in the heart contributes to the decline in nerve density in the ageing left ventricle, potentially increasing susceptibility to arrhythmias.
- Jennifer Harman
-
Review Article |
 Animal models to study cardiac regeneration
Animal models to study cardiac regeneration
Some species have a greater capacity for cardiac regeneration than others. In this Review, Weinberger and Riley summarize the diverse array of vertebrates that have been studied for their cardiac regenerative potential and the core mechanisms that regulate cardiac regeneration across vertebrate species.
- Michael Weinberger
- & Paul R. Riley
-
Review Article |
 The role of cardiac pericytes in health and disease: therapeutic targets for myocardial infarction
The role of cardiac pericytes in health and disease: therapeutic targets for myocardial infarction
In the infarcted heart, pericytes have crucial roles in inflammatory signalling, angiogenesis, and scar formation and stabilization. In this Review, Avolio and colleagues discuss the numerous roles of cardiac pericytes in homeostasis and disease and describe the potential of pericyte-based therapy for restoring the perivascular niche after myocardial infarction.
- Elisa Avolio
- , Paola Campagnolo
- & Paolo Madeddu
-
Research Highlight |
Promising novel siRNA for the treatment of hypertension
Patients with hypertension who receive a single subcutaneous dose of zilebesiran, a novel small-interfering RNA that inhibits hepatic angiotensinogen synthesis, have reductions in serum angiotensinogen levels and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure that last for up to 24 weeks, according to a phase I study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Riksen and colleagues discuss the molecular and cellular mechanisms of trained immunity, the activation of these mechanisms by cardiovascular risk factors, and how trained immunity might contribute to atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The authors also propose potential strategies for the therapeutic modulation of trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Niels P. Riksen
- , Siroon Bekkering
- & Mihai G. Netea
-
Research Highlight |
A fatty acid from mother’s milk drives cardiomyocyte maturation in newborn mice
The essential omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid γ-linolenic acid present in maternal milk coordinates cardiac adaptation and survival in newborn mice, according to a new study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Metabolic mechanisms in physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: new paradigms and challenges
Metabolic mechanisms in physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: new paradigms and challenges
In this Review, Ritterhoff and Tian describe the metabolic reprogramming that occurs in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure; discuss the contribution of metabolism to energy-generating and non-energy-generating functions, including signalling, protein function and gene expression regulation; and highlight the role of metabolism in non-cardiomyocytes and the potential to develop metabolic therapies for heart failure.
- Julia Ritterhoff
- & Rong Tian
-
Review Article |
 Flow-induced reprogramming of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis
Flow-induced reprogramming of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis
In this Review, Jo and colleagues discuss blood flow-induced mechanisms involved in endothelial cell dysfunction and atherosclerosis, including the emerging concept of disturbed-flow-induced reprogramming of endothelial cells as a pro-atherogenic mechanism, and highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting of flow-sensitive genes, proteins and pathways.
- Ian A. Tamargo
- , Kyung In Baek
- & Hanjoong Jo
-
Clinical Outlook |
 Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Identifying leukocyte phenotypes by scRNA-seq to predict cardiovascular risk
Contemporary tools to predict cardiovascular risk lack accuracy on an individual-patient level. The use of single-cell RNA sequencing to identify specific leukocyte patterns might overcome some of these limitations, propelling us towards a precision medicine approach.
- Johannes Gollmer
- & Andreas Zirlik
-
Review Article |
 Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
Hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing
In this Review, Kroemer and colleagues describe eight molecular hallmarks of cardiovascular ageing: disabled macroautophagy, loss of proteostasis, genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, cell senescence, dysregulated neurohormonal signalling and inflammation. Therapeutically targeting these hallmarks might attenuate residual cardiovascular risk in older individuals.
- Mahmoud Abdellatif
- , Peter P. Rainer
- & Guido Kroemer
-
Comment |
 Clonal haematopoiesis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Clonal haematopoiesis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is defined as an expansion of mutant blood stem cells in individuals without haematological malignancies. CHIP is linked to an increased risk of non-cancerous disorders such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, possibly because mutant innate immune cells have pro-inflammatory phenotypes. Prospective studies are needed to determine whether individuals with CHIP might benefit from anti-inflammatory therapies.
