Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
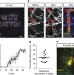 In vivo imaging and histochemistry are combined in the cryosection labelling and intravital microscopy technique
In vivo imaging and histochemistry are combined in the cryosection labelling and intravital microscopy technique
Imaging cells within live animals is important in biomedical research, but this process is limited by the availability of probes. Ritsma et al.combine intravital microscopy with immunohistochemistry to increase the panel of available reagents and examine the role of T cells in the migration of breast cancer cells.
- Laila Ritsma
- , Nienke Vrisekoop
- & Jacco van Rheenen
-
Article
| Open Access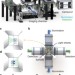 High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
Systematic large-scale analysis of embryonic development requires the processing of large amounts of microscopy data. Here Schmid et al.solve this problem by developing a high-speed imaging system that projects zebrafish embryos onto a ‘world map’ in real time, revealing characteristic migration patterns in the early endoderm.
- Benjamin Schmid
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article |
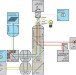 A hybrid high-speed atomic force–optical microscope for visualizing single membrane proteins on eukaryotic cells
A hybrid high-speed atomic force–optical microscope for visualizing single membrane proteins on eukaryotic cells
Scanning probe microscopy techniques are hard to apply to live cell membrane imaging at high resolution as the temporal and force sensitivity are insufficient to monitor the fast processes. Colom et al.present a solution to this problem by combining high-speed atomic force microscopy with optical microscopy.
- Adai Colom
- , Ignacio Casuso
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article |
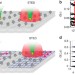 Stimulated emission depletion-based raster image correlation spectroscopy reveals biomolecular dynamics in live cells
Stimulated emission depletion-based raster image correlation spectroscopy reveals biomolecular dynamics in live cells
RICS is a fluorescence imaging technique used to reveal fast molecular dynamics inside living cells and tissues. Hedde et al.combine RICS with super-resolution STED microscopy (STED-RICS) to achieve an enhanced multiplexing capability and to extend the range of usable fluorophore concentrations.
- Per Niklas Hedde
- , René M. Dörlich
- & G. Ulrich Nienhaus
-
Article
| Open Access A nanometre-scale resolution interference-based probe of interfacial phenomena between microscopic objects and surfaces
A nanometre-scale resolution interference-based probe of interfacial phenomena between microscopic objects and surfaces
Interferometric techniques can provide valuable contact and profile information of microscopic objects on surfaces. This work uses reflection interference contrast microscopy to directly observe contact phenomena and presents novel analytical methods offering high-accuracy nanoscale resolution.
- Jose C. Contreras-Naranjo
- & Victor M. Ugaz
-
Article |
 In vivo imaging of virological synapses
In vivo imaging of virological synapses
In vitro, retroviruses spread between cells via structures resembling synapses. Sewaldet al. now demonstrate that virological synapses can also be observed in living mice by intravital microscopy, validating this concept in vivo.
- Xaver Sewald
- , David G. Gonzalez
- & Walther Mothes
-
Article |
 Measuring the size of individual particles from three-dimensional imaging experiments
Measuring the size of individual particles from three-dimensional imaging experiments
The degree of polydispersity of colloidal suspensions is known to have consequences for their physical properties. Kuritaet al. present a general method for determining the sizes of individual particles, and thus the polydispersity, using only the coordinates of the centre positions of spherical particles.
- Rei Kurita
- , David B. Ruffner
- & Eric R. Weeks
-
Article |
 Biocompatibility of a genetically encoded calcium indicator in a transgenic mouse model
Biocompatibility of a genetically encoded calcium indicator in a transgenic mouse model
Calcium-sensing fluorescent proteins such as TN-XXL are valuable tools for studying cellular function but, when expressed in mice, may affect animal physiology and behaviour. The authors of this paper create transgenic mice expressing TN-XXL and show that long-term expression of TN-XXL is tolerated well.
- Stephan Direnberger
- , Marsilius Mues
- & Oliver Griesbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Fibre-based technologies provide miniaturization, flexibility and the capability to access hard to reach areas. Čižmár and Dholakia exploit disorder in multimode fibres to enable a variety of imaging modalities, including bright- and dark-field microscopy and fluorescent imaging, using a single waveguide.
- Tomáš Čižmár
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
Article |
 Atom-specific spin mapping and buried topological states in a homologous series of topological insulators
Atom-specific spin mapping and buried topological states in a homologous series of topological insulators
Strategies to tune the surface properties of topological insulators are essential, if they are to find use in applications. Using a combination of theoretical and experimental techniques, this study examines how the properties of ordered ternary topological insulators vary with the content of group IV elements.
- Sergey V. Eremeev
- , Gabriel Landolt
- & Evgueni V. Chulkov
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus
Three-dimensional analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus
The influenza A virus genome consists of eight RNA segments, which permits genetic reassortment and contributes to the emergence of novel strains with pandemic potential. Here, electron tomography is used to study the three-dimensional structure of ribonucleoprotein complexes within progeny virions.
- Takeshi Noda
- , Yukihiko Sugita
- & Yoshihiro Kawaoka
-
Article |
 Revealing the role of defects in ferroelectric switching with atomic resolution
Revealing the role of defects in ferroelectric switching with atomic resolution
Ferroelectric materials are characterized by a spontaneous polarization, which in practical applications is manipulated by an electric field. This study examines how defects affect the switching with atomic resolution, by usingin situaberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy.
