News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Perspective |
 Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Although topological photonics has been an active field of research for some time, most studies still focus on the linear optical regime. This Perspective summarizes recent investigations into the nonlinear properties of discrete topological photonic systems.
- Alexander Szameit
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
News & Views |
 Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Even by shining classical light on a single opening, one can perform a double-slit experiment and discover a surprising variety of quantum mechanical multi-photon correlations — thanks to surface plasmon polaritons and photon-number-resolving detectors.
- Martijn Wubs
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Topological lasing demonstrated in the mode-locked regime
Topological lasing demonstrated in the mode-locked regime
The concept of temporal mode-locking has been leveraged to study the interplay between laser mode-locking and photonic lattices that exhibit non-Hermitian topological phenomena. The results suggest new opportunities to study nonlinear and non-Hermitian topological physics as well as potential applications to sensing, optical computing and frequency-comb design.
-
Article |
 Topological temporally mode-locked laser
Topological temporally mode-locked laser
Mode locking, which is a common technique to produce short laser pulses, is demonstrated in a topological laser.
- Christian R. Leefmans
- , Midya Parto
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article |
 Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Most applications of surface plasmons are based on their near-field properties. These properties are now shown to be governed by nonclassical scattering between multiparticle plasmonic subsystems.
- Mingyuan Hong
- , Riley B. Dawkins
- & Omar S. Magaña-Loaiza
-
Article |
 Deterministic generation of multidimensional photonic cluster states with a single quantum emitter
Deterministic generation of multidimensional photonic cluster states with a single quantum emitter
Cluster states made from multiple photons with a special entanglement structure are a useful resource for quantum technologies. Two-dimensional cluster states of microwave photons have now been deterministically generated using a superconducting circuit.
- Vinicius S. Ferreira
- , Gihwan Kim
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article |
 Quantized topological pumping in Floquet synthetic dimensions with a driven dissipative photonic molecule
Quantized topological pumping in Floquet synthetic dimensions with a driven dissipative photonic molecule
Although dissipation is often detrimental to the observation of topological effects, a photonic molecule driven at several incommensurate frequencies is shown to be a candidate system for quantized topological transport in synthetic dimensions.
- Sashank Kaushik Sridhar
- , Sayan Ghosh
- & Avik Dutt
-
Article |
 Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
A transducer that generates microwave–optical photon pairs is demonstrated. This could provide an interface between optical communication networks and superconducting quantum devices that operate at microwave frequencies.
- Srujan Meesala
- , Steven Wood
- & Oskar Painter
-
News & Views |
 Organic molecules pumped to resonance
Organic molecules pumped to resonance
Interacting emitters are the fundamental building blocks of quantum optics and quantum information devices. Pairs of organic molecules embedded in a crystal can become permanently strongly interacting when they are pumped with intense laser light.
- Stuart J. Masson
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 We can see clearly now
We can see clearly now
Adaptive optics allows scientists to correct for distortions of an image caused by the scattering of light. Anita Chandran illuminates the nature of the technique.
- Anita Mary Chandran
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Light passing through complex media is subject to scattering processes that mix together different photonic modes. This complexity can be harnessed to implement quantum operations.
- Suraj Goel
- , Saroch Leedumrongwatthanakun
- & Mehul Malik
-
Article |
 Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Quantum-correlated photons typically characterize strongly nonlinear quantum emitters. A two-photon correlation spectroscopy method now provides a powerful probe of weakly nonlinear many-body quantum systems.
- Lorenzo Scarpelli
- , Cyril Elouard
- & Thomas Volz
-
Article |
 Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
It has been suggested that Gaussian boson sampling may provide a quantum computational advantage for calculating the vibronic spectra of molecules. Now, an equally efficient classical algorithm has been identified.
- Changhun Oh
- , Youngrong Lim
- & Liang Jiang
-
Research Briefing |
 Optical trapping and tailoring of exciton-polariton condensates into macroscopic complexes
Optical trapping and tailoring of exciton-polariton condensates into macroscopic complexes
Subwavelength photonic gratings can host long-lived, negative-effective-mass photonic modes that couple strongly to electron transitions in constituent active materials. The resulting bosonic hybrid light–matter modes, or exciton-polaritons, can be optically configured to accumulate into various macroscopic artificial complexes and lattices of coherent quantum fluids.
-
News & Views |
 Optical Coriolis force guides light along Trojan beams
Optical Coriolis force guides light along Trojan beams
Trojan beams, which are optical counterparts of Trojan asteroids that maintain stable orbits alongside planets, have been successfully showcased in experiments, opening up possibilities for transporting light in unconventional settings.
- Tomáš Tyc
- & Tomáš Čižmár
-
Article |
 Guiding Trojan light beams via Lagrange points
Guiding Trojan light beams via Lagrange points
Twisted structures are shown to confine and guide light without total internal reflection, using an effect analogous to the stable Lagrange points in celestial mechanics.
- Haokun Luo
- , Yunxuan Wei
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
- Omar Di Stefano
- , Alessio Settineri
- & Franco Nori
-
News & Views |
 Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Understanding the mechanism underlying light-induced superconductivity could help manifest it at higher temperatures. Experiments now show that the excitation of a specific phonon leads to a resonant enhancement of this effect in K3C60.