- Herra Ahmad
- & Siddhartha Jaiswal
-
Comment |
 Mapping the functions of IgM antibodies in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Mapping the functions of IgM antibodies in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
IgM antibodies have gained much attention as risk markers of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but the exact antigenic determinants and the full spectrum of functions remain to be defined. A better understanding of the potentially diverse nature of the antigens that they recognize will help to dissect the function of IgM in atherosclerosis.
- Justine Deroissart
- & Christoph J. Binder
-
Comment |
 A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
Lipophagy is a type of selective autophagy that targets lipid droplets for degradation. Since the discovery of lipophagy in 2009, research has uncovered a central role for this process in cellular lipid metabolism, including in atherogenic foam cells. Therefore, increasing lipophagy might be a therapeutic target to reverse lipid build-up in atherosclerosis.
- Thomas Laval
- & Mireille Ouimet
-
Comment |
 A high-salt diet promotes atherosclerosis by altering haematopoiesis
A high-salt diet promotes atherosclerosis by altering haematopoiesis
Excessive salt intake is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease commonly associated with hypertension. However, we propose that a high-salt diet can promote cardiovascular and other diseases independently of high blood pressure through inflammatory pathways that increase the production of myeloid cells.
- Man K. S. Lee
- & Andrew J. Murphy
-
Review Article |
 Novel and future lipid-modulating therapies for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
Novel and future lipid-modulating therapies for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
In this Review, the authors discuss current treatment regimens for lowering plasma LDL cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, highlight treatment gaps and challenges, as well as describe opportunities raised by novel available therapies and potential future therapeutic approaches.
- Julia Brandts
- & Kausik K. Ray
-
Review Article |
 Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy
Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy
In this Review, Gawaz and colleagues discuss the pathophysiological role of platelets in acute myocardial ischaemia, vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic progression, summarize the current clinical concepts in antiplatelet therapy and describe novel therapeutic targets for antiplatelet drugs that are currently in development.
- Meinrad Gawaz
- , Tobias Geisler
- & Oliver Borst
-
Research Highlight |
A wearable sensor to measure troponin I levels
A wrist-worn, transdermal sensor can be used to measure plasma levels of cardiac troponin I, potentially facilitating the diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Promising findings for cell therapy in HFrEF
Findings from the DREAM-HF trial, the largest clinical trial of cell therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) to date, suggest that cardiac therapy with mesenchymal precursor cells might benefit patients with HFrEF, particularly those with inflammation.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Calcific aortic valve disease: mechanisms, prevention and treatment
Calcific aortic valve disease: mechanisms, prevention and treatment
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a common disorder characterized by thickening, fibrosis and mineralization of the aortic valve leaflets. In this Review, Mathieu and colleagues summarize the risk factors, genetics and molecular mechanisms involved in CAVD and the implications for treatment of the condition.
- Louis-Hippolyte Minvielle Moncla
- , Mewen Briend
- & Patrick Mathieu
-
Comment |
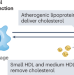 Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol are a risk factor for infection and hospitalization for infectious disease. Recent work suggests that inadequate levels of HDL particles of specific sizes — small and medium — account for this risk. In this Comment, we discuss the mechanistic implications of these observations and the methodologies used to quantify HDL size.
- Jay W. Heinecke
- & W. Sean Davidson
-
Research Highlight |
 A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function
A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function
Researchers have engineered a wearable device that adheres to the skin and uses ultrasound imaging and a deep learning model to produce a dynamic, real-time assessment of cardiac function.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Research Highlight |
 Base editing of CaMKIIδ shows promise as cardiac therapy
Base editing of CaMKIIδ shows promise as cardiac therapy
CRISPR–Cas9 base editing of the oxidative activation sites of CaMKIIδ protects the heart from ischaemia–reperfusion damage in mice.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Bile acid receptor protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy
Bile acid receptor protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy