Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Kekulé vortices in hexagonal lattices can host fractionalized charges at zero magnetic field, but have remained out of experimental reach. Here, the authors report a Kekulé vortex in the local density states of graphene around a chemisorbed hydrogen adatom.
- Yifei Guan
- , Clement Dutreix
- & Vincent T. Renard
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
The strong ionic bond in salt is broken by electrostatic interactions with water, but direct observation at the level of a single ion is challenging. Here, the authors have visualized the preferential dissolution of an anion by manipulating a single water molecule.
- Huijun Han
- , Yunjae Park
- & Hyung-Joon Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Defect engineering in topological materials is a frontier that promises tunable physical properties with rich applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the atomically precise engineering of vacancies in a topological semimetal, which locally tunes the magnetic properties.
- Hui Chen
- , Yuqing Xing
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface synthesis relies on carefully designed molecular precursors that are thermally activated to afford desired, covalently coupled architectures. Here, the authors study the intramolecular reactions of vinyl groups in a poly-para-phenylene-based model system and provide a comprehensive description of the reaction steps taking place on the Au(111) surface under ultrahigh vacuum conditions.
- Marco Di Giovannantonio
- , Zijie Qiu
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
The efficiency of upconversion electroluminescence remains very low for single-molecule emitters. Here, the authors report over one order of magnitude improvement in the emission efficiency via engineering energy-level alignments for triplet relayed upconversion involving only carrier injection.
- Yang Luo
- , Fan-Fang Kong
- & Zhen-Chao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access Surface-confined alternating copolymerization with molecular precision by stoichiometric control
Surface-confined alternating copolymerization with molecular precision by stoichiometric control
Conventional sequence-controlled copolymerization often suffers from strict requirements on reaction kinetics of comonomer pairs and tedious synthetic processes. Here, the authors demonstrate a sequence-controlled alternating copolymerization with molecular precision on a Ag(111) surface under thermodynamic control of the polymerization selectivity.
- Lingbo Xing
- , Jie Li
- & Kai Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Chemical identification of the building blocks of biopolymers often considerably relies on the presence of markers, extensive simulations, or is not possible at all. Here, the authors report a molecular probe-sensitisation approach addressing the identification of a specific amino acid within different peptides.
- Xu Wu
- , Bogdana Borca
- & Uta Schlickum
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access Strong signature of electron-vibration coupling in molecules on Ag(111) triggered by tip-gated discharging
Strong signature of electron-vibration coupling in molecules on Ag(111) triggered by tip-gated discharging
Electron-vibration coupling is driving advances in molecular electronics, spintronics, and quantum technology. Here, the authors succeeded in directly controlling vibronic excitations in tetrabromotetraazapyrene (TBTAP) molecules on the surface of Ag(111).
- Chao Li
- , Christoph Kaspar
- & Rémy Pawlak
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Nanographenes, as their name suggests, are small sections of graphene. They offer a diverse array of magnetic behaviors; for example, sublattice imbalances in the nanographene lead to unpaired spins. Here, Du et al uncover a large variation in the exchange energy in nanographenes, due to changes in the frontier orbital symmetries.
- Qingyang Du
- , Xuelei Su
- & Ping Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative study of Co3O4(111), CoFe2O4(111), and Fe3O4(111) thin film electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Comparative study of Co3O4(111), CoFe2O4(111), and Fe3O4(111) thin film electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Cobalt-based oxidic anodes with added iron are good electrocatalysts for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction, but the role of iron is still unclear. Here the authors investigate oxygen evolution reaction activity of three well-defined epitaxial thin-film electrodes to address this issue.
- Earl Matthew Davis
- , Arno Bergmann
- & Beatriz Roldan Cuenya
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality control of a single carbene molecule by tip-induced van der Waals interactions
Chirality control of a single carbene molecule by tip-induced van der Waals interactions
The control of molecular chirality is of great interest in stereochemistry and biochemistry. Here, the authors show how to alter the chirality dynamics of a single molecule through tip-induced van der Waals interactions.