- Jingdi Zhang
-
Article |
 Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Interactions between excitons and correlated electrons can lead to the formation of interesting states. Now, evidence suggests that these interactions can give rise to a Mott insulator of excitons.
- Zhen Lian
- , Yuze Meng
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
News & Views |
 Anti-laser shows how to make waves behave
Anti-laser shows how to make waves behave
A decade ago, the anti-laser made waves as a new type of perfect absorber that functions as a one-way trap door for light. Experiments have now demonstrated the control of light without absorbing it.
- A. Douglas Stone
-
Article |
 Coherent control of chaotic optical microcavity with reflectionless scattering modes
Coherent control of chaotic optical microcavity with reflectionless scattering modes
Non-Hermitian physics enables dynamic control of optical behaviour in real time, such as reflectionless scattering modes, which have now been demonstrated in a chaotic photonic microcavity.
- Xuefeng Jiang
- , Shixiong Yin
- & Andrea Alù
-
News & Views |
 Topological phase transitions have never been faster
Topological phase transitions have never been faster
A nonlinear optical approach has now enabled picosecond control of a complex band structure, driving a non-Hermitian topological phase transition across an exceptional-point singularity.
- Jiangbin Gong
- & Ching Hua Lee
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
The phase transition from a topologically trivial state to non-Hermitian conducting edge modes can be controlled by optical nonlinearities, achieving picosecond switching speeds.
- Tianxiang Dai
- , Yutian Ao
- & Jianwei Wang
-
Comment |
 Unfounded concerns about photovoltaic module toxicity and waste are slowing decarbonization
Unfounded concerns about photovoltaic module toxicity and waste are slowing decarbonization
Unsubstantiated claims that fuel growing public concern over the toxicity of photovoltaic modules and their waste are slowing their deployment. Clarifying these issues will help to facilitate the decarbonization that our world depends on.
- Heather Mirletz
- , Henry Hieslmair
- & Teresa M. Barnes
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
There is evidence that K3C60 can host a photo-induced superconducting state. Now, resonant excitation at low frequencies allows this phenomenon at room temperature and low pumping fluence.
- E. Rowe
- , B. Yuan
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme thermodynamics in nanolitre volumes through stimulated Brillouin–Mandelstam scattering
Extreme thermodynamics in nanolitre volumes through stimulated Brillouin–Mandelstam scattering
Material characterization of liquids in extreme thermodynamic conditions is a challenging technical problem. Brillouin scattering metrology in an optical fibre design with a sealed liquid core now enables spatially resolved temperature and pressure measurements, using carbon disulfide as an example.
- Andreas Geilen
- , Alexandra Popp
- & Birgit Stiller
-
Article |
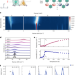 Fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Phonons that carry a large magnetic moment may be helpful for creating spintronic devices. Now this phenomenon is observed in an antiferromagnet and is enhanced by the critical fluctuations associated with a phase transition.
- Fangliang Wu
- , Song Bao
- & Qi Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Time interfaces for broadband coherent wave manipulation
Time interfaces for broadband coherent wave manipulation
Time-varying photonics offers ways to manipulate light–matter interactions as never thought before. An experiment with photonic time interfaces reveals how they can enable broadband coherent control of waves.
- Victor Pacheco-Peña
-
News & Views |
 Quantum optics meets attosecond science
Quantum optics meets attosecond science
Generating high harmonics or attosecond pulses of light is normally thought of as a classical process, but a theoretical study has now shown how the process could be driven by quantum light.
- Dong Hyuk Ko
- & P. B. Corkum
-
Article |
 High-harmonic generation driven by quantum light
High-harmonic generation driven by quantum light
High-harmonic generation is a source of high-frequency radiation and is typically driven by strong, but classical, laser fields. A theoretical study now shows that using quantum light states as the driver extends the spectrum of outgoing radiation in a controllable manner.
- Alexey Gorlach
- , Matan Even Tzur
- & Ido Kaminer
-
News & Views |
 Transmission matrices go nonlinear
Transmission matrices go nonlinear
Measuring the transmission matrix of disordered structures has so far been limited to the domain of linear systems. Now it has been measured for nonlinear disorder, with exciting implications for information capacity.
- Sushil Mujumdar
-
Article |
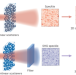
 Measuring the scattering tensor of a disordered nonlinear medium
Measuring the scattering tensor of a disordered nonlinear medium
Disordered media with their numerous scattering channels can be used as optical operators. Measurements of the scattering tensor of a second-harmonic medium extend this computing application to the nonlinear regime.
- Jungho Moon
- , Ye-Chan Cho
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article |
 Quadrature nonreciprocity in bosonic networks without breaking time-reversal symmetry
Quadrature nonreciprocity in bosonic networks without breaking time-reversal symmetry
Across platforms, nonreciprocity requires time-reversal symmetry to be broken. Interference of an excitation-preserving and a non-preserving interaction realizes unidirectional transport in a time-reversal-symmetric system.
