Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Comment |
 A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
A role for lipophagy in atherosclerosis
Lipophagy is a type of selective autophagy that targets lipid droplets for degradation. Since the discovery of lipophagy in 2009, research has uncovered a central role for this process in cellular lipid metabolism, including in atherogenic foam cells. Therefore, increasing lipophagy might be a therapeutic target to reverse lipid build-up in atherosclerosis.
- Thomas Laval
- & Mireille Ouimet
-
Review Article |
 Repurposing drugs to treat cardiovascular disease in the era of precision medicine
Repurposing drugs to treat cardiovascular disease in the era of precision medicine
Drugs can be repurposed for new therapeutic indications. In this Review, Mercola and colleagues summarize the latest techniques for systematic drug repurposing and re-engineering, which could increase the pace, efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drug discovery for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
- Mena Abdelsayed
- , Eric J. Kort
- & Mark Mercola
-
Review Article |
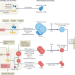 Metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in health and dyslipidaemia
Metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in health and dyslipidaemia
In this Review, Borén and colleagues provide an overview of the pathways involved in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein (TRL) assembly and intravascular processing, and discuss how the dysregulation of triglyceride transport can result in hypertriglyceridaemia.
- Jan Borén
- , Marja-Riitta Taskinen
- & Chris J. Packard
-
News & Views |
 Calcific aortic valve disease: turning therapeutic discovery up a notch
Calcific aortic valve disease: turning therapeutic discovery up a notch
Valve replacement is currently the only treatment for calcific aortic valve disease. Studies of an uncommon, genetic form of aortic valve disease have yielded in vitro and mouse models of the disease and a transcriptomic disease signature. Machine learning-driven screens for compounds that normalize this signature promise to enable medical management of aortic valve disease.
- Suya Wang
- & William T. Pu
-
-
Research Highlight |
Novel vasodilatory factor identified
Singlet molecular oxygen generated by endothelial indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 has an important pathophysiological role in mammals in the redox regulation of arterial relaxation and blood pressure during inflammatory conditions through the formation of a tryptophan-derived metabolite
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Cardioprotective effects of HDL cholesterol called into question
- Alexandra King
-
-
Year in Review |
 Heart failure therapy—technology to the fore
Heart failure therapy—technology to the fore
Studies published in 2011 in the field of heart failure have reinforced the benefit of cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with mild symptoms and confirmed the value of left ventricular assist devices and CABG surgery in selected patients. Conversely, the efficacy of nesiritide in acute heart failure has been questioned.
- John J. V. McMurray
-
Research Highlight |
 Dalcetrapib safely raises HDL-cholesterol level in the phase IIb dal-PLAQUE trial
Dalcetrapib safely raises HDL-cholesterol level in the phase IIb dal-PLAQUE trial
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Managing adverse effects and drug–drug interactions of antiplatelet agents
Managing adverse effects and drug–drug interactions of antiplatelet agents
Antiplatelet agents effectively reduce the incidence of ischemic events associated with plaque rupture but can cause adverse effects, most notably hemorrhage. Drs Kalyanasundaram and Lincoff address key adverse effects that are associated with antiplatelet agents and discuss potential interactions between these drugs and other medications.
- Arun Kalyanasundaram
- & A. Michael Lincoff
-
-
Review Article |
 Stable angina pectoris: antianginal therapies and future directions
Stable angina pectoris: antianginal therapies and future directions
Drs. Chaitman and Laddu review the various approved and experimental pharmacological approaches to treating angina in the context of data from clinical trials, and discuss ongoing and future studies. They also compare the merits of optimal medical therapy with prompt or delayed revascularization by percutaneous coronary intervention or CABG surgery as antianginal strategies.
- Bernard R. Chaitman
- & Abhay A. Laddu
-
-
News & Views |
Implications of high-dose statin link with incident diabetes
According to a meta-analysis of five clinical trials, high-dose statin therapy is associated with increased risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus. When treating patients with excessive levels of non-HDL cholesterols despite moderate-dose statin therapy, should we prescribe a strategy known to be efficacious, but associated with safety concerns, or should we prescribe combination therapy that has no proven effects on outcomes?
- Michael H. Davidson
-
Review Article |
 Novel HDL-directed pharmacotherapeutic strategies
Novel HDL-directed pharmacotherapeutic strategies
Novel atheroprotective therapies are needed to address the residual risk associated with atherothrombotic cardiovascular disease. In this Review, Drs deGoma and Rader discuss the mechanisms of HDL-targeted drugs, including agents that enhance or mimic apolipoprotein A-I activity, and summarize the development of these pharmacotherapies in preclinical and clinical studies.
- Emil M. deGoma
- & Daniel J. Rader
-
Research Highlight |
 Ticagrelor superior to clopidogrel in individuals predicted to be clopidogrel responders
Ticagrelor superior to clopidogrel in individuals predicted to be clopidogrel responders
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
News & Views |
Clopidogrel–PPI interaction, an ongoing controversy
Although a diminished pharmacodynamic effect of clopidogrel has been demonstrated in patients treated with proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), whether its clinical efficacy is reduced remains highly controversial. The FDA and European Medicines Agency recommend that PPIs and clopidogrel should not routinely be coadministered, and the 2010 expert consensus guidelines support this recommendation.
- Paul A. Gurbel
- & Udaya S. Tantry
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Clinical response to antiplatelet therapy—how much does genotype count?
Clinical response to antiplatelet therapy—how much does genotype count?
- Joana Osório
-
Research Highlight |
 Eptifibatide is noninferior to abciximab: implications for clinical practice
Eptifibatide is noninferior to abciximab: implications for clinical practice
- Alexandra King
-
Research Highlight |
 More MACE with zotarolimus-eluting stents than with sirolimus-eluting stents
More MACE with zotarolimus-eluting stents than with sirolimus-eluting stents
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
News & Views |
Aldosterone antagonists are underused by clinicians
Aldosterone antagonists decrease the mortality of patients with heart failure, but an observational study by Albert and colleagues has found that a surprisingly low number of patients receive aldosterone antagonists before discharge from hospital. This article highlights potential reasons for why there is such an underuse of efficient drugs in heart failure.
- Jane-Lise Samuel
- & Claude Delcayre
-
News & Views |
 Cangrelor for ACS—lessons from the CHAMPION trials
Cangrelor for ACS—lessons from the CHAMPION trials
The two CHAMPION trials failed to show superiority of cangrelor (a rapid-acting, reversible intravenous platelet P2Y12 adenosine receptor antagonist) versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. The CHAMPION PCI trial, however, did show a significant reduction in death and stent thrombosis suggesting benefit in those without clopidogrel pretreatment.
- David P. Faxon
-
-
News & Views |
 Dronedarone and amiodarone—the safety versus efficacy debate
Dronedarone and amiodarone—the safety versus efficacy debate
Amiodarone effectively maintains sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation, and although dronedarone is less effective it has a better safety profile. The choice of antiarrhythmic drug (or nonpharmacological strategy) depends on the ultimate goal of therapy, which should be considered in the context of the patient's clinical presentation and the treatment tailored to the individual.
- Eric N. Prystowsky
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biophysical chemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical ecology
- Chemical genetics
- Chemical libraries
- Chemical modification
- Chemical tools
- Cheminformatics
- Combinatorial libraries
- Computational chemistry
- DNA
- Drug delivery
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Ion channels
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Mechanism of action
- Membranes
- Metabolic pathways
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Natural products
- Networks and systems biology
- Nucleic acids
- Peptides
- Pharmacology
- Post-translational modifications
- Proteases
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Screening
- Small molecules
- Synthetic biology
- Target identification
- Target validation
- Transporters

 Monoclonal antibody therapy lowers LDL-cholesterol levels
Monoclonal antibody therapy lowers LDL-cholesterol levels Making the SWAP from clopidrogrel to prasugrel
Making the SWAP from clopidrogrel to prasugrel COPPS trial heralds new indication for colchicine
COPPS trial heralds new indication for colchicine Is tecarfarin a better anticoagulant than warfarin?
Is tecarfarin a better anticoagulant than warfarin?