- Peng Gao
- , Christopher T. Nelson
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional high-resolution quantitative microscopy of extended crystals
Three-dimensional high-resolution quantitative microscopy of extended crystals
X-ray ptychography has been used to extend the field of view in high-resolution quantitative imaging. Godardet al. develop Bragg-mode ptychography to reconstruct, in three dimensions, a crystalline specimen that is too large to be studied as a single object with a coherence-limited X-ray beam.
- P. Godard
- , G. Carbone
- & V. Chamard
-
Article
| Open Access A new regime for mechanical annealing and strong sample-size strengthening in body centred cubic molybdenum
A new regime for mechanical annealing and strong sample-size strengthening in body centred cubic molybdenum
Mechanical annealing is a process through which the dislocation density in submicrometre metal crystals can be removed purely by applying a mechanical stress. This study shows that mechanical annealing occurs in body centred cubic molybdenum, and not only in face centred crystals as previously thought.
- Ling Huang
- , Qing-Jie Li
- & Evan Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanical DNA origami 'single-molecule beacons' directly imaged by atomic force microscopy
Nanomechanical DNA origami 'single-molecule beacons' directly imaged by atomic force microscopy
DNA origami involves the folding of long single-stranded DNA into designed structures that may aid the development of useful nanomechanical DNA devices. In this study, DNA origami pliers and forceps are shown to undergo conformational changes on single-molecule binding.
- Akinori Kuzuya
- , Yusuke Sakai
- & Makoto Komiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring single-nanoparticle wetting properties by freeze-fracture shadow-casting cryo-scanning electron microscopy
Measuring single-nanoparticle wetting properties by freeze-fracture shadow-casting cryo-scanning electron microscopy
Being able to determine the wetting properties of individual nanoparticles would aid the preparation of particles with controlled surface properties. Isaet al. develop an in situ freeze-fracture shadow-casting method and use this to determine structural and thermodynamic properties of various 10 nm particles at fluid interfaces.
- Lucio Isa
- , Falk Lucas
- & Erik Reimhult
-
Article |
 Direct imaging of Joule heating dynamics and temperature profiling inside a carbon nanotube interconnect
Direct imaging of Joule heating dynamics and temperature profiling inside a carbon nanotube interconnect
The use of carbon nanotubes in nanoelectronics requires an understanding of their resistive, or Joule, heating at interconnects. Here, Joule heating dynamics are imaged in real time by following the evolution of resistive hot spots with a transmission electron microscope.
- Pedro M.F.J. Costa
- , Ujjal K. Gautam
- & Dmitri Golberg
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscale flux-closure domain formation in single-crystal BaTiO3
Mesoscale flux-closure domain formation in single-crystal BaTiO3
Flux-closure patterns are rarely observed in ferroelectric materials and almost exclusively form at the nanoscale. McQuaidet al. report mesoscopic dipole closure patterns formed in free-standing single-crystal lamellae of BaTiO3, thought to result from an unusual set of experimental conditions.
- R.G.P. McQuaid
- , L.J. McGilly
- & J.M. Gregg
-
Article |
 Imaging local electronic corrugations and doped regions in graphene
Imaging local electronic corrugations and doped regions in graphene
The unoccupied electronic levels of graphene are modified by corrugation, doping and presence of impurities. Here, the authors map discrete electronic domains within a single graphene sheet using scanning transmission X-ray microscopy and provide insight into the modification of unoccupied levels.
- Brian J. Schultz
- , Christopher J. Patridge
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Determination of nanoparticle size distribution together with density or molecular weight by 2D analytical ultracentrifugation
Determination of nanoparticle size distribution together with density or molecular weight by 2D analytical ultracentrifugation
Nanoparticles continue to find research and industrial applications, but no single technique exists to characterise their physical properties. Now, an analytical ultracentrifugation method is described which allows the simulataneous determination of nanoparticle size, density and molecular weight distribution.
- Randy P. Carney
- , Jin Young Kim
- & Osman M. Bakr
-
Article |
 Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Metal-based nanostructures offer a solution to scale down photonics to the nanoscale. Sorgeret al. directly demonstrate waveguiding of ultra-small propagating waves at visible and near-infrared frequencies using NSOM imaging, with the potential for nanoscale photonic applications such as bio-sensing.
- Volker J. Sorger
- , Ziliang Ye
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures
Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures
Solid gold is most stable as a face-centred cubic structure, and stable colloidal gold with hexagonal close packing has not been produced. Huanget al.prepare square gold sheets with hexagonal close packing that are stable under ambient conditions.
- Xiao Huang
- , Shaozhou Li
- & Hua Zhang
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atomic force microscopy
- Ca2+ imaging
- Confocal microscopy
- Cryoelectron microscopy
- Interference microscopy
- Light-sheet microscopy
- Multiphoton microscopy
- Phase-contrast microscopy
- Polarization microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
- Scanning probe microscopy
- Super-resolution microscopy
- Total internal reflection microscopy
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Transmission light microscopy
- Wide-field fluorescence microscopy

 An entanglement-enhanced microscope
An entanglement-enhanced microscope