- Yunjun Cao
- , Joel Mieres-Perez
- & Karina Morgenstern
-
Article
| Open Access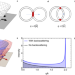 Determining spin-orbit coupling in graphene by quasiparticle interference imaging
Determining spin-orbit coupling in graphene by quasiparticle interference imaging
Graphene has many intriguing electronic properties. One of note is the absence of backscattering of electrons confined to a single valley. Spin-orbit interactions can allow backscattering, and here, Sun et al. use this spin-orbit coupling dependence of backscattering to measure the strength of the spin-orbit interaction in a graphene/tungsten selenide heterostructure.
- Lihuan Sun
- , Louk Rademaker
- & Christoph Renner
-
Article
| Open Access Single-electron charge transfer into putative Majorana and trivial modes in individual vortices
Single-electron charge transfer into putative Majorana and trivial modes in individual vortices
Majorana bound states are an elusive but promising platform for future topological quantum computation. Here, the authors use local shot noise spectroscopy to determine the nature of charge transfer into zero-energy bound states in superconducting vortices and rule out the presence of impurity states.
- Jian-Feng Ge
- , Koen M. Bastiaans
- & Milan P. Allan
-
Article
| Open Access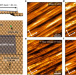 Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Catalytic CO2 dissociation pathways are selectively determined by surface geometry in heterogeneous catalysis. The authors find that the stepped Cu surfaces effectively affect CO2 activation in elementary reaction steps at the atomic level
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Youngseok Yu
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access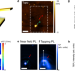 Direct nano-imaging of light-matter interactions in nanoscale excitonic emitters
Direct nano-imaging of light-matter interactions in nanoscale excitonic emitters
Authors investigate quasi-2D nanoscale emitters on different substrates with tapping mode tip-enhanced spectroscopy. They visualize in-plane near-field and radiative energy propagation via Surface plasmon polaritons launched by the nanoscale emitters on dielectric/Au or SiO2/Si substrates.
- Kiyoung Jo
- , Emanuele Marino
- & Deep Jariwala
-
Article
| Open Access Condensation and asymmetric amplification of chirality in achiral molecules adsorbed on an achiral surface
Condensation and asymmetric amplification of chirality in achiral molecules adsorbed on an achiral surface
The origin of homochirality in nature is an important but open question. Here, the authors provide insight into the physicochemical origin of homochirality through surface adsorption on the model of adlayers of achiral carbon monoxide molecules on an achiral Au(111) surface.
- Huiru Liu
- , Heping Li
- & Lan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of electron orbital signatures of single atoms within metal-phthalocyanines using atomic force microscopy
Observation of electron orbital signatures of single atoms within metal-phthalocyanines using atomic force microscopy
Resolving the orbital structure of single atoms is challenging and of great importance for understanding basic chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate that the orbital occupation difference of single Fe/Co atoms within molecules can be distinguished with high resolution AFM imaging and spectroscopy.
- Pengcheng Chen
- , Dingxin Fan
- & Nan Yao
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of enetriynes
On-surface synthesis of enetriynes
Enetriynes, which belong to the enyne family, are characterized by a distinct electron-rich carbon-bonding scheme. Here, the authors report the formation of enetriynes with high selectivity by tetramerization of terminal alkynes on Ag(100).
- Nan Cao
- , Biao Yang
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article
| Open Access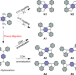 Real-space imaging of a phenyl group migration reaction on metal surfaces
Real-space imaging of a phenyl group migration reaction on metal surfaces
On-surface synthesis allows fabrication of nanostructures with atomic precision and may follow different routes compared to in-solution chemistry. Here the authors, using scanning probe microscopy techniques, observe a phenyl group migration reaction on three different metal surfaces forming polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which cannot be accessed by in-solution chemistry.
- Zilin Ruan
- , Baijin Li
- & Jinming Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of accelerating hydrogen spillover via surface-lattice-confinement effect
Direct observation of accelerating hydrogen spillover via surface-lattice-confinement effect
Hydrogen spillover is a surface phenomenon encountered in catalytic reactions. Here the authors show that the surface-lattice-confinement effect can regulate the hydrogen spillover directions and accelerate spillover rates. It is intrinsically related to the local surface geometries and coordination numbers of surface O sites.