- Clara C. Wanjura
- , Jesse J. Slim
- & Andreas Nunnenkamp
-
News & Views |
 A metallic road to localization
A metallic road to localization
Whether Anderson localization of light is possible in three dimensions has long been an open question. Numerical calculations have now shown that it can be done with a disordered arrangement of metal particles.
- Diederik S. Wiersma
-
Article
| Open Access Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb interactions in free-electron beams are usually seen as an adverse effect. The creation of distinctive number states with one, two, three and four electrons now reveals unexpected opportunities for electron microscopy and lithography from Coulomb correlations.
- Rudolf Haindl
- , Armin Feist
- & Claus Ropers
-
-
Article |
 Nonlinear-optical quantum control of free-electron matter waves
Nonlinear-optical quantum control of free-electron matter waves
Although massive electrons and massless photons are known to interact, their study has so far been confined to the linear regime. Experiments showing two-photon coherent control of a free-electron matter wave now introduce non-linearities.
- Maxim Tsarev
- , Johannes W. Thurner
- & Peter Baum
-
Article |
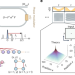 Programmable large-scale simulation of bosonic transport in optical synthetic frequency lattices
Programmable large-scale simulation of bosonic transport in optical synthetic frequency lattices
Analogue photonic simulators have so far suffered from severe finite size effects and limited programmability. Now, a frequency-mode photonic simulator enables the simulation of large-scale models in two and three dimensions.
- Alen Senanian
- , Logan G. Wright
- & Peter L. McMahon
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry gives rise to an elegant catastrophe
Symmetry gives rise to an elegant catastrophe
Imposing PT-symmetry and pseudo-Hermitian symmetry on an electric circuit with non-reciprocal couplings results in a complex morphology of degenerate eigenvalues that might yield new possibilities in sensing and dynamical engineering.
- Savannah Garmon
-
Article |
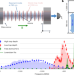 Spectral engineering of cavity-protected polaritons in an atomic ensemble
Spectral engineering of cavity-protected polaritons in an atomic ensemble
Engineering the frequency spectrum of systems of multiple quantum emitters is the key for many quantum technologies. A cavity quantum electrodynamics experiment now demonstrates the real-time frequency modulation of cavity-protected polaritons.
- Mohamed Baghdad
- , Pierre-Antoine Bourdel
- & Romain Long
-
Article |
 Experimental super-Heisenberg quantum metrology with indefinite gate order
Experimental super-Heisenberg quantum metrology with indefinite gate order
Normally, quantum operations are thought of as being applied in a particular order, but it is possible to create superpositions of different orders. An experiment now demonstrates this indefinite causal order may give an advantage for quantum sensing.
- Peng Yin
- , Xiaobin Zhao
- & Guang-Can Guo
-
Research Briefing |
 Realization of a continuous time crystal in a photonic metamaterial
Realization of a continuous time crystal in a photonic metamaterial
Time crystals are a new state of matter. Conventional crystal properties are periodic in space, while the properties of a time crystal are periodic in time. A continuous quantum time crystal has recently been realized, and now, using optically driven many-body interactions in a nano-mechanical photonic metamaterial, a classical continuous time crystal has been created.
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-symmetry-protected topological states
Sub-symmetry-protected topological states
Some topological boundary states are symmetry protected. Experiments with photonic lattices now show that the protection via sub-symmetry is enough to ensure topological modes, even if the full symmetry and topological invariant are destroyed.
- Ziteng Wang
- , Xiangdong Wang
- & Hrvoje Buljan
-
Article |
 Bloch oscillations of coherently driven dissipative solitons in a synthetic dimension
Bloch oscillations of coherently driven dissipative solitons in a synthetic dimension
Synthetic dimensions can introduce band properties without a periodic structure in real space, but they have largely been studied in linear systems. A study using an optical resonator has now shown non-linear soliton states in synthetic frequency space.
- Nicolas Englebert
- , Nathan Goldman
- & Julien Fatome
-
News & Views |
 Ground-state cooling goes 2D
Ground-state cooling goes 2D
Levitated nanoparticles can now be cooled to the motional ground state in two dimensions. This advance could enable a new generation of macroscopic quantum experiments.
- Dalziel J. Wilson
-
Article |
 Simultaneous cavity cooling of all six degrees of freedom of a levitated nanoparticle
Simultaneous cavity cooling of all six degrees of freedom of a levitated nanoparticle
Optically trapped and levitated nanoparticles can be used to study macroscopic quantum effects, but fully controlling their motion is difficult. Now, all six roto-translational degrees of freedom have been cooled, although not to the quantum ground state.
- A. Pontin
- , H. Fu
- & P. F. Barker
-
News & Views |
 An optical double-slit experiment in time
An optical double-slit experiment in time
Time-varying photonics constitutes an emerging concept where a material’s time-dependence is used to achieve novel functionalities. A temporal double-slit-diffraction experiment demonstrates the feasibility of time-modulating materials to control light.
- Francisco J. Rodríguez-Fortuño

 Electrons bunch up in quantum light
Electrons bunch up in quantum light Fruity blues
Fruity blues Noble sandwich
Noble sandwich Tweezers on repeat
Tweezers on repeat