- Yijing Liu
- , Rankun Zhang
- & Qiang Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
One of the possible events signaling a neutrinoless double beta decay is a Xe atom decaying into a Ba ion and two electrons. Aiming at the realisation of a detector for such a process, the authors show that Ba ions can be efficiently trapped (chelated) in vacuum by an organic molecule layer on a surface.
- P. Herrero-Gómez
- , J. P. Calupitan
- & J. T. White
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule binding to surface-supported single-site transition-metal reaction centres
Small molecule binding to surface-supported single-site transition-metal reaction centres
Surface-supported metalorganics promise the best of homogenous and heterogeneous catalysts. Here the authors show that small molecules bind to an iron-terpyridine site on silver via surface bound intermediates by following molecules one at a time.
- M. DeJong
- , A. J. A. Price
- & S. A. Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds yields N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs
Selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds yields N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs
Selective activation of C–H bonds is a key challenge in organic reactions. Here, the authors achieve the selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds, leading to the formation of N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs.
- Yixuan Gao
- , Li Huang
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Competing electronic states emerging on polar surfaces
Competing electronic states emerging on polar surfaces
Defect-free surfaces with excess charge are typically described as a homogeneous 2D electron gas. Here, in contrast, the authors find that the KTaO3(001) surface hosts a charge density wave coexisting with a pattern of electron polarons, highly localized states of excess electrons bound to a lattice distortion.
- Michele Reticcioli
- , Zhichang Wang
- & Cesare Franchini
-
Article
| Open Access Scanning gradiometry with a single spin quantum magnetometer
Scanning gradiometry with a single spin quantum magnetometer
Scanning NV center magnetometry enables imaging of weak magnetic fields at the nanoscale. Huxter et al. achieve an order-of-magnitude improvement in sensitivity by converting a spatial field gradient into an AC field by mechanical oscillations of the sensor, and image stray fields from atomic steps in an antiferromagnet.
- W. S. Huxter
- , M. L. Palm
- & C. L. Degen
-
Article
| Open Access Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons – mixed states of photons and anisotropic lattice vibrations – offer appealing properties for nanophotonic applications. Here, the authors show that the plasmon-phonon hybridization upon electronic doping in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures can induce topological transitions of the polariton wavefront.
- Francesco L. Ruta
- , Brian S. Y. Kim
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Periodic corner holes on the Si(111)-7×7 surface can trap silver atoms
Periodic corner holes on the Si(111)-7×7 surface can trap silver atoms
Positioning and trapping single atoms at specific sites of surfaces is a challenging goal that can advance the development of single atom devices. Here the authors demonstrate that single Ag atoms are trapped inside corner holes of the Si(111)-7×7 surface for more than 4 days at room temperature, and suggest that this behavior may be shared by other elements.
- Jacek R. Osiecki
- , Shozo Suto
- & Arunabhiram Chutia
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic overlayer of permeable microporous cuprous oxide on palladium promotes hydrogenation catalysis
Atomic overlayer of permeable microporous cuprous oxide on palladium promotes hydrogenation catalysis
It remains a challenge to fabricate metal catalysts with interfacial active sites distributed on the whole two-dimensional (2D) surface of metal nanoparticles. Here the authors demonstrate that the overgrowth of atomic-thick porous Cu2O on Pd readily creates an unprecedented 2D catalytically active metal-support interface with significantly enhanced catalysis toward the semi-hydrogenation of alkynes.
- Kunlong Liu
- , Lizhi Jiang
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Here, the authors report the use of ultrahigh vacuum tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to characterize the oxidation processes of monolayer borophene with atomic-scale resolution and single-bond sensitivity, demonstrating the potential of the technique for probing the local chemistry of surface adsorbates on low-dimensional materials.
- Linfei Li
- , Jeremy F. Schultz
- & Nan Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of triangulene trimers via dehydration reaction
On-surface synthesis of triangulene trimers via dehydration reaction
Preparing triangulene-based high spin structures is of interest for molecular spintronics. Here, the authors generate high spin triangulene trimers on Au(111) via a surface-assisted dehydration reaction.
- Suqin Cheng
- , Zhijie Xue
- & Ping Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Binary-state scanning probe microscopy for parallel imaging
Binary-state scanning probe microscopy for parallel imaging
High-throughput imaging has generally been challenging for scanning probe microscopy techniques. Here, the authors introduce binary-state scanning probe microscopy, which uses a cantilever-free elastomeric probes and a hierarchical measurement architecture for parallel topography imaging.
- Gwangmook Kim
- , Eoh Jin Kim
- & Wooyoung Shim
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging of far-from-equilibrium carrier and vibrational dynamics
Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging of far-from-equilibrium carrier and vibrational dynamics
Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging has enabled the study of nanoscale dynamics, but has been limited to probing short-lived carrier lifetimes. Here, the authors present pump-probe nano-spectroscopy with enhanced sensitivity to image both carrier and vibrational dynamics associated with long-lived excitations.
- Jun Nishida
- , Samuel C. Johnson
- & Markus B. Raschke
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-substituted undecacenes
On-surface synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-substituted undecacenes
Heteroatom substitution in larger acenes represents a fundamental step towards precise engineering of the remarkable electronic properties of the acene family. Here, the authors present an on-surface synthesis strategy and detailed characterization for three undecacene analogs substituted with four nitrogen atoms.
- Kristjan Eimre
- , José I. Urgel
- & Carlo A. Pignedoli
-
Article
| Open Access 6 nm super-resolution optical transmission and scattering spectroscopic imaging of carbon nanotubes using a nanometer-scale white light source
6 nm super-resolution optical transmission and scattering spectroscopic imaging of carbon nanotubes using a nanometer-scale white light source
The authors present a super-resolution hyperspectral imaging technique using a nanoscale white light source generated by superfocusing light from a tungsten-halogen lamp. They achieve 6 nm resolution, measuring longitudinal and transverse optical electronic transitions in single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Xuezhi Ma
- , Qiushi Liu
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Lightwave-driven scanning tunnelling spectroscopy of atomically precise graphene nanoribbons
Lightwave-driven scanning tunnelling spectroscopy of atomically precise graphene nanoribbons
Here, the authors perform lightwave-driven terahertz scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy of graphene nanoribbons with atomic resolution in three dimensions, revealing localized wavefunctions that are inaccessible by conventional scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- S. E. Ammerman
- , V. Jelic
- & T. L. Cocker
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz response of monolayer and few-layer WTe2 at the nanoscale
Terahertz response of monolayer and few-layer WTe2 at the nanoscale
The behaviour of Tungsten ditelluride (WTe2) in few-layer form is not yet fully characterized. Here the authors use a near-field terahertz microscopy technique to observe the electromagnetic responses of WTe2 flakes from one to several layers and to study their semimetallic/ semiconducting behavior.
- Ran Jing
- , Yinming Shao
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Correlative 3D microscopy of single cells using super-resolution and scanning ion-conductance microscopy
Correlative 3D microscopy of single cells using super-resolution and scanning ion-conductance microscopy
Methods for imaging the 3D cell surface often require physical interaction. Here the authors report the combination of scanning ion conductance microscopy (SICM) and live-cell super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) for the non-invasive topographical imaging of soft biological samples.
- Vytautas Navikas
- , Samuel M. Leitao
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of N-heterocyclic carbenes on Au(111)
Self-assembly of N-heterocyclic carbenes on Au(111)
Although N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are a promising class of ligands for forming robust self-assembled monolayers on metals, many questions remain about their behavior on surfaces. Here, the authors address these fundamental questions—such as the factors controlling NHC orientation, mobility, and ability to self-assemble—through an in-depth examination of NHC overlayers on Au(111).
- Alex Inayeh
- , Ryan R. K. Groome
- & Alastair B. McLean
-
Article
| Open Access The limits of near field immersion microwave microscopy evaluated by imaging bilayer graphene moiré patterns
The limits of near field immersion microwave microscopy evaluated by imaging bilayer graphene moiré patterns
Here, the authors image twisted bilayer graphene using scanning microwave imaging microscopy, revealing structures with sizes down to 1 nm. They show that is possible by using spontaneously forming nanoscale water menisci that concentrates the microwave fields in small regions.
- Douglas A. A. Ohlberg
- , Diego Tami
- & Gilberto Medeiros-Ribeiro
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale electric-field imaging based on a quantum sensor and its charge-state control under ambient condition
Nanoscale electric-field imaging based on a quantum sensor and its charge-state control under ambient condition
Previous work has demonstrated electric-field detection with nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond; however, nanoscale electric-field imaging has not been shown. Here, the authors use individual nitrogen-vacancy centers to map out electric field contours from a tip of an atomic force microscope with 10 nm resolution.
- Ke Bian
- , Wentian Zheng
- & Ying Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface preparation of coordinated lanthanide-transition-metal clusters
On-surface preparation of coordinated lanthanide-transition-metal clusters
The preparation of lanthanide-transition metal clusters containing multiple lanthanide atoms remains challenging. Here, the authors present the controlled on-surface formation of ligand-stabilized heterometallic Ce/Au clusters containing two, three and four Ce atoms bridged by Au adatoms.
- Jing Liu
- , Jie Li
- & Yongfeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Vibronic coupling is a key feature of molecular electronic transitions, but its visualization in real space is an experimental challenge. Here the authors, using scanning tunneling microscopy induced luminescence, resolve the effect of vibronic coupling with different modes on the electron distributions in real space in a single pentacene molecule.
- Fan-Fang Kong
- , Xiao-Jun Tian
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Probing resonating valence bond states in artificial quantum magnets
Probing resonating valence bond states in artificial quantum magnets
The resonating valence bond state is a spin-liquid state where spins continuously alter their singlet partners. Here Yang et al. use spin-1/2 atoms precision-placed by a scanning tunnelling microscope to create artificial quantum magnets exhibiting the resonating valence bond state.
- Kai Yang
- , Soo-Hyon Phark
- & Christopher P. Lutz
-
Article
| Open Access How the anisotropy of surface oxide formation influences the transient activity of a surface reaction
How the anisotropy of surface oxide formation influences the transient activity of a surface reaction
Surface oxide formation under reaction conditions may change the catalytic activity of a catalyst. Here, the authors explore the effect of atomic structure of Rh surfaces on the surface oxide formation and its influence on catalytic activity in hydrogen oxidation, revealing a high transient activity.
- P. Winkler
- , J. Zeininger
- & G. Rupprechter
-
Article
| Open Access Creating a regular array of metal-complexing molecules on an insulator surface at room temperature
Creating a regular array of metal-complexing molecules on an insulator surface at room temperature
Arrays of ordered metal atoms on bulk insulating materials are promising for future applications, such as optoelectronics and data storage. Here, the authors demonstrate a strategy to create an ordered metal array based on tailored anchoring and hard-sphere repulsion of metal-complexing molecules.
- Simon Aeschlimann
- , Sebastian V. Bauer
- & Angelika Kühnle
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-printed cellular tips for tuning fork atomic force microscopy in shear mode
3D-printed cellular tips for tuning fork atomic force microscopy in shear mode
The authors investigate 3D-printed tips, based on controlled microstructural architectured materials, as probes for shear-mode atomic force microscopy. They demonstrate that the tailored stiffness and energy-absorbing behaviour of the material are beneficial for improving image quality.
- Liangdong Sun
- , Hongcheng Gu
- & Zhongze Gu
-
Article
| Open Access How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
Direct observation of carbon dioxide dissociation provides an origin of catalytic conversion for industrial chemical reactions. Here, the authors reveal their molecular interactions on the rhodium catalyst at near-ambient pressure by interface science techniques and computational calculations.
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Hyunwoo Ha
- & Jeong Young Park

 Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping
Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping